Java--集合--LinkedList
- LinkedList全面说名
-
LinkedList底层机制
-

-
package com.model.linkedlist; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/6/12 9:21 */ public class LinkedListDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 模拟一个双向链表 Node a=new Node("a"); Node b=new Node("b"); Node c=new Node("c"); Node first=a; Node last=c; a.next=b; b.next=c; c.pre=b; b.pre=a; while(true){ if (first==null){ break; } System.out.println(first.toString()); first=first.next; } while(true){ if (last==null){ break; } System.out.println(last.toString()); last=last.pre; } //添加一个元素,在a和b之间 Node B=new Node("B"); B.next=b; B.pre=a; b.pre=B; a.next=B; //循环遍历验证 first=a; last=c; while(true){ if (first==null){ break; } System.out.println(first.toString()); first=first.next; } } } class Node{ protected Node next; protected Node pre; protected Object item; public Node(Object item) { this.item = item; } @Override public String toString() { return "Node{" + "item=" + item + '}'; } }
-
-
LinkedList底层结构
-

-
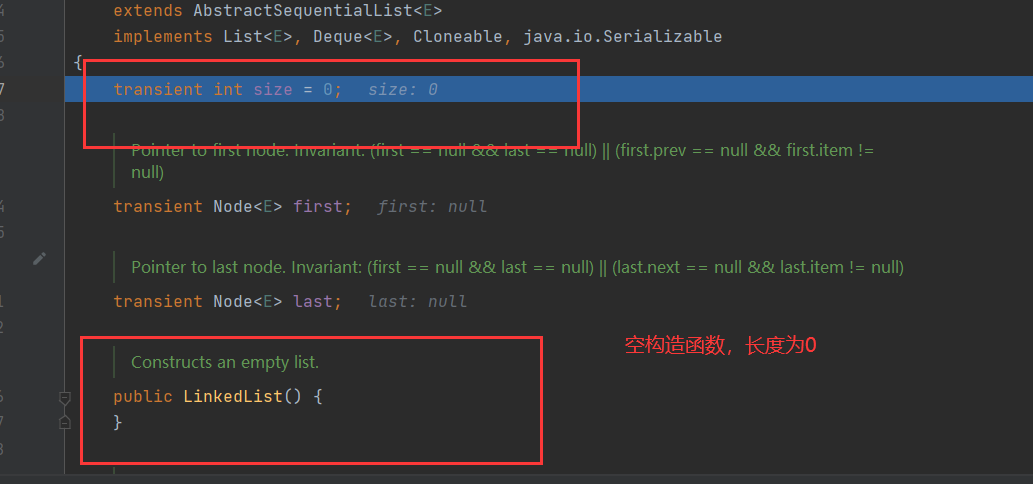
执行 :new LinkedList();
-
-
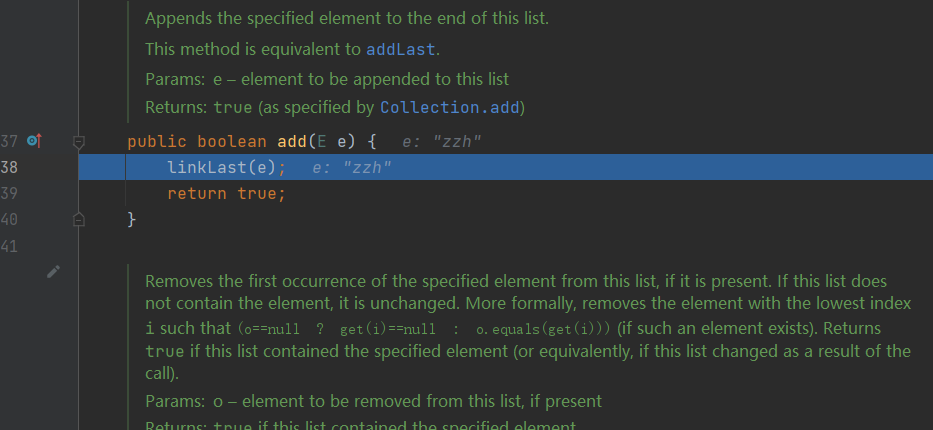
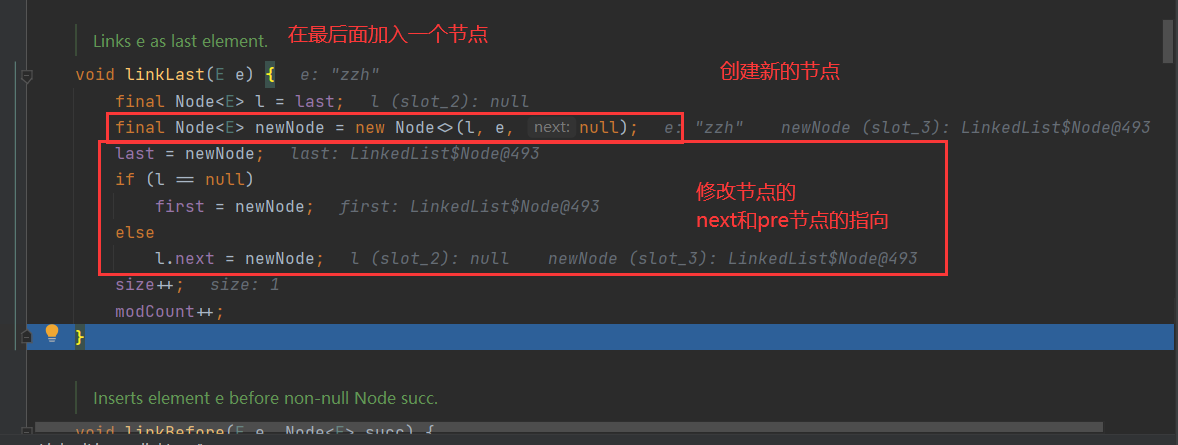
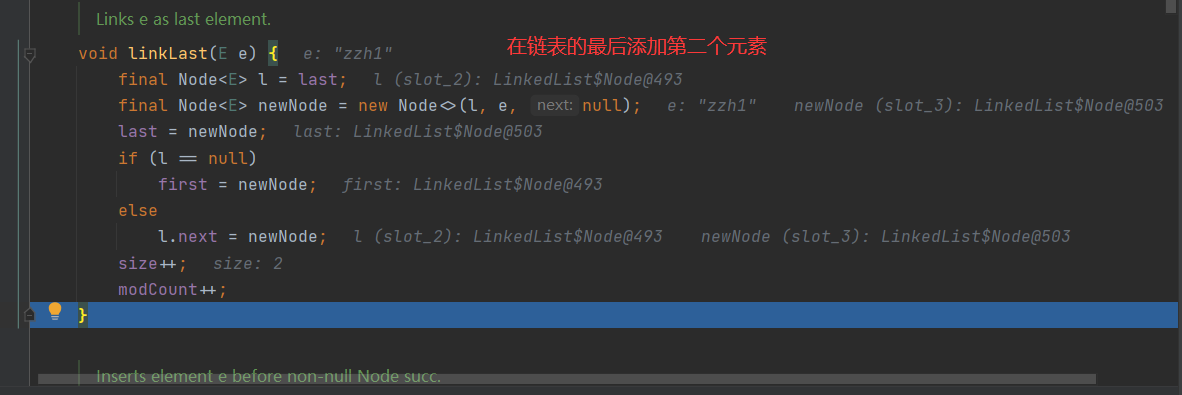
执行 linkedList.add()
-
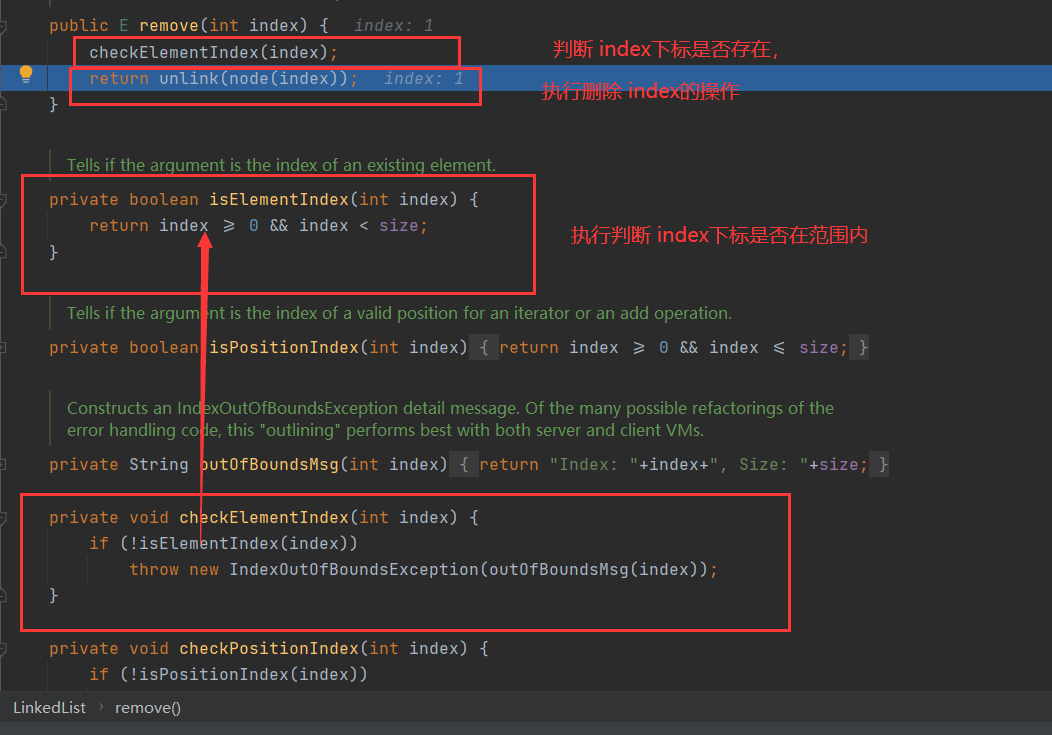
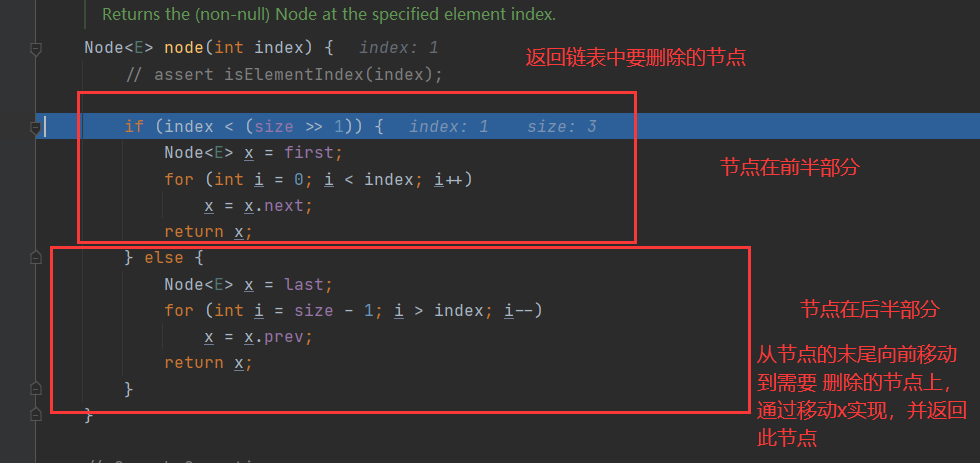
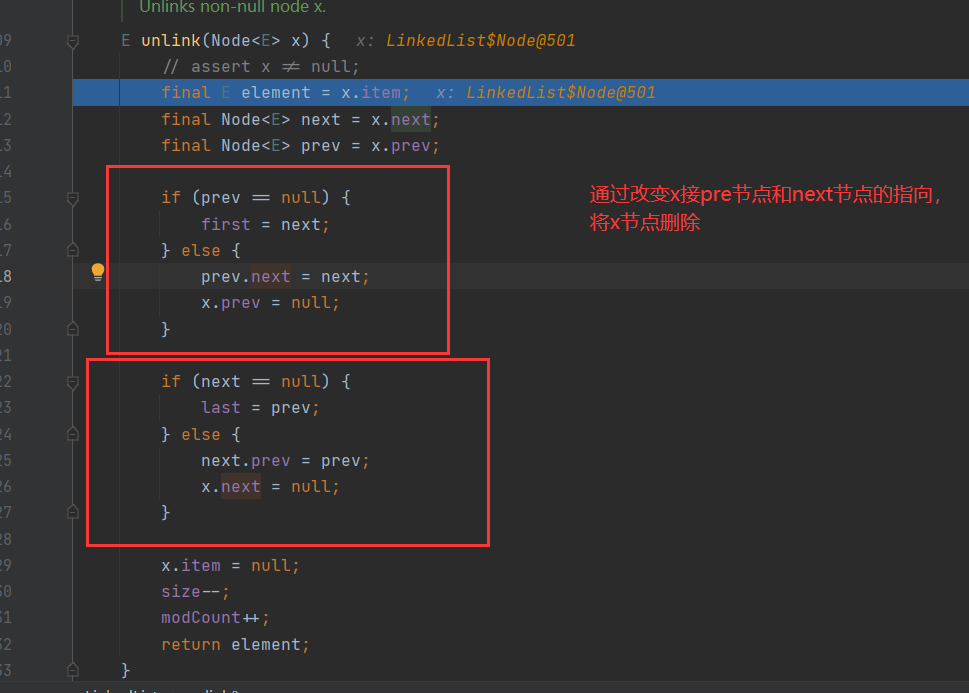
执行 linkedList.remove(1);
-
-
-
package com.model.linkedlist; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; /** * @Description:测试类 * @Author: 张紫韩 * @Crete 2021/6/12 9:49 */ public class LinkedListDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Object> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); linkedList.add("zzh"); linkedList.add("zzh1"); linkedList.add("zzh2"); linkedList.remove(1); Iterator<Object> iterator = linkedList.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Object next = iterator.next(); System.out.println(next); } for (Object o:linkedList){ System.out.println(o); } for (int i=0;i<linkedList.size();i++){ System.out.println(linkedList.get(i)); } } /** * CRUD:增删改查 * * 1.new LinkedList(): * * public LinkedList() { * } * 这是first,last,size都为空 * 2. * */ }
-
-
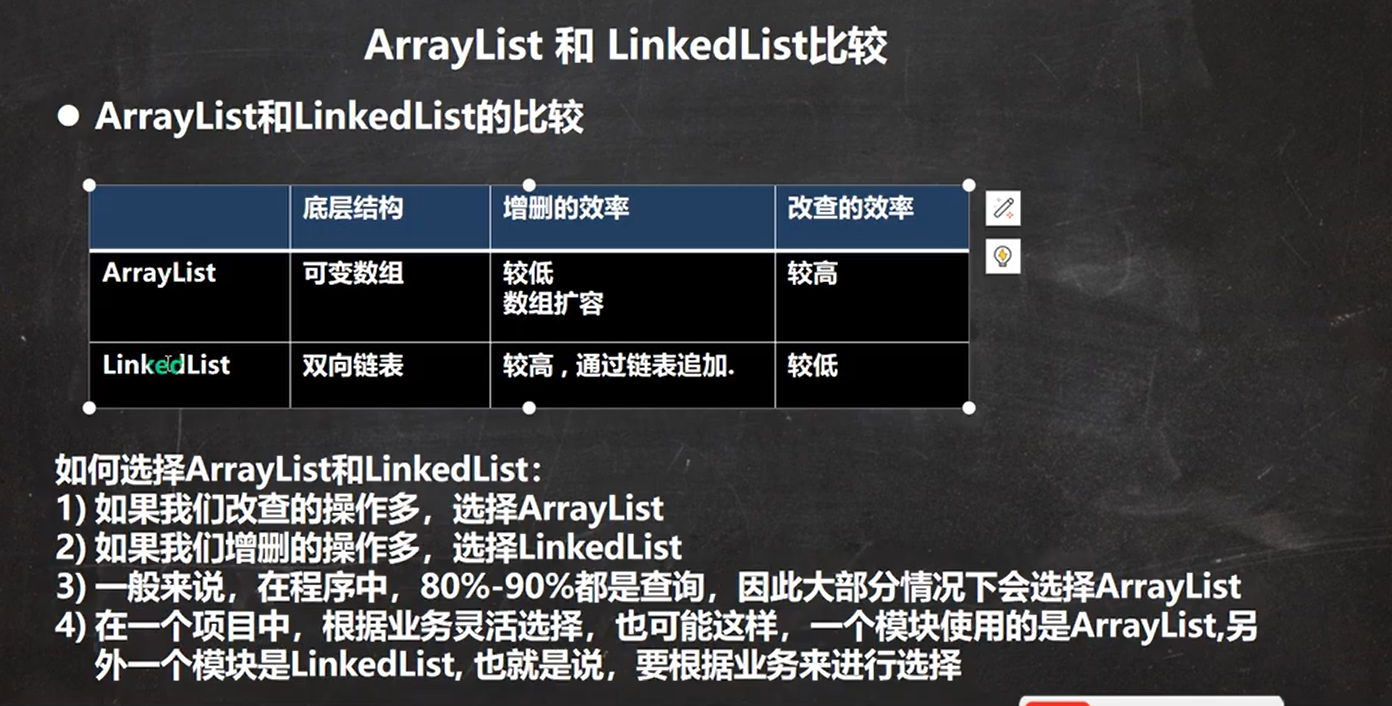
ArrayList和LinkedList的比较
-