mysql-4
目录
操作表的SQL语句补充
1.修改表名
alter table 表名 rename 新表名;
2.新增字段
alter table 表名 add 字段名 字段类型(数字) 约束条件;
alter table 表名 add 字段名 字段类型(数字) 约束条件 after 已经存在的字段;
alter table 表名 add 字段名 字段类型(数字) 约束条件 first;
3.修改字段
alter table 表名 change 旧字段 新字段 字段类型(数字) 约束条件;
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 新的字段类型(数字) 约束条件;
4.删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;
表查询关键字
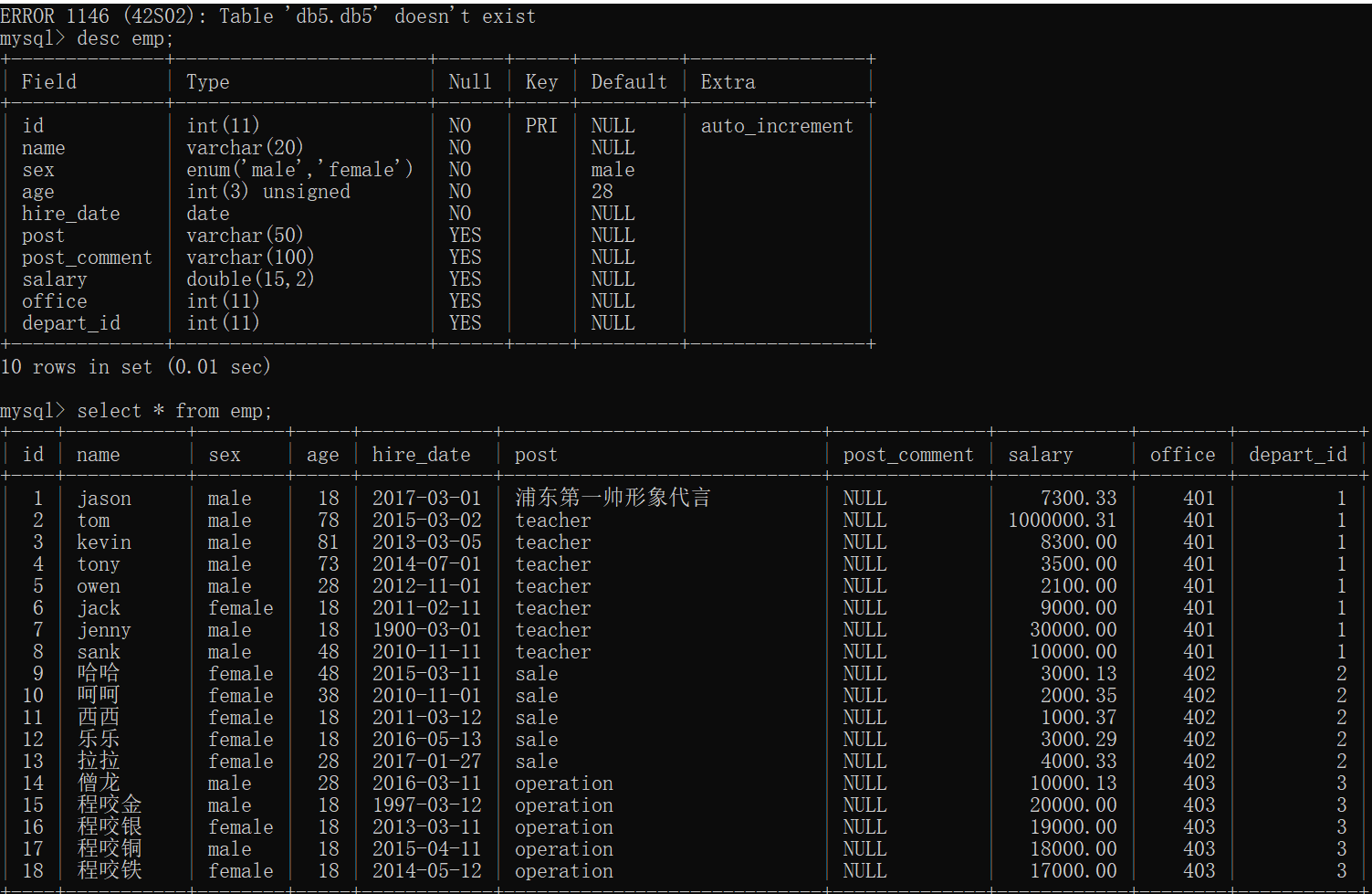
1.数据准备(直接拷贝)
create table emp(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null,
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', #大部分是男的
age int(3) unsigned not null default 28,
hire_date date not null,
post varchar(50),
post_comment varchar(100),
salary double(15,2),
office int, #一个部门一个屋子
depart_id int
);
#三个部门:教学,销售,运营
insert into emp(name,sex,age,hire_date,post,salary,office,depart_id) values
('jason','male',18,'20170301','浦东第一帅形象代言',7300.33,401,1), #以下是教学部
('tom','male',78,'20150302','teacher',1000000.31,401,1),
('kevin','male',81,'20130305','teacher',8300,401,1),
('tony','male',73,'20140701','teacher',3500,401,1),
('owen','male',28,'20121101','teacher',2100,401,1),
('jack','female',18,'20110211','teacher',9000,401,1),
('jenny','male',18,'19000301','teacher',30000,401,1),
('sank','male',48,'20101111','teacher',10000,401,1),
('哈哈','female',48,'20150311','sale',3000.13,402,2),#以下是销售部门
('呵呵','female',38,'20101101','sale',2000.35,402,2),
('西西','female',18,'20110312','sale',1000.37,402,2),
('乐乐','female',18,'20160513','sale',3000.29,402,2),
('拉拉','female',28,'20170127','sale',4000.33,402,2),
('僧龙','male',28,'20160311','operation',10000.13,403,3), #以下是运营部门
('程咬金','male',18,'19970312','operation',20000,403,3),
('程咬银','female',18,'20130311','operation',19000,403,3),
('程咬铜','male',18,'20150411','operation',18000,403,3),
('程咬铁','female',18,'20140512','operation',17000,403,3);
查询关键字之select与from
"""
SQL语句的关键字编写顺序与执行顺序是不一致的!!!
eg: select name from emp;
肯定是先支持from确定表 之后执行select确定字段
编写SQL语句针对select和from可以先写个固定模板
select * from 表名 其他操作
select后的字段可能是实际的 也可能是通过SQL动态产生的 所以可以先用*占位最后再修改
"""
select
自定义查询表中字段对应的数据
from
指定操作的对象(到底是哪张表 也可能是多张)
查询关键字之where筛选
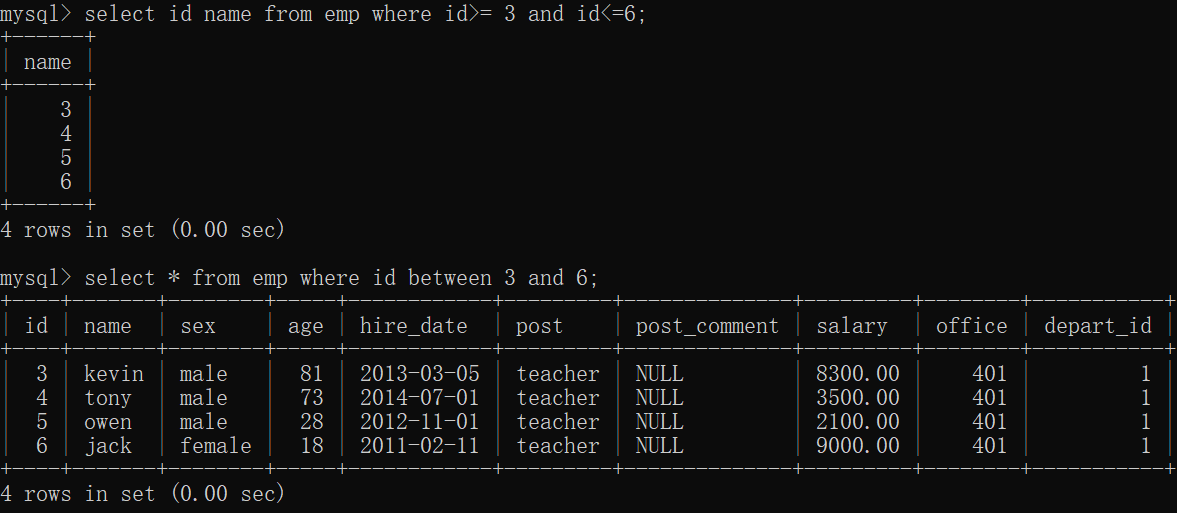
# 1.查询id大于等于3小于等于6的数据
select id,name from emp where id >= 3 and id <= 6;
select * from emp where id between 3 and 6;
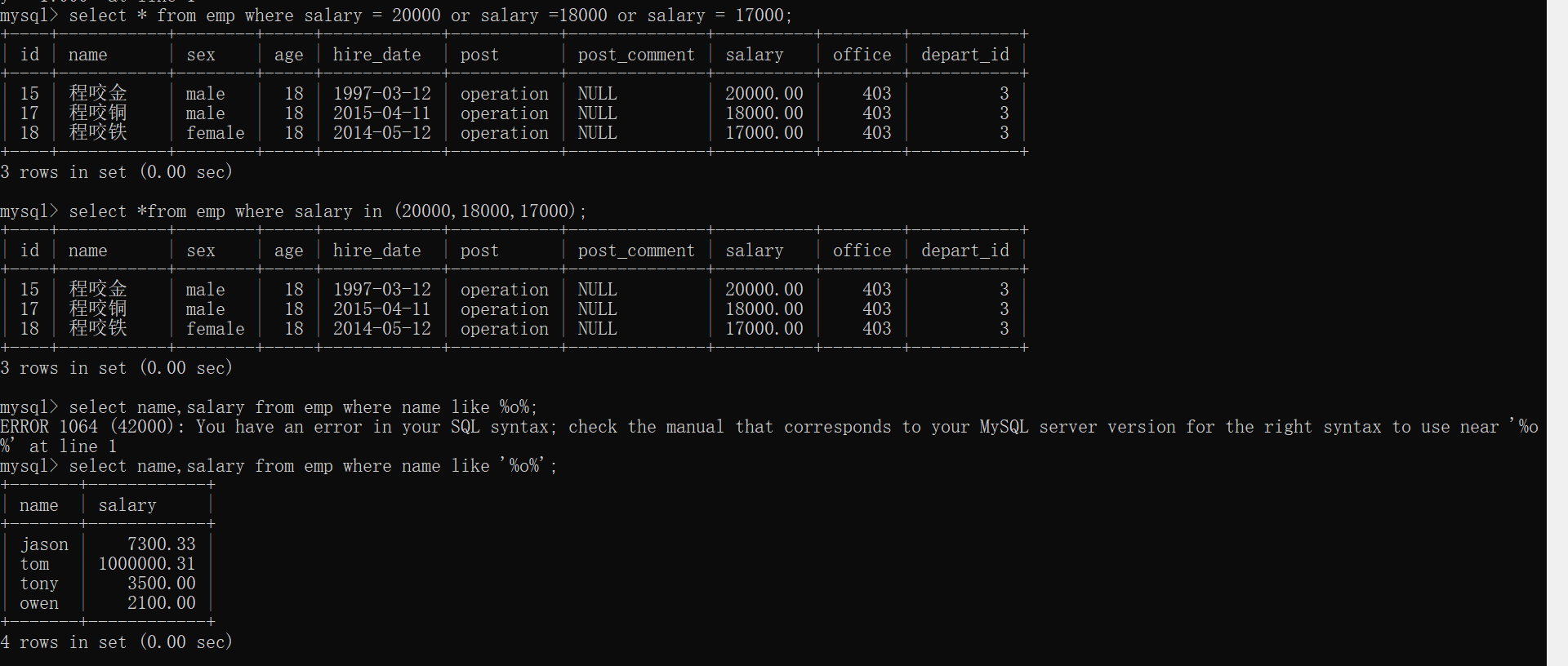
# 2.查询薪资是20000或者18000或者17000的数据
select * from emp where salary = 20000 or salary = 18000 or salary = 17000;
select * from emp where salary in (20000,18000,17000); # 简写
# 3.查询员工姓名中包含o字母的员工姓名和薪资
# 在你刚开始接触mysql查询的时候,建议你按照查询的优先级顺序拼写出你的sql语句
"""
先是查哪张表 from emp
再是根据什么条件去查 where name like ‘%o%’
再是对查询出来的数据筛选展示部分 select name,salary
"""
select name,salary from emp where name like '%o%';
# 4.查询员工姓名是由四个字符组成的员工姓名与其薪资
select name,salary from emp where name like '____';
select name,salary from emp where char_length(name) = 4;
# 5.查询id小于3或者大于6的数据
select * from emp where id not between 3 and 6;
# 6.查询薪资不在20000,18000,17000范围的数据
select * from emp where salary not in (20000,18000,17000);
# 7.查询岗位描述为空的员工名与岗位名 针对null不能用等号,只能用is
select name,post from emp where post_comment = NULL; # 查询为空!
select name,post from emp where post_comment is NULL;
select name,post from emp where post_comment is not NULL;
查询关键字之group by分组
分组:按照一些指定的条件将单个单个的数据分为一个个整体
"""
分组之后我们研究的对象应该是以组为单位 不应该再直接获取单个数据项 如果获取了应该直接报错 select后面可以直接填写的字段名只能是分组的依据(其他字段需要借助于一些方法才可以获取)
set global sql_mode='strict_trans_tables,only_full_group_by';
"""
select post from emp group by post;
"""
我们写SQL是否需要使用分组 可以在题目中得到答案
每个、平均、最大、最小
配合分组常见使用的有聚合函数
max 最大值
min 最小值
sum 总和
count 计数
avg 平均
"""
获取每个部门的最高工资
# 以组为单位统计组内数据>>>聚合查询(聚集到一起合成为一个结果)
# 每个部门的最高工资
select post,max(salary) from emp group by post;
补充:在显示的时候还可以给字段取别名
select post as '部门',max(salary) as '最高工资' from emp group by post;
as也可以省略 但是不推荐省 因为寓意不明确
# 每个部门的最低工资
select post,min(salary) from emp group by post;
# 每个部门的平均工资
select post,avg(salary) from emp group by post;
# 每个部门的工资总和
select post,sum(salary) from emp group by post;
# 每个部门的人数
select post,count(id) from emp group by post;
查询分组之后的部门名称和每个部门下所有的学生姓名
# group_concat(分组之后用)不仅可以用来显示除分组外字段还有拼接字符串的作用
select post,group_concat(name) from emp group by post;
select post,group_concat(name,"_SB") from emp group by post;
select post,group_concat(name,": ",salary) from emp group by post;
select post,group_concat(salary) from emp group by post;
查询关键字之having过滤
where与having的功能其实是一样的 都是用来筛选数据
只不过where用于分组之前的筛选 而having用于分组之后的筛选
为了人为的区分 所以叫where是筛选 having是过滤
1、统计各部门年龄在30岁以上的员工平均工资,并且保留平均工资大于10000的部门
select post,avg(salary) from emp
where age >= 30
group by post
having avg(salary) > 10000;
查询关键字之distinct去重
去重的前提是数据必须一模一样
select distinct age from emp;
查询关键字之order by排序
select * from emp order by salary asc; #默认升序排
select * from emp order by salary desc; #降序排
select * from emp order by age desc; #降序排
#先按照age降序排,在年轻相同的情况下再按照薪资升序排
select * from emp order by age desc,salary asc;
# 统计各部门年龄在10岁以上的员工平均工资,并且保留平均工资大于1000的部门,然后对平均工资进行排序
select post,avg(salary) from emp
where age > 10
group by post
having avg(salary) > 1000
order by avg(salary)
;
查询关键字之limit分页
# 限制展示条数
select * from emp limit 3;
# 查询工资最高的人的详细信息
select * from emp order by salary desc limit 1;
# 分页显示
select * from emp limit 0,5; # 第一个参数表示起始位置,第二个参数表示的是条数,不是索引位置
select * from emp limit 5,5;
查询关键字之regexp正则
select * from emp where name regexp '^j.*(n|y)$';
多表查询思路
子查询
将一张表的查询结果括号括起来当做另外一条SQL语句的条件
eg:类似以日常生活中解决问题的方式
第一步干什么
第二步基于第一步的结果在做操作 ...
连表操作
先将所有涉及到结果的表全部拼接到一起形成一张大表 然后从大表中查询数据
#建表
create table dep1(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
);
create table emp1(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
gender enum('male','female') not null default 'male',
age int,
dep_id int
);
#插入数据
insert into dep1 values
(200,'技术'),
(201,'人力资源'),
(202,'销售'),
(203,'运营'),
(205,'安保')
;
insert into emp1(name,gender,age,dep_id) values
('jason','male',18,200),
('dragon','female',48,201),
('kevin','male',18,201),
('nick','male',28,202),
('owen','male',18,203),
('jerry','female',18,204);
子查询
# 查询jason的部门名称
1.先获取jason的部门编号
select dep_id from emp1 where name = 'jason'; # 200
2.根据部门编号获取部门名称
select name from dep1 where id = 200;
子查询
select name from dep1 where id = (select dep_id from emp1 where name = 'jason');
连表操作
select * from emp1,dep1; # 笛卡尔积
'''我们不会使用笛卡尔积来求数据 效率太低 连表有专门的语法'''
inner join 内连接
只拼接两边都有的字段数据
left join 左连接
以左表为基准 展示所有的数据 没有对应则NULL填充
right join 右连接
以右表为基准 展示所有的数据 没有对应则NULL填充
union 全连接
select * from emp1 left join dep1 on emp1.dep_id = dep1.id
union
select * from emp1 right join dep1 on emp1.dep_id = dep1.id;





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)