LLM学习(4)——构建 RAG 应用
4.1 接入Langchain
首先我们导入所有需要的库文件
import google.generativeai as genai
import os
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
from langchain_google_genai import GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import create_retrieval_chain
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chain
import sys
from langchain.vectorstores.chroma import Chroma
import gradio as gr
我们使用langchain_google_genai中的ChatGoogleGenerativeAI导入模型另外Langchain现在还没有把genai并入所有要想安装相应的包还需要运行
!pip install -U langchain-google-genai
另外出来使用 API 密钥设置 GOOGLE_API_KEY 的环境变量
你还可以显式的使用 google_api_key kwarg 将您的 API 密钥传递给 ChatGoogle 构造函数
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-pro",google_api_key=api_key)
# 这里换成自己的代理端口
os.environ['http_proxy'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:10809'
os.environ['https_proxy'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:10809'
GOOGLE_API_KEY="AIzaSyBZFSrCWg7Ow2D3I2rMbf37qXp1SlF9T5k"
os.environ["GOOGLE_API_KEY"] =GOOGLE_API_KEY
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-pro")
result = llm.invoke("Write a ballad about LangChain")
print(type(result))
print(result.content)
下面的图片是相应的结果

4.2 向量库的搭建
4.2.1 加载向量数据库
path = '输入自己的持久化向量库的位置记得改'
embeddings = GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings(model="models/embedding-001",task_type="retrieval_document")
vectordb=Chroma(
persist_directory=path,
embedding_function=embeddings
)
print(f"向量库中存储的数量:{vectordb._collection.count()}")
question = "什么是prompt engineering?"
docs = vectordb.similarity_search(question,k=3)
print(f"检索到的内容数:{len(docs)}")
for i, doc in enumerate(docs):
print(f"检索到的第{i}个内容: \n {doc.page_content}", end="\n-----------------------------------------------------\n")
下面是导入我的向量库的结果

4.2.2 构建检索问答链
PromptTemplate函数是 Langchain 官方提供语言模型的提示模板,提示模板由字符串模板组成。它接受来自用户的一组参数,这些参数可用于生成语言模型的提示,而且可以使用 f-strings(默认)或 jinja2 语法对模板进行格式化。下面的Code中的{context}和{input}就是相应的需要输入的参数。然后使用 from_template 把我们预定义的模板template转换成PromptTemplate对象。接着我们使用 create_stuff_documents_chain 函数去创建一个链用于把输入的文档列表也就是 prompt 格式化然后传给 LLM。
接着通过 create_retrieval_chain 去构建检索器然后传递给llm
这样我们就有了两个连接的链,检索问答链 retrieval_chain构建完成
template = """
You are a helpful AI assistant.
Answer based on the context provided.
context: {context}
input: {input}
answer:
"""
retriever=vectordb.as_retriever()
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
combine_docs_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, prompt)
retrieval_chain = create_retrieval_chain(retriever, combine_docs_chain)
接下来测试
question_1 = "什么是南瓜书?"
print("南瓜书是:")
result=retrieval_chain.invoke({"input":question_1})
print(result["answer"])

4.2.3 添加 memory
memory 功能的实现非常的简单只需要再template模板构建的时候给予适当的提示词"you have a conversation with a human
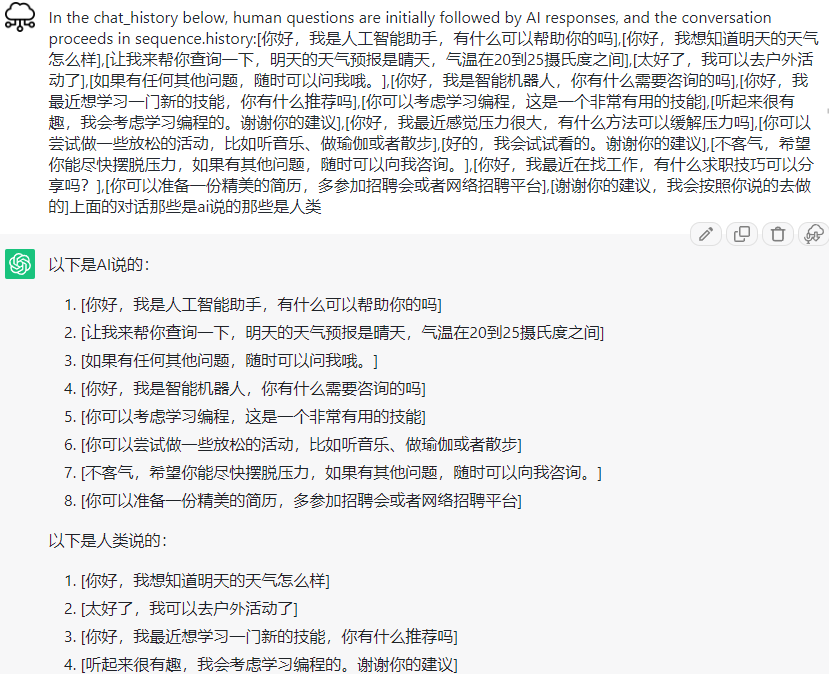
chat_history:{chat_history}" 然后输入参数的时候把所有的参数包括历史对话一起输入就行。这里要注意的是你要显式的指出那些对话是AI说的那些是人类说的,不然AI可能分别不出来或者你可以给他一个类似于"In the chat_history below, human questions are initially followed by AI responses, and the conversation proceeds in sequence."的提示也可以有一定效果。如图(1)你可以发现AI可以准确区分理解这种提示。也可以如下面的Code一样chat_history.append({"user":input}) chat_history.append({"AI":result["answer"]})
我认为这样可能会得到更好的结果,因为一旦history过多,而且你的问题中出现了 ai 可能会产生混乱如图(2)。他在途中好像忘记了"the conversation proceeds in sequence"不过这种情况也说明了 ai 的性能因为他可能真的读懂了对话的含义不然无法理解语义按照语义,而是简单的按照排序输出。然后在我强调ai和人类是一句一句对话的时候他更倾向于给他们打上label然后一句一句输出而不是理解我所说的是历史记录是一句一句对话的如图(3)


template = """
You are a helpful AI assistant and you have a conversation with a human
chat_history:{chat_history}
Answer based on the context provided.
context: {context}
input: {input}
answer:
"""
chat_history=[]
retriever=vectordb.as_retriever()
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
print(prompt)
combine_docs_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, prompt)
retrieval_chain = create_retrieval_chain(retriever, combine_docs_chain)
input="我可以学习到关于提示工程的知识吗?"
result=retrieval_chain.invoke({"input":input,"chat_history":chat_history})
print(result["answer"])
chat_history.append({"user":input})
chat_history.append({"AI":result["answer"]})
print(chat_history)
input="为什么需要学习这方面的知识?"
result=retrieval_chain.invoke({"input":input,"chat_history":chat_history})
print(result["answer"])
下面是两个问题分别的结果


我们可以看到图(5)首先第一个问题的问答被添加到history中了,其次第二个问题他虽然没有给出答案但是他明确知道了我们问的"这方面知识"指的是提示工程而不是其他
4.3 应用搭建
用tranform_history去转换历史消息然后传递给模型其他部分和4.1与4.2的内容一致,不多阐述。
template = """
You are a helpful AI assistant and you have a conversation with a human
chat_history:{chat_history}
Answer based on the context provided.
context: {context}
input: {input}
answer:
"""
chat_history=[]
retriever=vectordb.as_retriever()
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
combine_docs_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, prompt)
retrieval_chain = create_retrieval_chain(retriever, combine_docs_chain)
# Transform Gradio history to Gemini format
def transform_history(history):
new_history = []
for chat in history:
new_history.append({"user":chat[0]})
new_history.append({"AI":chat[1]})
return new_history
def response(message, history):
history = transform_history(history)
result=retrieval_chain.invoke({"input":message,"chat_history":history})
return result["answer"]
# Each character of the answer is displayed
gr.ChatInterface(response,
title='Gemini Chat',
textbox=gr.Textbox(placeholder="Question to Gemini"),
retry_btn=None).launch(share=True,debug=True)
这样我们就得到了一个简单的QA检索。
还可以进一步的加上radio去选择模式和api输入窗口如下
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
from langchain_google_genai import GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import create_retrieval_chain
from langchain.chains.combine_documents import create_stuff_documents_chain
from langchain.vectorstores.chroma import Chroma
import gradio as gr
import os
os.environ['http_proxy'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:10809'
os.environ['https_proxy'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:10809'
# llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-pro",google_api_key="AIzaSyBZFSrCWg7Ow2D3I2rMbf37qXp1SlF9T5k")
# result = llm.invoke("message")
# print(result.content)
def get_chat_qa_chain(chat_history,api_key,message):
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-pro",google_api_key=api_key)
path = 'your path'
embeddings = GoogleGenerativeAIEmbeddings(model="models/embedding-001",task_type="retrieval_document",google_api_key=api_key)
vectordb=Chroma(
persist_directory=path,
embedding_function=embeddings
)
template = """You are a helpful AI assistant and you have a conversation with a human
chat_history:{chat_history}
Answer based on the context provided.
context: {context}
input: {input}answer: """
retriever=vectordb.as_retriever()
prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(template)
combine_docs_chain = create_stuff_documents_chain(llm, prompt)
retrieval_chain = create_retrieval_chain(retriever, combine_docs_chain)
result=retrieval_chain.invoke({"input":message,"chat_history":chat_history})
return result["answer"]
def get_qa_chain(api_key,message):
return get_chat_qa_chain(chat_history=[None],api_key=api_key,message=message)
def get_qa(api_key,message):
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-pro",google_api_key=api_key)
result = llm.invoke(message)
print(result.content)
return result.content
def transform_history(history):
new_history=[]
for chat in history:
new_history.append({"user":chat[0]})
new_history.append({"AI":chat[1]})
return new_history
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
radio = gr.Radio(
["qa", "chat_qa", "none"], label="What mode do you want?"
)
def radio_change(R):
global select_mode
select_mode=R
radio.change(fn=radio_change,inputs=radio)
api_key=gr.Textbox(lines=1, placeholder="AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA", label="your api_key")
def api_change(A):
global API_key
API_key=A
api_key.change(fn=api_change,inputs=api_key)
chatbot = gr.Chatbot()
msg=gr.Textbox()
def select(message,chat_history):
print(message)
global select_mode
global API_key
# print(API_key)
# print(select_mode)
# print('Stop0')
bot_message=""
history=transform_history(chat_history)
if select_mode=="none":
bot_message=get_qa(api_key=API_key,message=message)
# print('Stop2')
elif select_mode=="qa":
bot_message=get_qa_chain(api_key=API_key,message=message)
# print('Stop3')
elif select_mode=="chat_qa":
bot_message=get_chat_qa_chain(history,API_key,message)
# print('Stop4')
chat_history.append((message, bot_message))
# print('Stop5')
return "", chat_history
msg.submit(select,[msg,chatbot],[msg,chatbot])
demo.launch(share=True,debug=True)
展示


4.4 总结和疑问:
我遇到的最大的问题是参数的传递,submit的返回值是(message,chat_history)的形式但是模型的输入却不知这些,而且再使用radio和gr.Textbox输入模式选择和api的时候,我遇到了一个现在也没有弄明白的问题,按道理来说radio参数我没有传给其他函数应该是不能使用这个参数的,但是他却正常使用了,而且还是值传递???我再def内部打印radio还真打印出来了radio,但是他却没有接收到了输入只是一个None的Radio对象,然后我使用global想把这种值传递改成应用但是却失败,最后只能分别定义callback在callback函数里面把radio和api赋值给新建的参数然后用global传递新建的参数的应用。头疼。

