pandas -- 处理非数值型数据 -- 数据分析三剑客(核心)
开发环境
- anaconda
- 集成环境:集成好了数据分析和机器学习中所需要的全部环境
- 安装目录不可以有中文和特殊符号
- jupyter
- anaconda提供的一个基于浏览器的可视化开发工具
为什么学习pandas
- numpy已经可以帮助我们进行数据的处理了,那么学习pandas的目的是什么呢?
- numpy能够帮助我们处理的是数值型的数据,当然在数据分析中除了数值型的数据还有好多其他类型的数据(字符串,时间序列),那么pandas就可以帮我们很好的处理除了数值型的其他数据!
什么是pandas
首先先来认识pandas中的两个常用的类
- Series
- DataFrame
Series
Series的概述
- Series是一种类似与一维数组的对象,由下面两个部分组成:
- values:一组数据(ndarray类型)
- index:相关的数据索引标签
Series的创建
- 由列表或numpy数组创建
- 由字典创建
from pandas import Series
s = Series(data=[1,2,3,'four'])
s
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 four
dtype: object
import numpy as np
s = Series(data=np.random.randint(0,100,size=(3,)))
s
0 3
1 43
2 82
dtype: int64
# index用来指定显示索引
# 为什么需要有显示索引
# 显示索引可以增强Series的可读性
s = Series(data=[1,2,3,'four'],index=['a','b','c','d'])
s
a 1
b 2
c 3
d four
dtype: object
dic = {
'语文':100,
'数学':99,
'理综':250
}
s = Series(data=dic)
s
语文 100
数学 99
理综 250
dtype: int64
Series的索引和切片
s[0]
100
s.语文
100
s[0:2]
语文 100
数学 99
dtype: int64
Series的常用属性
- shape
- size
- index
- values
s.shape
(3,)
s.size
3
s.index # 返回索引
Index(['语文','数学','理综'], dtype='object')
s.values # 返回值
array([100, 99, 250])
s.dtype # 元素的类型
dtype('int64')
s = Series(data=[1,2,3,'four'],index=['a','b','c','d'])
s.dtype # 数据类型O表示的是Object(字符串类型)
dtype('O')
Series的常用方法
- head()
- tail()
- unique()
- isnull()
- notnull()
- add()
- sub()
- mul()
- div()
s = Series(data=np.random.randint(60,100,size=(10,)))
s
0 79
1 61
2 79
3 60
4 68
5 77
6 76
7 99
8 69
9 89
s.head(3) # 显示前n个数据
0 79
1 61
2 79
dtype: int64
s.tail(3) # 显示后n个元素
7 99
8 69
9 89
dtype: int64
s.unique() # 去重
array([79, 61, 60, 68, 77, 76, 99, 69, 89])
s.isnull() # 用于判断每一个元素是否为空,为空返回True,否则返回False
0 False
1 False
2 False
3 False
4 False
5 False
6 False
7 False
8 False
9 False
dtype: bool
s.notnull()
0 True
1 True
2 True
3 True
4 True
5 True
6 True
7 True
8 True
9 True
dtype: bool
Series的算术运算
法则:索引一致的元素进行算数运算否则补空
s1 = Series(data=[1,2,3],index=['a','b','c'])
s2 = Series(data=[1,2,3],index=['a','d','c'])
s = s1 + s2
s
a 2.0
b NaN
c 6.0
d NaN
dtype: float64
s.isnull()
a False
b True
c False
d True
dtype: bool
DataFrame(重点)
- DataFrame是一个【表格型】的数据结构。DataFrame由按一定顺序排列的多列数据组成。设计初衷是将Series的使用场景从一维拓展到多维。DataFrame既有行索引,也有列索引。
- 行索引:index
- 列索引:columns
- 值:values
DataFrame的创建
- ndarray创建
- 字典创建
from pandas import DataFrame
df = DataFrame(data=[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
df
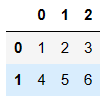
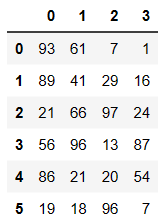
df = DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(0,100,size=(6,4)))
df
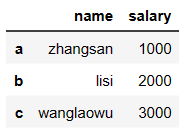
dic = {
'name':['zhangsan','lisi','wanglaowu'],
'salary':[1000,2000,3000]
}
df = DataFrame(data=dic,index=['a','b','c'])
df
DataFrame的属性
- values
- columns
- index
- shape
df.values
array([['zhangsan', 1000],
['lisi', 2000],
['wanglaowu', 3000]], dtype=object)
df.columns
Index(['name', 'salary'], dtype='object')
df.index
Index(['a', 'b', 'c'], dtype='object')
df.shape
(3, 2)
============================================
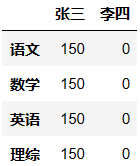
根据以下考试成绩表,创建一个DataFrame,命名为df:
张三 李四
语文 150 0
数学 150 0
英语 150 0
理综 300 0
============================================
dic = {
'张三':[150,150,150,150],
'李四':[0,0,0,0]
}
df = DataFrame(data=dic,index=['语文','数学','英语','理综'])
df
DataFrame的索引和切片操作
- 索引
- df[col]:取列
- df.loc[index]:取行
- df.iloc[index,col]:取元素
- 切片
- df[index1:index3]:切行
- df.iloc[:,col1:col3]:切列
DataFrame索引操作
- 对行进行索引
- 对列进行索引
- 对元素进行索引
df = DataFrame(data=np.random.randint(60,100,size=(8,4)),columns=['a','b','c','d'])
df
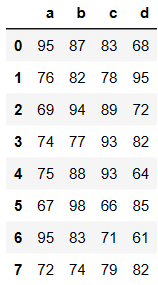
df['a'] # 取单列,如果df有显示的索引,通过索引机制取行或者取列的时候只可以使用显示索引
0 95
1 76
2 69
3 74
4 75
5 67
6 95
7 72
Name: a, dtype: int64
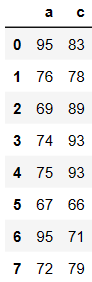
df[['a','c']] #取多列
iloc: 通过隐式索引取行
loc: 通过显示索引取行
# 取单行
df.loc[0]
a 95
b 87
c 83
d 68
Name: 0, dtype: int64
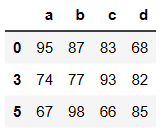
# 取多行
df.iloc[[0,3,5]]
# 取单个元素
df.iloc[0,2]
83
df.loc[0,'a']
95
# 取多个元素
df.iloc[[1,3,5],2]
1 78
3 93
5 66
Name: c, dtype: int64
DataFrame的切片操作
- 对行进行切片
- 对列进行切片
# 切行
df[0:2]
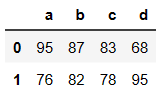
# 切列
df.iloc[:,0:2]
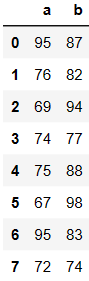
DataFrame的运算
- 同Series
============================================
假设ddd是期中考试成绩,ddd2是期末考试成绩,请自由创建ddd2,并将其与ddd相加,求期中期末平均值。
假设张三期中考试数学被发现作弊,要记为0分,如何实现?
李四因为举报张三作弊立功,期中考试所有科目加100分,如何实现?
后来老师发现有一道题出错了,为了安抚学生情绪,给每位学生每个科目都加10分,如何实现?
============================================
dic = {
'张三':[150,150,150,150],
'李四':[0,0,0,0]
}
df = DataFrame(data=dic,index=['语文','数学','英语','理综'])
qizhong = df
qimo = df
(qizhong + qizhong) / 2 # 期中期末的平均值
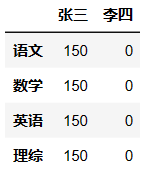
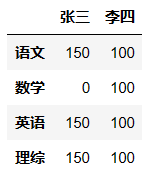
qizhong.loc['数学','张三'] = 0
qizhong # 将张三的数学成绩修改为0
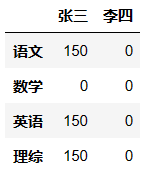
# 将李四的所有成绩+100
qizhong['李四']+=100
qizhong
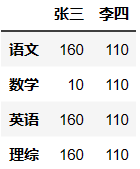
qizhong += 10
qizhong # 将所有学生的成绩+10
其他常用的数学函数
时间数据类型的转换
- pd.to_datetime(col)
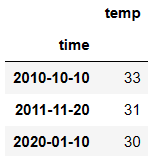
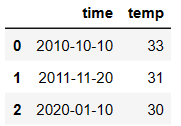
dic = {
'time':['2010-10-10','2011-11-20','2020-01-10'],
'temp':[33,31,30]
}
df = DataFrame(data=dic)
df
# 查看time列的类型
df['time'].dtype
dtype('O')
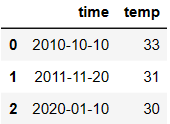
import pandas as pd
# 将time列的数据类型转换成时间序列类型
df['time'] = pd.to_datetime(df['time'])
df
df['time']
0 2010-10-10
1 2011-11-20
2 2020-01-10
Name: time, dtype: datetime64[ns]
将某一列设置为行索引
- df.set_index()
# 将time列作为源数据的行索引
# 改变原始 df 的数据,inplace=True
df.set_index('time',inplace=True)
df