设计模式:装饰器(Decorator)模式
设计模式:装饰器(Decorator)模式
一、前言
装饰器模式也是一种非常重要的模式,在Java以及程序设计中占据着重要的地位。比如Java的数据流处理,我们可能看到数据流经过不同的类的包装和包裹,最终形成了我们需要的流,比如说从二进制到字节流再到字符流,这中间其实就是经过了装饰器的处理,在不改变原来的数据的基础上,加入属于自己的特征,就像是在一块蛋糕上加上一些水果等装饰品,这样输出的结果就不同了,我们将这种能产生类似于洋葱一样层层包裹的数据格式的设计模式成为装饰器模式。
那么为什么装饰器这样神奇呢,几乎可以让我们无穷尽的包裹自身,在计算机中凡是能够无穷尽的重复某一件事物,必然不能设定固定的数据,只能按照用户的随意设置来计算,那么递归的魅力就在此彰显出来了,通过递归可以实现这一点,那么如何递归呢,我们想到一层套一层的数据结构(链表、二叉树等),就必须在“自身”中包含“自身”;前一个“自身”可以是我们的子类,因为子类有着父类的所有特点,后一个“自身”就是具有最抽象资格的“自身”,正是因为足够抽象使得任何继承与这个抽象类的类都能通过里氏代换原则转换到这个抽象类。实现了递归,我们只需要停止条件就可以了,停止条件就是用户在Main中对原数据包裹的层数,肯定是有限的,因此停止是必然的。这样我们仿似看到一个原始数据,被一层层的进行包裹,加入新的内容,最终使用最顶层的输出方法将这个结果呈现给我们。同样的我们还可以反着看,当递归开始的时候,在最顶层等待下一层的数据,然后使用顶层的方式来封装,而下一层被启动执行到关键步骤时会等待下下一层的数据返回给自身,然后是用自己的方式来封装,就这样一直等待下去,直到最底层的数据(本来就有)得到之后,然后一步步的返回过来,在相应的层次进行相应的封装,最后得到了最终的数据。这就是装饰器模式,所有的类其实最终都是同源(一致性)的,有最终的祖先,如下图所示。
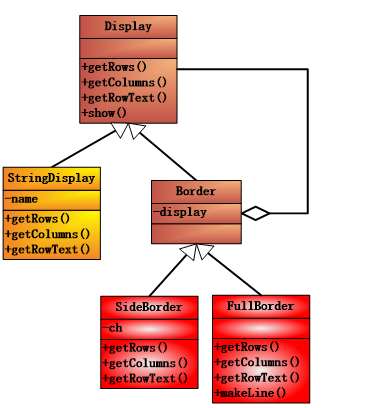
二、代码
上图中,StringDisplay是保存原始数据的,而Border中将父类的引用组合进入自身,形成了递归的必然条件,之后让子类(SideBorder和FullBorder)来使用这个引用,从而根据自身的实际情况(要怎样装饰)来进行包装,将原始的数据getRowText(rowID)进行包裹,最终通过同源祖先类的show()方法来现实,这里祖先类Display使用了面向抽象编程的模板方法,相信大家都能看出来。对比与上一个组合模式,我们可以看到上面的部分还是很相似的,但是在composite中,都实现了add()方法,通过容器来进行组织,并且使用委托机制来存储所有的有着共同父类的元素,在显示的时候使用了树的深度优先遍历。而在装饰器模式中,我们使用的递归从上到下,沿着display的指向一点点的走到了底部,并且最终返回了过来。遍历的方式有着相似之处也有着不同之处。这里要说明的是,建议大家在show()的地方打个断点,然后跟踪进去,一点点的看看我们的程序到底是怎么组织起来的,只有这样我们才能理解递归的含义,对装饰器有一个更深层次的认识。
Display 类:
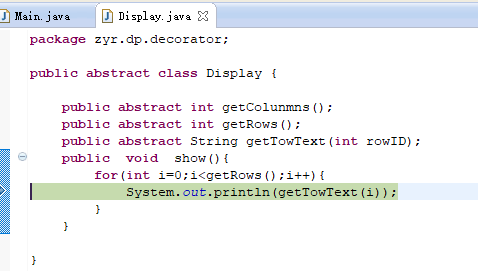
1 package zyr.dp.decorator; 2 3 public abstract class Display { 4 5 public abstract int getColunmns(); 6 public abstract int getRows(); 7 public abstract String getTowText(int rowID); 8 public void show(){ 9 for(int i=0;i<getRows();i++){ 10 System.out.println(getTowText(i)); 11 } 12 } 13 14 }
StringDisplay类:
1 package zyr.dp.decorator; 2 3 public class StringDisplay extends Display { 4 5 String name; 6 7 public StringDisplay(String name){ 8 this.name=name; 9 } 10 11 public int getColunmns() { 12 return name.getBytes().length; 13 } 14 15 public int getRows() { 16 return 1; 17 } 18 19 public String getTowText(int rowID) { 20 if(rowID==0){ 21 return name; 22 }else{ 23 return null; 24 } 25 } 26 27 }
Border类:
1 package zyr.dp.decorator; 2 3 public abstract class Border extends Display { 4 5 protected Display display; 6 public Border(Display display){ 7 this.display=display; 8 } 9 }
SideBorder类:
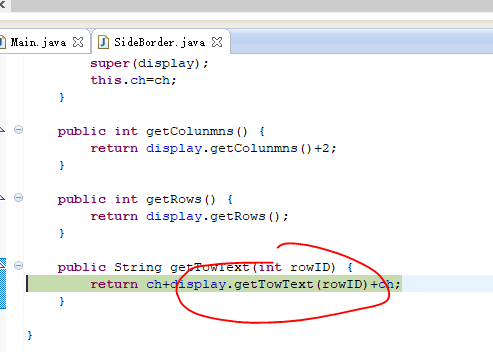
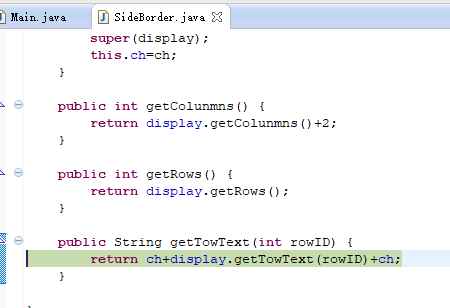
1 package zyr.dp.decorator; 2 3 public class SideBorder extends Border { 4 5 String ch; 6 protected SideBorder(Display display,String ch) { 7 super(display); 8 this.ch=ch; 9 } 10 11 public int getColunmns() { 12 return display.getColunmns()+2; 13 } 14 15 public int getRows() { 16 return display.getRows(); 17 } 18 19 public String getTowText(int rowID) { 20 return ch+display.getTowText(rowID)+ch; 21 } 22 23 }
FullBorder类:
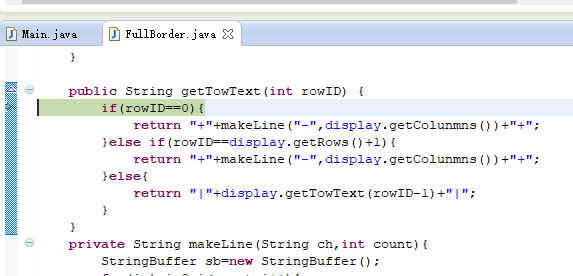
1 package zyr.dp.decorator; 2 3 public class FullBorder extends Border { 4 5 public FullBorder(Display display) { 6 super(display); 7 } 8 9 public int getColunmns() { 10 return display.getColunmns()+2; 11 } 12 13 public int getRows() { 14 return display.getRows()+2; 15 } 16 17 public String getTowText(int rowID) { 18 if(rowID==0){ 19 return "+"+makeLine("-",display.getColunmns())+"+"; 20 }else if(rowID==display.getRows()+1){ 21 return "+"+makeLine("-",display.getColunmns())+"+"; 22 }else{ 23 return "|"+display.getTowText(rowID-1)+"|"; 24 } 25 } 26 private String makeLine(String ch,int count){ 27 StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(); 28 for(int i=0;i<count;i++){ 29 sb.append(ch); 30 } 31 return sb.toString(); 32 } 33 34 }
Main类:
1 package zyr.dp.decorator; 2 3 public class Main { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Display d1=new StringDisplay("朱彦荣"); 8 d1.show(); 9 System.out.println("\n"); 10 Display d2=new SideBorder(d1,"*"); 11 d2.show(); 12 System.out.println("\n"); 13 Display d3=new FullBorder(d2); 14 d3.show(); 15 System.out.println("\n"); 16 Display d4=new SideBorder( 17 new FullBorder( 18 new FullBorder( 19 new SideBorder( 20 new FullBorder( 21 new StringDisplay("李山秀") 22 ), 23 "#" 24 ) 25 ) 26 ), 27 "*" 28 ); 29 d4.show(); 30 } 31 32 }
运行结果:

我们来跟踪一下d4.show()的执行过程:
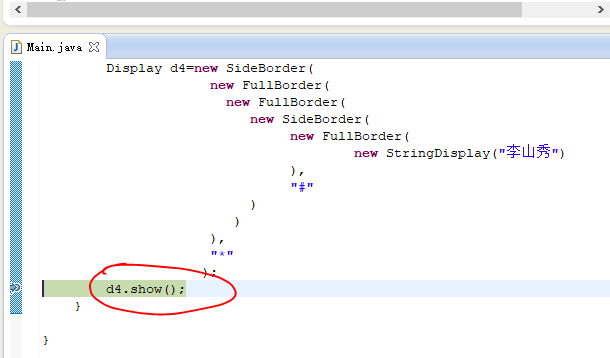
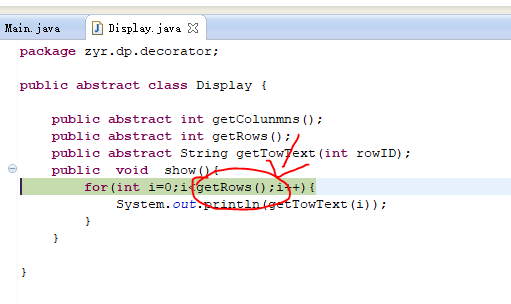

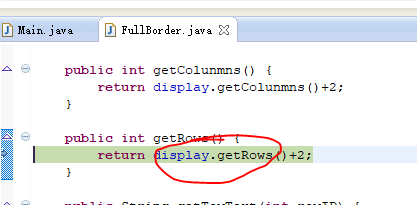

多次跟踪,最终到了终点,然后一步步回溯过去。跟踪下一条语句:

。。。
。。。
。。。
就是这样不断地深入,得到结果之后,一步步返回,最后输出的。
三、总结
继承保证了父类和子类的一致性(有共同的方法),委托保证了使用委托的类和被委托对象的一致性。正如Border和Display有着一些相同的方法名称,以及一些委托处理方法。可以看到装饰模式中,保证了装饰边框与被装饰物体的一致性(有共同父类),使用了模板方法,这个方法几乎无处不在呀,同样使用了委托(组合),通过在原始数据上面一层层的包裹,最终得到了我们想要的输出,有着非常广泛的用处。

