软工实践第二次作业
此版本为旧版本
github地址
PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | ||
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 800 | |
| Development | 开发 | ||
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 120 | 180 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 20 | 20 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 10 | 10 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 10 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 30 | 30 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 240 | 360 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 120 | 60 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 20 | 20 |
| Reporting | 报告 | ||
| Test Repor | 测试报告 | 60 | 60 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 60 | 50 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 90 | 50 |
| 合计 | 800 | 850 | |
计算模块接口的设计与实现过程。
- 定义了一个结构体头文件和四个函数体头文件。
/***********************单词结构体***********************/
struct word
{
char name[30];
int num;
struct word *next;
};
-
各个接口间独立,分别向文件中输入结果。
-
算法的关键在于建立结构体链表来保存字符数组和次数,出现新的单词就增加节点。

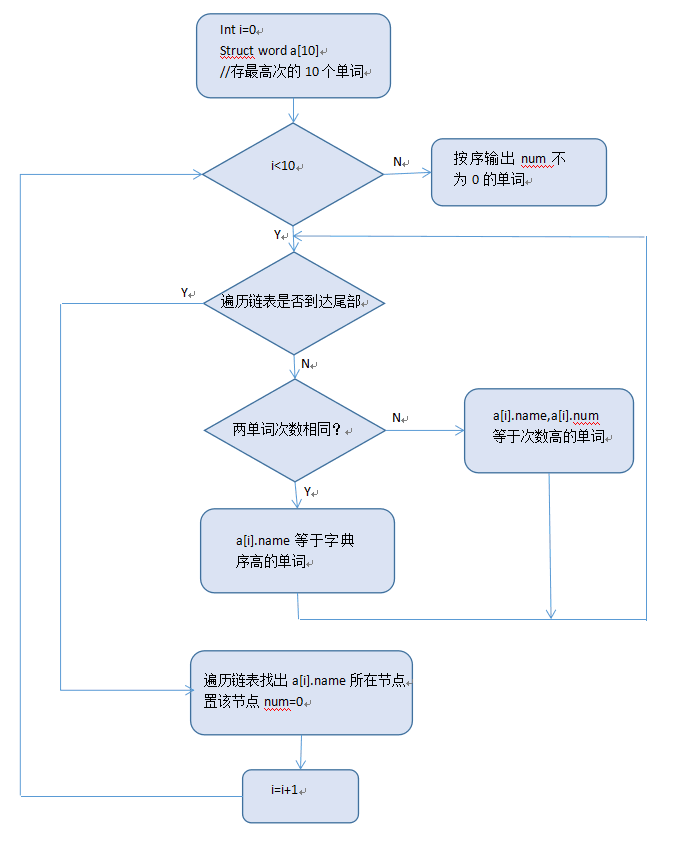
- 在统计频率时,原本想的是记下来每个单词出现的频率后再排序,这样会用到O(N*log N)。在查阅一些资料后,后来才发现可以直接保存频率最高的几个单词,遍历的同时替换就可以了,降到了O(N)。下图为排序过程
###性能改进
(1)一开始用cout,cout输出流函数来输入输出,发现耗费资源。
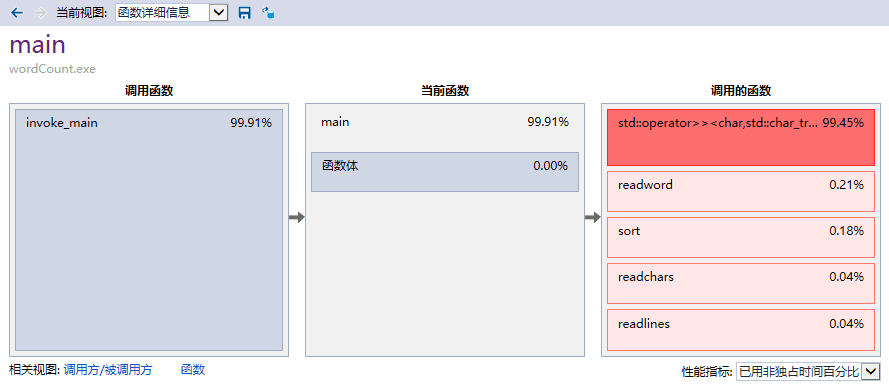
(2)改用scanf,printf函数。<VS用scanf_s函数更安全!>
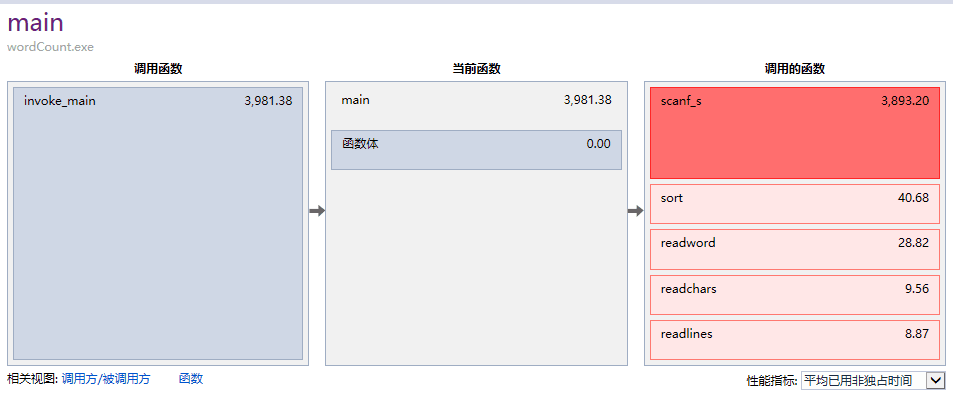
(3)发现还是很耗费资源于是改用gatchar()

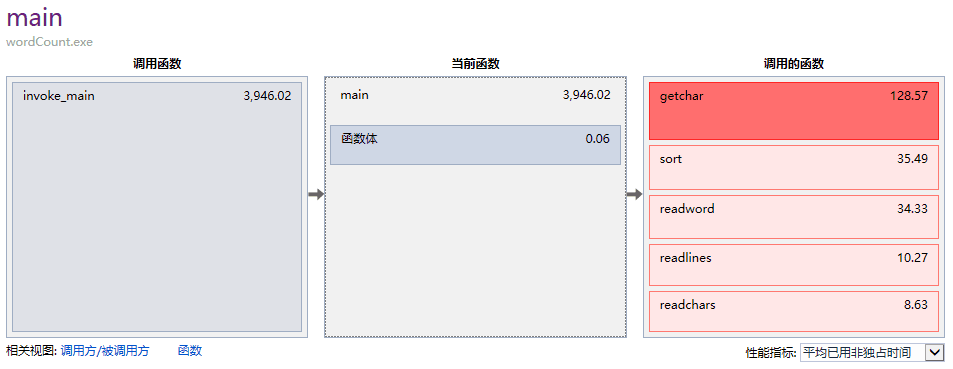
耗时减少,资源节约很多
单元测试
单元测试结果
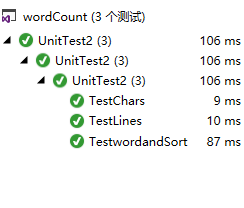
展示测试求字符总数的函数的单元测试代码
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CppUnitTest.h"
#include"../wordCount/readchars.h"
#include"../wordCount/structword.h"
#include"../wordCount/readlines.h"
#include"../wordCount/readword.h"
#include"../wordCount/sort.h"
using namespace Microsoft::VisualStudio::CppUnitTestFramework;
namespace UnitTest2
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest2)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestChars)//测试字符数函数
{
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
char filename[60] = "C:/Users/Mac/Desktop/1234.txt";
int file_chars = 0;
struct word * head = new word;
head->next = NULL;
Assert::AreEqual(0, readchars(*&head, filename, file_chars));
}
}
思路:如果可以正确打开文件并且成功运行会返回0,测试该模块是否与0相等,附上读取字符数的代码。
#include"pch.h"
#include"readchars.h"
#include"structword.h"
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
/**********************读取字符*********************/
int readchars(struct word *& head, char *filename, int file_chars)
{
FILE *file = _fsopen(filename, "r", _SH_DENYNO);
if (!file)
{
printf( "打开文件错误!" );
return 0;
}
char chars = -1;
while (1)
{
chars = fgetc(file);
if (chars == EOF)
break;
file_chars++;
}
std::ofstream openfile("C:/Users/Mac/Desktop/result.txt", std::ios::trunc);
openfile << "characters:" << file_chars << endl;
openfile.close();
return 0;
}
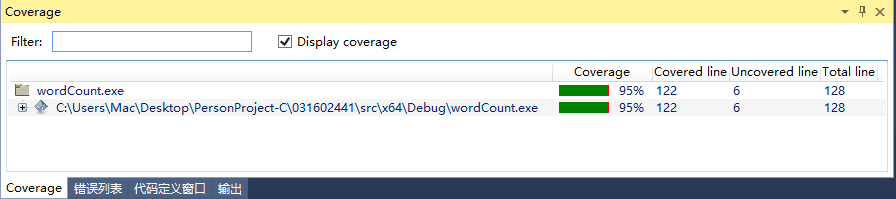
单元测试测试覆盖率
异常处理模块
异常处理:
文件路径大于60字符或者路径无效时显示无法打开文件并退出
FILE *file = _fsopen(filename, "r", _SH_DENYNO);
if (!file)
{
printf( "打开文件错误!" );
return 0;
}
单元测试
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest2)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestChars)
{
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
char filename[60] = "mm";
int file_chars = 0;
struct word * head = new word;
head->next = NULL;
Assert::AreEqual(0, readchars(*&head, filename, file_chars));
}
filename为无效地址
结果通过测试

总结
我用了很长的时间来做这次作业,在这次作业的过程中遇到了很多困难也学到了很多知识。通过这次学习我知道了以后可以通过单元测试来增加代码的可靠性,也知道了如何将函数封装成头文件。遇到的困难有些已经解决,有些还需要继续深入研究。写这个程序我也没有用到特别复杂的算法,在与其他同学交流解题思路的过程中,我深刻的意识到了自己的不足以及与别人的差距。以后,我一定丰富自己的知识,将之前那些看不懂就放到一边的算法拾起来。
学习记录
问题
(1)vs2017无法查找或打开 pdb 文件
(2)单元测试方法1单元测试方法2
(3)C语言中 scanf_s和 scanf 区别
C++中函数strcpy和strcpy_s
(4)C如何在一个文件里调用另一个源文件中的函数
(5)struct重定义//重复包含头文件
(6)性能分析报告与性能优化
(7)看代码覆盖率使用OpenCppCoverage插件


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号