linux驱动移植-中断子系统整体框架
在之前的文章中,我们曾经学习过按键驱动的编写,其中我们就使用到了外部中断,我们是通过request_irq函数实现中断注册的。这一节我们将深入了解linux的中断实现机制。
一、中断介绍
1.1 什么是中断
中断是由软件或者硬件触发的一种事件,可以引起CPU的注意。
举个例子:当我们在键盘上按下一个按键时,接下来我们期望发生什么?操作系统和计算机应该做什么?为简单起见,假设每个外围设备都有一条连接CPU的中断线,设备可以通过它向 CPU 发出中断信号,但是,中断不会直接发送给 CPU。在中断信号到达CPU之前,都会首先经过一个叫做中断控制器(Interrupt Controller)的硬件,其作用是根据中断源(Interrupt Source)的优先级对中断进行派发。
在SMP系统,也就是多核情况下,外部的中断控制器有可能会于多个CPU相连,这时候当一个中断产生时,中断控制器有两种方式将此中断送到CPU上,分别是静态分发和动态分发。区别就是静态分发设置了指定中断送往指定的一个或多个CPU上。动态分发则是由中断控制器控制中断应该发往哪个CPU或CPU组。
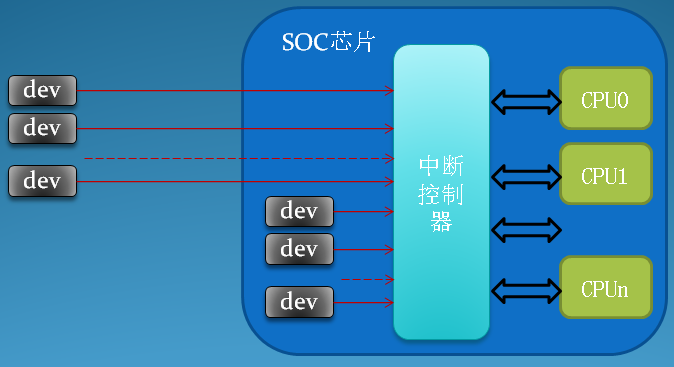
1.2 中断控制器
中断控制器负责收集所有中断源发起的中断,现有的中断控制器几乎都是可编程的,通过对中断控制器的编程,可以控制每个中断源的优先级,还可以打开和关闭某一个中断源等。在多核系统,甚至可以控制某个中断送入哪个CPU进行处理。
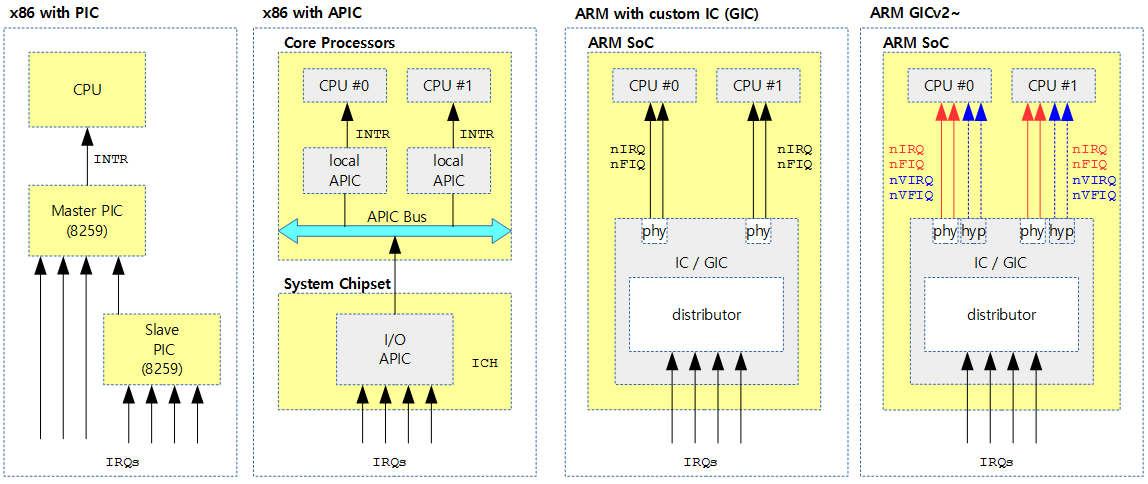
每种架构的中断控制器配置都不一样,比如:
- x86带PIC:在单核x86 架构中,使用并配置了多个 8259 PIC充当中断控制器;
- x86 与 APIC:在多核x86系统中,使用了一个叫做APIC(Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller)的中断控制器,一个APIC由两个独立的设备组成:local APIC和I/O APIC;
- ARM架构,使用较多的中断控制器是VIC(Vector Interrupt Controller),进入多核时代,使用较多的是GIC(Generic Interrupt Controller);
1.3 中断产生
在硬件电路中,中断的产生发生一般只有两种,分别是:电平触发方式和边沿触发方式。这里以ARM处理器为例,介绍硬件中断的产生流程:
- 当一个外部设备产生中断,中断信号会沿着中断线到达中断控制器;
- 中断控制器接收到该外部设备的中断信号后首先会检测中断屏蔽寄存器是否屏蔽该中断(一般为INTMASK寄存器);
- 如果没有屏蔽该中断,则设置中断所在的中断请求寄存器位(一般为INTPEND寄存器);
- 并将IRQ拉高用于通知CPU;
- CPU接收到IRQ中断后,检查CPSR寄存器的I标志位是否禁止了总中断,若禁止了则忽略;
- 然后CPU跳转到中断向量处开始执行中断处理程序;
1.4 GIC
GIC版本包括V1~V4,每个 GIC 版本的主要特点:
- GIC v1
- 最多支持 8 个 PE;
- 可处理多达 1020 个中断源;
- 安全扩展支持;
- 用于 ARM Cortex-A5、A9、R7 等;
- GIC v2
- 包括所有 v1 功能;
- 添加虚拟化功能;
- ARM Cortex-A7、A15、A53、A57、…… 等;
- GIC v2m 是添加了 MSI(基于消息的中断)功能的模型;
- GIC v3
- 包括所有 v2 功能;
- 最多支持 128 个 PE,每个集群 8 个 PE;
- 能够处理超过 1020 个中断源;
- 支持 MSI 方法以及信号(v1 和 v2 中使用的传统)方法;添加了高级安全功能,可根据非安全组和安全组分离中断处理;
- MSI 在 SPI 和 LPI 中可用;
- 除了 SPI、PPI 和 SGI 之外,还支持 LPI(局部特定外设中断);
- 支持亲和路由功能;
- ARM Cortex-A53、A57、A72、…… 等;
- GICv4
- 包括所有 v3 功能;
- 直接注入虚拟中断;
- ARM Cortex-A53、A57、A72、…… 等;
1.5 硬件中断号(hwirq)h和IRQ编号
硬件中断号,或者说是物理中断号,也就是芯片手册上写的那个编号。
Linux为系统中注册的每一个中断源,都会分配一个唯一的编号用于识别该中断,我们称之为IRQ编号。它是一个 虚拟的中断ID,和硬件无关,仅仅是被CPU用来标识一个外设中断。
有了硬件中断号,为什么还给每个硬件中断号分配一个IRQ编号?
这种主要是因为有的处理器芯片中有多个中断控制器,比如S5PV210有四个中断控制器,分别管理各自的32个中断:
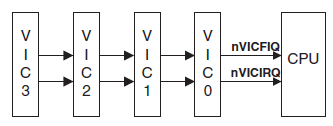
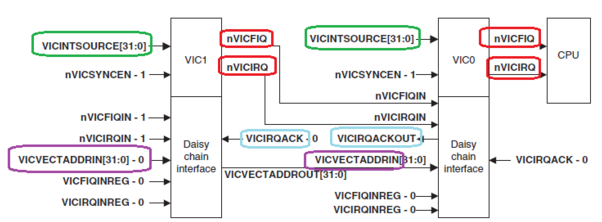
每个终端控制器各自都对应32个硬件中断,这32个硬件中断的编号都是从0到31,那CPU收到中断后,软件单凭0到31中断号是分不清这个中断到底是从哪个中断控制器派发过来的,它需要的是中断控制器自身的编号加上硬件中断号。
IRQ编号贯穿在整个linux的中断子系统中。在移动设备中,每个中断源的IRQ编号都会在arch相关的一些头文件中,例如arch/arm/mach-s3c24xx/include/mach/irqs.h。
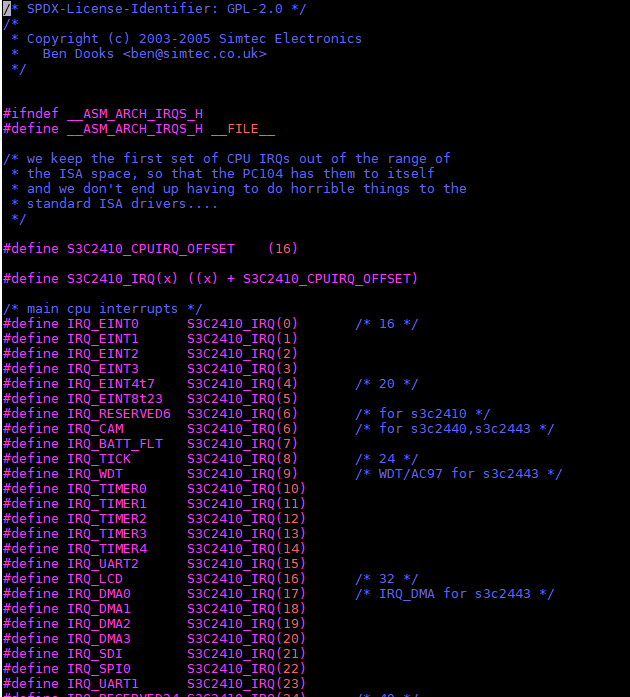
可以看到Linux为S3C2410分配的中断号是从16开始的,这主要是因为0~15被用作软件中断了,关于软件中断后面我们再介绍。
驱动程序在请求中断服务时,它会使用IRQ编号注册该中断,中断发生时,CPU通常会从中断控制器中获取相关信息,然后计算出相应的IRQ编号,然后把该IRQ编号传递到相应的驱动程序中。
此外,Linux引入了中断域struct irq_domain,通过中断域实现了将中断控制器的硬件中断号转换成Linux IRQ编号的机制。
二、中断注册
linux中断子系统向驱动程序提供了注册中断的API,下面我们将会一一介绍。
2.1 request_threaded_irq
request_threaded_irq函数:将中断线程化,中断将作为内核线程运行,可被赋予不同的实时优先级。在负载较高时,中断线程可以被挂起,以避免某些更高优先级的实时任务得不到及时响应。
int __must_check request_threaded_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, irq_handler_t thread_fn, unsigned long flags, const char *name, void *dev);
参数如下:
- irq:中断号,所申请的中断向量;
- handler:中断处理服务函数,该函数工作在中断上下文中,如果不需要,可以传入NULL,但是不可以和thread_fn同时为NULL;
- thread_fn:中断线程的回调函数,工作在内核进程上下文中,如果不需要,可以传入NULL,但是不可以和handler同时为NULL;
- flags:指定中断属性、中断触发方式(一般用宏定义表示)等,定义在linux/interrupt.h中;
- name:指定中断的名称;用命令cat /proc/interrupts可查看系统中断申请与使用情况;
- dev:传入中断处理程序的参数,可以为NULL,但在注册共享中断时,此参数不能为NULL。该参数可作为共享中断时的中断区别参数,还可以把其传给一个结构体变量,用于保存一个设备的信息,使中断处理函数可以获得该设备的信息;
2.1 request_irq
如果不需要将中断线程化,一般使用以下函数即可:
int __must_check request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long flags, const char *name, void *dev) { return request_threaded_irq(irq, handler, NULL, flags, name, dev); }
之前我们在按键驱动程序中就是用了这个函数注册了几个外部中断。
三、中断子系统(Generic irq)的软件抽象
我们可以用下面的图示表示通用中断子系统的层次结构:
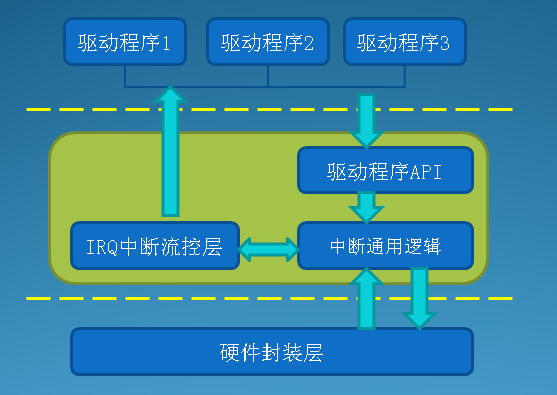
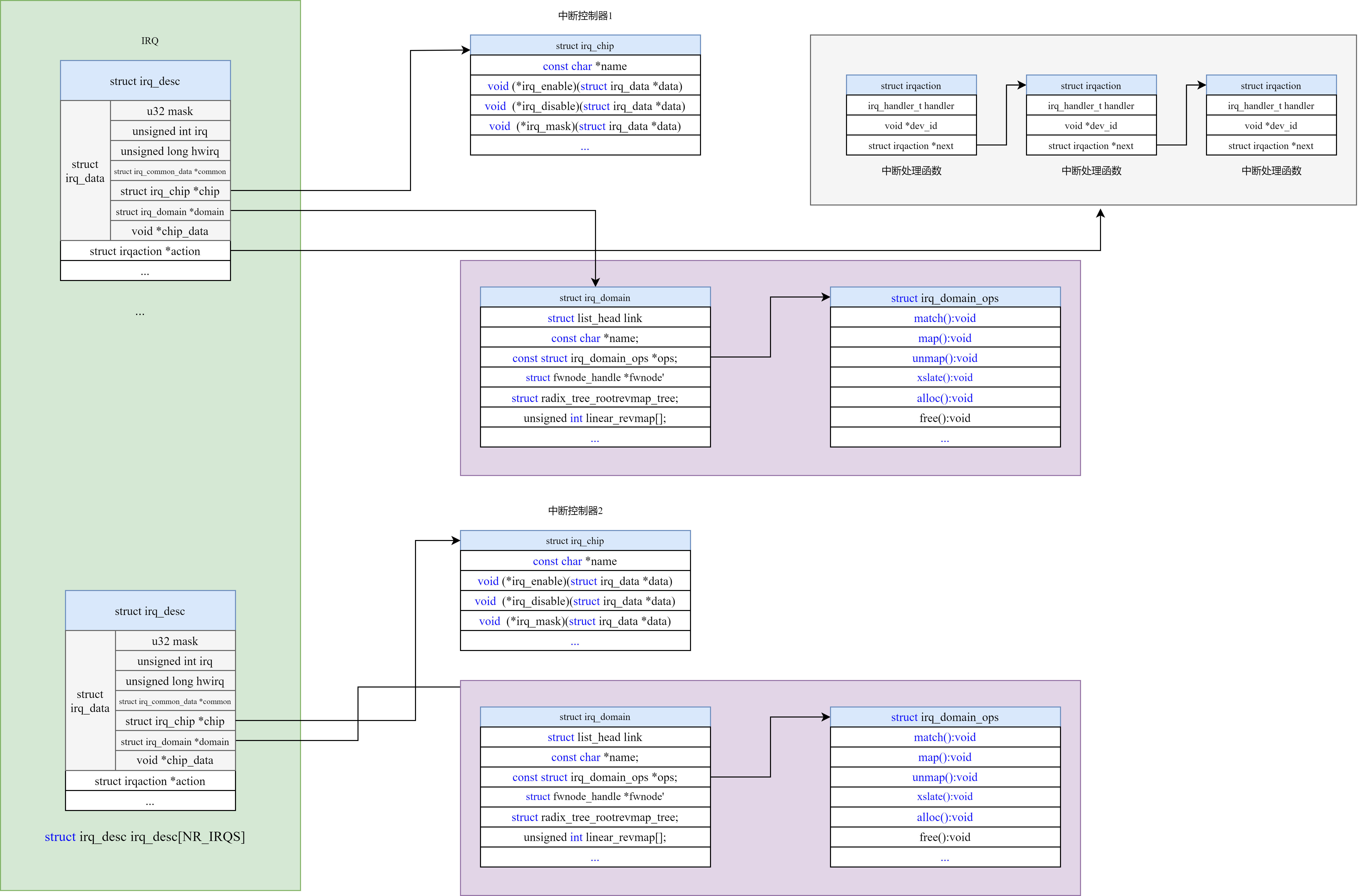
3.1 硬件封装层struct irq_chip
硬件封装层它包含了体系架构相关的所有代码,其使用struct irq_chip对中断控制器的接口抽象;其中的成员大多用于操作底层硬件,比如设置寄存器以屏蔽中断,使能中断,清除中断等。
我们看看irq_chip的部分定义,定义在include/linux/irq.h文件中:
struct irq_chip { struct device *parent_device; //指向父设备 const char *name; // /proc/interrupts中显示的名字 unsigned int (*irq_startup)(struct irq_data *data); //启动中断,如果设置成NULL,则默认为enable 开总中断 void (*irq_shutdown)(struct irq_data *data); //关闭中断,如果设置成NULL,则默认为disable 关总中断 void (*irq_enable)(struct irq_data *data); //中断使能,如果设置成NULL,则默认为chip->unmask 单个IRQ void (*irq_disable)(struct irq_data *data); //中断禁止 单个IRQ void (*irq_ack)(struct irq_data *data); //开始新的中断 void (*irq_mask)(struct irq_data *data); //中断源屏蔽 void (*irq_mask_ack)(struct irq_data *data); //应答并屏蔽中断 void (*irq_unmask)(struct irq_data *data); //解除中断屏蔽 void (*irq_eoi)(struct irq_data *data); //中断处理结束后调用 int (*irq_set_affinity)(struct irq_data *data, const struct cpumask *dest, bool force); //在SMP中设置CPU亲和力 int (*irq_retrigger)(struct irq_data *data); //重新发送中断到CPU int (*irq_set_type)(struct irq_data *data, unsigned int flow_type); //设置中断触发类型 int (*irq_set_wake)(struct irq_data *data, unsigned int on); //使能/禁止电源管理中的唤醒功能 void (*irq_bus_lock)(struct irq_data *data); //慢速芯片总线上的锁 void (*irq_bus_sync_unlock)(struct irq_data *data); //同步释放慢速总线芯片的锁 void (*irq_cpu_online)(struct irq_data *data); void (*irq_cpu_offline)(struct irq_data *data); void (*irq_suspend)(struct irq_data *data); void (*irq_resume)(struct irq_data *data); void (*irq_pm_shutdown)(struct irq_data *data); void (*irq_calc_mask)(struct irq_data *data); void (*irq_print_chip)(struct irq_data *data, struct seq_file *p); int (*irq_request_resources)(struct irq_data *data); void (*irq_release_resources)(struct irq_data *data); void (*irq_compose_msi_msg)(struct irq_data *data, struct msi_msg *msg); void (*irq_write_msi_msg)(struct irq_data *data, struct msi_msg *msg); int (*irq_get_irqchip_state)(struct irq_data *data, enum irqchip_irq_state which, bool *state); int (*irq_set_irqchip_state)(struct irq_data *data, enum irqchip_irq_state which, bool state); int (*irq_set_vcpu_affinity)(struct irq_data *data, void *vcpu_info); void (*ipi_send_single)(struct irq_data *data, unsigned int cpu); void (*ipi_send_mask)(struct irq_data *data, const struct cpumask *dest); unsigned long flags; };
因为不同芯片的中断控制器对其挂接的IRQ有不同的控制方法,因而这个结构体主要是由一组用于回调(callback),指向系统实际的中断控制器所使用的控制方法的函数指针构成。
我们只要对每个中断控制器实现以上接口(不必全部),并把它和相应的IRQ关联起来,上层的实现即可通过这些接口访问中断控制器。
3.2 中断通用逻辑层
中断通用逻辑层通过标准的封装接口(实际上就是struct irq_chip定义的接口)访问并控制中断控制器的行为,体系相关的中断入口函数在获取IRQ编号后,通过中断通用逻辑层提供的标准函数,把中断调用传递到中断流控层中。
中断通用逻辑层实现了对中断系统几个重要数据的管理,并提供了一系列的辅助管理函数。同时,该层还实现了中断线程的实现和管理,共享中断和嵌套中断的实现和管理,另外它还提供了一些接口函数,它们将作为硬件封装层和中断流控层以及驱动程序API层之间的桥梁,例如以下API:
int generic_handle_irq(unsigned int irq); struct irq_desc *irq_to_desc(unsigned int irq); int irq_set_chip(unsigned int irq, struct irq_chip *chip); ...
其中irq_to_desc函数可以通过IRQ编号获取到irq_desc结构的指针。
irq_set_chip用于绑定IRQ到指定的中断控制器chip。
3.3 中断流控层
所谓中断流控是指合理并正确地处理连续发生的中断,比如一个中断在处理中,同一个中断再次到达时如何处理,何时应该屏蔽中断,何时打开中断,何时回应中断控制器等一系列的操作。
该层实现了与体系和硬件无关的中断流控处理操作,它针对不同的中断电气类型(level,edge......),实现了对应的标准中断流控处理函数,在这些处理函数中,最终会把中断控制权传递到驱动程序注册中断时传入的处理函数或者是中断线程中。目前内核提供了以下几个主要的中断流控函数的实现:
void handle_simple_irq(struct irq_desc *desc); void handle_level_irq(struct irq_desc *desc); //电平中断流控处理程序 void handle_edge_irq(struct irq_desc *desc); //边沿触发中断流控处理程序 voif handle_fasteoi_irq(struct irq_desc *desc); // 需要eoi的中断处理器使用的中断流控处理程序 voif handle_percpu_irq(struct irq_desc *desc); //该irq只有单个cpu响应时使用的流控处理程序 ...
这些函数在include/linux/irqdesc.h中声明。
3.4 驱动程序API
该部分向驱动程序提供了一系列的API,用于向系统申请/释放中断,打开/关闭中断,设置中断类型和中断唤醒系统的特性等操作。驱动程序的开发者通常只会使用到这一层提供的这些API即可完成驱动程序的开发工作,其他的细节都由另外几个软件层较好地“隐藏”起来了,驱动程序开发者无需再关注底层的实现。其中的一些API如下:
void disable_irq_nosync(unsigned int irq); bool disable_hardirq(unsigned int irq); void disable_irq(unsigned int irq); void disable_percpu_irq(unsigned int irq); void enable_irq(unsigned int irq); void enable_percpu_irq(unsigned int irq, unsigned int type); bool irq_percpu_is_enabled(unsigned int irq); void irq_wake_thread(unsigned int irq, void *dev_id); void disable_nmi_nosync(unsigned int irq); void disable_percpu_nmi(unsigned int irq); void enable_nmi(unsigned int irq); void enable_percpu_nmi(unsigned int irq, unsigned int type); int prepare_percpu_nmi(unsigned int irq); void teardown_percpu_nmi(unsigned int irq);
这些函数在include/linux/interrupt.h中声明。
四、中断描述符
每一个IRQ中断在linux中断子系统中通过struct irq_desc描述,我们称之为中断描述符。所有的irq_desc结构的组织方式有两种。
4.1 基于数组方式
平台相关板级代码事先根据系统中的IRQ数量,定义常量:NR_IRQS,在kernel/irq/irqdesc.c中使用该常量定义irq_desc结构数组:
struct irq_desc irq_desc[NR_IRQS] __cacheline_aligned_in_smp = { [0 ... NR_IRQS-1] = { .handle_irq = handle_bad_irq, .depth = 1, .lock = __RAW_SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(irq_desc->lock), } };
基于线性数组的中断描述符是一块静态内存,常驻于内存中,该方式是一种简单的线性映射,通过IRQ编号就可以直接获取到中断描述符。后面的代码介绍也是以这种方式进行讲解。
4.2 基于基数树方式(radix tree)
当内核的配置项CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ被选中时,内核使用基数树(radix tree)来管理irq_desc结构,这一方式可以动态地分配irq_desc结构,对于那些具备大量IRQ数量或者IRQ编号不连续的系统,使用该方式管理irq_desc对内存的节省有好处,而且对那些自带中断控制器管理设备自身多个中断源的外部设备,它们可以在驱动程序中动态地申请这些中断源所对应的irq_desc结构,而不必在系统的编译阶段保留irq_desc结构所需的内存。
4.3 struct irq_desc
在include/linux/irqdesc.h中定义irq_desc结构:
/** * struct irq_desc - interrupt descriptor * @irq_common_data: per irq and chip data passed down to chip functions * @kstat_irqs: irq stats per cpu * @handle_irq: highlevel irq-events handler * @preflow_handler: handler called before the flow handler (currently used by sparc) * @action: the irq action chain * @status: status information * @core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it: core internal status information * @depth: disable-depth, for nested irq_disable() calls * @wake_depth: enable depth, for multiple irq_set_irq_wake() callers * @tot_count: stats field for non-percpu irqs * @irq_count: stats field to detect stalled irqs * @last_unhandled: aging timer for unhandled count * @irqs_unhandled: stats field for spurious unhandled interrupts * @threads_handled: stats field for deferred spurious detection of threaded handlers * @threads_handled_last: comparator field for deferred spurious detection of theraded handlers * @lock: locking for SMP * @affinity_hint: hint to user space for preferred irq affinity * @affinity_notify: context for notification of affinity changes * @pending_mask: pending rebalanced interrupts * @threads_oneshot: bitfield to handle shared oneshot threads * @threads_active: number of irqaction threads currently running * @wait_for_threads: wait queue for sync_irq to wait for threaded handlers * @nr_actions: number of installed actions on this descriptor * @no_suspend_depth: number of irqactions on a irq descriptor with * IRQF_NO_SUSPEND set * @force_resume_depth: number of irqactions on a irq descriptor with * IRQF_FORCE_RESUME set * @rcu: rcu head for delayed free * @kobj: kobject used to represent this struct in sysfs * @request_mutex: mutex to protect request/free before locking desc->lock * @dir: /proc/irq/ procfs entry * @debugfs_file: dentry for the debugfs file * @name: flow handler name for /proc/interrupts output */ struct irq_desc { struct irq_common_data irq_common_data; struct irq_data irq_data; unsigned int __percpu *kstat_irqs; irq_flow_handler_t handle_irq; #ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_PREFLOW_FASTEOI irq_preflow_handler_t preflow_handler; #endif struct irqaction *action; /* IRQ action list */ unsigned int status_use_accessors; unsigned int core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it; // istate成员 unsigned int depth; /* nested irq disables */ unsigned int wake_depth; /* nested wake enables */ unsigned int tot_count; unsigned int irq_count; /* For detecting broken IRQs */ unsigned long last_unhandled; /* Aging timer for unhandled count */ unsigned int irqs_unhandled; atomic_t threads_handled; int threads_handled_last; raw_spinlock_t lock; struct cpumask *percpu_enabled; // 单个IRQ针对单个CPU中断使能 const struct cpumask *percpu_affinity; #ifdef CONFIG_SMP const struct cpumask *affinity_hint; struct irq_affinity_notify *affinity_notify; #ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_PENDING_IRQ cpumask_var_t pending_mask; #endif #endif unsigned long threads_oneshot; atomic_t threads_active; wait_queue_head_t wait_for_threads; #ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP unsigned int nr_actions; unsigned int no_suspend_depth; unsigned int cond_suspend_depth; unsigned int force_resume_depth; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS struct proc_dir_entry *dir; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS struct dentry *debugfs_file; const char *dev_name; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ struct rcu_head rcu; struct kobject kobj; #endif struct mutex request_mutex; int parent_irq; struct module *owner; const char *name; } ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
对于irq_desc中的主要字段做一个解释:
- irq_data: 这个单独介绍,比较重要。
- handle_irq:中断流控处理函数;
- kstat_irqs:用于irq的一些统计信息,这些统计信息可以从proc文件系统中查询;
- action :中断响应链表,当一个irq被触发时,内核会遍历该链表,调用action结构中的回调handler或者激活其中的中断线程,之所以实现为一个链表,是为了实现中断的共享,多个设备共享同一个irq,这在外围设备中是普遍存在的;
- status_use_accessors: 记录该irq的状态信息,内核提供了一系列irq_settings_xxx的辅助函数访问该字段,详细请查看kernel/irq/settings.h;
- depth: 用于管理enable_irq()/disable_irq()这两个API的嵌套深度管理,每次enable_irq时该值减去1,每次disable_irq时该值加1,只有depth==0时才真正向硬件封装层发出关闭irq的调用,只有depth==1时才会向硬件封装层发出打开irq的调用。disable的嵌套次数可以比enable的次数多,此时depth的值大于1,随着enable的不断调用,当depth的值为1时,在向硬件封装层发出打开irq的调用后,depth减去1后,此时depth为0,此时处于一个平衡状态,我们只能调用disable_irq,如果此时enable_irq被调用,内核会报告一个irq失衡的警告,提醒驱动程序的开发人员检查自己的代码;
- lock:用于保护irq_desc结构本身的自旋锁;
- affinity_hit:用于提示用户空间,作为优化irq和cpu之间的亲缘关系的依据;
- pending_mask:用于调整irq在各个cpu之间的平衡;
- wait_for_threads:用于synchronize_irq(),等待该irq所有线程完成;
其中core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it(也就是istate成员)的可能取值如下,该位主要用来标识当前中断处理程序所处状态:
enum { IRQS_AUTODETECT = 0x00000001, // 处于自动侦测状态 IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED = 0x00000002, // 被视为“伪中断”并被禁用 IRQS_POLL_INPROGRESS = 0x00000008, // 正处于轮询调用action IRQS_ONESHOT = 0x00000020, // 表示只执行一次,由IRQF_ONESHOT转换而来,在中断线程化执行完成后需要小心对待,见irq_finalize_oneshot()。 IRQS_REPLAY = 0x00000040, // 重新发送一次中断 IRQS_WAITING = 0x00000080, // 处于等待状态 IRQS_PENDING = 0x00000200, // 该中断被挂起 IRQS_SUSPENDED = 0x00000800, // 该中断被暂停 };
4.4 struct irqaction
irq_desc中的action是IRQ对应的中断处理函数(ISR - Interrupt Service Routine),ISR应该就是一个函数指针,可这里却是一个指向struct irqaction的指针,该类型定义在include/linux/interrupt.h文件。
这是因为在早期的一些处理器中,硬件中断的数目很少,而且有些中断编号已经永久性地分配给了标准的系统组件(比如keyboard和timer),为了服务于更多的设备,只能对有限的IRQ中断号进行共享。这样,同一个中断号就会对应多个不同的处理函数,这些处理函数通过一个单向链表串联在一起的。
/** * struct irqaction - per interrupt action descriptor * @handler: interrupt handler function * @name: name of the device * @dev_id: cookie to identify the device * @percpu_dev_id: cookie to identify the device * @next: pointer to the next irqaction for shared interrupts * @irq: interrupt number * @flags: flags (see IRQF_* above) * @thread_fn: interrupt handler function for threaded interrupts * @thread: thread pointer for threaded interrupts * @secondary: pointer to secondary irqaction (force threading) * @thread_flags: flags related to @thread * @thread_mask: bitmask for keeping track of @thread activity * @dir: pointer to the proc/irq/NN/name entry */ struct irqaction { irq_handler_t handler; // 用户注册的中断处理函数,primary handler void *dev_id; // 设备标识、一般为字符串指针 void __percpu *percpu_dev_id; // dev_id struct irqaction *next; // 指向下一个成员 irq_handler_t thread_fn; // 中断线程处理函数,threaded interrupt handler struct task_struct *thread; // 如果中断线程化,这里保存中断线程的task_struct数据结构 struct irqaction *secondary; unsigned int irq; // IRQ编号 unsigned int flags; // 注册中断时的中断标志,IRQF_* unsigned long thread_flags; // 中断线程相关标志 unsigned long thread_mask; // 在共享中断中,每一个action都有一个Bit来表示 const char *name; // 中断名称、产生中断的硬件的名称 struct proc_dir_entry *dir; // 指向IRQ相关的 /proc/irq } ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
当一个中断发生的时候,IRQ对应action链表上的handler都将被依次执行,以判断是否是自己的设备产生的中断,这主要靠读取自己设备的中断状态寄存器来完成。因此共享中断时,即便不是你的设备产生的中断,你的handler也会被调用到。为了避免无谓的消耗,需要一进handler就立刻进行判断,如果不是,就尽快的退出。
当一个设备从挂接的IRQ线上卸载时,设备对应的struct irqaction也应该相应地从IRQ action链表中移除,此时需要一个表示挂接在同一个IRQ上的不同设备的标识,这个标识就是dev_id。内核通对比dev_id,来找到那个应该移除的struct irqaction。
有了中断共享,处理起来着实麻烦了很多,好在新的硬件平台上的设计已经很少采用外设共享IRQ的方式了,因为现在SOC能提供的有中断功能的GPIO已经非常多,足够使用了。
4.5 struct irq_data
至于irq_desc中的irq_data,在前面已经出现过了,irq_chip结构体中的每个函数指针都会携带一个指向struct irq_data的指针作为参数,可见这个irq_data与中断控制器关系密切。也就是说,在irq_desc的定义中,与中断控制器紧密联系的这部分被单独提取出来,构成了irq_data结构体,其在include/linux/irq.h中定义:
/** * struct irq_data - per irq chip data passed down to chip functions * @mask: precomputed bitmask for accessing the chip registers * @irq: interrupt number * @hwirq: hardware interrupt number, local to the interrupt domain * @common: point to data shared by all irqchips * @chip: low level interrupt hardware access * @domain: Interrupt translation domain; responsible for mapping * between hwirq number and linux irq number. * @parent_data: pointer to parent struct irq_data to support hierarchy * irq_domain * @chip_data: platform-specific per-chip private data for the chip * methods, to allow shared chip implementations */ struct irq_data { u32 mask; unsigned int irq; unsigned long hwirq; struct irq_common_data *common; struct irq_chip *chip; struct irq_domain *domain; #ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY struct irq_data *parent_data; #endif void *chip_data; };
结构中的各字段;
- irq:该结构所对应的IRQ编号;
- hwirq:硬件IRQ编号;
- node:通常用于hwirq和irq之间的映射操作;
- state_use_accessors:硬件封装层需要使用的状态信息,不要直接访问该字段,内核定义了一组函数用于访问该字段:irqd_xxxx(),参见include/linux/irq.h;
- chip:指向该irq所属的中断控制器的irq_chip结构指针,两者的关系是通过irq_set_chip函数绑定的;
- handler_data:每个irq的私有数据指针,该字段由硬件封转层使用,例如用作底层硬件的多路复用中断;
- chip_data:中断控制器的私有数据,该字段由硬件封转层使用;
- msi_desc:用于PCIe总线的MSI或MSI-X中断机制;
- affinity:记录该irq与cpu之间的亲缘关系,它其实是一个bit-mask,每一个bit代表一个cpu,置位后代表该cpu可能处理该irq;
4.5.1 irq_common_data
irq_common_data定义如下:
/** * struct irq_common_data - per irq data shared by all irqchips * @state_use_accessors: status information for irq chip functions. * Use accessor functions to deal with it * @node: node index useful for balancing * @handler_data: per-IRQ data for the irq_chip methods * @affinity: IRQ affinity on SMP. If this is an IPI * related irq, then this is the mask of the * CPUs to which an IPI can be sent. * @effective_affinity: The effective IRQ affinity on SMP as some irq * chips do not allow multi CPU destinations. * A subset of @affinity. * @msi_desc: MSI descriptor * @ipi_offset: Offset of first IPI target cpu in @affinity. Optional. */ struct irq_common_data { unsigned int __private state_use_accessors; #ifdef CONFIG_NUMA unsigned int node; #endif void *handler_data; struct msi_desc *msi_desc; cpumask_var_t affinity; #ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_EFFECTIVE_AFF_MASK cpumask_var_t effective_affinity; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_IPI unsigned int ipi_offset; #endif };
其中state_use_accessors的可能取值如下,该参数不同位区间有不同的意义,主要用来标识当前中断状态信息:
/* * Bit masks for irq_common_data.state_use_accessors * * IRQD_TRIGGER_MASK - Mask for the trigger type bits * IRQD_SETAFFINITY_PENDING - Affinity setting is pending * IRQD_ACTIVATED - Interrupt has already been activated * IRQD_NO_BALANCING - Balancing disabled for this IRQ * IRQD_PER_CPU - Interrupt is per cpu * IRQD_AFFINITY_SET - Interrupt affinity was set * IRQD_LEVEL - Interrupt is level triggered * IRQD_WAKEUP_STATE - Interrupt is configured for wakeup * from suspend * IRQD_MOVE_PCNTXT - Interrupt can be moved in process * context * IRQD_IRQ_DISABLED - Disabled state of the interrupt * IRQD_IRQ_MASKED - Masked state of the interrupt * IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS - In progress state of the interrupt * IRQD_WAKEUP_ARMED - Wakeup mode armed * IRQD_FORWARDED_TO_VCPU - The interrupt is forwarded to a VCPU * IRQD_AFFINITY_MANAGED - Affinity is auto-managed by the kernel * IRQD_IRQ_STARTED - Startup state of the interrupt * IRQD_MANAGED_SHUTDOWN - Interrupt was shutdown due to empty affinity * mask. Applies only to affinity managed irqs. * IRQD_SINGLE_TARGET - IRQ allows only a single affinity target * IRQD_DEFAULT_TRIGGER_SET - Expected trigger already been set * IRQD_CAN_RESERVE - Can use reservation mode */ enum { IRQD_TRIGGER_MASK = 0xf, // 该中断触发类型 IRQD_SETAFFINITY_PENDING = (1 << 8), IRQD_ACTIVATED = (1 << 9), IRQD_NO_BALANCING = (1 << 10), IRQD_PER_CPU = (1 << 11), IRQD_AFFINITY_SET = (1 << 12), IRQD_LEVEL = (1 << 13), IRQD_WAKEUP_STATE = (1 << 14), IRQD_MOVE_PCNTXT = (1 << 15), IRQD_IRQ_DISABLED = (1 << 16), // 该中断处于关闭状态 IRQD_IRQ_MASKED = (1 << 17), // 该中断被屏蔽中 IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS = (1 << 18), IRQD_WAKEUP_ARMED = (1 << 19), IRQD_FORWARDED_TO_VCPU = (1 << 20), IRQD_AFFINITY_MANAGED = (1 << 21), IRQD_IRQ_STARTED = (1 << 22), IRQD_MANAGED_SHUTDOWN = (1 << 23), IRQD_SINGLE_TARGET = (1 << 24), IRQD_DEFAULT_TRIGGER_SET = (1 << 25), IRQD_CAN_RESERVE = (1 << 26), };
4.6 struct irq_domain
我们之前说过,通过中断域可以将中断控制器的硬件中断号转换成Linux全局的虚拟中断号,每一个中断控制器都有自己的struct irq_domain结构,该类型定义在include/linux/irqdomain.h:
/** * struct irq_domain - Hardware interrupt number translation object * @link: Element in global irq_domain list. * @name: Name of interrupt domain * @ops: pointer to irq_domain methods * @host_data: private data pointer for use by owner. Not touched by irq_domain * core code. * @flags: host per irq_domain flags * @mapcount: The number of mapped interrupts * * Optional elements * @fwnode: Pointer to firmware node associated with the irq_domain. Pretty easy * to swap it for the of_node via the irq_domain_get_of_node accessor * @gc: Pointer to a list of generic chips. There is a helper function for * setting up one or more generic chips for interrupt controllers * drivers using the generic chip library which uses this pointer. * @parent: Pointer to parent irq_domain to support hierarchy irq_domains * @debugfs_file: dentry for the domain debugfs file * * Revmap data, used internally by irq_domain * @revmap_direct_max_irq: The largest hwirq that can be set for controllers that * support direct mapping * @revmap_size: Size of the linear map table @linear_revmap[] * @revmap_tree: Radix map tree for hwirqs that don't fit in the linear map * @linear_revmap: Linear table of hwirq->virq reverse mappings */ struct irq_domain { struct list_head link; const char *name; const struct irq_domain_ops *ops; void *host_data; unsigned int flags; unsigned int mapcount; /* Optional data */ struct fwnode_handle *fwnode; enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token; struct irq_domain_chip_generic *gc; #ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY struct irq_domain *parent; #endif #ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_IRQ_DEBUGFS struct dentry *debugfs_file; #endif /* reverse map data. The linear map gets appended to the irq_domain */ irq_hw_number_t hwirq_max; unsigned int revmap_direct_max_irq; unsigned int revmap_size; struct radix_tree_root revmap_tree; // 基于基数树 struct mutex revmap_tree_mutex; unsigned int linear_revmap[]; // 基于线性 };
其中:
- linear_revmap(基于数组方式):保存了一个线性的lookup table(查找表),硬件中断号(hwirq)作为数组的下标,IRQ作为数组元素的值;
- revmap_size(基于数组的方式):等于线性lookup table的大小;
- hwirq_max:保存了硬件中断号的最大值;
- remap_tree(基于基数树方式):宏定义为xarry类型,硬件中断号作为查找和添加remap_tree节点的key,IRQ编号作为节点的value;
4.6.1 irq_domain_ops
irq_domain_ops 结构体是Linux内核中用于描述中断域的操作集的一个结构体。它包含了一组函数指针,这些函数指针用于定义中断域的各种行为。
struct irq_domain_ops { int (*match)(struct irq_domain *d, struct device_node *node, enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token); int (*select)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_fwspec *fwspec, enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token); int (*map)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq, irq_hw_number_t hw); void (*unmap)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq); int (*xlate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct device_node *node, const u32 *intspec, unsigned int intsize, unsigned long *out_hwirq, unsigned int *out_type); #ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY /* extended V2 interfaces to support hierarchy irq_domains */ int (*alloc)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq, unsigned int nr_irqs, void *arg); void (*free)(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int virq, unsigned int nr_irqs); void (*activate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_data *irq_data); void (*deactivate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_data *irq_data); int (*translate)(struct irq_domain *d, struct irq_fwspec *fwspec, unsigned long *out_hwirq, unsigned int *out_type); #endif };
此外irq_domain_ops中所定义的函数完成的比较重要,其成员:
- match:在从设备树中创建中断域时被调用,用于匹配与该中断域相关的设备节点;
- select:在请求中断时被调用,用于选择实际处理中断的硬件中断号;
- map:建立硬件中断号到IRQ编号映射关系时会回调该函数,比如irq_create_mapping调用了该函数;
- unmap:在解除IRQ编号和硬件中断号之间的映射关系时被调用;
- xlate:在从设备树中解析中断信息时被调用,用于将设备节点中的interrupt属性信息转换为对应的硬件中断号和中断类型;在xlate的函数参数中,node代表dts中对应的设备节点,out_hwirq是翻译后形成的硬件中断号,out_type是翻译后形成的终端类型;
如果内核启用了扩展的 IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY 功能,则还可以使用以下额外的回调函数:
- alloc:在分配多个连续的中断号时被调用,用于获取一组新的中断号;
- free:在释放分配的一组中断号时被调用;
- activate:在激活中断时被调用,可用于启动中断控制器等驱动程序;
- deactivate:在禁用中断时被调用,可用于停止中断控制器等驱动程序;
- translate:在从设备树中解析中断信息时被调用,用于将设备树描述的中断信息转换为实际中断源和中断类型;
需要注意的是,这些回调函数并不一定都需要实现。例如,如果使用线性中断域实现中断管理,就不需要实现 alloc 和 free 回调函数。
4.6.2 基数树和线性映射
基数树其实是一种稀疏的多级数组,当中断总数减少时,它所需要的节点的总数也减少,就可以退化成单级数组,也就是线性映射。
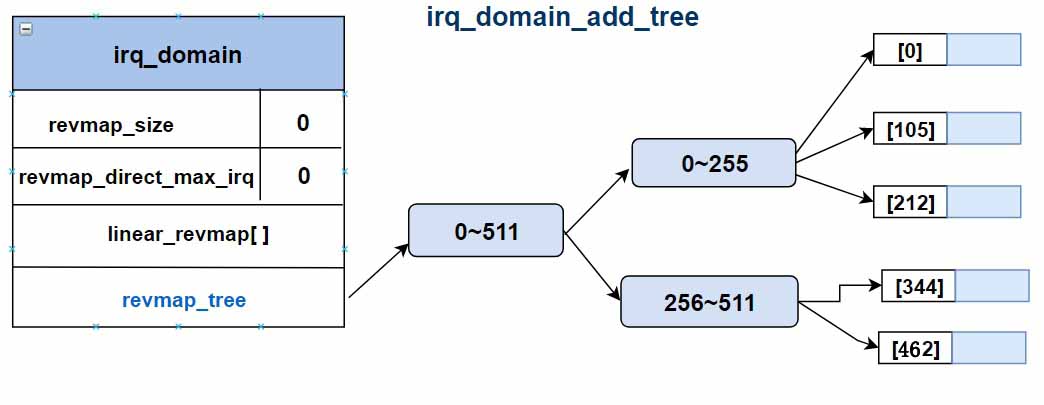
成员hwirq_max是决定采用哪种数据结构的依据,其分界线一般为256,大于256采用radix tree映射,小于256则采用线性映射。在大多数系统中,中断的总数都不会超过256,所以实际应用以线性映射居多。
线性映射的优点是查找时间固定,但要求数组大小必须等于hwirq_max的大小,假设hwirq_max的值是64,即便现在只有0和63两个中断,中间暂未使用的部分也需要连续占满。radix tree映射的优缺点与之正好相反。
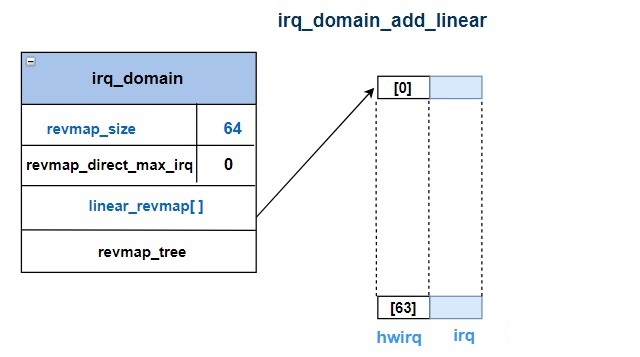
在使用中断域时,需要实现自己的irq_domain_ops结构体,并将其作为参数传递给irq_domain_add_linear、irq_domain_add_tree等函数来注册中断域。此外,还需要在初始化设备时调用irq_create_mapping函数来创建硬件中断号到IRQ编号的映射关系,以便Linux内核在处理中断时能够正确地识别中断源并通知相应的设备驱动程序进行处理。
五、中断子系统执行流程
下面我们大致介绍一下当一个中断发生时,中断子系统的整体执行流程:
5.1 分配irq_desc
系统启动阶段,取决于内核的配置,内核会通过数组或基数树分配好足够多的irq_desc结构;比如我们使用的S3C2440中断控制器支持32个主中断源,24个外部中断、15个内部子中断,那么这里至少会分配16(软中断) + 32 + 24 + 15个irq_desc结构。
5.2 初始化irq_chip
根据不同的体系结构,初始化中断相关的硬件,尤其是中断控制器;
5.3 填充irq_desc
为每个必要irq的irq_desc结构填充默认的字段,例如irq编号,irq_chip指针,根据不同的中断类型配置流控handler;
通过上面的介绍,我们知道每个中断,对应一个irq_desc结构,通过irq_set_chip将IRQ绑定到指定的中断控制器irq_chip,绑定之后就可以使用irq_chip提供的各种处理函数了。
比如内核提供的用于禁止一个IRQ的irq_disable,它就是通过该IRQ对应的irq_desc的irq_data字段,找到对应的irq_chip,进而回调irq_chip中的irq_disable函数,在kernel/irq/chip.c文件中定义:
void irq_enable(struct irq_desc *desc) { if (!irqd_irq_disabled(&desc->irq_data)) { unmask_irq(desc); } else { irq_state_clr_disabled(desc); if (desc->irq_data.chip->irq_enable) { desc->irq_data.chip->irq_enable(&desc->irq_data); irq_state_clr_masked(desc); } else { unmask_irq(desc); } } }
挂接在同一个中断控制器上的IRQ有相同的控制方法,比如irq_enable都是通过写入这个中断控制器的一组寄存器实现,只是不同IRQ的使能需要写入寄存器中不同的bits。这里的irq_enable只是用于使能单个IRQ的,而不是使能整个中断控制器。
虽然是使能单个IRQ,但由于这是在中断控制器层面的操作,因而对所有挂接这个中断控制器的CPU都有效,如果要控制单个IRQ对单个CPU有效,则可以借助irq_desc中的percpu_enabled位域,实现irq_percpu_enable()函数。
要关闭一个CPU对所有中断的响应,应该使用local_irq_disable()/local_irq_save()函数,以x86为例,这是通过关中断指令cli实现的。这种中断关闭只对执行关中断指令的CPU有效,要想直接关闭所有CPU对所有中断的响应,通常是不行的。
系统中如果只有一个中断控制器,其实是不需要什么绑定的,可是随着芯片功能越来越强,硬件也越来越复杂,现在的很多系统已经不止一个中断控制器了。
5.4 中断注册
设备驱动程序在初始化阶段,利用request_threaded_irq申请中断服务,两个重要的参数是handler和thread_fn;
5.5 中断触发
当设备触发一个中断后,CPU会进入事先设定好的中断入口,它属于底层体系相关的代码,它通过中断控制器获得irq编号,在对irq_data结构中的某些字段进行处理后,会将控制权传递到中断流控层(通过irq_desc->handle_irq);
中断流控处理代码在作出必要的流控处理后,通过irq_desc->action链表,取出驱动程序申请中断时注册的handler和thread_fn,根据它们的赋值情况,或者只是调用handler回调,或者启动一个线程执行thread_fn,又或者两者都执行;
至此,中断最终由驱动程序进行了响应和处理;
参考文章:
[4]Linux的中断处理机制 [四] - softirq(1)
[5]Linux的中断处理机制 [五] - softirq(2)
[6]Linux中的中断处理机制 [六] - 从tasklet到中断线程化
[7]ARM的中断处理 [一]
[8]ARM的中断处理 [二]
[9]【原创】Linux中断子系统(一)-中断控制器及驱动分析
[11]The Linux Kernel documentation Linux generic IRQ handling
[12]Linux 内部
[14]Interrupts -1- (Interrupt Controller)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号