Java--算法--赫夫曼
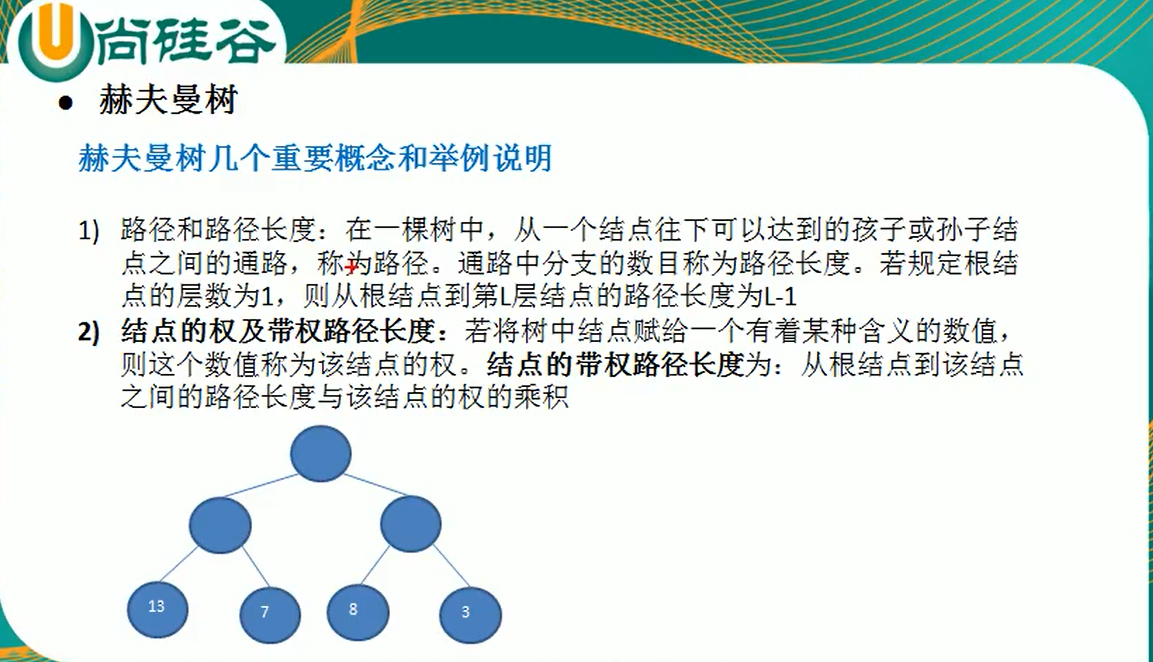
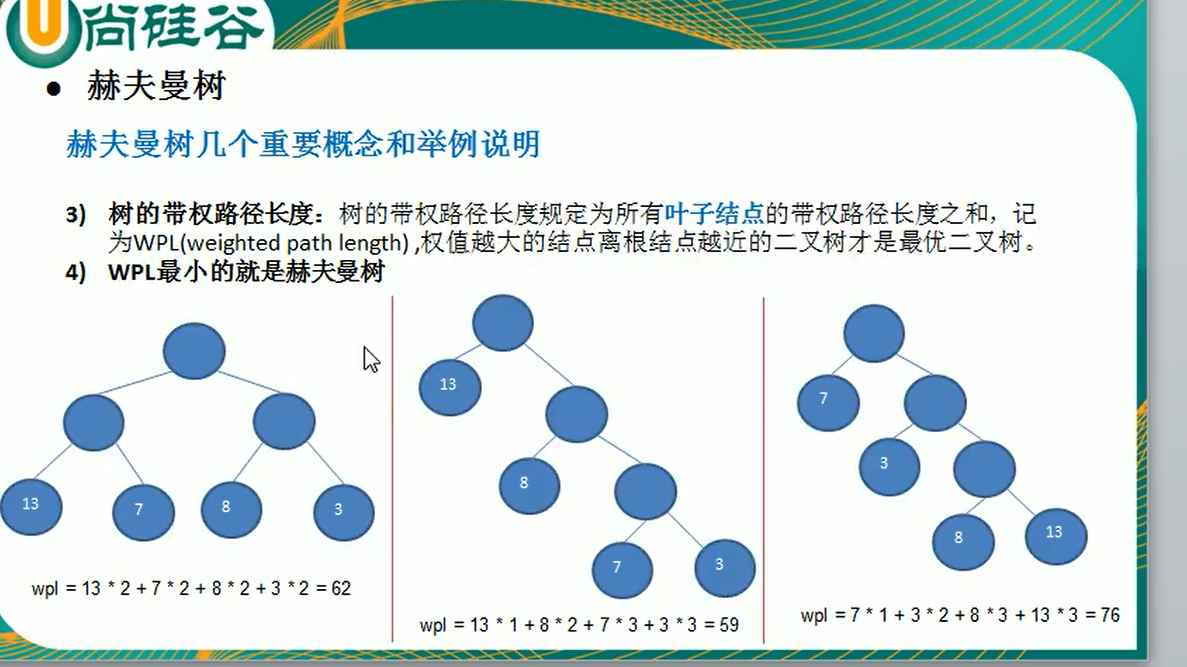
- 赫夫曼树的基本介绍:
-
赫夫曼树的代码实现
-

-
package com.model.tree; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/14 20:40 * 哈夫曼树的实现 */ public class TreeDemo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array={13,7,8,3,29,6,1}; TreeNode root = buildHuffmanTree(array); root.preOrder(); } public static TreeNode buildHuffmanTree(int[] array){ // 1.将所有的节点放到一个集合中 ArrayList<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int num:array){ list.add(new TreeNode(num)); } while(list.size()>1) { // 2.对集合的元素进行排序 Collections.sort(list); // 3.将集合中的两个最小值拿出来,根据最小值创建一个他们的父节点,再将节点挂在父结点上 TreeNode left = list.get(0); TreeNode right = list.get(1); TreeNode parent = new TreeNode(left.getValue() + right.getValue()); parent.setLeft(left); parent.setRight(right); // 4.讲最小值从集合中删除,讲父节点加入到结合中,重复上述过程知道集合中只剩一个父节点为止 list.remove(left); list.remove(right); list.add(parent); } // 返回父节点 return list.get(0); } } class TreeNode implements Comparable<TreeNode>{ private int value; private TreeNode left; private TreeNode right; public TreeNode() { } public TreeNode(int value) { this.value = value; } // 先序遍历 public void preOrder(){ if (this==null){ return; }else { System.out.println(this.toString()); if (this.left!=null){ this.left.preOrder(); } if (this.right!=null){ this.right.preOrder(); } } } @Override public String toString() { return "TreeNode{" + "value=" + value + '}'; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public TreeNode getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(TreeNode left) { this.left = left; } public TreeNode getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(TreeNode right) { this.right = right; } @Override public int compareTo(TreeNode o) { return this.value-o.value; } }
-
-
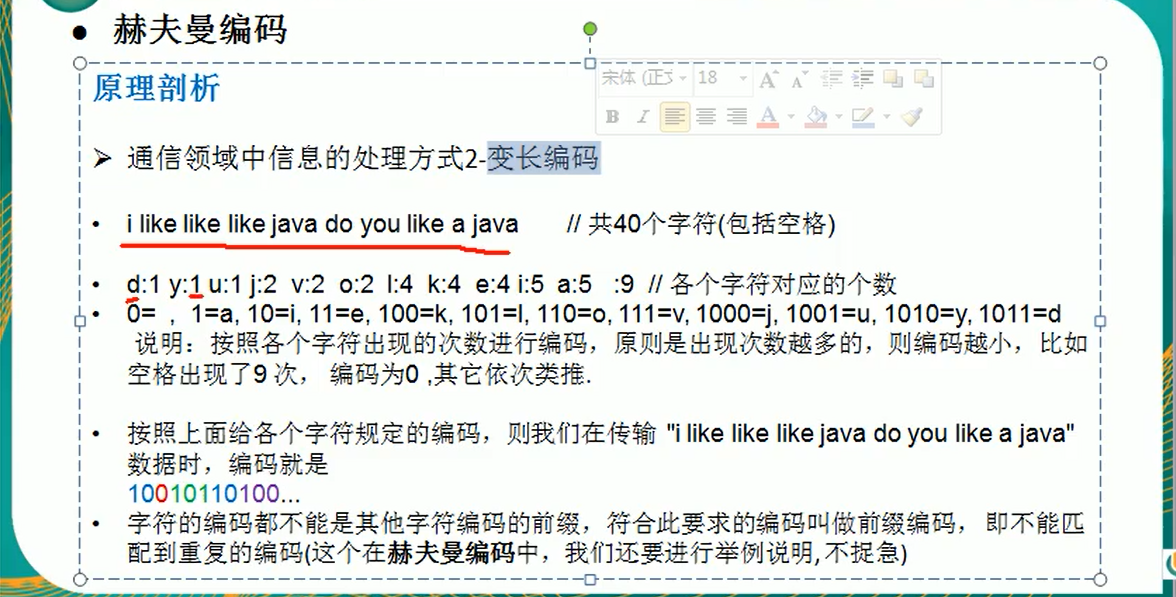
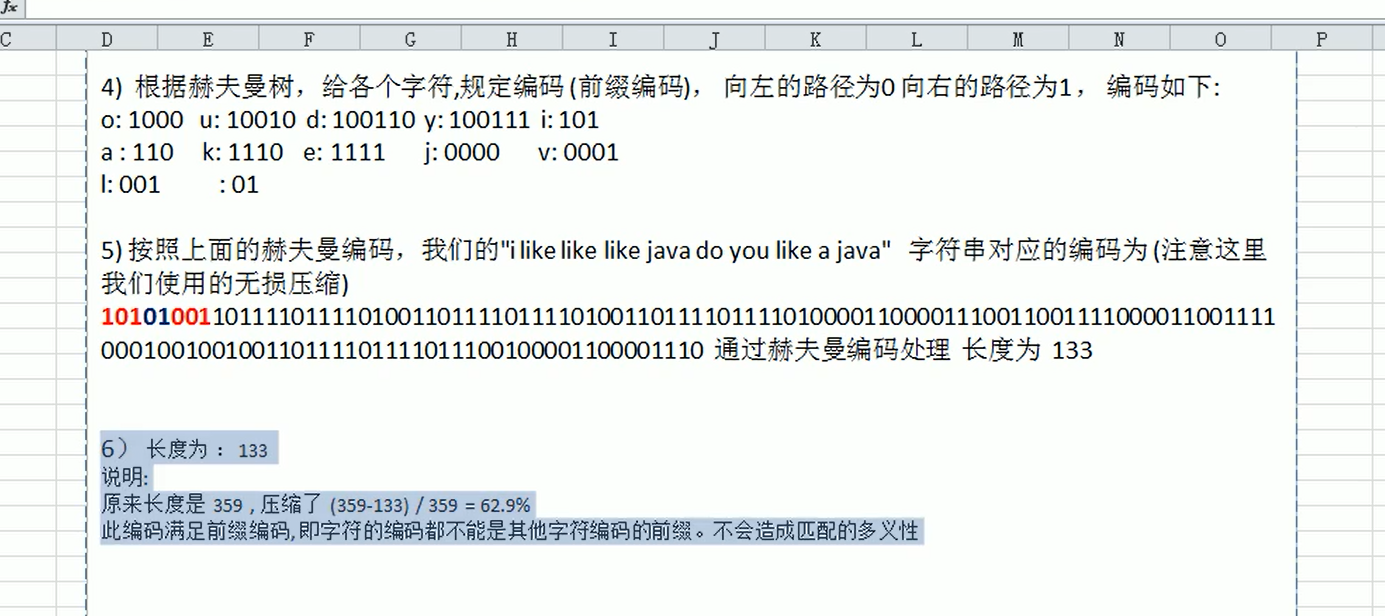
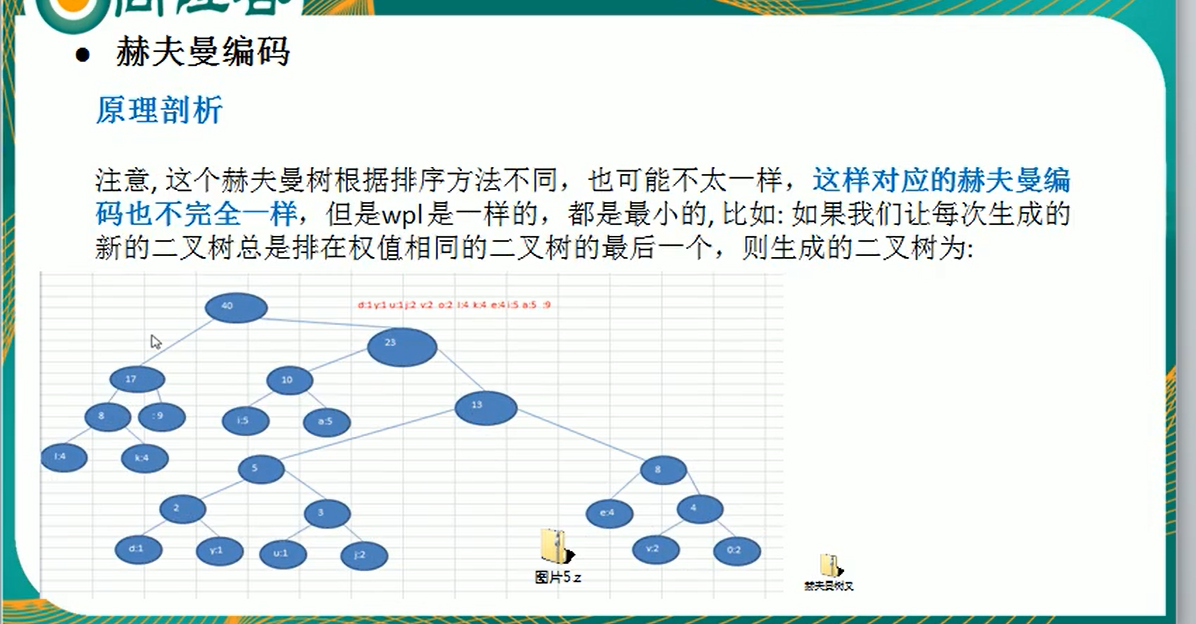
赫夫曼编码的基本介绍:
-
-
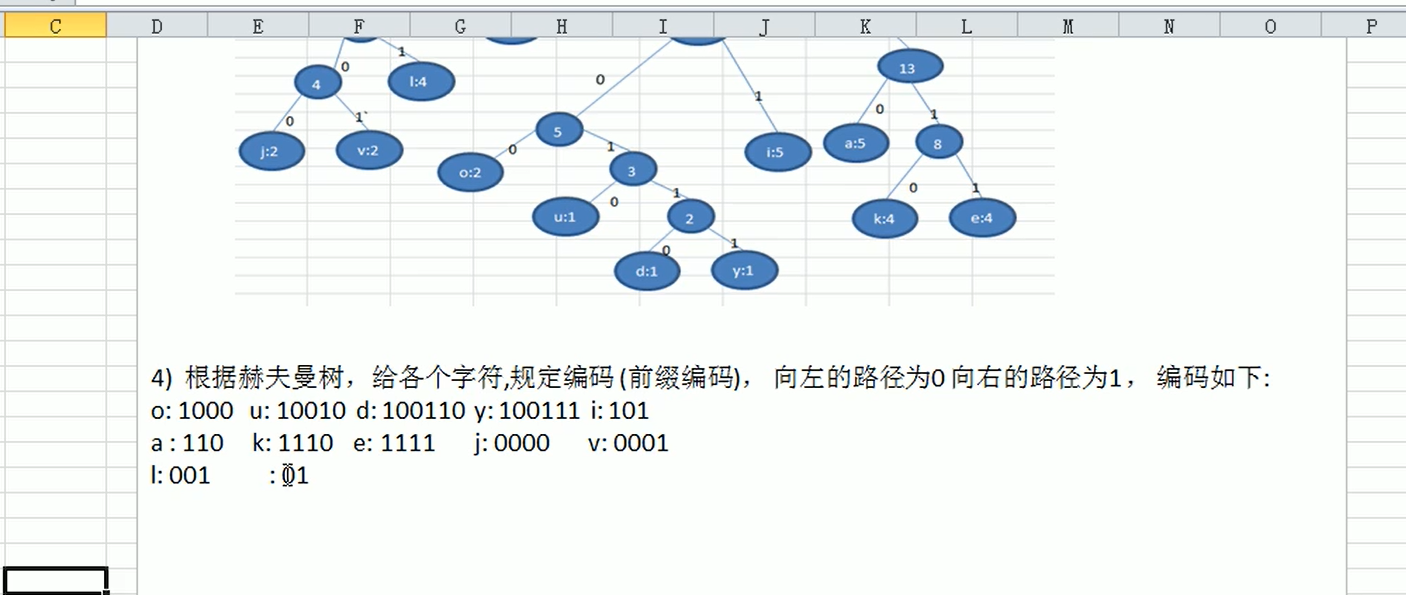
赫夫曼编码的代码实现:
-
-

-
package com.model.tree; import java.util.*; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/15 9:22 * 实现HuffmanCode赫夫曼编码 */ public class TreeDemo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "i like like like java do you like a java"; List<HuffmanNode> nodeList = getNode02(str); // nodeList.forEach(System.out::println); HuffmanNode huffTree = buildHuffTree(nodeList); huffTree.preOrder(); } public static HuffmanNode buildHuffTree(List<HuffmanNode> nodeList){ while(nodeList.size()>1){ Collections.sort(nodeList); HuffmanNode left = nodeList.get(0); HuffmanNode right = nodeList.get(1); HuffmanNode patent=new HuffmanNode(null,left.getWeight()+right.getWeight()); patent.setLeft(left); patent.setRight(right); nodeList.add(patent); nodeList.remove(left); nodeList.remove(right); } return nodeList.get(0); } //将字符串的内容放入到List中,Node中data是值,weight是值出现的次数 public static List<HuffmanNode> getNode(String str) { ArrayList<HuffmanNode> res = new ArrayList<>(); byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); boolean flag = false; for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) { for (HuffmanNode temp : res) { if (temp.getData() == bytes[i]) { int weight = temp.getWeight(); temp.setWeight((++weight)); flag = true; } } if (flag == false) { res.add(new HuffmanNode(bytes[i], 1)); } else { flag = false; } } return res; } public static List<HuffmanNode> getNode02(String str) { ArrayList<HuffmanNode> res = new ArrayList<>(); byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); HashMap<Byte, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) { Integer value = map.get(bytes[i]); if (value != null) { map.put(bytes[i], (++value)); } else { map.put(bytes[i], 1); } } for (Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { res.add(new HuffmanNode(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue())); } return res; } } class HuffmanNode implements Comparable<HuffmanNode> { private Byte data; //数据本身 private int weight; //权值 private HuffmanNode left; private HuffmanNode right; // 前序遍历 public void preOrder(){ if (this==null){ return; }else { System.out.println(this.toString()); if (this.left!=null){ this.left.preOrder(); } if (this.right!=null){ this.right.preOrder(); } } } @Override public String toString() { return "HuffmanNode{" + "data=" + data + ", weight=" + weight + '}'; } public HuffmanNode getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(HuffmanNode left) { this.left = left; } public HuffmanNode getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(HuffmanNode right) { this.right = right; } public Byte getData() { return data; } public void setData(Byte data) { this.data = data; } public int getWeight() { return weight; } public void setWeight(int weight) { this.weight = weight; } public HuffmanNode() { } public HuffmanNode(Byte data, int weight) { this.data = data; this.weight = weight; } @Override public int compareTo(HuffmanNode o) { return this.weight - o.weight; } }
-
-
package com.model.tree; import java.util.*; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/15 9:22 * 实现HuffmanCode赫夫曼编码 */ public class TreeDemo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "i like like like java do you like a java"; //// 生成的所有的节点 // List<HuffmanNode> nodeList = getNode02(str); // nodeList.forEach(System.out::println); //// 生成的赫夫曼树 // System.out.println("赫夫曼树:"); // HuffmanNode huffTree = buildHuffTree(nodeList); // huffTree.preOrder(); //// 生成的赫夫曼编码: // Map<Byte, String> map = getHuffCode(huffTree); // System.out.println("赫夫曼编码:"); // for (Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry: map.entrySet()){ // System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"\t"+entry.getValue()); // } // //的到字符串对应的赫夫曼编码字符串101010001011111111001000101111111 // Byte[] huffCoding = zip(str, map);//压缩后的赫夫曼编码的字节数组 // System.out.println("压缩后的字节数组:"+Arrays.toString(huffCoding)); Byte[] zip = huffmanZip(str); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(zip)); System.out.println("节省空间:"+(str.length()- zip.length)); } // 5.对所有的方法进行封装,传入字符串,返回字符串对应的赫夫曼编码(压缩后的) public static Byte[] huffmanZip(String str){ // 对字符串转为转为字节数组,通过统计字节数组的中元素出现次数,创建节点,在将节点放在一个list中 List<HuffmanNode> nodeList = getNode02(str); // 通过list中的节点创建赫夫曼树 HuffmanNode huffTree = buildHuffTree(nodeList); // 根据赫夫曼树创建赫夫曼编码表 Map<Byte, String> huffCodeTable = getHuffCode(huffTree); // 根据编码表和字符串的到字符串对应的赫夫曼编码,并对赫夫曼编码进行压缩 Byte[] resCoding = zip(str, huffCodeTable); return resCoding; } // 4.利用赫夫曼编码表得到字符串对应的赫夫曼编码,然后对字符串的赫夫曼编码进行压缩处理 public static Byte[] zip(String str,Map<Byte,String> huffCode){ byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();//将字符串转为字节数组 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); for (Byte b:bytes){//利用赫夫曼编码表对字符串进行赫夫曼编码,的到对用的赫夫曼编码字符串 builder.append(huffCode.get(b)); } // 对字符串对应的赫夫曼编码进行压缩处理, //八位一个二进制的数,转为一个数,压缩到byte数组中 int len=0; if (builder.length()%8==0){ len=builder.length()/8; }else { len=builder.length()/8+1; } Byte[] resCoding=new Byte[len];//最终返回的压缩后的赫夫曼编码的字节数组 int index=0; for (int i=0;i<builder.length();i+=8){ String substring=""; if (i+8>builder.length()){ substring=builder.substring(i); }else { substring = builder.substring(i, i + 8); } // 将8位二进制的数转为byte放在byte数组中 byte res = (byte) Integer.parseInt(substring, 2); if (index<len) { resCoding[index] = res; index++; } } return resCoding; } // 3. 根据赫夫曼树的到编码表 public static Map<Byte,String> getHuffCode(HuffmanNode huffmanTree){ if (huffmanTree==null){ return null; } Map<Byte,String> map = new HashMap<>(); getHuffCode(huffmanTree, "", new StringBuilder(),map); return map; } private static void getHuffCode(HuffmanNode node, String code, StringBuilder builder,Map<Byte,String> map) { StringBuilder newBuilder = new StringBuilder(builder); newBuilder.append(code); if (node != null) { if (node.getData() == null) { getHuffCode(node.getLeft(), "0", newBuilder,map); getHuffCode(node.getRight(), "1", newBuilder,map); }else { map.put(node.getData(), newBuilder.toString()); } } } //2.根据节点创建赫夫曼树 public static HuffmanNode buildHuffTree(List<HuffmanNode> nodeList) { while (nodeList.size() > 1) { Collections.sort(nodeList); HuffmanNode left = nodeList.get(0); HuffmanNode right = nodeList.get(1); HuffmanNode patent = new HuffmanNode(null, left.getWeight() + right.getWeight()); patent.setLeft(left); patent.setRight(right); nodeList.add(patent); nodeList.remove(left); nodeList.remove(right); } return nodeList.get(0); } //1.将字符串的内容放入到List中,Node中data是值,weight是值出现的次数 public static List<HuffmanNode> getNode(String str) { ArrayList<HuffmanNode> res = new ArrayList<>(); byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); boolean flag = false; for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) { for (HuffmanNode temp : res) { if (temp.getData() == bytes[i]) { int weight = temp.getWeight(); temp.setWeight((++weight)); flag = true; } } if (flag == false) { res.add(new HuffmanNode(bytes[i], 1)); } else { flag = false; } } return res; } public static List<HuffmanNode> getNode02(String str) { ArrayList<HuffmanNode> res = new ArrayList<>(); byte[] bytes = str.getBytes(); HashMap<Byte, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) { Integer value = map.get(bytes[i]); if (value != null) { map.put(bytes[i], (++value)); } else { map.put(bytes[i], 1); } } for (Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { res.add(new HuffmanNode(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue())); } return res; } } class HuffmanNode implements Comparable<HuffmanNode> { private Byte data; //数据本身 private int weight; //权值 private HuffmanNode left; private HuffmanNode right; // 前序遍历 public void preOrder() { if (this == null) { return; } else { System.out.println(this.toString()); if (this.left != null) { this.left.preOrder(); } if (this.right != null) { this.right.preOrder(); } } } @Override public String toString() { return "HuffmanNode{" + "data=" + data + ", weight=" + weight + '}'; } public HuffmanNode getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(HuffmanNode left) { this.left = left; } public HuffmanNode getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(HuffmanNode right) { this.right = right; } public Byte getData() { return data; } public void setData(Byte data) { this.data = data; } public int getWeight() { return weight; } public void setWeight(int weight) { this.weight = weight; } public HuffmanNode() { } public HuffmanNode(Byte data, int weight) { this.data = data; this.weight = weight; } @Override public int compareTo(HuffmanNode o) { return this.weight - o.weight; } }
-
-
赫夫曼编码的解压:
-

-
// 赫夫曼编码的解压 // 1.压缩形式的赫夫曼编码变为二级制形式的赫夫曼编码 // 2.二进制编码格式的赫夫曼编码变为字符串 Map<Byte, String> huffCodeTable = getHuffCodeTable(buildHuffTree(getNode(str))); byte[] bytes = Unzip(zip, (HashMap<Byte, String>) huffCodeTable); System.out.println(new String(bytes));
-
public static byte[] Unzip(Byte[] huffmanZipCoding, HashMap<Byte, String> huffmanCodeTable) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); // 1.通过压缩的哈夫曼编码,的到二进制形式的哈夫曼编码的字符串 for (int i = 0; i < huffmanZipCoding.length; i++) { if (i == (huffmanZipCoding.length - 1)) { builder.append(byteToBitString(false, huffmanZipCoding[i]));//十进制转为二级制的补码 } else { builder.append(byteToBitString(true, huffmanZipCoding[i]));//十进制转为二级制的补码 } } System.out.println(builder.toString()); // 2. 得到反向的哈夫曼编码表,通过哈夫曼编码的到对应的值 HashMap<String, Byte> unHuffmanCodeTable = new HashMap<>(); for (Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry : huffmanCodeTable.entrySet()) { unHuffmanCodeTable.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey()); } // 3.循环二进制编码的字符串,的到于赫夫曼反表对用的 byte值,将其加入到集合中,返回集合 ArrayList<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < builder.length();) { int count = 1; while (i + count <= builder.length()) { String s = builder.substring(i, i + count); if (unHuffmanCodeTable.get(s) != null) { list.add(unHuffmanCodeTable.get(s)); break; } count++; } i += count; } byte[] res = new byte[list.size()]; for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) { res[i] = list.get(i); } return res; } public static String byteToBitString(boolean flag, byte b) { int temp = b; if (flag && b >= 0) { //如果是正数我们需要补高位,我们补成九位数100000001,再进行截取 temp |= 256; } //如果temp是整数时,转为字符串就是 1,我们需要进行补位->00000001 // 整数的补码还是它本身我们需要进行补位 String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp); //返回的是temp对应的二级制的补码 if (flag) { return str.substring(str.length() - 8); } else { return str; } }
-
-
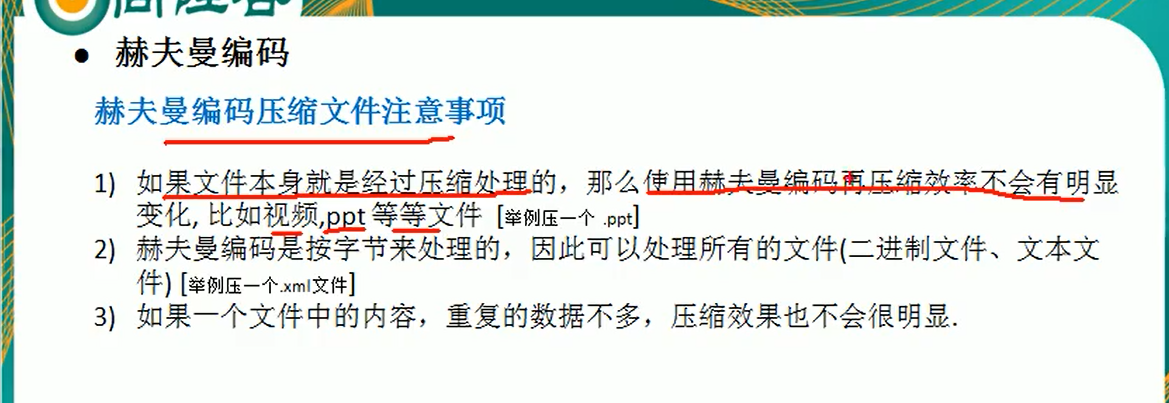
赫夫曼编码-文件压缩:
-

-

-
package com.model.tree; import javax.lang.model.element.NestingKind; import java.io.*; import java.util.*; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/7/15 20:17 * 赫夫曼编码实现对文件的压缩 */ public class TreeDemo07 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 压缩文件 String fileInName="D:\\qq\\IDEA\\IdeaProjects\\java_mianshi\\mianshi_suanfa\\src\\main\\resources\\File\\a.png"; String fileOutName="D:\\qq\\IDEA\\IdeaProjects\\java_mianshi\\mianshi_suanfa\\src\\main\\resources\\File\\a1.zip"; fileZip(fileInName, fileOutName); System.out.println("压缩成功~"); // 解压文件 String zipFile="D:\\qq\\IDEA\\IdeaProjects\\java_mianshi\\mianshi_suanfa\\src\\main\\resources\\File\\a.zip"; String unZipFile="D:\\qq\\IDEA\\IdeaProjects\\java_mianshi\\mianshi_suanfa\\src\\main\\resources\\File02\\a2.png"; fileUnZip(zipFile, unZipFile); System.out.println("解压成功~"); } // 解压文件 public static void fileUnZip(String zipFile, String dstFile) throws IOException { FileInputStream in=null; ObjectInputStream ois=null; OutputStream out=null; try { in=new FileInputStream(zipFile); ois=new ObjectInputStream(in); out=new FileOutputStream(dstFile); Byte[] huffmanCode= (Byte[]) ois.readObject(); Map<Byte,String> huffmanCodeTable = (Map<Byte, String>) ois.readObject(); byte[] unZipCode = unzip(huffmanCode, huffmanCodeTable); out.write(unZipCode); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { in.close(); out.close(); ois.close(); } } // 压缩文件 public static void fileZip(String fileInName, String fileOutName) throws IOException { FileInputStream in = null; FileOutputStream out = null; ObjectOutputStream oos = null; try { in = new FileInputStream(fileInName); out = new FileOutputStream(fileOutName); oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out); byte[] readByte = new byte[in.available()]; // 对读取到的二进制数组进行哈夫曼编码,在进行压缩 Byte[] huffmanZipCode = huffmanZip(readByte); //将压缩后的文件写入到文件中 oos.writeObject(huffmanZipCode); // 赫夫曼编码表写入到文件中 Map<Byte, String> huffCodeTable = getHuffCodeTable(getHuffmanTree(getHuffmanNodeList(readByte))); oos.writeObject(huffCodeTable); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); e.printStackTrace(); } finally { in.close(); out.close(); oos.close(); } } // 对文件进行解压需要的方法 public static byte[] unzip(Byte[] huffmanZipCoding, Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodeTable) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); // 1.通过压缩的哈夫曼编码,的到二进制形式的哈夫曼编码的字符串 for (int i = 0; i < huffmanZipCoding.length; i++) { if (i == (huffmanZipCoding.length - 1)) { builder.append(byteToBitString(false, huffmanZipCoding[i]));//十进制转为二级制的补码 } else { builder.append(byteToBitString(true, huffmanZipCoding[i]));//十进制转为二级制的补码 } } System.out.println(builder.toString()); // 2. 得到反向的哈夫曼编码表,通过哈夫曼编码的到对应的值 HashMap<String, Byte> unHuffmanCodeTable = new HashMap<>(); for (Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry : huffmanCodeTable.entrySet()) { unHuffmanCodeTable.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey()); } // 3.循环二进制编码的字符串,的到于赫夫曼反表对用的 byte值,将其加入到集合中,返回集合 ArrayList<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < builder.length(); ) { int count = 1; while (i + count <= builder.length()) { String s = builder.substring(i, i + count); if (unHuffmanCodeTable.get(s) != null) { list.add(unHuffmanCodeTable.get(s)); break; } count++; } i += count; } byte[] res = new byte[list.size()]; for (int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) { res[i] = list.get(i); } return res; } public static String byteToBitString(boolean flag, byte b) { int temp = b; if (flag && b >= 0) { //如果是正数我们需要补高位,我们补成九位数100000001,再进行截取 temp |= 256; } //如果temp是整数时,转为字符串就是 1,我们需要进行补位->00000001 // 整数的补码还是它本身我们需要进行补位 String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp); //返回的是temp对应的二级制的补码 if (flag) { return str.substring(str.length() - 8); } else { return str; } } // 对文件进行压缩需要的方法 // 5.对所有的方法进行封装,传入字符串,返回字符串对应的赫夫曼编码(压缩后的) public static Byte[] huffmanZip(byte[] bytes) { // 对字符串转为转为字节数组,通过统计字节数组的中元素出现次数,创建节点,在将节点放在一个list中 List<HuffmanNode> nodeList = getHuffmanNodeList(bytes); // 通过list中的节点创建赫夫曼树 HuffmanNode huffTree = getHuffmanTree(nodeList); // 根据赫夫曼树创建赫夫曼编码表 Map<Byte, String> huffCodeTable = getHuffCodeTable(huffTree); // 根据编码表和字符串的到字符串对应的赫夫曼编码,并对赫夫曼编码进行压缩 Byte[] resCoding = getZipCode(bytes, huffCodeTable); return resCoding; } // 4.利用赫夫曼编码表得到字符串对应的赫夫曼编码,然后对字符串的赫夫曼编码进行压缩处理 public static Byte[] getZipCode(byte[] bytes, Map<Byte, String> huffCode) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); for (Byte b : bytes) {//利用赫夫曼编码表对字符串进行赫夫曼编码,的到对用的赫夫曼编码字符串 builder.append(huffCode.get(b)); } // 对字符串对应的赫夫曼编码进行压缩处理, //八位一个二进制的数,转为一个数,压缩到byte数组中 int len = 0; if (builder.length() % 8 == 0) { len = builder.length() / 8; } else { len = builder.length() / 8 + 1; } Byte[] resCoding = new Byte[len];//最终返回的压缩后的赫夫曼编码的字节数组 int index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < builder.length(); i += 8) { String substring = ""; if (i + 8 > builder.length()) { substring = builder.substring(i); } else { substring = builder.substring(i, i + 8); } // 将8位二进制的数转为byte放在byte数组中 byte res = (byte) Integer.parseInt(substring, 2); if (index < len) { resCoding[index] = res; index++; } } return resCoding; } // 3. 根据赫夫曼树的到编码表 public static Map<Byte, String> getHuffCodeTable(HuffmanNode huffmanTree) { if (huffmanTree == null) { return null; } Map<Byte, String> map = new HashMap<>(); getHuffCodeTable(huffmanTree, "", new StringBuilder(), map); return map; } private static void getHuffCodeTable(HuffmanNode node, String code, StringBuilder builder, Map<Byte, String> map) { StringBuilder newBuilder = new StringBuilder(builder); newBuilder.append(code); if (node != null) { if (node.getData() == null) { getHuffCodeTable(node.getLeft(), "0", newBuilder, map); getHuffCodeTable(node.getRight(), "1", newBuilder, map); } else { map.put(node.getData(), newBuilder.toString()); } } } //2.根据节点创建赫夫曼树 public static HuffmanNode getHuffmanTree(List<HuffmanNode> nodeList) { while (nodeList.size() > 1) { Collections.sort(nodeList); HuffmanNode left = nodeList.get(0); HuffmanNode right = nodeList.get(1); HuffmanNode patent = new HuffmanNode(null, left.getWeight() + right.getWeight()); patent.setLeft(left); patent.setRight(right); nodeList.add(patent); nodeList.remove(left); nodeList.remove(right); } return nodeList.get(0); } //1.将字符串的内容放入到List中,Node中data是值,weight是值出现的次数 public static List<HuffmanNode> getHuffmanNodeList(byte[] bytes) { ArrayList<HuffmanNode> res = new ArrayList<>(); HashMap<Byte, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) { Integer value = map.get(bytes[i]); if (value != null) { map.put(bytes[i], (++value)); } else { map.put(bytes[i], 1); } } for (Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { res.add(new HuffmanNode(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue())); } return res; } }
-
-