shell脚本语法(脚本组成、如何运行、一些特殊符号、重定向、数学运算、退出脚本)
shell脚本就是将完成一个任务的所有命令按照执行的先后顺序,自上而下写入到一个文本文件中,然后给予执行权限!
脚本的命名要有意义,建议用.sh结尾,例如:check_memory.sh
1,脚本组成:
(1)解释环境:脚本开头必须指定运行环境,以“#!”来指明。(#号代表注释,“#!”是特例)例如:#! /bin/bash 指定该脚本运行解析由/bin/bash来完成!
除了上面那种写法,还有一种:#!/usr/bin/env bash
(2)脚本信息:
#Aurhor:
#Create Time:
#Release(版本号):1.0
#Script Description:
(3)执行代码:
2,如何运行一个脚本
两种方法:
(1)给予执行权限:chmod u+x filename
[root@CentOs home]# vim hello.sh
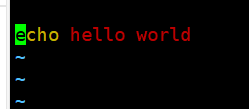
[root@CentOs home]# chmod 700 hello.sh
[root@CentOs home]# ./hello.sh
hello world
[root@CentOs home]#
(2)利用解释器直接运行:bash filename
[root@CentOs home]# chmod 644 hello.sh
[root@CentOs home]# ll
总用量 4
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 60 3月 22 22:51 dockerfile
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 19 3月 26 17:56 hello.sh
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 18 3月 25 17:28 java
drwx------. 4 slime slime 211 3月 23 15:05 slime
drwx------. 2 Slime Slime 83 3月 15 23:17 Slime
[root@CentOs home]# ./hello.sh
-bash: ./hello.sh: 权限不够
[root@CentOs home]#
这时我们可以这样来执行:
[root@CentOs home]# bash hello.sh
hello world
[root@CentOs home]# sh hello.sh
hello world
我们可以看一下有多少种shell
[root@CentOs home]# cat /etc/shells
/bin/sh
/bin/bash
/usr/bin/sh
/usr/bin/bash
[root@CentOs home]#
3,shell中的特殊符号
~ 家目录 如:cd ~ 代表进入家目录
! 执行历史命令 如:!!执行上一条命令
$ 取变量内容符
[root@CentOs shell]# echo $USER
root
[root@CentOs shell]#
这是因为计算机中设置了 USER=root
+ - * / % 加、减、乘、除、取余
& 后台执行
* 通配符,匹配所有
[root@CentOs shell]# ls ./*
./hello.sh
[root@CentOs shell]#
? 通配符,匹配一个字符(回车除外)
; 一行执行多个命令,用分号隔开
| 管道符
\ 转义字符(转回原本的意思)
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 3 * 3
expr: 语法错误
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 3 \* 3
9
[root@CentOs shell]#
`` 反引号,命令中执行命令
[root@CentOs shell]# echo "Date is: `date +%F`"
Date is: 2022-03-26
[root@CentOs shell]# echo "Date is:";date +%F
Date is:
2022-03-26
[root@CentOs shell]#
' ' 把字符串引起来,但是不解释变量(相当于原样输出)
[root@CentOs shell]# echo '$USER'
$USER
" " 把字符串引起来
[root@CentOs shell]# echo "$USER"
root
4,重定向
(1)输出重定向
在输出重定向中,> 代表的是覆盖,>> 代表的是追加。
[root@CentOs shell]# echo hello > test
[root@CentOs shell]# cat test
hello
[root@CentOs shell]# echo heihei >> test
[root@CentOs shell]# cat test
hello
heihei
[root@CentOs shell]#
(2)输入重定向
例如:
wc [选项] [文件名]
其中,-c选项统计字节数,-w选项统计单词数,-l选项统计行数。
[root@CentOs shell]# cat test
hello
heihei
[root@CentOs shell]# wc -l < test
2
[root@CentOs shell]#
[root@CentOs shell]# wc -l << END
> 123
> 233
> 435
> 534
> END
4
[root@CentOs shell]#
wc 命令会一直等待用输入,直到遇见分界符 END 才结束读取。
<< 之后的分界符可以自由定义,只要再碰到相同的分界符,两个分界符之间的内容将作为命令的输入(不包括分界符本身)
5,数学运算
(1)expr命令:只能做整数运算,样式比较古板,注意空格!
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 1 + 3
4
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 3 - 2
1
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 3 \* 3 注意:*出现应该转义,否则认为是通配符
9
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 4 / 3
1
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 5 % 2
1
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 1 + 3.2
expr: 非整数参数
[root@CentOs shell]#
[root@CentOs shell]# echo $?
2
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 5 % 2
1(非0代表上一条命令执行不成功)
[root@CentOs shell]# echo $?
0(0代表上一条命令执行成功)
[root@CentOs shell]#
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 7 + 1.9 ; echo $?
expr: 非整数参数
2
[root@CentOs shell]# expr 7 + 9 > /dev/null ; echo $? (把结果输入到回收站,并判断是否执行成功!)
0
[root@CentOs shell]#
(2)使用计数器bc运算
[root@CentOs shell]# bc
bc 1.06.95
Copyright 1991-1994, 1997, 1998, 2000, 2004, 2006 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY.
For details type `warranty'.
1+3
4
scale=2(小数点支持两位)
100/3
33.33
quit(退出)
(3)命令行使用交互计算
计算内存使用率:
[root@CentOs shell]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1819 294 1195 2 328 1377
Swap: 2047 77 1970
[root@CentOs shell]# echo "scale=2;294*100/1819" | bc
16.16
[root@CentOs shell]# echo "`echo "scale=2;294*100/1819" | bc`%"
16.16%
[root@CentOs shell]# echo "当前内存使用率:`echo "scale=2;293*100/1819" | bc`%"
当前内存使用率:16.10%
[root@CentOs shell]#
(4)(())做运算
[root@CentOs shell]# echo $((100%3))
1
[root@CentOs shell]# echo $((10**3)) 幂次运算
1000
[root@CentOs shell]#
6,退出脚本
exit NUM :退出脚本,释放系统资源,NUM代表一个整数,代表返回值!
(NUM的范围是0-255)
[root@CentOs shell]# vim exit_code.sh
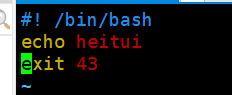
[root@CentOs shell]# bash exit_code.sh
heitui
[root@CentOs shell]# echo $?
43
[root@CentOs shell]#





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律