这次作业要求来自于:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/gzcc/GZCC-16SE1/homework/2753
1.列表,元组,字典,集合分别如何增删改查及遍历。
(1)列表
增加元素
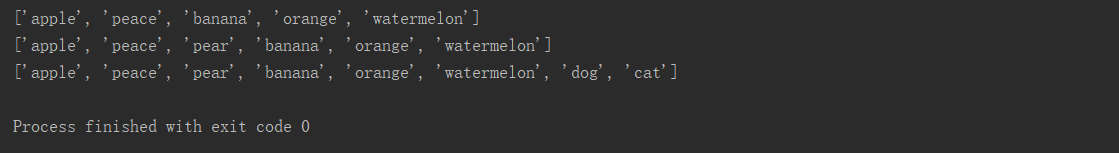
#append():在列表最后添加元素
list=['apple','peace','banana','orange'] list.append('watermelon') print(list)
#insert():根据列表索引值添加元素 list.insert(2,'pear') print(list)
#extend():合并列表 list_1=['dog','cat'] list.extend(list_1) print(li
删除元素
#pop():删除列表最后一个元素,或者根据索引值删除元素
list=['apple','peace','banana','orange'] list.pop(1) print(list)
#remove():根据元素值删除指定的元素 list=['apple','peace','banana','orange'] list.remove('banana') print(list)
#del:删除列表或者切片删除 list=['apple','peace','banana','orange'] del list[1:2] print(list)
#clear():删除整个列表 list=['apple','peace','banana','orange'] list.clear() print(list)

修改元素
#list[]='':元素赋值
list=['apple','peace','banana','orange'] list[2]='mango'
#list[index:index1]='','',:切片赋值 print(list) list[1:3]='lemon','longan' print(list)

查找元素
list=['apple','peace','banana','orange']
#[index]:查看当前索引的元素 print(list[2])
#[index:index1]:查看当前间隔索引的元素 print(list[1:3])
#[index:]:查看当前索引后面的元素 print(list[2:])
#[:index]:查看当前索引前面的元素 print(list[:1])
#[:]:查看所有元素 print(list[:])
#[:index:index1]:查看第一个索引前面有间隔的元素(第二个索引为间隔数) print(list[:3:2])
#[-1]:查看最后一个元素 print(list[-1])

遍历元素
list=['apple','peace','banana','orange'] for x in list: print(x)

(2)元组
增加元素:元组与列表类似,不同之处在于元组的元素不能修改。
#创建元组只包含一个元素时,需要在元素后面添加逗号
tup=(1998,) print(tup)
#“+”对元组进行连接组合 tup1 = (12, 34.56) tup2 = ('abc', 'xyz') tup3 = tup1 + tup2 print(tup3)

删除元素:元组中的元素值是不允许删除的,但可以用del来删除整个元组
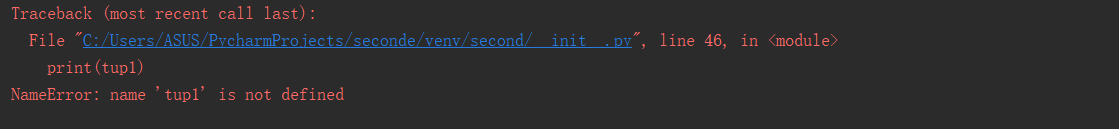
#del :元组被删除后,输出变量会有异常信息
tup1 = (12, 34.56) del tup1 print(tup1)
修改元素
tup1 = (12,34.56) tup1=tup1[0:2] print(tup1) tup1 = (12,34.56) tup1=tup1[1] print(tup1)

查找元素
#[index:]:查找索引后面的元素
tup1 = (12,34.56) print(tup1[1:])

(3)字典
增加元素
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'}
dict1 = { 'abc': 456 }
dict['heihgt']=180
print(dict)
#update():将两个字典相加
dict.update(dict1)
print(dict)

删除元素
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First','Height':180}
del dict['Age']
print(dict)
dict.pop('Name')
print(dict)
dict.popitem()
print(dict)
del dict
print(dict)
dict1 = { 'abc': 456 }
dict1.clear()
print(dict1)

修改元素
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'}
dict1 = { 'Name': 'John' }
dict['Name']='Mike'
print(dict)
dict.update(dict1)
print(dict)

查找元素
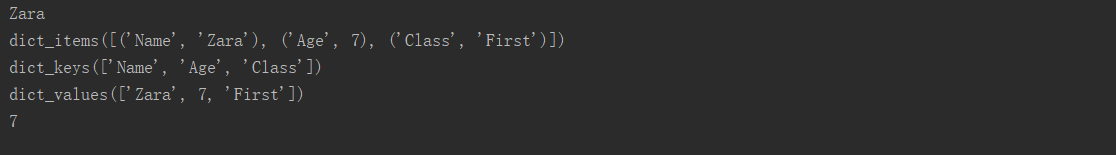
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'}
print(dict['Name'])
print(dict.items())
print(dict.keys())
print(dict.values())
print(dict.get('Age'))
(4)集合
增加元素
list=['apple','peace','banana','orange'] set = set(list) print(set) set.add('lemon') print(set)

删除元素
list={'apple','peace','banana','orange'}
list.pop()
print(list)
list.remove('apple')
print(list)
list.clear()
print(list)
del list
print(list)

修改元素
list={'apple','peace','banana','orange'}
list_1={'dog','cat'}
list=list|list_1
print(list)
list=list&list_1
print(list)

查找元素
list={'apple','peace','banana','orange'}
print(list.__str__())

2.总结列表,元组,字典,集合的联系与区别。参考以下几个方面:
(1)列表
- 列表list用" [ ]"表示
- 列表是有序的,通过索引值进行增删改查及遍历
- 列表是可变的,可随时改变
- 列表是可重复的
- 以值的方式存储,通过索引值查找
(2)元组
- 元组tuple用 "( )"表示
- 元组是有序的,与列表相同
- 一旦初始化就不能修改,与列表不同
- 元组是可以重复的
- 以值的方式存储,通过索引值查找
(3)字典
- 字典dict用"{ }"表示
- 字典是无序的,故不能进行索引操作
- 字典是可修改的,通过键(key)进行修改
- 字典的键不可以重复,值可以重复
- 以键值对(key-value)的方式存储,通过键来查找
(4)集合
- 集合set用 "{ }"表示
- 集合是无序的
- 集合可以改变的,用&|-进行集合与或减运算
- 集合是不能重复的
- 以值的方式存储,通过_str_来查找所有元素
和list比较,dict有以下特点:查找和插入的速度极快,不会随着key的增加而变慢;需要占用大量的内存,内存浪费多。而list相反:查找和插入的时间随着元素的增加而增加;占用空间小,浪费内存很少。所以,dict是用空间来换取时间的一种方法。
3.词频统计
- 1.下载一长篇小说,存成utf-8编码的文本文件 file
- 2.通过文件读取字符串 str
- 3.对文本进行预处理
- 4.分解提取单词 list
- 5.单词计数字典 set , dict
- 6.按词频排序 list.sort(key=lambda),turple
- 7.排除语法型词汇,代词、冠词、连词等无语义词,自定义停用词表或用stops.txt
- 8.输出TOP(20)
- 9.可视化:词云
排序好的单词列表word保存成csv文件
import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame(data=word).to_csv('big.csv',encoding='utf-8')
线上工具生成词云:
https://wordart.com/create
代码如下
# 读文本和格式化单词函数 def get_text(): f = open(r'G:\大三下学期\python\novel.txt', encoding='utf8') #读取文件的全部内容 text = f.read() f.close() #删除不必要的符号 sign = '[].?!:\"\',\n“”' for i in sign: text = text.replace(i, ' ') #把所有字母转换成小写字母 text = text.lower() #把字母每个分隔开 text = text.split() return text #统计数量并排序单词函数 def get_wordsort(wordlist): #排除连词、冠词、代词、系动词无语义词 exclude = {'it', 'if', 'the', 'at', 'for', 'on', 'and', 'in', 'to', 'of', 'a', 'was', 'be', 'were', 'in', 'about', 'from', 'with', 'without', 'an', 'one', 'another' , 'others', 'that', 'they', 'himself', 'itself', 'themselves', 'if', 'when', 'before', 'though', 'although', 'while', 'as', 'as long as', 'i', 'he', 'him', 'she', 'out', 'is', 's', 'no', 'not', 'you', 'me', 'his', 'but','we','us','their','our','her'} wordset = set(wordlist) - exclude #把留下的单词存入字典并统计数量 worddict = {} for q in wordset: worddict[q] = wordlist.count(q) #字典转换成列表对单词进行排序 wordsort = list(worddict.items()) wordsort.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) return wordsort #调用get_text函数获取单词 wordlist = get_text() #调用get_wordsort函数排序单词数量 wordsort=get_wordsort(wordlist) # print(wordsort) #导入pandas依赖,对单词数量进行保存成csv类型文件 import pandas pandas.DataFrame(data=wordsort).to_csv('F:\\zyx\\novel.csv',encoding='utf-8')
运行结果生成novel.csv文件
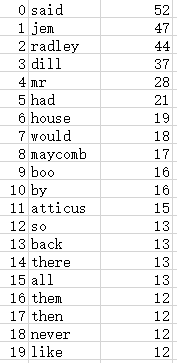
利用novel.csv文件生成单词TOP(20):
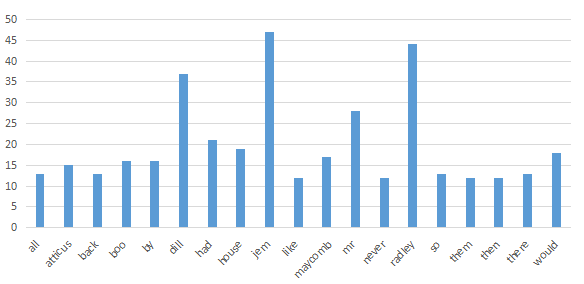
利用word art线上工具生成词云
















