12.18
实验5
MapReduce初级编程实践
1.实验目的
(1)通过实验掌握基本的MapReduce编程方法;
(2)掌握用MapReduce解决一些常见的数据处理问题,包括数据去重、数据排序和数据挖掘等。
2.实验平台
(1)操作系统:Linux(建议Ubuntu16.04或Ubuntu18.04)
(2)Hadoop版本:3.1.3
3.实验步骤
(一)编程实现文件合并和去重操作
对于两个输入文件,即文件A和文件B,请编写MapReduce程序,对两个文件进行合并,并剔除其中重复的内容,得到一个新的输出文件C。下面是输入文件和输出文件的一个样例供参考。
输入文件A的样例如下:
|
20170101 x 20170102 y 20170103 x 20170104 y 20170105 z 20170106 x |
输入文件B的样例如下:
|
20170101 y 20170102 y 20170103 x 20170104 z 20170105 y |
根据输入文件A和B合并得到的输出文件C的样例如下:
|
20170101 x 20170101 y 20170102 y 20170103 x 20170104 y 20170104 z 20170105 y 20170105 z 20170106 x |
代码:
package org.example.five;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class Merge {
/**
* @paramargs
* 对 A,B 两个文件进行合并,并剔除其中重复的内容,得到一个新的输出文件 C
*/
//重载 map 函数,直接将输入中的 value 复制到输出数据的 key 上
public static class Map extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text>{
private static Text text = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws
IOException,InterruptedException{
text = value;
context.write(text, new Text(""));
}
}
//重载 reduce 函数,直接将输入中的 key 复制到输出数据的 key 上
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context )
throws IOException,InterruptedException{
context.write(key, new Text(""));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("fs.default.name","hdfs://192.168.91.128:9000");
String[] otherArgs = new String[]{"input","output"}; /* 直接设置输入参
数 */
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf,"Merge and duplicate removal");
job.setJarByClass(Merge.class);
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
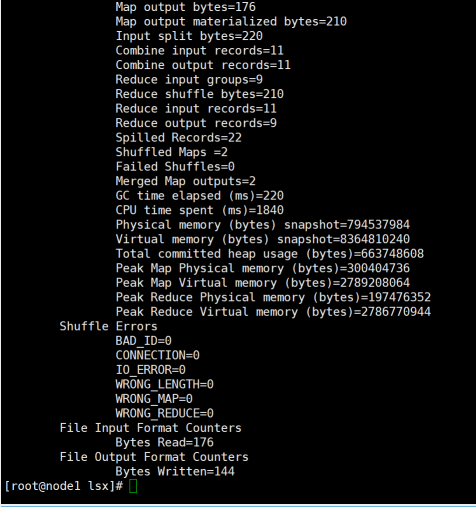
(二)编写程序实现对输入文件的排序
现在有多个输入文件,每个文件中的每行内容均为一个整数。要求读取所有文件中的整数,进行升序排序后,输出到一个新的文件中,输出的数据格式为每行两个整数,第一个数字为第二个整数的排序位次,第二个整数为原待排列的整数。下面是输入文件和输出文件的一个样例供参考。
输入文件1的样例如下:
|
33 37 12 40 |
输入文件2的样例如下:
|
4 16 39 5 |
输入文件3的样例如下:
|
1 45 25 |
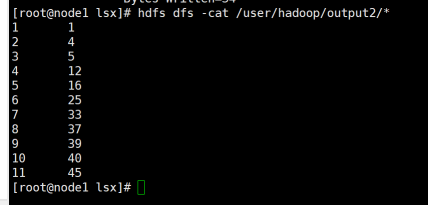
根据输入文件1、2和3得到的输出文件如下:
|
1 1 2 4 3 5 4 12 5 16 6 25 7 33 8 37 9 39 10 40 11 45 |
package org.example.five;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class MergeSort {
/**
* @paramargs 输入多个文件,每个文件中的每行内容均为一个整数
* 输出到一个新的文件中,输出的数据格式为每行两个整数,第一个数字为第二个整
* 数的排序位次,第二个整数为原待排列的整数
*/
//map 函数读取输入中的 value,将其转化成 IntWritable 类型,最后作为输出 key
public static class Map extends Mapper<Object, Text, IntWritable,
IntWritable> {
private static IntWritable data = new IntWritable();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws
IOException, InterruptedException {
String text = value.toString();
data.set(Integer.parseInt(text));
context.write(data, new IntWritable(1));
}
}
//reduce 函数将 map 输入的 key 复制到输出的 value 上,然后根据输入的 value-list中元素的个数决定 key 的输出次数,定义一个全局变量 line_num 来代表 key 的位次
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<IntWritable, IntWritable,
IntWritable, IntWritable> {
private static IntWritable line_num = new IntWritable(1);
public void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (IntWritable val : values) {
context.write(line_num, key);
line_num = new IntWritable(line_num.get() + 1);
}
}
}
//自定义 Partition 函数,此函数根据输入数据的最大值和 MapReduce 框架中Partition 的数量获取将输入数据按照大小分块的边界,然后根据输入数值和边界的关系返回对应的 Partiton ID
public static class Partition extends Partitioner<IntWritable,
IntWritable> {
public int getPartition(IntWritable key, IntWritable value, int
num_Partition) {
int Maxnumber = 65223;//int 型的最大数值
int bound = Maxnumber / num_Partition + 1;
int keynumber = key.get();
for (int i = 0; i < num_Partition; i++) {
if (keynumber < bound * (i + 1) && keynumber >= bound * i) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("fs.default.name", "hdfs://master:9000");
String[] otherArgs = new String[]{"input", "output"}; /* 直接设置输入参 数 */
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "Merge and sort");
job.setJarByClass(MergeSort.class);
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(Partition.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
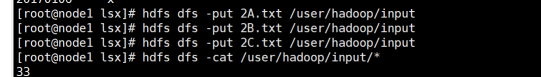
①上传文件到hdfs
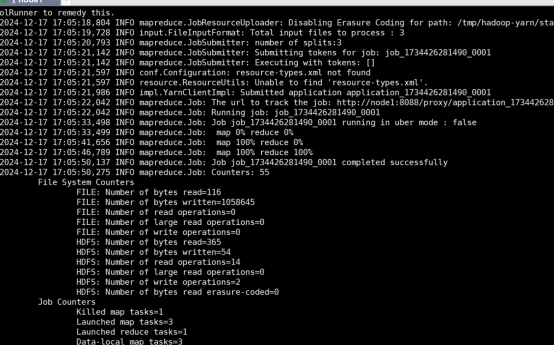
②运行代码
(三)对给定的表格进行信息挖掘
下面给出一个child-parent的表格,要求挖掘其中的父子辈关系,给出祖孙辈关系的表格。
输入文件内容如下:
|
child parent Steven Lucy Steven Jack Jone Lucy Jone Jack Lucy Mary Lucy Frank Jack Alice Jack Jesse David Alice David Jesse Philip David Philip Alma Mark David Mark Alma |
输出文件内容如下:
|
grandchild grandparent Steven Alice Steven Jesse Jone Alice Jone Jesse Steven Mary Steven Frank Jone Mary Jone Frank Philip Alice Philip Jesse Mark Alice Mark Jesse |
package org.example.five;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class simple_data_mining {
public static int time = 0;
/**
* @paramargs 输入一个 child-parent 的表格
* 输出一个体现 grandchild-grandparent 关系的表格
*/
//Map 将输入文件按照空格分割成 child 和 parent,然后正序输出一次作为右表,反序输出一次作为左表,需要注意的是在输出的 value 中必须加上左右表区别标志
public static class Map extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, Text> {
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws
IOException, InterruptedException {
String child_name = new String();
String parent_name = new String();
String relation_type = new String();
String line = value.toString();
int i = 0;
while (line.charAt(i) != ' ') {
i++;
}
String[] values = {line.substring(0, i), line.substring(i + 1)};
if (values[0].compareTo("child") != 0) {
child_name = values[0];
parent_name = values[1];
relation_type = "1";//左右表区分标志
context.write(new Text(values[1]), new
Text(relation_type + "+" + child_name + "+" + parent_name));
//左表
relation_type = "2";
context.write(new Text(values[0]), new
Text(relation_type + "+" + child_name + "+" + parent_name));
//右表
}
}
}
public static class Reduce extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (time == 0) { //输出表头
context.write(new Text("grand_child"), new
Text("grand_parent"));
time++;
}
int grand_child_num = 0;
String grand_child[] = new String[10];
int grand_parent_num = 0;
String grand_parent[] = new String[10];
Iterator ite = values.iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
String record = ite.next().toString();
int len = record.length();
int i = 2;
if (len == 0) continue;
char relation_type = record.charAt(0);
String child_name = new String();
String parent_name = new String();
//获取 value-list 中 value 的 child
while (record.charAt(i) != '+') {
child_name = child_name + record.charAt(i);
i++;
}
i = i + 1;
//获取 value-list 中 value 的 parent
while (i < len) {
parent_name = parent_name + record.charAt(i);
i++;
}
//左表,取出 child 放入 grand_child
if (relation_type == '1') {
grand_child[grand_child_num] = child_name;
grand_child_num++;
} else {//右表,取出 parent 放入 grand_parent
grand_parent[grand_parent_num] = parent_name;
grand_parent_num++;
}
}
if (grand_parent_num != 0 && grand_child_num != 0) {
for (int m = 0; m < grand_child_num; m++) {
for (int n = 0; n < grand_parent_num; n++) {
context.write(new Text(grand_child[m]), new
Text(grand_parent[n]));
//输出结果
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("fs.default.name", "hdfs://master:9000");
String[] otherArgs = new String[]{"input", "output"}; /* 直接设置输入参
数 */
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "Single table join ");
job.setJarByClass(simple_data_mining.class);
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
①上传文件

②代码运行
4.实验报告
|
题目: |
MapReduce初级编程实践 |
姓名 |
陈庆振 |
日期 12.2 |
|
||||
|
实验内容与完成情况: 文件合并和去重操作: 编写MapReduce程序,对两个输入文件A和B进行合并,并剔除重复内容,生成新的输出文件C。实验成功,合并去重功能正常。 输入文件排序: 编写MapReduce程序,读取多个输入文件中的整数,进行升序排序,并输出排序位次和原整数。实验成功,排序功能正常。 信息挖掘: 编写MapReduce程序,挖掘给定的child-parent表格中的父子辈关系,输出祖孙辈关系的表格。实验成功,信息挖掘功能正常。 |
||||
|
出现的问题:在配置Hadoop运行环境时,遇到了配置文件路径错误的问题,导致无法正确运行MapReduce任务。 在实现排序功能时,由于MapReduce框架的默认行为,遇到了数据分布不均匀的问题。 |
||||
|
解决方案(列出遇到的问题和解决办法,列出没有解决的问题):对于配置文件路径错误,通过检查和修正Hadoop配置文件中的路径设置,确保所有路径正确无误,问题得以解决。 对于数据分布不均匀的问题,通过调整Partitioner类,使得数据能够更均匀地分布到各个Reducer上,从而解决了问题。 |
||||


