爬虫学习-02
一、requests高级用法
ssl认证(了解项)
http和https的区别?
HTTP协议以明文方式发送内容,不提供任何方式的数据加密。HTTP协议不适合传输一些敏感信息,比如:信用卡号、密码等支付信息。
https则是具有安全性的ssl加密传输协议。
http和https使用的是完全不同的连接方式,用的端口也不一样,前者是80,后者是443。并且https协议需要到ca申请证书。
HTTPS协议是由SSL+HTTP协议构建的可进行加密传输、身份认证的网络协议,要比http协议安全。简言之:https = http + ssl/tsl 非对称加密之后传输的,需要有公钥私钥,在浏览器里内置了,公钥需要有被浏览器认证过的机构签发的,有锁的就是安全的

- 没有被认证过的机构,签发的证书,用的时候浏览器会显示不安全
代码展示
# 1 ssl认证
# 1.1 不认证证书了
import requests
respone = requests.get('https://www.12306.cn', verify=False) # 不验证证书,报警告,返回200
print(respone.status_code)
# 1.2 手动携带证书访问
import requests
respone = requests.get('https://www.12306.cn', cert=('/path/server.crt', '/path/key'))
print(respone.status_code)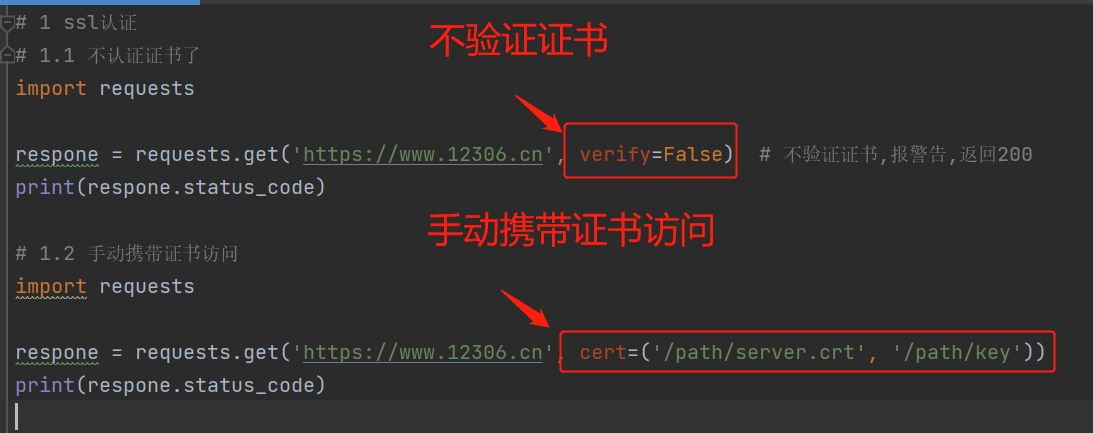
使用代理(重要项)
- 我们做频率限制和封账号,一般都是通过ip或用户id限制,做爬虫的目的,就是要避免这些
- 封ip:代理
- 封账号:注册很多小号
- 代理是什么?
- 反向代理为何叫反向代理详情:
https://www.zhihu.com/question/24723688/answer/2771833737?utm_campaign=shareopn&utm_content=group1_Answer&utm_medium=social&utm_oi=41967790587904&utm_psn=1579135646907764736&utm_source=wechat_session- 正向代理:代理客户端
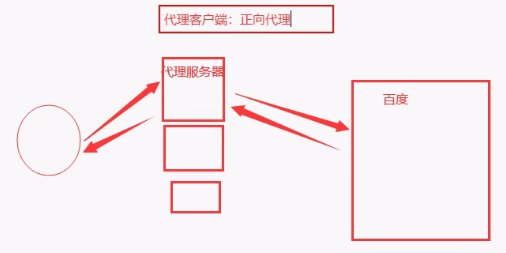
- 反向代理:代理服务端
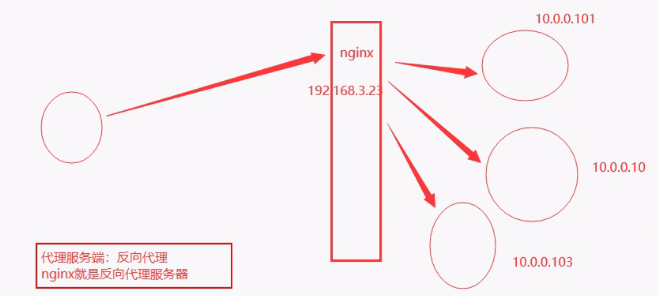
- 代理有收费的和免费的(免费的基本有些爬不到)
- 发送http请求,使用代理发送
使用代理ip发送请求
import requests
proxies = {
'http': '192.168.10.102:9003',
}
respone=requests.get('https://www.baidu.com',proxies=proxies)
print(respone.text)超时设置
respone=requests.get('https://www.baidu23.com',timeout=3)
print(respone)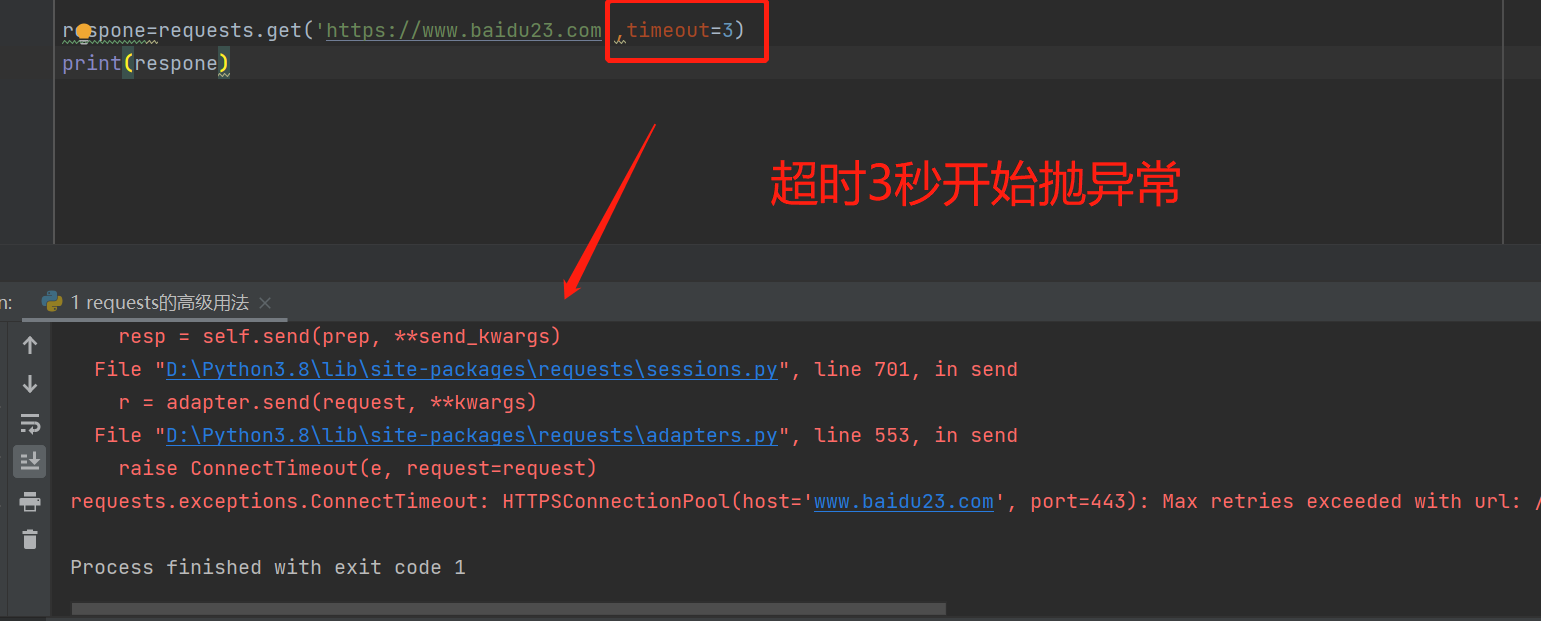
异常处理
- 出问题打印相关的错误,代码健壮一些
# import requests
# from requests.exceptions import * #可以查看requests.exceptions获取异常类型
# try:
# r=requests.get('http://www.baidu.com',timeout=0.00001)
# except ReadTimeout:
# print('===:')
# except ConnectionError: #网络不通
# print('-----')
# except Timeout:
# print('aaaaa')
#
# except RequestException:
# print('Error')上传文件
- 写后端给第三方交互的时候会上传文件
# files={'file':open('a.txt','rb')}
# respone=requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post',files=files)
# print(respone.text)二、代理池搭建
gitthub开源的,代理池的代码,本地跑起来
- 爬虫技术:爬取免费的代理网站,获取免费代理,验证过后,存到本地
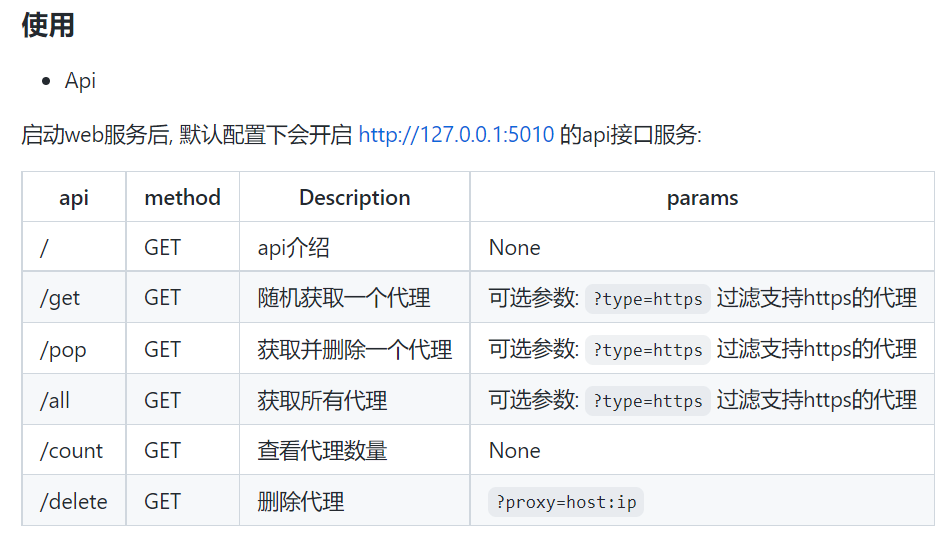
- 使用flask搭建一个web后端,访问某个接口就可以随机返回一个可用的代理地址
https://github.com/jhao104/proxy_pool
搭建步骤
- 把人家的东西克隆下来
git clone https://github.com/jhao104/proxy_pool.git - 创建虚拟环境
mkvirtualenv -p python3 crawl,
- 安装依赖:
pip install -r requirements.txt - 修改配置文件settings.py——>redis服务启动(别忘了)
-
# 配置API服务 HOST = "0.0.0.0" # IP PORT = 5000 # 监听端口 # 配置数据库 DB_CONN = 'redis://127.0.0.1:8888/0' # 配置 ProxyFetcher PROXY_FETCHER = [ "freeProxy01", "freeProxy02", ] - 启动爬虫,启动web服务
- 启动调度程序:
python proxyPool.py schedule - 启动webApi:
python proxyPool.py server
- 启动调度程序:
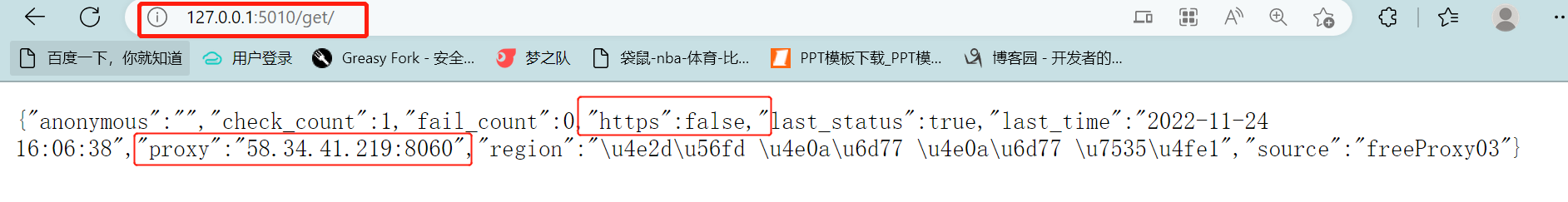
- 随机获取ip
- 127.0.0.1:5000/get
代码展示
import requests
# http://127.0.0.1:5010/get/
# 获取一个随机ip 转成json的格式
res = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:5010/get/').json()
if res['https']:
http = 'https'
else:
http = 'http'
proxie = {
http: res['proxy']
}
print(proxie)
res = requests.get('https://www.cnblogs.com/liuqingzheng/p/16005896.html', proxies=proxie)
print(res.status_code)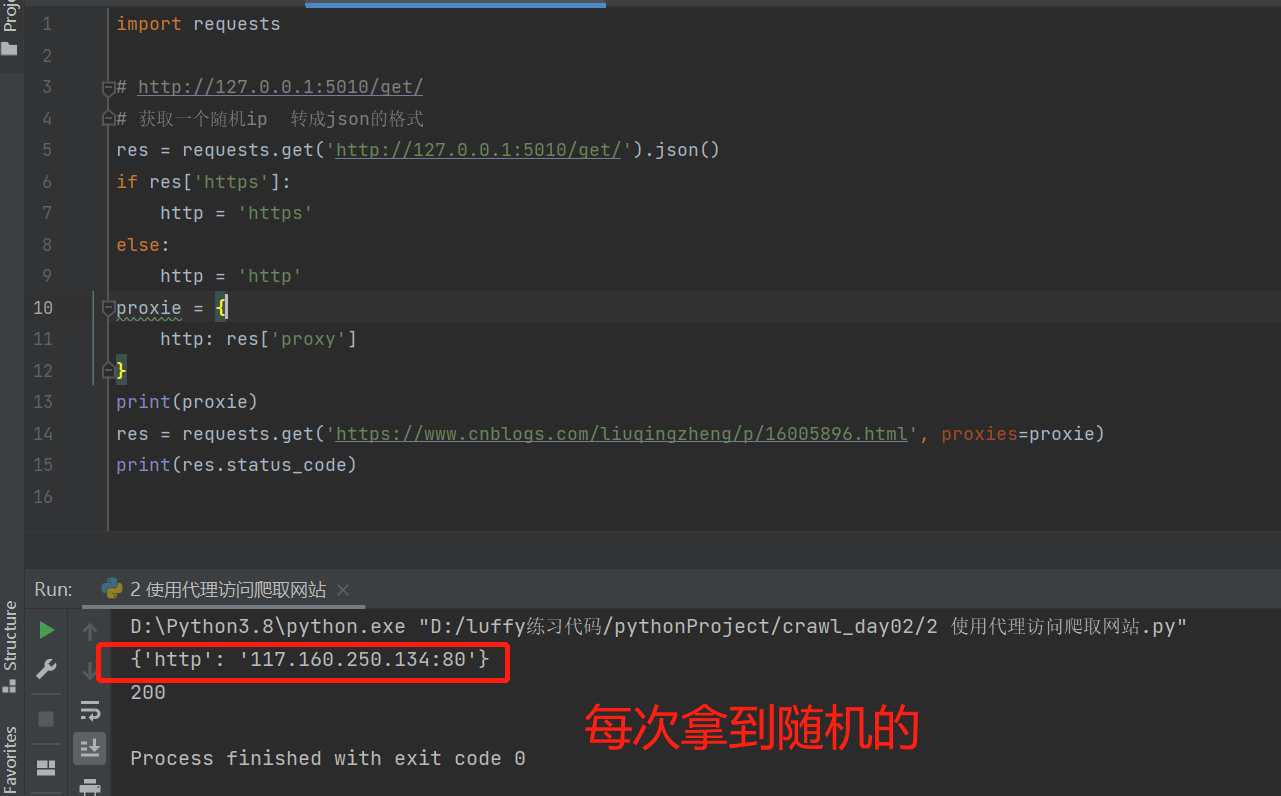
django后端获取客户端的ip
我们作为后端,用户用代理池访问我们的服务端,想看看他的真实ip地址
# 写一个返回用户ip地址的django程序
def ip_test(request):
# 获取客户端ip
ip=request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
return HttpResponse('您的ip是:%s'%ip)
#部署在云服务器
#本地使用requests+代理访问,查看是否返回代理的ip地址
import requests
res = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:5010/get/').json()
if res['https']:
http = 'https'
else:
http = 'http'
proxie = {
http: http+'://'+res['proxy']
}
print(proxie)
# 服务端部署在本地,是访问不到的,内网穿透,或者部署在服务器上
# res = requests.get('http://192.168.1.143:8000/ip/', proxies=proxie)
# res = requests.get('https://46b3k95600.zicp.fun/ip/', proxies=proxie) # 不生效
res = requests.get('http://101.133.225.166/ip/', proxies=proxie)
print(res.text)
# 如果代理不可用,就不用代理了三、爬取视频网站
- requests 爬取好多网站,但是咱们爬回来没法解析。
re“正则匹配” - requests+正则 整站爬取视频
- 梨视频;
https://www.pearvideo.com/
- 梨视频;
- 发的ajax GET请求
- 一共24个li标签,我们要解析出里面的东西
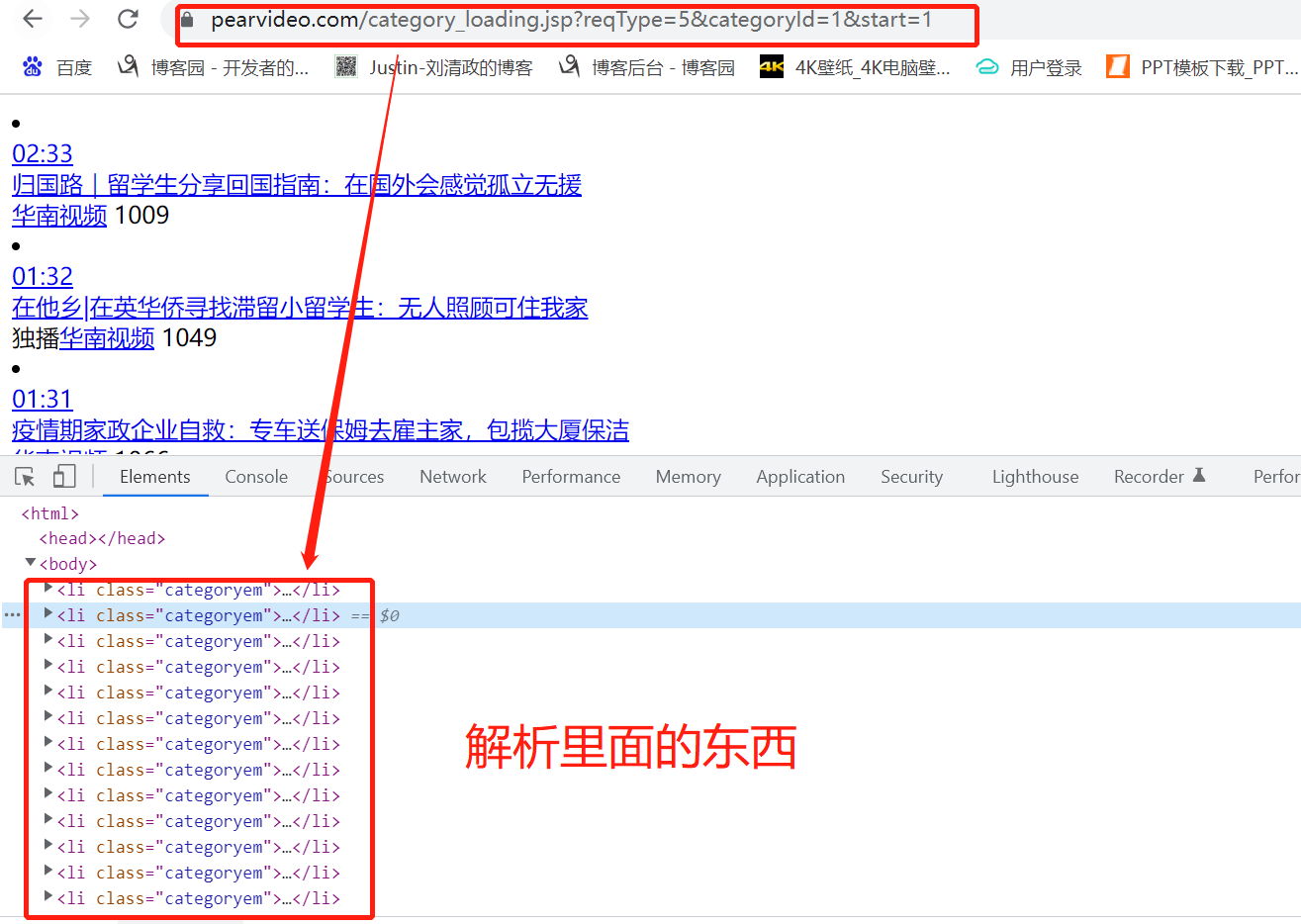
- 使用正则,通过a标签解析出该页面所有的视频地址,findall查找所有,视频的前缀地址+video

- 当我们访问这个地址的时候,他先把这个页面加载出来,又发了ajax请求把视频加载回来,再用js操作,我们要获取mp4,对比两个请求头,发现咱们模拟的不像,没有
Referer,后来对比发现是video和视频id号,进行修改拿到MP4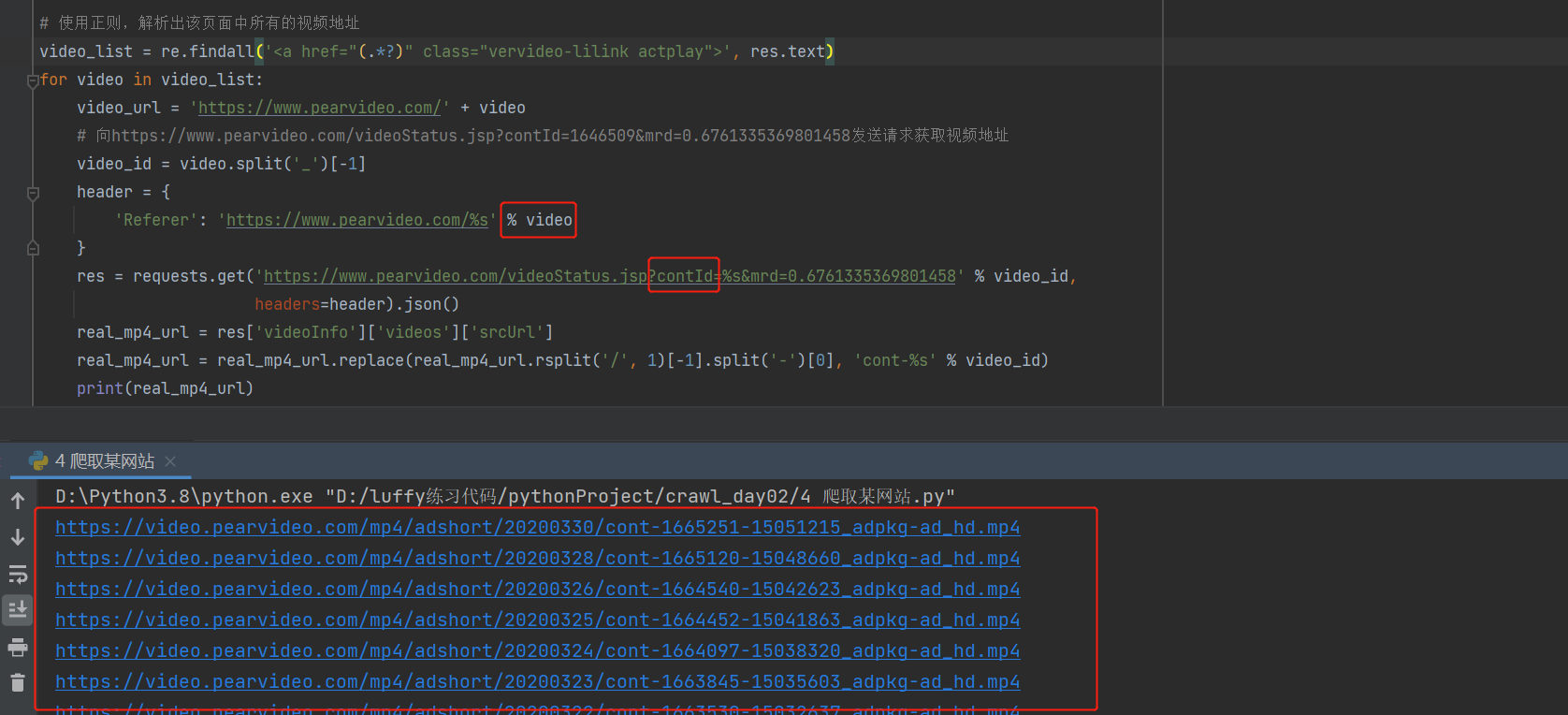
- 但是你拿这个地址访问的时候你发现访问不到404,这是他的第二层反扒
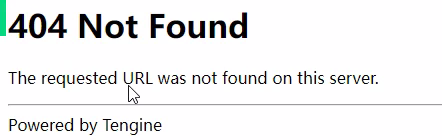
- 与他真正能播的地址对比,真地址的是
cont_id号 - 创建文件,通过单条线程一个个下载到本地
代码展示
import requests
import re
res = requests.get('https://www.pearvideo.com/category_loading.jsp?reqType=5&categoryId=1&start=1')
# 使用正则,解析出该页面中所有的视频地址
video_list = re.findall('<a href="(.*?)" class="vervideo-lilink actplay">', res.text)
for video in video_list:
video_url = 'https://www.pearvideo.com/' + video
# 向https://www.pearvideo.com/videoStatus.jsp?contId=1646509&mrd=0.6761335369801458发送请求获取视频地址
video_id = video.split('_')[-1]
header = {
'Referer': 'https://www.pearvideo.com/%s' % video
}
res = requests.get('https://www.pearvideo.com/videoStatus.jsp?contId=%s&mrd=0.6761335369801458' % video_id,
headers=header).json()
real_mp4_url = res['videoInfo']['videos']['srcUrl']
real_mp4_url = real_mp4_url.replace(real_mp4_url.rsplit('/', 1)[-1].split('-')[0], 'cont-%s' % video_id)
res = requests.get(real_mp4_url)
with open('./video/%s.mp4' % video_id, 'wb') as f:
for line in res.iter_content():
f.write(line)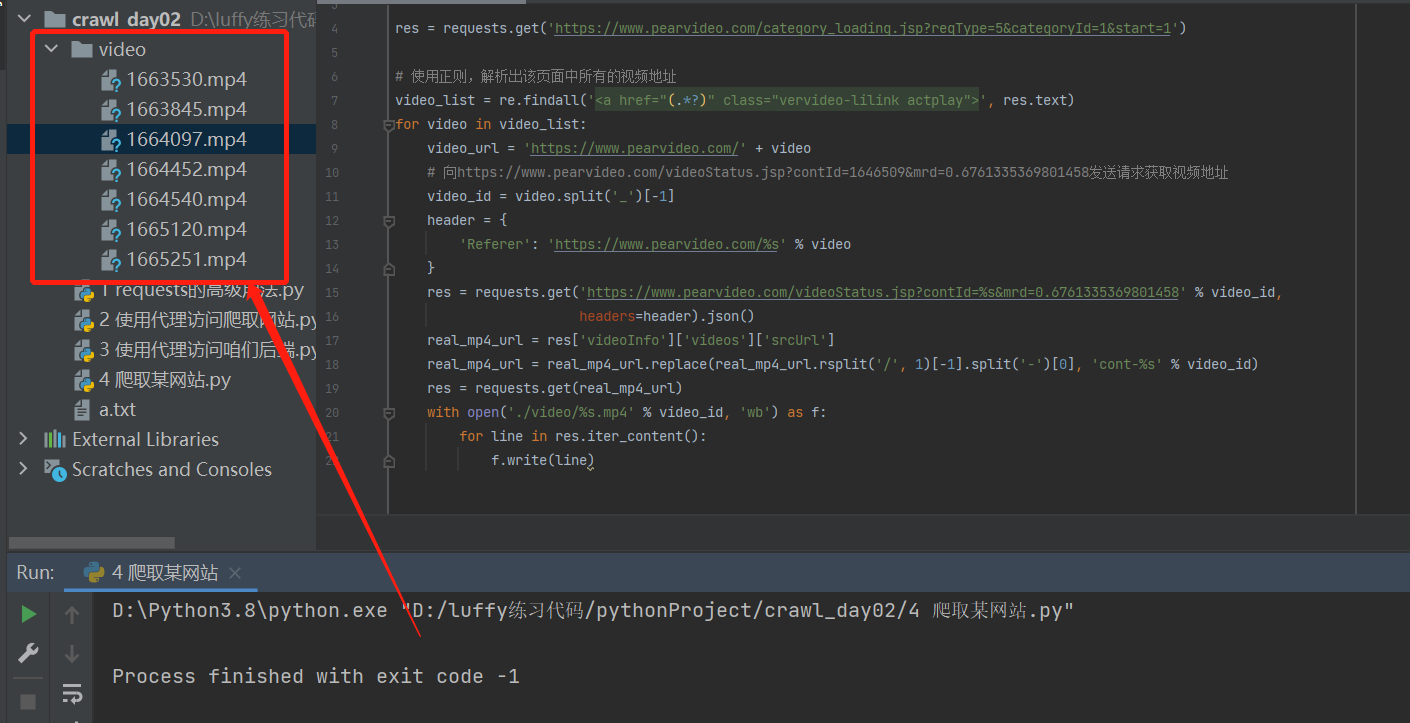
四、爬取新闻
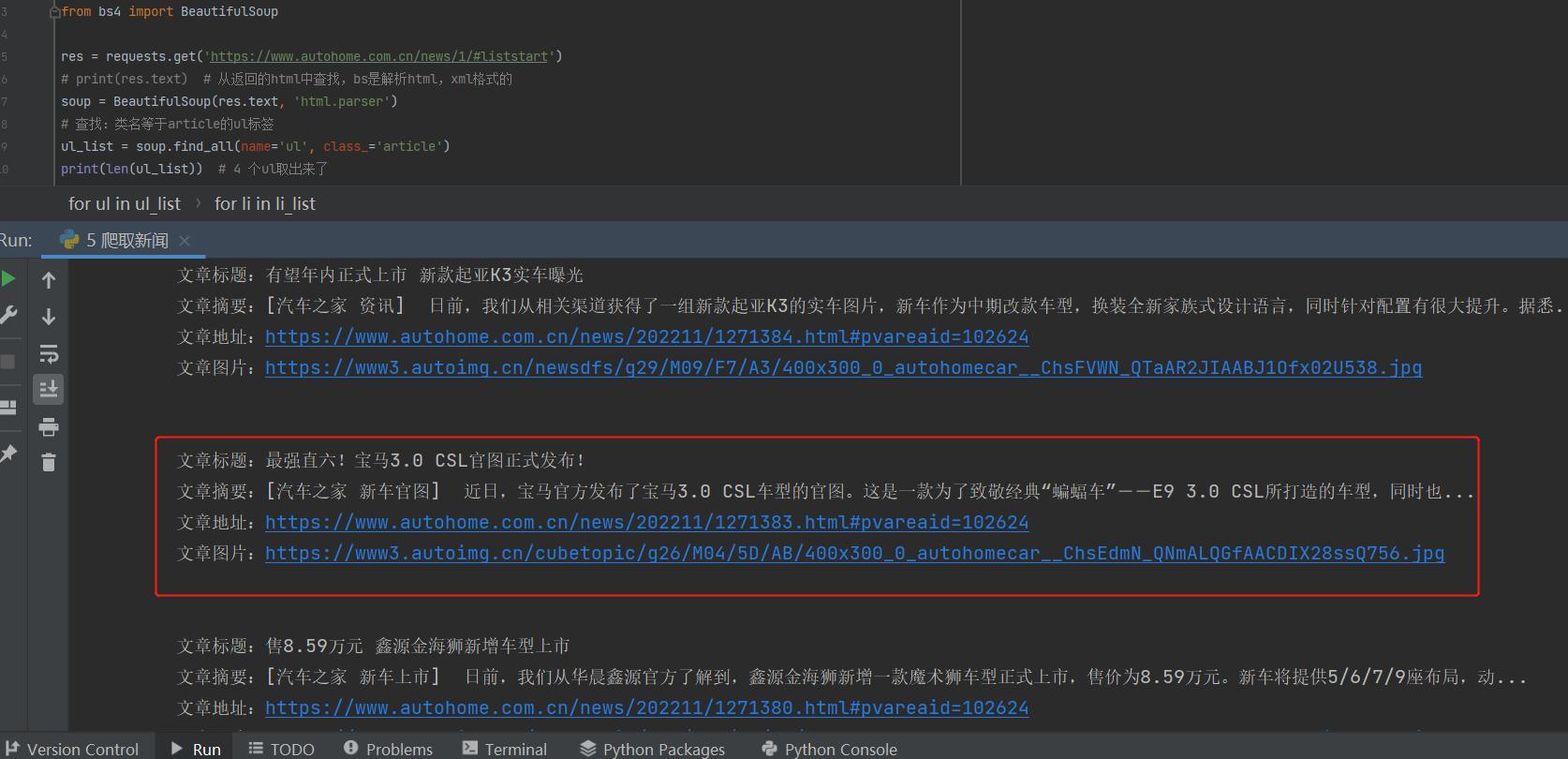
- requests+BautifulSoup4(专业的解析库还有:bs4,lxml...)
- 以这个地址为例:汽车之家
https://www.autohome.com.cn/news/,爬新闻标题、图片等、、、 - 一个
li标签就是一个新闻 - bs4是解析html、xml格式的,从返回的html中查找
- 传入的参数,使用
html.parser解析方式 - 查找类名等于article的ul标签,共计4个
- 再从
ul标签里找所有的li标签,再找h3标签里所有的文本内容 - 再同样取出文章标题、文章摘要、文章地址、文章图片
五、
Beautiful Soup是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库
- 下载:
pip3 install BeautifulSoup4
解析库解释
- BeautifulSoup('要解析的内容:xml格式字符串', "html.parser") 内置解析库html.parser
- BeautifulSoup('要解析的内容:xml格式字符串', "lxml") 速度快 必须要装lxml pip3 install lxml

from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" id='id_p' name='lqz' xx='yy'>lqz is handsome <b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml')
# 1 美化html:了解 # 有换行、缩进等、、、
# print(soup.prettify())
# 2 遍历文档树
'''
#遍历文档树:即直接通过标签名字选择,特点是选择速度快,但如果存在多个相同的标签则只返回第一个
#1、用法
#2、获取标签的名称
#3、获取标签的属性
#4、获取标签的内容
#5、嵌套选择
#6、子节点、子孙节点
#7、父节点、祖先节点
#8、兄弟节点
'''
# 1 基本用法,直接 .标签名字
# res=soup.title
# print(res)
# res=soup.a
# print(res)
# 可以嵌套使用
# res=soup.head.title
# print(res)
# 2 获取标签的名称
# 拿到的所有标签都是一个对象,Tag对象 bs4.element.Tag
# res=soup.head.title
# res=soup.body
# print(res.name)
# 3 获取标签的属性
# res=soup.p
# print(res.attrs) # 属性字典
# 4 获取标签的内容
# res = soup.p
# print(res.text) # 把该标签子子孙孙内容拿出来拼到一起 字符串
# print(res.string) # None 必须该标签没有子标签,才能拿出文本内容
# print(list(res.strings) )# generator 生成器,把子子孙孙的文本内容放到生成器中
# 5 嵌套选择
# res=soup.html.body.a
# print(res.text)
# 6、子节点、子孙节点
# print(soup.p.contents) #p下所有子节点
# print(soup.p.children) #得到一个迭代器,包含p下所有子节点
# 7、父节点、祖先节点
# print(soup.a.parent) #获取a标签的父节点,直接父节点
# print(list(soup.a.parents)) #找到a标签所有的祖先节点,父亲的父亲,父亲的父亲的父亲...
# 8、兄弟节点
# print(soup.a.next_sibling) # 下一个兄弟
# print(soup.a.previous_sibling) # 上一个兄弟
print(list(soup.a.next_siblings)) #下面的兄弟们=>生成器对象
print('-----')
print(list(soup.a.previous_siblings)) #上面的兄弟们=>生成器对象




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)