linux驱动移植-IO多路复用模型(poll机制)
一、Linux IO模型
1.1 按键测试程序存在的问题
上一小节写到的中断方式获取按键值时,应用程序不停的查询是否有按键发生改变,大部分时间程序都处在read休眠的那个位置。
#include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> int main(int argc,char **argv) { int fd,ret; unsigned int key_val = 0; fd = open("/dev/buttons", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { printf("can't open!\n"); return -1; } while (1) { ret = read(fd, &key_val, 1); // 读取一个字节值,(当在等待队列时,本进程就会进入休眠状态) 只有按键按下或者松开,才会返回 if(ret < 0){ printf("read error\n"); continue; } printf("key_val = 0x%x\n", key_val); } return 0; }
实际上这是一个同步IO操作,因为一个read操作就阻塞了当前线程,导致其他代码无法执行。解决这个问题有若干种办法:
- 异步IO操作:当代码需要执行一个耗时的IO操作时,它只发出IO指令,并不等待IO结果,然后就去执行其他代码了。一段时间后,当IO返回结果时,再通知调用者。
- 采用多线程解决并发的问题,但是系统不能无上限地增加线程。由于系统切换线程的开销也很大,所以,一旦线程数量过多,CPU的时间就花在线程切换上了,真正运行代码的时间就少了,结果导致性能严重下降;
1.2 IO模型
Linux下有五种IO模型:
- 阻塞IO;
- 非阻塞IO;
- 多路复用IO;
- 信号驱动IO;
- 异步IO;
前四种都是同步IO,只有最后一种是异步IO。
Linux为了OS的安全性等的考虑,进程是无法直接操作IO设备的,其必须通过系统调用请求内核来协助完成IO动作,而内核会为每个IO设备维护一个buffer。
对于一个设备IO ,这里我们以read举例,它会涉及到两个系统对象,一个是调用这个IO的进程或线程(process or thread),另一个就是系统内核(kernel)。当一个read操作发生时,它会经历两个阶段:
- 等待设备数据准备就绪阶段:用户进程发起请求,内核接收到请求,从IO设备中获取数据到buffer,等待数据准备 (Waiting for the data to be ready);
- 将设备数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间阶段:将buffer中的数据copy到用户进程的地址空间,即将数据从内核拷贝到用户进程中 (Copying the data from the kernel to the process);

在异步IO模型中,当用户进程发起系统调用后,立刻就可以开始去做其它的事情,然后直到IO执行的两个阶段都完成之后,内核会给用户进程发送通知,告诉用户进程操作已经完成了。
异步IO的读操作是通过aio_read实现的,具体可以参考linux下aio异步读写详解与实例。

关于这五种IO模型的具体区别可以查看博客:Linux IO模型介绍以及同步异步阻塞非阻塞的区别。这里我们就简单的概述一下:
- 异步IO和同步IO的主要区别在于IO操作的第二阶段,同步IO用户进程会发生堵塞,而异步IO用户进程不会发生堵塞;
- 阻塞IO和非阻塞IO主要就在于当设备没有数据时,我们调用read函数是立即返回还是处于睡眠状态;
1.3 同步IO
实际上同步IO操作包含了多种IO模型,我们依然以按键测试应用程序中调用read函数作为例子进行讲解。
(1) 阻塞IO模型
也就是我们上面这个例子,调用read函数线程一直处于阻塞状态,一直等到有按键变化,才会将数据从内核拷贝到用户空间。

(2) 非阻塞IO模型
如果我们在open函数打开/dev/buttons设备时,指定了O_NONBLOCK标志,read函数就不会阻塞。如果没有按键发生改变,就会立即返回-1。

我们采用轮询的方式去调用read函数,类似下面的伪代码:
while(1) { ret1 = read(设备1); if(ret1 > 0) 处理数据; ret2 = read(设备2); if(ret2 > 0) 处理数据; .............................. }
采用这种方式,调用者只是查询一下,并不会阻塞在这里,这样我们可以同时监控多个设备。上面的代码也会存在另一个问题,线程会在不停的轮询,会导致CPU使用率急剧升高。
因此我们可以在循环的最后加入一定时长的睡眠,但是这么做又会有另一个问题,如果设备有数据到达由于睡眠可能导致数据处理不及时。因此又衍生了IO多路复用模型解决这个问题。
(3) IO多路复用模型;
IO多路复用就是通过一种机制,一个进程/线程可以监视多个设备,一旦某个设备就绪(一般是读就绪或者写就绪),能够通知程序进行相应的读写操作。
在linux操作系统中,目前支持IO多路复用的系统调用有select、pselect、poll、epoll。
在调用read之前先调用select/poll/epoll 等函数,它们可以阻塞地同时监视多个设备,还可以设定阻塞等待的超时时间,并且当内核准备好数据的时候会通知调用者,这时候再去调用read读取数据。

(4) 信号驱动IO模型
这个下一篇博客单独介绍。

1.4 改造目标
这一节我们将利用IO多路复用中的poll函数,对按键驱动程序进行改造,达到如下目标:
- 当有按键改变时,我们再去调用read函数,否则进程就阻塞(通过poll函数设置等待超时时间);
二、linux poll机制分析
当应用程序调用poll函数的时候,会通过swi软件中断进入到内核层,然后调用sys_poll系统调用。
2.1 poll
poll函数原型如下:
int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
参数如下:
- *fds:是一个poll文件描述符结构体数组(可以处理多个poll),结构体pollfd如下,其中events和revents值参数如下;
struct pollfd { int fd; /* file descriptor 文件描述符*/ short events; /* requested events 请求的事件*/ short revents; /* returned events 返回的事件(函数返回值)*/ };
|
常量 |
说明 |
|
POLLIN |
普通或优先级带数据可读 |
|
POLLRDNORM |
normal普通数据可读 |
|
POLLRDBAND |
优先级带数据可读 |
|
POLLPRI |
Priority高优先级数据可读 |
|
POLLOUT |
普通数据可写 |
|
POLLWRNORM |
normal普通数据可写 |
|
POLLWRBAND |
band优先级带数据可写 |
|
POLLERR |
发生错误 |
|
POLLHUP |
发生挂起 |
|
POLLNVAL |
描述字不是一个打开的文件 |
- nfds:表示多少个fd,如果1个,就填入1;
- timeout:超时时间,单位ms;
返回值:
- 0:表示超时或者fd文件描述符无法打开;
- -1:表示错误;
- >0时 :就是上面表格中几个常量;
2.2 sys_poll
我们在fs/select.c文件中,找到sys_poll函数原型:
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(poll, struct pollfd __user *, ufds, unsigned int, nfds, int, timeout_msecs) { struct timespec64 end_time, *to = NULL; int ret; if (timeout_msecs >= 0) { to = &end_time; poll_select_set_timeout(to, timeout_msecs / MSEC_PER_SEC, NSEC_PER_MSEC * (timeout_msecs % MSEC_PER_SEC)); } ret = do_sys_poll(ufds, nfds, to); if (ret == -EINTR) { struct restart_block *restart_block; restart_block = ¤t->restart_block; restart_block->fn = do_restart_poll; restart_block->poll.ufds = ufds; restart_block->poll.nfds = nfds; if (timeout_msecs >= 0) { restart_block->poll.tv_sec = end_time.tv_sec; restart_block->poll.tv_nsec = end_time.tv_nsec; restart_block->poll.has_timeout = 1; } else restart_block->poll.has_timeout = 0; ret = -ERESTART_RESTARTBLOCK; } return ret; }
这里sys_poll函数声明都是使用了宏SYSCALL_DEFINE3,如何具体展开的可以参考Linux系统调用之SYSCALL_DEFINE。这个函数有三个参数:
- struct pollfd __user * ufds:poll函数传进来的;
- unsigned int nfds:poll函数传进来的;
- int timeout_msecs:poll函数传进来的;
接下来,我们分析该函数的执行流程:
- 首先,如果设定了超时时间不为0,会调用 poll_select_set_timeout 函数将超时时间转换为 timespec64 结构变量,注意超时时间将会以当前时间(monotonic clock)为基础,转换为未来的一个超时时间点(绝对时间);
- 然后调用了do_sys_poll,这个函数很重要;
- 最后对返回结果进行校验;
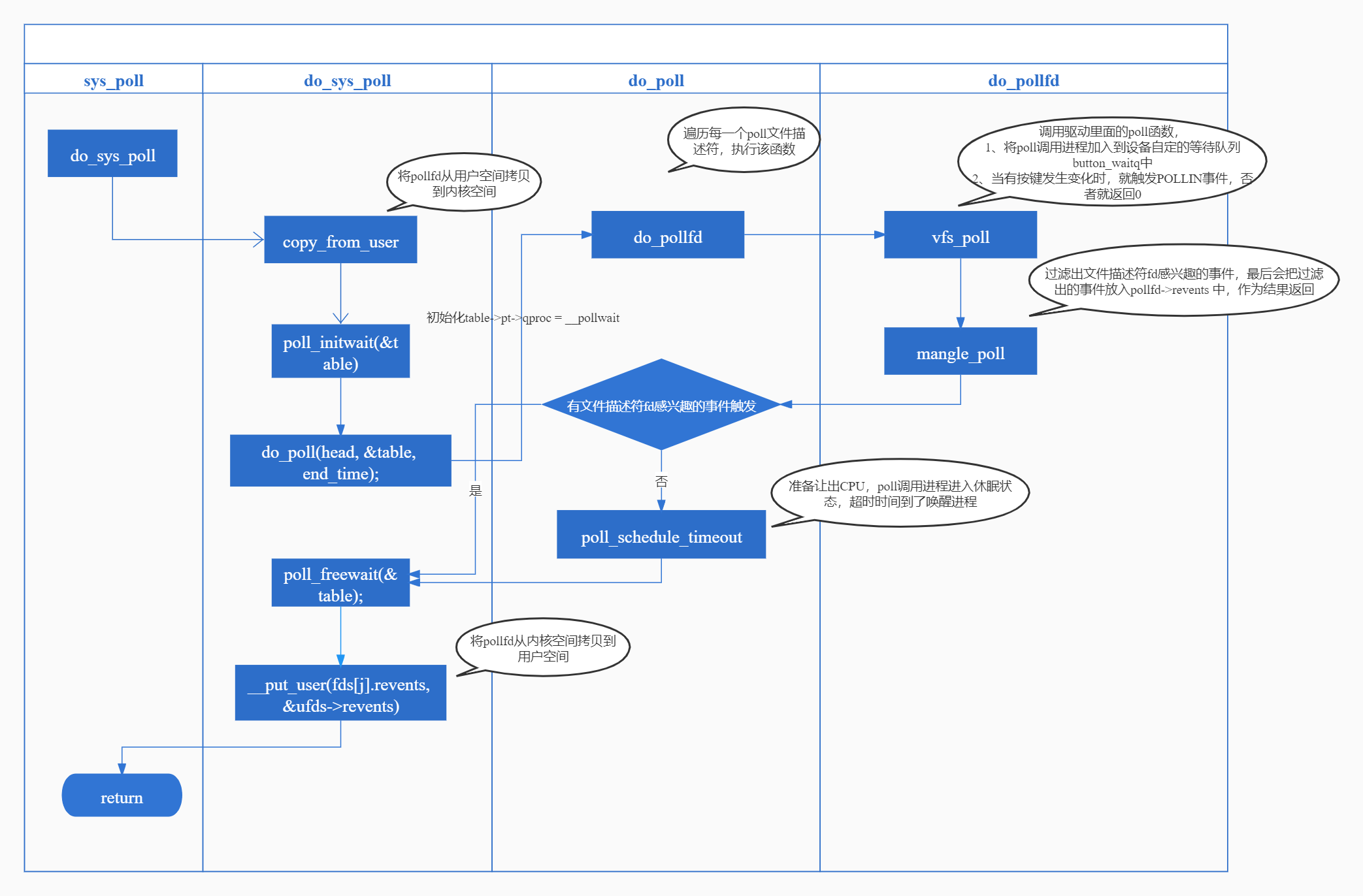
2.3 do_sys_poll
do_sys_poll它也位于fs\Select.c:

static int do_sys_poll(struct pollfd __user *ufds, unsigned int nfds, struct timespec64 *end_time) { struct poll_wqueues table; int err = -EFAULT, fdcount, len, size; /* Allocate small arguments on the stack to save memory and be faster - use long to make sure the buffer is aligned properly on 64 bit archs to avoid unaligned access */ long stack_pps[POLL_STACK_ALLOC/sizeof(long)]; struct poll_list *const head = (struct poll_list *)stack_pps; struct poll_list *walk = head; unsigned long todo = nfds; if (nfds > rlimit(RLIMIT_NOFILE)) return -EINVAL; len = min_t(unsigned int, nfds, N_STACK_PPS); for (;;) { walk->next = NULL; walk->len = len; if (!len) break; if (copy_from_user(walk->entries, ufds + nfds-todo, sizeof(struct pollfd) * walk->len)) goto out_fds; todo -= walk->len; if (!todo) break; len = min(todo, POLLFD_PER_PAGE); size = sizeof(struct poll_list) + sizeof(struct pollfd) * len; walk = walk->next = kmalloc(size, GFP_KERNEL); if (!walk) { err = -ENOMEM; goto out_fds; } } poll_initwait(&table); fdcount = do_poll(head, &table, end_time); poll_freewait(&table); for (walk = head; walk; walk = walk->next) { struct pollfd *fds = walk->entries; int j; for (j = 0; j < walk->len; j++, ufds++) if (__put_user(fds[j].revents, &ufds->revents)) goto out_fds; } err = fdcount; out_fds: walk = head->next; while (walk) { struct poll_list *pos = walk; walk = walk->next; kfree(pos); } return err; }
该函数主要做了以下事情:
- 在内核栈分配空间,通过poll_list链表保存ufds(struct pollfd类型数组);
- 进入for(;;):
- 将pollfd从用户空间拷贝到内核空间;
- 调用poll_initwait;
- 调用do_poll完成poll的实际调用处理;
- 将每个fd上产生的事件revents再从内核空间拷贝到用户空间;

从图中可以看到这里将ufds数组中的poll文件描述符拆分存放在poll_list连表中。链表每一个元素存放len成员指定个数个poll文件描述符。
2.4 poll_initwait
poll_initwait(&table) 对poll_wqueues 结构体变量table进行初始化:table->pt->qproc = __pollwait:
void poll_initwait(struct poll_wqueues *pwq) { init_poll_funcptr(&pwq->pt, __pollwait); pwq->polling_task = current; pwq->triggered = 0; pwq->error = 0; pwq->table = NULL; pwq->inline_index = 0; }
其中struct poll_wqueues结构如下:
/* * Structures and helpers for select/poll syscall */ struct poll_wqueues { poll_table pt; struct poll_table_page *table; struct task_struct *polling_task; int triggered; int error; int inline_index; struct poll_table_entry inline_entries[N_INLINE_POLL_ENTRIES]; };
函数指针 table->pt->_qproc 被初始化指向 __pollwait 函数,这个和 poll 调用过程中阻塞与唤醒机制相关,后面将介绍。
2.5 do_poll
do_sys_poll函数在调用完poll_initwait(&table) 之后,随后即调用 do_poll 函数完成 poll 操作,最后将每个文件描述符fd产生的事件再拷贝到内核空间。

static int do_poll(struct poll_list *list, struct poll_wqueues *wait, struct timespec64 *end_time) { poll_table* pt = &wait->pt; ktime_t expire, *to = NULL; int timed_out = 0, count = 0; u64 slack = 0; __poll_t busy_flag = net_busy_loop_on() ? POLL_BUSY_LOOP : 0; unsigned long busy_start = 0; /* Optimise the no-wait case */ if (end_time && !end_time->tv_sec && !end_time->tv_nsec) { pt->_qproc = NULL; timed_out = 1; } if (end_time && !timed_out) slack = select_estimate_accuracy(end_time); for (;;) { struct poll_list *walk; bool can_busy_loop = false; for (walk = list; walk != NULL; walk = walk->next) { struct pollfd * pfd, * pfd_end; pfd = walk->entries; pfd_end = pfd + walk->len; for (; pfd != pfd_end; pfd++) { /* * Fish for events. If we found one, record it * and kill poll_table->_qproc, so we don't * needlessly register any other waiters after * this. They'll get immediately deregistered * when we break out and return. */ if (do_pollfd(pfd, pt, &can_busy_loop, busy_flag)) { count++; pt->_qproc = NULL; /* found something, stop busy polling */ busy_flag = 0; can_busy_loop = false; } } } /* * All waiters have already been registered, so don't provide * a poll_table->_qproc to them on the next loop iteration. */ pt->_qproc = NULL; if (!count) { count = wait->error; if (signal_pending(current)) count = -EINTR; } if (count || timed_out) break; /* only if found POLL_BUSY_LOOP sockets && not out of time */ if (can_busy_loop && !need_resched()) { if (!busy_start) { busy_start = busy_loop_current_time(); continue; } if (!busy_loop_timeout(busy_start)) continue; } busy_flag = 0; /* * If this is the first loop and we have a timeout * given, then we convert to ktime_t and set the to * pointer to the expiry value. */ if (end_time && !to) { expire = timespec64_to_ktime(*end_time); to = &expire; } if (!poll_schedule_timeout(wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE, to, slack)) timed_out = 1; } return count; }
do_poll函数主要做了以下事情:
- timeout设置为0时,会将 pt->_qproc 设置为NULL,同时不阻塞,相当于退化为轮询操作;
- 设置了有效的超时时间后,会设置slack;
- for(;;):
- 遍历每一个poll文件描述符:
- 调用do_pollfd,如果do_pollfd返回非负值,表示发现事件触发,此时无需再将当前进程加入到相应的等待队列;
- pt->_qproc = NULL,当前进程已经在上述的遍历中被加入到各个fd对应驱动的等待队列,所以这里直接设置为NULL;
- 如果发现事件触发,或者time_out=1,提前退出循环;
- 调用poll_schedule_timeout,使当前poll调用进程进行休眠,让出CPU,超时时间到达时返回,设置timed_out=1,在下一个轮询后返回上层调用;
- 遍历每一个poll文件描述符:
do_poll 函数首先从头部到尾部遍历链表 poll_list ,对每一项 pollfd 调用 do_pollfd 函数。 do_pollfd 函数主要将当前 poll 调用进程加入到每个 pollfd 对应fd所关联的底层驱动等待队列中。 do_pollfd 调用后,如果某个fd已经产生事件,count将会自增,那么后续遍历其他fd时,无需再将当前进程加入到对应的等待队列中, poll 调用也将返回而不是睡眠(schedule)。
2.6 do_pollfd
do_poll函数在遍历poll文件描述符时,会执行do_pollfd函数:
/* * Fish for pollable events on the pollfd->fd file descriptor. We're only * interested in events matching the pollfd->events mask, and the result * matching that mask is both recorded in pollfd->revents and returned. The * pwait poll_table will be used by the fd-provided poll handler for waiting, * if pwait->_qproc is non-NULL. */ static inline __poll_t do_pollfd(struct pollfd *pollfd, poll_table *pwait, bool *can_busy_poll, __poll_t busy_flag) { int fd = pollfd->fd; __poll_t mask = 0, filter; struct fd f; if (fd < 0) goto out; mask = EPOLLNVAL; f = fdget(fd); if (!f.file) goto out; /* userland u16 ->events contains POLL... bitmap */ filter = demangle_poll(pollfd->events) | EPOLLERR | EPOLLHUP; pwait->_key = filter | busy_flag; mask = vfs_poll(f.file, pwait); if (mask & busy_flag) *can_busy_poll = true; mask &= filter; /* Mask out unneeded events. */ fdput(f); out: /* ... and so does ->revents */ pollfd->revents = mangle_poll(mask); return mask; }
do_pollfd 主要完成与底层VFS中的驱动程序 file->f_op->poll(file,pwait),这就跟驱动扯上关系了, __pollwait在这里就被用到了。
static inline __poll_t vfs_poll(struct file *file, struct poll_table_struct *pt) { if (unlikely(!file->f_op->poll)) return DEFAULT_POLLMASK; return file->f_op->poll(file, pt); }
仍然以我们的按键驱动为例。我们会编写button_poll函数(后面会介绍):
- 调用 poll_wait(file, &button_waitq, pt)将poll调用进程加入到设备自定义的等待队列button_waitq中;
- 当有按键发生变化时,就触发POLLIN事件,否者就返回0;
然后调用mangle_poll过滤出每个文件描述符感兴趣的事件,最后会把过滤出的事件放入pollfd->revents 中,作为结果返回,如果没有文件描述符fd感兴趣的事件则返回的值为0。
2.7 _pollwait
在button_poll驱动程序中,我们调用poll_wait:
void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p) { if (p && p->_qproc && wait_address) p->_qproc(filp, wait_address, p); }
poll_wait 进而调用到 poll_table p->_qproc ,而后者通过 poll_initwait(&table) 被初始化为 __pollwait ,参数wait_address为我们按键驱动程序中声明的等待队列button_waitq。
static void __pollwait(struct file *filp, wait_queue_head_t *wait_address, poll_table *p) { struct poll_wqueues *pwq = container_of(p, struct poll_wqueues, pt); struct poll_table_entry *entry = poll_get_entry(pwq); if (!entry) return; entry->filp = get_file(filp); entry->wait_address = wait_address; entry->key = p->_key; init_waitqueue_func_entry(&entry->wait, pollwake); entry->wait.private = pwq; add_wait_queue(wait_address, &entry->wait); }
将当前poll调用进程添加到button_waitq等待队列中,一旦有按键发生变化,就会唤醒等待队列中的所有进程,从而唤醒poll机制。
2.8 poll_schedule_timeout
在该函数中首先会设置当前进程状态为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE,在该状态下,进程如果休眠的话可以被信号和wake_up唤醒。
static int poll_schedule_timeout(struct poll_wqueues *pwq, int state, ktime_t *expires, unsigned long slack) { int rc = -EINTR; set_current_state(state); if (!pwq->triggered) rc = schedule_hrtimeout_range(expires, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS); __set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); /* * Prepare for the next iteration. * * The following smp_store_mb() serves two purposes. First, it's * the counterpart rmb of the wmb in pollwake() such that data * written before wake up is always visible after wake up. * Second, the full barrier guarantees that triggered clearing * doesn't pass event check of the next iteration. Note that * this problem doesn't exist for the first iteration as * add_wait_queue() has full barrier semantics. */ smp_store_mb(pwq->triggered, 0); return rc; }
do_poll最后调用poll_schedule_timeout,让本进程休眠一段时间,注意应用程序执行poll调用后,如果timeout没超时或者count为0则进程会进入休眠。那么谁会唤醒进程呢?
- 休眠指定的超时时间到了;
- 驱动程序条件就绪时,就会把button_waits队列上挂着的进程唤醒;
2.9 总结
poll 系统调用的整体过程可以概括为下图:
三、按键驱动-poll改造
3.1 button_poll
在上一级驱动程序里添加如下代码:
#include <linux/poll.h> //添加头文件 static unsigned int button_poll(struct file *file, poll_table *wait) { unsigned int ret = 0; // 将当前进程放到button_waitq列表 poll_wait(file, &button_waitq, wait); /* 中断发生了,即按键发生改变 */ if(ev_press) ret |= POLLIN; return ret; } static struct file_operations button_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = button_open, .read = button_read, .release = button_close, .poll = button_poll, };
我们将当前进程加入了button_waitq等待队列中了。这样当按键中断发生时,wake_up_interruptible会唤醒等待队列中的所有进程,从而唤醒当前进程。
当没有按键发生改变时返回0,当有按键发生改变,返回POLLIN,其中参数意义之前已经介绍过。
3.2 修改button_read
static ssize_t button_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ppos) { int count; if (size != 1){ printk("read error\n"); return -EINVAL; } /* 如果没有按键动作, 休眠 */ // wait_event_interruptible(button_waitq, ev_press); /* 如果有按键动作, 上传key_val给用户层 */ count = copy_to_user(buf, &key_val, 1); /* 数据发完后,立马设为休眠状态,避免误操作 */ ev_press = 0; return count; }
这里屏蔽了wait_event_interruptible函数的调用,这个函数本质也是条件参数没有满足时,会进行休眠状态,并把当前进程加入到button_waitq等待队列中。我们已经通过poll机制实现了这个功能,所以这里就不需要了。
3.3 修改测试应用程序
#include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <poll.h> int main(int argc,char **argv) { int fd,ret; unsigned int key_val = 0; struct pollfd key_fds; fd = open("/dev/buttons", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { printf("can't open!\n"); return -1; } key_fds.fd = fd; key_fds.events = POLLIN; // poll直接返回需要的条件 while (1) { /* 调用sys_poll系统调用,如果5S内没有产生POLLIN事件,那么返回,如果有POLLIN事件,直接返回 */ ret = poll(&key_fds, 1, 5000); if(!ret) // 超时 { printf("time out\n"); } else // poll机制被唤醒,表示有数据可读 { ret = read(fd, &key_val, 1); //读取按键值 if(ret < 0){ printf("read error\n"); continue; } printf("key_val = 0x%x\n", key_val); } } return 0; }
3.4 下载到开发板测试
按照上一节的方式安装驱动,测试应用程序。效果如下:
[root@zy:/]# ./main time out time out time out key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x81 key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x81 time out key_val = 0x3 key_val = 0x3 key_val = 0x83
若5S没有数据,则打印time out。
3.4 程序整体执行流程
- 当执行应用程序时,首先打开/dev/buttons设备;
- 接着进入死循环调用poll(fds, 1, 5000),系统调用sys_poll最后调用到do_poll函数(死循环函数)里陷入休眠(休眠前先执行了一次驱动里的button_poll函数);
- 当有按键按下时,调用wake_up_interruptible唤醒当前进程;
- 重新循环执行do_poll函数第一个if函数的判断语句,此时button_poll函数返回非0值,执行count++;再往下执行第二个if语句break退出循环;
- 将pollfd从内核空间拷贝到用户空间,sys_poll系统调用返回count;
- 此时再调用read将键值读出来;
- 当5秒内没有操作按键时,也会退出poll(fds, 1, 5000),打印time out;
四、代码下载
Young / s3c2440_project[drivers]
参考文章:
[4]select、poll、epoll之间的区别总结[整理]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号