学习c++ofstream和ifstream
定义数据流对象指针
对文件进行读写操作首先必须要定义一个数据流对象指针,数据流对象指针有三种类型,它们分别是:
Ifstream:表示读取文件流,使用的时候必须包含头文件“ifstream”;
ofstream:表示文件写入流,使用的时候必须包含头文件“ofstream”;
fstream:表示文件读取/写入流,使用的时候必须包含头文件“fstream”;
ofstream是从内存到硬盘,ifstream是从硬盘到内存
打开文件
打开文件有两种方式。一种其一是使用open函数,其二是使用数据流对象的构造函数。这两个函数调用的参数基本上一致的。
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("file.dat", ios::out | ios::in );
| 参数 | 打开方式 |
|---|---|
| ios::in | 为输入(读)打开文件 |
| ios::out | 为输出(写)打开文件 |
| ios::app | 所有输出附加在文件末尾 |
| ios::trunc | 若文件已存在先删除文件 |
| ios::binary | 二进制方式 |
文件读写操作
由于类ofstream, ifstream 和fstream 是分别从ostream, istream 和iostream 中引申而来的,所以文件的读写操作与使用控制台函数cin和cout一样,“<<”表示对文件进行写操作,“>>”表示对文件进行读操作。根据数据流读写的状态,有4个验证函数,它们分别是:
· bad()
如果在读写过程中出错,返回 true 。例如:当我们要对一个不是打开为写状态的文件进行写入时,或者我们要写入的设备没有剩余空间的时候。
· fail()
除了与bad() 同样的情况下会返回 true 以外,加上格式错误时也返回true ,例如当想要读入一个整数,而获得了一个字母的时候。
· eof()
如果读文件到达文件末尾,返回true。
· good()
这是最通用的:如果调用以上任何一个函数返回true 的话,此函数返回 false 。
获得或设置流指针
Long tellg() 和 long tellp()这两个成员函数不用传入参数,返回一个整数。tellg()用于.ifstream,指向下一个将被读取的元素。tellp()用于.ofstream,指向写入下一个元素的位置。
seekp:设置输出文件流的文件流指针位置
seekg:设置输入文件流的文件流指针位置
关闭文件
close();
例子
- 向文件中写入数据
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ofstream file1("C:/Users/Mac/Desktop/1234.txt");
if(!file1)
{
cout<<"文件不能打开"<<endl;
}
else
{
file1<<"learning ios is very useful!"<<endl;
file1<<"1 2 3 4 "<<endl;
}
file1.close();
}

- 逐词读取
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream file2("C:/Users/Mac/Desktop/1234.txt");
if(!file2)
{
cout<<"文件不能打开"<<endl;
}
else
{
string s;
while(file2>>s)
{
cout<<s<<endl;
}
file2.close();
}
}
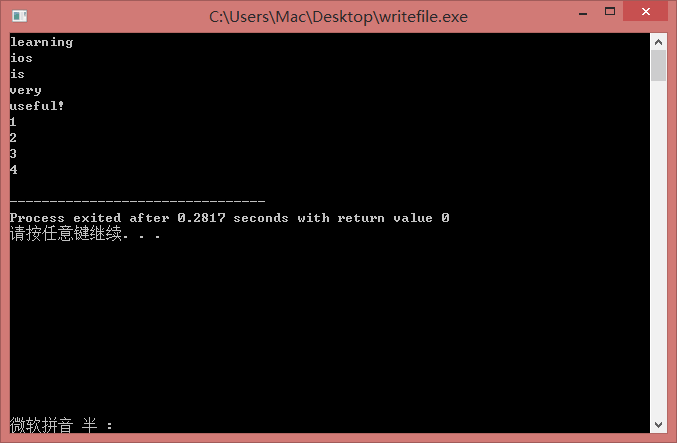
- 逐行读取,行存入字符数组
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream file2("C:/Users/Mac/Desktop/1234.txt");
if(!file2)
{
cout<<"文件不能打开"<<endl;
}
else
{
char s[100];
while(file2.getline(s,100))
{
cout<<s<<endl;
}
file2.close();
}
}
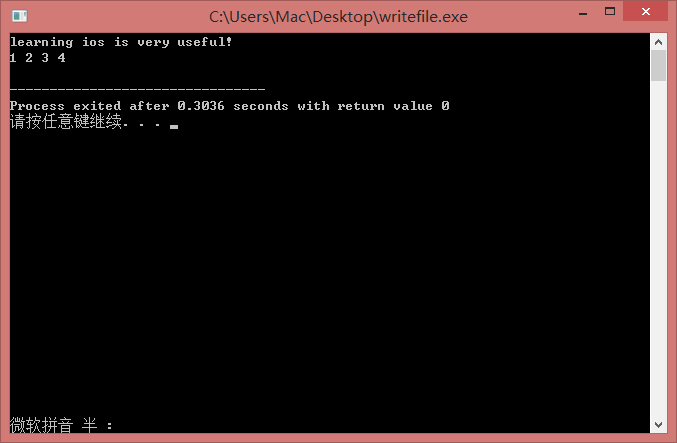
- 逐行读取,行存入字符串
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream file2("C:/Users/Mac/Desktop/1234.txt");
if(!file2)
{
cout<<"文件不能打开"<<endl;
}
else
{
string s;
while(getline(file2,s))
{
cout<<s<<endl;
}
file2.close();
}
}
结果如上图


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号