线程池
1 线程池的概念
线程池,其实就是一个容纳多个线程的容器,其中的线程可以反复使用,省去了频繁创建线程对象的操作,无需反复创建线程而消耗过多资源。
2.使用线程池的方式-----Runnable接口
线程池都是通过线程池工厂创建,再调用线程池中的方法获取线程,再通过线程去执行任务方法
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"..."+i); } } }
public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.从线程池工厂获取线程池对象 ExecutorService es=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //2.线程池中会看看哪个线程有空找那个个线程帮你执行线程任务 es.submit(new MyRunnable()); //销毁线程池 es.shutdown(); } }
3.使用线程池的方式------Callable接口
与Runnable接口功能相似,用来指定线程的任务。
public class MyCallable implements Callable<String>{ public String call() throws Exception { return "abc"; } }
public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { //1.先从线程池工厂中获取线程池对象 ExecutorService es=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //2.执行线程任务 Future<String> str=es.submit(new MyCallable()); //3.从Future对象中获取返回值 String s=str.get(); System.out.println(s); //销毁线程池 es.shutdown(); } }
线程池练习:返回两个数相加的结果
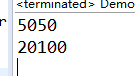
public class Demo05 { //线程实现计算 //由两个线程分别计算1...100的和 1....200的和 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { ExecutorService es=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); Future<Integer> f=es.submit(new CallSum(100)); System.out.println(f.get()); Future<Integer> f1=es.submit(new CallSum(200)); System.out.println(f1.get()); //销毁线程池 es.shutdown(); } }




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步