linux驱动移植-按键中断驱动
一、按键硬件资源
1.1 硬件接线
查看Mini2440原理图、S3C2440数据手册,了解如何读取按键的状态。这里粗略介绍一下Mini2440 K1~K6的接线方式,以及寄存器的设置,这里简单说一下,就不具体介绍了:
- K1~K6依次对应引脚GPG0、GPG3、GPG5、GPG6、GPG7、GPG11,以K1为例;
- 按键按下引脚输入低电平、按键松开引脚输入高电平;
- 配置控制寄存器GPGCON(0x56000060)的bit[1:0]=00,使GPB5引脚为输入模式;
- 读取配置数据寄存器GPGDAT(0x56000064)的bit0的电位;
二、读取按键状态方式
试想一下,如果我们想判断按键K1有没有按下或者松开,我们有几种方式:
- 通过轮询的方式,不停的去GPGDATA寄存器的状态,从而得到K1按键的状态;这种方式会导致CPU占用率急剧升高;
- 采用中断的方式,按键按下时K1为低电平,松开时为高电平,采用双边沿触发方式;可以极大的提高CPU运行效率;
三、linux中的中断
3.1 中断介绍
中断就是CPU正常运行期间,由于内、外部事件引起的CPU暂时停止正在运行的程序,去执行该内部事件或外部事件的引起的服务中去,服务执行完毕后再返回断点处继续执行的情形。
中断不属于任何一个进程,因此不能在中断程序中休眠和调用schedule函数放弃CPU,实现中断处理函数有一个原则,就是尽可能的处理并返回。
3.2 Linux中断处理程序架构
linux操作系统是多个进程执行,宏观上达到并行运行的状态,外设中断则会打断内核中任务调度和运行,如果中断函数耗时过长则使得系统实时性和并发性降低。
为保证系统实时性,中断服务程序必须足够简短,但实际应用中某些时候发生中断时必须处理大量的事务,这时候如果都在中断服务程序中完成,则会严重降低中断的实时性,基于这个原因,linux系统提出了一个概念:把中断服务程序分为两部分-顶半部-底半部。
- 顶半部:完成尽可能少的比较紧急的任务,它往往只是简单的读取寄存器中的中断状态并清除中断标志后就进行”登记中断“(也就是将底半部处理程序挂到设备的底半部执行队列中)的工作;
- 底半部:中断处理的大部分工作都在底半部,它几乎做了中断处理程序的所有事情;
Linux中断顶-底部分区别:
- 顶半部由外设中断触发,底半部由顶半部触发;
- 顶半部不会被其他中断打断,底半部是可以被打断的;
- 顶半部分处理任务要快,主要任务、耗时任务放在底半部;
一般来说,在中断顶半部执行完毕,底半部即在内核的调度下被执行,当然如果有其他更高优先级需处理的任务,会先处理该任务再调度处理底半部,或者在系统空闲时间进行处理。
3.3 linux中断处理程序设计原则
对于Linux系统设备而言,一个完整的中断程序由顶半部和底半部分共同构成,在编写设备驱动程序前,就需考虑好顶半部和底半部的分配。很多时候顶半部与底半部并没有严格的区分界限,主要由程序员根据实际设计,如某些外设中断可以没有底半部。关于顶底半部的划分原则,就是主要事务、耗时事务划分在底半部处理。可以参考以下原则:
- 与硬件相关的操作,如操作寄存器,必须放在顶半部;
- 对时间敏感、要求实时性的任务放在顶半部;
- 该任务不能被其他中断或者进程打断的放在顶半部;
- 实时性要求不高的任务、耗时任务放在底半部;
四、按键中断驱动程序
这里我们先动手跟着学习按键中断程序的编写,熟悉一下中断程序编写的流程。至于具体中断的实现原理,我们后面文章会进行介绍。
在/work/sambashare/drivers下新建3.button_dev文件夹,用来编写我们的按键中断程序。
4.1 注册中断
GPG0、GPG3、GPG5、GPG6、GPG7、GPG11对应的外部中断依次为EINT8、EINT11、EINT13、EINT14、EINT15、EINT19。
这里通过request_irq函数注册GPG0、GPG3、GPG5、GPG6、GPG7、GPG11为外部中断,触发方式为双边沿。
/* GPG0、GPG3、GPG5、GPG6、GPG7、GPG11配置为中断功能 IRQ_EINTX 定义在 arch/arm/mach-s3c24xx/include/mach/irqs.h */ static int button_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { /* 注册中断 */ request_irq(IRQ_EINT8,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K1",&pins_desc[0]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT11,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K2",&pins_desc[1]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT13,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K3",&pins_desc[2]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT14,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K4",&pins_desc[3]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT15,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K5",&pins_desc[4]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT19,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K6",&pins_desc[5]); return 0; }
函数request_irq原型:
int request_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler, unsigned long irqflags, const char *devname, void *dev_id)
其中:
- irq:要分配的硬件中断号,定义在arch/arm/mach-s3c24xx/include/mach/irqs.h,被linux/irq.h调用;
- handler:向系统登记的中断处理程序,这是一个回调函数,中断发生时,系统调用这个函数;
- irqflags:标记中断处理属性的标志位,这里设置为IRQT_BOTHEDGE、双边沿触发;
- dev_name:驱动设备的字符串名称,用来在/pro/interrupt/xx中显示中断的所有者;
- dev_id:用于共享中断号的非NULL标识,若中断没有被共享,dev_id可以设置为NULL。共享中断号时,该标识必须是全局唯一的,在释放中断时会用到它。驱动程序也可以用它来指向自己的私有数据区。一般将它设置为这个设备device结构本身,中断处理程序可以用dev_id找到相应的产生这个中断的设备;
这里我们EINT8、EINT11、EINT13、EINT14、EINT15、EINT19中断共用一个中断处理程序,因此我们将dev_id字段设置为一个结构体,用来标识唯一设备。
struct pin_desc{ unsigned int pin; unsigned int key_val; }; /* * S3C2410_GPG(x) 定义在arch/arm/mach-s3c24xx/include/mach/gpio-samsung.h */ static struct pin_desc pins_desc[6] = { {S3C2410_GPG(0), 0x01}, {S3C2410_GPG(3), 0x02}, {S3C2410_GPG(5), 0x03}, {S3C2410_GPG(6), 0x04}, {S3C2410_GPG(7), 0x05}, {S3C2410_GPG(11), 0x06}, };
pin_desc用来保存当前设备的引脚名称和初始值(并不是引脚电平值,这是一个虚拟的值,可以用来区分是哪个按键)。
4.2 释放中断
我们在.close函数中通过free_irq函数进行释放中断资源:
/* * 释放中断资源 */ static int button_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { free_irq(IRQ_EINT8, &pins_desc[0]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT11, &pins_desc[1]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT13, &pins_desc[2]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT14, &pins_desc[3]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT15, &pins_desc[4]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT19, &pins_desc[5]); return 0; }
4.3 中断处理程序
中断发生时,系统调用这个函数,传入的参数包括硬件的中断号,dev_id。dev_id是request_ird函数传递给系统的参数的参数dev_id。
/* * 中断处理服务 */ static irqreturn_t button_irq(int irq, void *dev_id) { struct pin_desc *pindesc = (struct pin_desc *)dev_id; unsigned int pinval; pinval = gpio_get_value(pindesc->pin); if (pinval){ /* 松开 */ key_val = 0x80 | pindesc->key_val; } else{ /* 按下 */ key_val = pindesc->key_val; } ev_press = 1; /* 表示中断发生了,退出等待队列 */ wake_up_interruptible(&button_waitq); /* 唤醒休眠的进程 */ return IRQ_RETVAL(IRQ_HANDLED); }
这里通过gpio_get_value获取引脚的电平。
gpio_get_value(unsigned int pin);
其中:
- pin: 引脚名称,例如:S3C2410_GPG(0),定义在<mach/gpio-samsung.h>;
正常来说:在使用GPIO时,一般我们需要先调用gpio_request方法申请GPIO,然后才会进行GPIO的读取、配置等操作,这里忽略了GPIO的申请过程。
如果引脚为高电平,我们就将key_val设备值设置为0x8x,否则为初始值,key_val声明如下:
/* 键值: 按下时, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06 */ /* 键值: 松开时, 0x81, 0x82, 0x83, 0x84, 0x85, 0x86 */ static unsigned char key_val;
此外,中断发生了,我们设置全局变量ev_press为1。然后从button_waitq队列中唤醒休眠的进程。等待队列头的声明如下:
/* 定义并初始化等待队列头 */ static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(button_waitq);
然后调用wake_up_interruptible唤醒button_waitq等待队列中的所有进程,并将进程的状态设置为TASK_RUNNING。
注意:后面我都会称button_waitq为等待队列是为了方便理解,自己明白这是一个等待队列头就好,通过这个头我们能找到等待队列中的所有元素。
4.4 button_read函数
static ssize_t button_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ppos) { int count; if (size != 1) // 需要读取长度 return -EINVAL; /* 如果没有按键动作, 休眠 */ wait_event_interruptible(button_waitq, ev_press); /* 如果有按键动作, 上传key_val给用户层 */ count = copy_to_user(buf, &key_val, 1); /* 数据发完后,立马设为休眠状态,避免误操作 */ ev_press = 0; return count; }
wait_event_interruptible函数做了以下事情:
- 创建等待队列元素,并将当前进程关联到等待队列button_waitq中;
- 将当前进程的状态设置成TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE,该状态下的进程如果休眠的话可以被信号和wake_up及变体函数唤醒;
- 然后调用schedule,而schedule会将位于TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE状态的当前进程从runqueue队列中删除。从runqueue队列中删除的结果是,当前这个进程将不再参与调度,除非通过其他函数将这个进程重新放入这个runqueue队列中;
- 当进程条件得到满足时,将等待队列元素从等待队列中移除;
成功地唤醒一个被wait_event_interruptible进程,需要满足以下条件:
- condition为真的前提下;
- 调用wake_up或者其变体,亦或者调用发送信号的系统函数;
当进程唤醒后,上传key_val给用户层。数据发完后,立马设为休眠状态,避免误操作。
4.5 注册button驱动程序
static struct file_operations button_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = button_open, .read = button_read, .release = button_close, }; static dev_t devid; // 起始设备编号 static struct cdev button_cdev; // 保存操作结构体的字符设备 static struct class *button_cls; static struct device *button_dev; static int button_init(void) { int ret; /* 动态分配字符设备: (major,0) */ ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devid, 0, 1,"button"); // ls /proc/devices看到的名字 /* 返回值为负数,表示操作失败 */ if(ret < 0){ printk("alloc char dev region error\n"); goto fail_devid; } /* 初始化字符设备,添加字符设备 */ cdev_init(&button_cdev, &button_fops); ret = cdev_add(&button_cdev, devid, 1); /* 返回值为负数,表示操作失败 */ if (ret < 0) { printk("char device add failed\n"); goto fail_cdev; }else{ printk("char device add success\n"); } /* 创建类,它会在sys目录下创建/sys/class/button这个类 */ button_cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "button"); if(IS_ERR(button_cls)){ printk("can't create class\n"); ret = PTR_ERR(button_cls); goto fail_class; } /* 在/sys/class/button下创建buttons设备,然后mdev通过这个自动创建/dev/buttons这个设备节点 */ button_dev = device_create(button_cls, NULL, devid, NULL, "buttons"); if(IS_ERR(button_dev)){ printk("create device failed\n"); ret = PTR_ERR(button_dev); goto fail_device; }else{ printk("create device success\n"); } return 0; fail_device: class_destroy(button_cls); fail_class: cdev_del(&button_cls); fail_cdev: unregister_chrdev_region(devid, 1); fail_devid: return ret; }
4.6 卸载button驱动程序
static void __exit button_exit(void) { printk("button driver exit\n"); /* 注销类、以及类设备 /sys/class/button会被移除*/ device_destroy(button_cls, devid); class_destroy(button_cls); cdev_del(&button_cdev); unregister_chrdev_region(devid, 1); return; }
4.7 button_dev.c完整代码

#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/io.h> #include <linux/uaccess.h> #include <linux/gpio.h> #include <linux/irq.h> // 包含了mach/irqs.h #include <linux/interrupt.h> #include <linux/gpio/machine.h> #include <mach/gpio-samsung.h> /* 全局静态变量:希望全局变量仅限于在本源文件中使用,在其他源文件中不能引用,也就是说限制其作用域只在 定义该变量的源文件内有效,而在同一源程序的其他源文件中不能使用 */ #define OK (0) #define ERROR (-1) #define __IRQT_FALEDGE IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_FALLING #define __IRQT_RISEDGE IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_RISING #define __IRQT_LOWLVL IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_LOW #define __IRQT_HIGHLVL IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH #define IRQT_NOEDGE (0) #define IRQT_RISING (__IRQT_RISEDGE) #define IRQT_FALLING (__IRQT_FALEDGE) #define IRQT_BOTHEDGE (__IRQT_RISEDGE|__IRQT_FALEDGE) #define IRQT_LOW (__IRQT_LOWLVL) #define IRQT_HIGH (__IRQT_HIGHLVL) #define IRQT_PROBE IRQ_TYPE_PROBE /* 定义并初始化等待队列 */ static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(button_waitq); /* * 定义中断事件标志 * 0:进入等待队列 1:退出等待队列 */ static int ev_press =0; /* 键值: 按下时, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06 */ /* 键值: 松开时, 0x81, 0x82, 0x83, 0x84, 0x85, 0x86 */ static unsigned char key_val; struct pin_desc{ unsigned int pin; unsigned int key_val; }; /* * S3C2410_GPG 定义在arch/arm/mach-s3c24xx/include/mach/gpio-samsung.h */ static struct pin_desc pins_desc[6] = { {S3C2410_GPG(0), 0x01}, {S3C2410_GPG(3), 0x02}, {S3C2410_GPG(5), 0x03}, {S3C2410_GPG(6), 0x04}, {S3C2410_GPG(7), 0x05}, {S3C2410_GPG(11), 0x06}, }; /* * 中断处理服务 */ static irqreturn_t button_irq(int irq, void *dev_id) { struct pin_desc *pindesc = (struct pin_desc *)dev_id; unsigned int pinval; pinval = gpio_get_value(pindesc->pin); if (pinval){ /* 松开 */ key_val = 0x80 | pindesc->key_val; } else{ /* 按下 */ key_val = pindesc->key_val; } ev_press = 1; /* 表示中断发生了,退出等待队列 */ wake_up_interruptible(&button_waitq); /* 唤醒休眠的进程 */ return IRQ_RETVAL(IRQ_HANDLED); } /* GPG0、GPG3、GPG5、GPG6、GPG7、GPG11配置为中断功能 IRQ_EINTX 定义在 arch/arm/mach-s3c24xx/include/mach/irqs.h */ static int button_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { /* 注册中断,这里没有判断中断是否申请成功 */ int ret = request_irq(IRQ_EINT8,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K1",&pins_desc[0]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT11,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K2",&pins_desc[1]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT13,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K3",&pins_desc[2]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT14,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K4",&pins_desc[3]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT15,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K5",&pins_desc[4]); request_irq(IRQ_EINT19,button_irq,IRQT_BOTHEDGE,"K6",&pins_desc[5]); return 0; } static ssize_t button_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ppos) { int count; if (size != 1) return -EINVAL; /* 如果没有按键动作, 休眠, */ wait_event_interruptible(button_waitq, ev_press); /* 如果有按键动作, 上传key_val给用户层 */ count = copy_to_user(buf, &key_val, 1); /* 数据发完后,立马设为休眠状态,避免误操作 */ ev_press = 0; return count; } /* * 释放中断资源 */ int button_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { free_irq(IRQ_EINT8, &pins_desc[0]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT11, &pins_desc[1]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT13, &pins_desc[2]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT14, &pins_desc[3]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT15, &pins_desc[4]); free_irq(IRQ_EINT19, &pins_desc[5]); return 0; } static struct file_operations button_fops = { .owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = button_open, .read = button_read, .release = button_close, }; static dev_t devid; // 起始设备编号 static struct cdev button_cdev; // 保存操作结构体的字符设备 static struct class *button_cls; static struct device *button_dev; static int button_init(void) { int ret; /* 动态分配字符设备: (major,0) */ ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devid, 0, 1,"button"); // ls /proc/devices看到的名字 /* 返回值为负数,表示操作失败 */ if(ret < 0){ printk("alloc char dev region error\n"); goto fail_devid; } /* 初始化字符设备,添加字符设备 */ cdev_init(&button_cdev, &button_fops); ret = cdev_add(&button_cdev, devid, 1); /* 返回值为负数,表示操作失败 */ if (ret < 0) { printk("char device add failed\n"); goto fail_cdev; }else{ printk("char device add success\n"); } /* 创建类,它会在sys目录下创建/sys/class/button这个类 */ button_cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "button"); if(IS_ERR(button_cls)){ printk("can't create class\n"); ret = PTR_ERR(button_cls); goto fail_class; } /* 在/sys/class/button下创建buttons设备,然后mdev通过这个自动创建/dev/buttons这个设备节点 */ button_dev = device_create(button_cls, NULL, devid, NULL, "buttons"); if(IS_ERR(button_dev)){ printk("create device failed\n"); ret = PTR_ERR(button_dev); goto fail_device; }else{ printk("create device success\n"); } return 0; fail_device: class_destroy(button_cls); fail_class: cdev_del(&button_cls); fail_cdev: unregister_chrdev_region(devid, 1); fail_devid: return ret; } static void __exit button_exit(void) { printk("button driver exit\n"); /* 注销类、以及类设备 /sys/class/button会被移除*/ device_destroy(button_cls, devid); class_destroy(button_cls); cdev_del(&button_cdev); unregister_chrdev_region(devid, 1); return; } module_init(button_init); module_exit(button_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
4.8 Makefile
KERN_DIR :=/work/sambashare/linux-5.2.8 all: make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean: make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean rm -rf modules.order obj-m += button_dev.o
五、按键驱动测试应用程序
在3.button_dev下创建test文件夹,保存测试应用程序。
5.1 main.c
#include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> int main(int argc,char **argv) { int fd,ret; unsigned int key_val = 0; fd = open("/dev/buttons", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { printf("can't open!\n"); return -1; } while (1) { ret = read(fd, &key_val, 1); // 读取一个字节值,(当在等待队列时,本进程就会进入休眠状态) if(ret < 0){ printf("read error\n"); continue; } printf("key_val = 0x%x\n", key_val); } return 0; }
5.2 Makefile
all: arm-linux-gcc -march=armv4t -o main main.c clean: rm -rf *.o main
六、烧录开发板测试
按键驱动目录结构如下:
6.1 编译驱动
执行make命令编译驱动,并将驱动程序拷贝到nfs文件系统:
cd /work/sambashare/drivers/3.button_dev make cp /work/sambashare/drivers/3.button_dev/button_dev.ko /work/nfs_root/rootfs
安装驱动:
[root@zy:/]# insmod button_dev.ko led_dev: loading out-of-tree module taints kernel. register_chrdev_region ok
查看设备节点文件:
[root@zy:/]# ls /dev/buttons -l crw-rw---- 1 0 0 249, 0 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/buttons
6.2 中断查看
运行命令cat /proc/interrupts可以查看当前系统有哪些中断服务:
[root@zy:/]# cat /proc/interrupts CPU0 29: 144431 s3c 13 Edge samsung_time_irq 32: 0 s3c 16 Edge s3c2410-lcd 42: 0 s3c 26 Edge ohci_hcd:usb1 43: 0 s3c 27 Edge s3c2440-i2c.0 55: 2897 s3c-ext 7 Edge eth0 56: 21 s3c-ext 8 Edge K1 59: 3 s3c-ext 11 Edge K2 61: 20 s3c-ext 13 Edge K3 62: 67 s3c-ext 14 Edge K4 63: 9 s3c-ext 15 Edge K5 67: 6 s3c-ext 19 Edge K6 74: 118 s3c-level 0 Edge s3c2440-uart 75: 780 s3c-level 1 Edge s3c2440-uart 87: 0 s3c-level 13 Edge s3c2410-wdt
可以看到我们注册的外部中断8、11、13、14、15、19.
6.3 编译测试应用程序
执行make命令编译测试应用程序,并将测试应用程序拷贝到nfs文件系统:
cd test make cp ./main /work/nfs_root/rootfs
运行应用程序:
./main
按下按键K1:
[root@zy:/]# ./main key_val = 0x1 key_val = 0x81
按下按键K3:
key_val = 0x3 key_val = 0x83
6.4 卸载驱动
通过用lsmod可以查看当前安装了哪些驱动:
[root@zy:/]# lsmod button_dev 2521 0 - Live 0xbf000000 (O)
卸载时直接运行:
rmmod button_dev
6.5 程序整体执行流程
- 当调用insmod装载驱动后,会调用button_init注册/dev/buttons字符设备;
- ./main运行应用程序后,应用程序执行open进行系统调用到button_open,驱动程序调用request_irq进行6个按键中断的注册;
- 然后应用程序继续执行read进行系统调用到button_read,进而调用wait_event_interruptible程序休眠;
- 只有当按键按下或松开触发中断程序button_irq执行,函数里调用wake_up_interruptible唤醒休眠的进程;
- button_read然后将驱动里读到的按键值调用copy_to_user拷贝到用户空间,应用程序再将按键值打印出来;
七、等待队列知识补充
在Linux中,等待队列以循环链表为基础结构,包括两种数据结构:等待队列头(wait_queue_head_t)和等待队列元素(wait_queue_entry_t),整个等待队列由等待队列头进行管理。具体可以参考Linux等待队列(Wait Queue)。下图大致是等待队列的结构图:
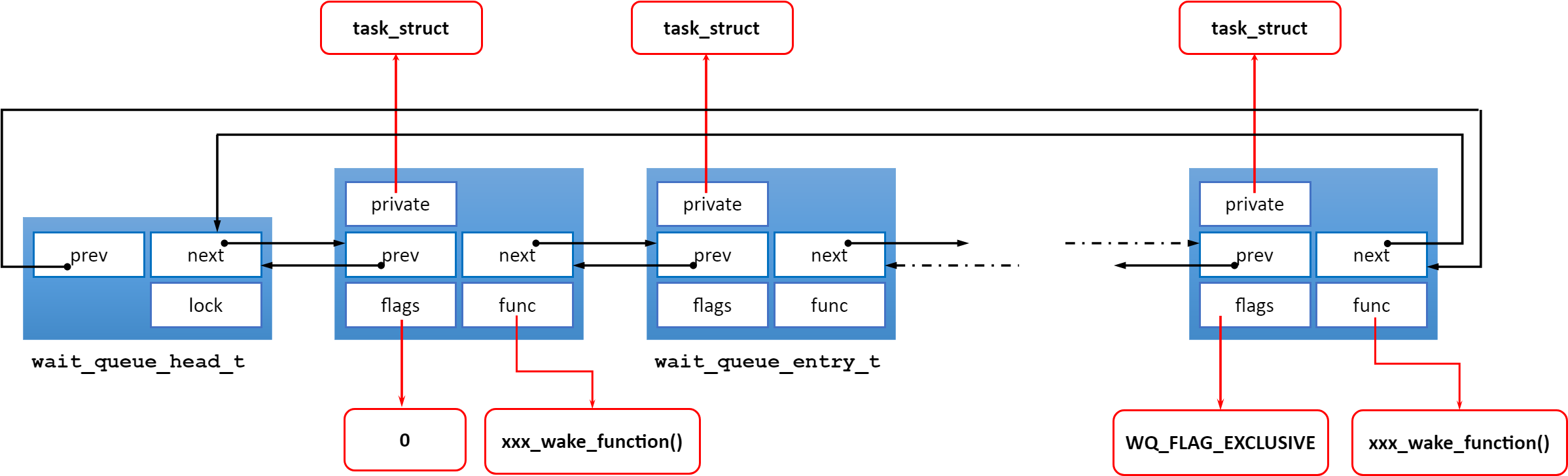
等待队列头结构包括一个自旋锁和一个链表头(prev、next)。等待队列元素除了包括链表项(prev、next),还包括:
- flags : 标识队列元素状态和属性;
- *private : 用于指向关联进程 task_struct 结构体的指针;
- func : 函数指针,用于指向等待队列被唤醒时的回调的唤醒函数;
八、代码下载
Young / s3c2440_project[drivers]
参考文章:
[3]Linux驱动中的 wait_event_interruptible 与 wake_up_interruptible 深度理解



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号