Spring Boot -- 钩子接口使用及原理
一、钩子接口介绍
Spring 提供了非常多的扩展接口,官方将这些接口称之为钩子,这些钩子会在特定的时间被回调,以此来增强 Spring 功能,众多优秀的框架也是通过扩展这些接口,来实现自身特定的功能,如 SpringBoot、mybatis 等。
二、Aware接口
Aware从字面的意思理解就是"知道"、“感知”的意思,是用来获取Spring内部对象的接口。Aware自身是一个顶级接口,它有一系列子接口,在一个 Bean 中实现这些子接口并重写里面的 set 方法后,Spring 容器启动时,就会回调该 set 方法,而相应的对象会通过方法参数传递进去。我们以其中的 ApplicationContextAware 接口为例。
2.1、ApplicationContextAware
大部分 Aware 系列接口都有一个规律,它们以对象名称为前缀,获取的就是该对象,所以 ApplicationContextAware 获取的对象是 ApplicationContext 。
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the ApplicationContext that this object runs in.
* Normally this call will be used to initialize the object.
* <p>Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an init callback such
* as {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}
* or a custom init-method. Invoked after {@link ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher} and
* {@link MessageSourceAware}, if applicable.
* @param applicationContext the ApplicationContext object to be used by this object
* @throws ApplicationContextException in case of context initialization errors
* @throws BeansException if thrown by application context methods
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException
*/
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
ApplicationContextAware 源码非常简单,其继承了 Aware 接口,并定义一个 set 方法,参数就是 ApplicationContext 对象,当然,其它系列的 Aware 接口也是类似的定义。其具体使用方式如下:
package com.zy.example;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AwareTest implements ApplicationContextAware {
/*
* 保存应用上下文
*/
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
//输出所有BeanDefinition name
for(String name:applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
log.info(name);
}
}
}
在 Spring 启动过程中,会回调 setApplicationContext 方法,并传入 ApplicationContext 对象,之后就可对该对象进行操作。我们获取到ApplicationContext对象,并将所有BeanDefinition名称输出:

其它系列的 Aware 接口也是如此使用。具体的调用时机会在后面详细介绍。
以下是几种常用的 Aware 接口:
- BeanFactoryAware:获取 BeanFactory 对象,它是基础的容器接口。
- BeanNameAware:获取 Bean 的名称。
- EnvironmentAware:获取 Environment 对象,它表示整个的运行时环境,可以设置和获取配置属性。
- ApplicationEventPublisherAware:获取 ApplicationEventPublisher 对象,它是用来发布事件的。
- ResourceLoaderAware:获取 ResourceLoader 对象,它是获取资源的工具。
三、InitializingBean, DisposableBean
3.1、InitializingBean
InitializingBean 是一个可以在 Bean 的生命周期执行自定义操作的接口,凡是实现该接口的 Bean,在初始化阶段都可以执行自定义的操作。
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} after it has set all bean properties
* and satisfied {@link BeanFactoryAware}, {@code ApplicationContextAware} etc.
* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall
* configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such as failure to set an
* essential property) or if initialization fails for any other reason
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
从 InitializingBean 源码中可以看出它有一个 afterPropertiesSet 方法,当一个 Bean 实现该接口时,在 Bean 的初始化阶段,会回调 afterPropertiesSet 方法,其初始化阶段具体指 Bean 设置完属性之后。
3.2、DisposableBean
同理,DisposableBean在Bean销毁时执行自定义的操作,必须资源的释放。
public interface DisposableBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} on destruction of a bean.
* @throws Exception in case of shutdown errors. Exceptions will get logged
* but not rethrown to allow other beans to release their resources as well.
*/
void destroy() throws Exception;
}
比如:
package com.zy.example;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Component;
@Data
@Component
@Slf4j
public class BeanTest implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
/*
* 构造函数
*/
public BeanTest(){
log.info("New object...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
log.info("Destroying ...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
log.info("Initializing ....");
}
}

四、BeanPostProcessor、BeanFactoryPostProcessor
4.1、BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor 和 InitializingBean 有点类似,也是可以在 Bean 的生命周期执行自定义操作,一般称之为 Bean 的后置处理器,不同的是, BeanPostProcessor 可以在 Bean 初始化前、后执行自定义操作,且针对的目标也不同,InitializingBean 针对的是实现 InitializingBean 接口的 Bean,而 BeanPostProcessor 针对的是所有的 Bean。并且postProcessBeforeInitialization在对象创建之后,afterPropertiesSet之前执行,而postProcessAfterInitialization在afterPropertiesSet之后执行:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
// Bean 初始化前调用
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
// Bean 初始化后调用
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
所有的 Bean 在初始化前、后都会回调接口中的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 和 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法,入参是当前正在初始化的 Bean 对象和 BeanName。值得注意的是 Spring 内置了非常多的 BeanPostProcessor ,以此来完善自身功能,这部分会在后面文章深入讨论。
我们扩充我们的测试类AwareTest :
package com.zy.example;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AwareTest implements ApplicationContextAware, BeanPostProcessor {
/*
* 保存应用上下文
*/
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
//输出所有BeanDefinition name
for(String name:applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
log.info(name);
}
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if(beanName.equals("beanTest")) {
log.info("postProcessBeforeInitialization:" + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if(beanName.equals("beanTest")) {
log.info("postProcessAfterInitialization:" + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}
BeanTest :
package com.zy.example;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Component;
@Data
@Component
@Slf4j
public class BeanTest implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean, BeanNameAware {
/*
* 保存当前bean name
*/
private String beanName;
/*
* 构造函数
*/
public BeanTest(){
log.info("New object...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
log.info("Destroying ...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
log.info("Initializing ....");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
this.beanName = name;
log.info("Current bean name:" + name);
}
}

可以看到beanTest对象先是被实例化出来,然后执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization,再执行InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet,最后执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法。而ApplicationContextAware的setApplicationContext方法执行时所有BeanDefinition都已加载,但还未实例化Bean
BeanPostProcessor 使用场景其实非常多,因为它可以获取正在初始化的 Bean 对象,然后可以对Bean 对象做一些定制化的操作,如:判断该 Bean 是否为某个特定对象、获取 Bean 的注解元数据等。事实上,Spring 内部也正是这样使用的,之前我们介绍的Spring Boot -- Spring AOP原理及简单实现手写AOP时也是利用了BeanPostProcessor的特性,我们对@Pointcut注解指定的Bean都进行了代理处理。
4.2、BeanFactoryPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 是 Bean 工厂的后置处理器,一般用来修改上下文中的 BeanDefinition,修改 Bean 的属性值。
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
// 入参是一个 Bean 工厂:ConfigurableListableBeanFactory。该方法执行时,所有 BeanDefinition 都已被加载,但还未实例化 Bean。
// 可以对其进行覆盖或添加属性,甚至可以用于初始化 Bean。
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 源码非常简单,其提供了一个 postProcessBeanFactory 方法,当所有的 BeanDefinition 被加载时,该方法会被回调。值得注意的是,Spring 内置了许多 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的实现,以此来完善自身功能。 这里,我们来实现一个自定义的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor:
package com.zy.example;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AwareTest implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
log.info("------------------------------------------postProcessBeanFactory-------------------------");
String beanNames[] = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
log.info(beanDefinition.toString());
}
}
}
主要是通过 Bean 工厂获取所有的 BeanDefinition 。

可以看到,BeanDefinition 正确输出,里面是一些 Bean 的相关定义,如:是否懒加载、Bean 的 Class 以及 Bean 的属性等。
五、Import
在博客Spring Boot -- Spring AOP原理及简单实现中我们已经粗略的介绍过整个注解了,Import经常用在@Enable 模块注解中,比如:@EnableDiscoveryClient,用于将应用注册到Eureka Server并将Eureka Server有的服务拉取到微服务系统。点开EnableDiscoveryClient源码,便会发现里面用到了@import注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableDiscoveryClient {
/**
* If true, the ServiceRegistry will automatically register the local server.
*/
boolean autoRegister() default true;
}
此外,还有之前我们介绍到的@EnableConfigurationProperties注解,用来注册 Properties 配置类和绑定配置属性:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(EnableConfigurationPropertiesImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableConfigurationProperties {
/**
* Convenient way to quickly register {@link ConfigurationProperties} annotated beans
* with Spring. Standard Spring Beans will also be scanned regardless of this value.
* @return {@link ConfigurationProperties} annotated beans to register
*/
Class<?>[] value() default {};
}
那么,这个@import的作用是什么呢,它是如何工作的呢?我们在项目里如何应用@import导入我们自定义的类?
5.1、导了一个普通的类
Spring 3.0之前,我们的Bean可以通过xml配置文件与扫描特定包下面的类来将类注入到Spring IOC容器内。Spring 3.0之后提供了JavaConfig的方式,也就是将Spring IOC容器里Bean的元信息以java代码的方式进行描述。我们可以通过@Component与@Bean这两个注解配合使用来将原来配置在xml文件里的bean通过java代码的方式进行描述。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Import {
//这里说了可以配合 Configuration , ImportSelector, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 来使用噢 或者常用的(regular component classes )也就是Bean
/**
* {@link Configuration}, {@link ImportSelector}, {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar}
* or regular component classes to import.
*/
Class<?>[] value();
}
从源码里可以看出Import可以配合 Configuration , ImportSelector, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 来使用,下面的or表示也可以把Import当成普通的Bean来使用,只是使用方式上有点区别,@Import只允许放到类上面,不能放到方法上。下面我们来看具体的使用方式。
我们移除BeanTest类上的@Component注解,这里我们可以利用Import将BeanTest导入Spring容器中,直接将类的class加到Import的value里即可:
@Configuration
@Import(value={BeanTest.class})
public class Config {
}
这种方式注入类在Spring内部用的并不多。
5.2、通过ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar注册Bean
Import注解通过配合ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar类将类注入Spring IOC容器里。ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar类的源码如下:
public interface ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
/**
* Register bean definitions as necessary based on the given annotation metadata of
* the importing {@code @Configuration} class.
* <p>Note that {@link BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor} types may <em>not</em> be
* registered here, due to lifecycle constraints related to {@code @Configuration}
* class processing.
* @param importingClassMetadata annotation metadata of the importing class
* @param registry current bean definition registry
*/
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry);
}
从上面的代码可以看出在注入Spring IOC容器的时候,我们肯定是通过registry这个变量了,而importingClassMetadata可以得到被@Import注解修饰的类的所有元数据对象。我们自定义的BeanTestRegistrar类定义如下:
package com.zy.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
public class BeanTestRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
/*
* 一般通过 AnnotationMetadata 进行业务判断,然后通过 BeanDefinitionRegistry 直接注册 Bean
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(BeanTest.class);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(BeanTest.class.getName(), beanDefinition);
}
}
此时我们已经移除了BeanTest类上的@Cofiguration注解,所以,BeanTest不会自动加入到 Spring 容器中。并修改App类。代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
@Import(value = BeanTestRegistrar.class)
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args){
//整个程序入口 启动Spring Boot项目
SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
}
}
之后通过@Import 导入自定义的BeanTestRegistrar,前面也说过,@Import 一般配合 @Configuration 使用,而 @SpringBootApplication 中包含了 @Configuration 注解:
我们运行代码,通过importingClassMetadata对象可以获取到@Import注解修饰的类App、以及类上的所有注解:

注意:上面的启动类上面只有两个注解,而右边结果有4个注解,主要是因为我运行的代码是用了4个注解,而放代码的时候把多余的两个移除了,方便理解。
此外,通过ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的方式我们可以对类进行个性化的定制,比如对需要传入的参数进行修改,也可以通过ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar注入一批相似的类。有BeanDefinitionRegistry对象也有可以控制Spring IOC容器里Bean的定义,想做些什么也就方便很多了。
5.3、通过ImportSelector方式注册Bean
上面通过ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar的方式注入的实例需要我们操作BeanDefinitionRegistry 对象,而通过ImportSelector方式我们可以不操作BeanDefinitionRegistry 对象,只需要告诉容器我们需要注入类的完整类名就好。ImportSelector类的源码如下:
public interface ImportSelector {
/**
* Select and return the names of which class(es) should be imported based on
* the {@link AnnotationMetadata} of the importing @{@link Configuration} class.
*/
String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata);
}
通过selectImport方法的参数可以得到被@Import注解的类的所有元数据对象,该方法的返回值是类的全路径数据,我们移除AwareTest类上面的@Component注解,并自定义ImportSelector的实现类:
package com.zy.example;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportSelector;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
@Slf4j
public class AwareTestSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
if (importingClassMetadata.hasAnnotation("org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication")) {
// 判断是否包含某个注解
log.info("包含这个注解");
}
return new String[]{"com.zy.example.AwareTest"};
}
}
之后通过 @Import 导入自定义的AwareTestSelector :
@SpringBootApplication
@Import(value = {AwareTestSelector.class})
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args){
//整个程序入口 启动Spring Boot项目
SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
}
}
六、FactoryBean
FactoryBean 也是一种 Bean,不同于普通的 Bean,它是用来创建 Bean 实例的,属于工厂 Bean,不过它和普通的创建不同,它提供了更为灵活的方式,其实现有点类似于设计模式中的工厂模式和修饰器模式。 Spring 框架内置了许多 FactoryBean 的实现,它们在很多应用如(Spring的AOP、ORM、事务管理)及与其它第三框架(ehCache)集成时都有体现。
public interface FactoryBean<T> {
// 该方法会返回该 FactoryBean “生产”的对象实例,我们需要实现该方法以给出自己的对象实例化逻辑
T getObject() throws Exception;
// Bean的类型
Class<?> getObjectType();
// 是否是单例
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
自定义FactoryBean:
@Component
public class TestFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Test> {
@Override
public Test getObject() throws Exception {
// 这里可以灵活的创建 Bean,如:代理、修饰
return new Test();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
}
Test 类:
public class Test {
public void hello() {
System.out.println("Test -- hello");
}
}
启动类:
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args){
//整个程序入口 启动Spring Boot项目
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
Test bean = (Test) run.getBean("testFactoryBean");
bean.hello();
}
}
输出:

可以看到,启动类中 getBean 的参数是 testFactoryBean ,从这可以看出,当容器中的 Bean 实现了 FactoryBean 后,通过 getBean(String BeanName) 获取到的 Bean 对象并不是 FactoryBean 的实现类对象,而是这个实现类中的 getObject() 方法返回的对象。如果想获取 FactoryBean 的实现类,需通过这种方式:getBean(&BeanName),在 BeanName 之前加上&。
更多详细的使用信息参考博客Spring中FactoryBean的作用和实现原理。
七、ApplicationListener
ApplicationListener 是 Spring 实现事件机制的核心接口,属于监听器设计模式,一般配合 ApplicationEvent 使用。在 Spring 容器启动过程中,会在相应的阶段通过 ApplicationContext 发布 ApplicationEvent 事件,比如:ApplicationStartedEvent、ApplicationReadyEvent,之后所有的 ApplicationListener 会被回调,在onApplicationEvent方法中,根据事件类型,执行不同的操作。
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
}
自定义 ApplicationListener:
@Component
public class TestApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof TestApplicationEvent) {
TestApplicationEvent testApplicationEvent = (TestApplicationEvent) event;
System.out.println(testApplicationEvent.getName());
}
}
}
当自定义的 TestApplicationListener 被回调时,判断当前发布的事件类型是否是自定义的 TestApplicationEvent,如果是则输出事件名称。
自定义 TestApplicationEvent:
package com.zy.example;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
public class TestApplicationEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String name;
public TestApplicationEvent(Object source, String name) {
super(source);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
启动类:
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class App {
public static void main(String[] args){
//整个程序入口 启动Spring Boot项目
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
run.publishEvent(new TestApplicationEvent(new App(),"Test 事件"));
}
}
通过 ApplicationContext 发布 TestApplicationEvent 事件。当然也可以在业务代码中通过 ApplicationContextAware 获取 ApplicationContext 发布事件。
输出:

关于更多事件监听机制,可以参考博客:Spring Boot -- 启动流程分析之SpringApplication。
八、自动装配@EnableAutoConfiguration
之前我们介绍了@Inport注解,Spring Boot的自动装配就是利用@Inport注解实现的。我们都知道 Spring Boot 的启动过程非常简单,只需要启动一个 main 方法,项目就可以运行,就算依赖了诸多外部模块如:MVC、Redis等,也不需要我们进行过多的配置,那它的底层原理是什么呢?接下来,我们就一起去看一看。
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args){
//整个程序入口 启动Spring Boot项目
SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
}
}
我们需要关注的是 @SpringBootApplication 这个注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
String[] excludeName() default {};
/**
* Base packages to scan for annotated components. Use {@link #scanBasePackageClasses}
* for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names.
* <p>
* <strong>Note:</strong> this setting is an alias for
* {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} only. It has no effect on {@code @Entity}
* scanning or Spring Data {@link Repository} scanning. For those you should add
* {@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan @EntityScan} and
* {@code @Enable...Repositories} annotations.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #scanBasePackages} for specifying the packages to
* scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned.
* <p>
* Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that
* serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
* <p>
* <strong>Note:</strong> this setting is an alias for
* {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} only. It has no effect on {@code @Entity}
* scanning or Spring Data {@link Repository} scanning. For those you should add
* {@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan @EntityScan} and
* {@code @Enable...Repositories} annotations.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses")
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
/**
* Specify whether {@link Bean @Bean} methods should get proxied in order to enforce
* bean lifecycle behavior, e.g. to return shared singleton bean instances even in
* case of direct {@code @Bean} method calls in user code. This feature requires
* method interception, implemented through a runtime-generated CGLIB subclass which
* comes with limitations such as the configuration class and its methods not being
* allowed to declare {@code final}.
* <p>
* The default is {@code true}, allowing for 'inter-bean references' within the
* configuration class as well as for external calls to this configuration's
* {@code @Bean} methods, e.g. from another configuration class. If this is not needed
* since each of this particular configuration's {@code @Bean} methods is
* self-contained and designed as a plain factory method for container use, switch
* this flag to {@code false} in order to avoid CGLIB subclass processing.
* <p>
* Turning off bean method interception effectively processes {@code @Bean} methods
* individually like when declared on non-{@code @Configuration} classes, a.k.a.
* "@Bean Lite Mode" (see {@link Bean @Bean's javadoc}). It is therefore behaviorally
* equivalent to removing the {@code @Configuration} stereotype.
* @since 2.2
* @return whether to proxy {@code @Bean} methods
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
我们来看一看它的组成部分:
- @SpringBootConfiguration:它里面标注了 @Configuration 注解,表明这是个配置类,功能与 @Configuration 无异。
- @EnableAutoConfiguration:这个就是实现自动装配的核心注解,是用来激活自动装配的,其中默认路径扫描以及组件装配、排除等都通过它来实现。
- @ComponentScan:这是用来扫描被 @Component标注的类 ,只不过这里是用来过滤 Bean 的,指定哪些类不进行扫描,而且用的是自定义规则。
- Class<?>[] exclude():根据class来排除,排除指定的类加入spring容器,传入的类型是class类型。且继承自 @EnableAutoConfiguration 中的属性。
- String[] excludeName():根据class name来排除,排除特定的类加入spring容器,参数类型是class的全类名字符串数组。同样继承自 @EnableAutoConfiguration。
- String[] scanBasePackages():可以指定多个包名进行扫描。继承自 @ComponentScan 。
- Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses():可以指定多个类或接口的class,然后扫描 class 所在包下的所有组件。同样继承自 @ComponentScan 。
8.1、@EnableAutoConfiguration 实现
上面我们说到 @EnableAutoConfiguration 是实现自动装配的核心注解,是用来激活自动装配的,看注解前缀我们应该知道这是 Spring @Enable 模块驱动的设计模式,所以它必然会有 @Import 导入的普通类或实现 ImportSelector 或、ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口的类。接着,我们来看看它的定义:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
可以看到它由两部分组成:
- @AutoConfigurationPackage:这是用来将启动类所在包,以及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到Spring容器中,这里的组件是指被 @Component或其派生注解标注的类。这也就是为什么不用标注@ComponentScan的原因。
- @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):这里导入的是实现了 ImportSelector 接口的类,组件自动装配的逻辑均在重写的 selectImports 方法中实现。 接下来我们就来看看这两者具体是怎么实现的。
8.2、获取默认包扫描路径
我们先来看看 Spring Boot 是如何通过 @AutoConfigurationPackage 注解获取默认包扫描路径的,进入它的实现:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}
可以看到它是通过 @Import 导入了 AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar 类,该类实现了 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口,所以按照@Import小节中介绍的,它是在重写的方法中直接注册相关组件。继续往下:
/**
* {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar} to store the base package from the importing
* configuration.
*/
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName());
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImport(metadata));
}
}
这里的meatadata元信息,就是启动类的注解信息:
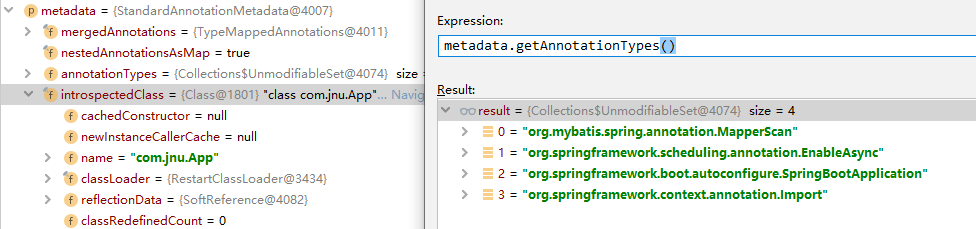
接着我们看一下PackageImport的实现:
/**
* Wrapper for a package import.
*/
private static final class PackageImport {
private final String packageName;
PackageImport(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
this.packageName = ClassUtils.getPackageName(metadata.getClassName());
}
String getPackageName() {
return this.packageName;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) {
return false;
}
return this.packageName.equals(((PackageImport) obj).packageName);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.packageName.hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Package Import " + this.packageName;
}
}
这里主要是通过 metadata 元数据信息构造 PackageImport 类。先获取启动类的类名,再通过 ClassUtils.getPackageName 获取启动类所在的包名com.jnu。我们接着往下看:
public static void register(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String... packageNames) {
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(BEAN)) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(BEAN);
ConstructorArgumentValues constructorArguments = beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
constructorArguments.addIndexedArgumentValue(0, addBasePackages(constructorArguments, packageNames));
}
else {
GenericBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new GenericBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(BasePackages.class);
beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addIndexedArgumentValue(0, packageNames);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(BEAN, beanDefinition);
}
}
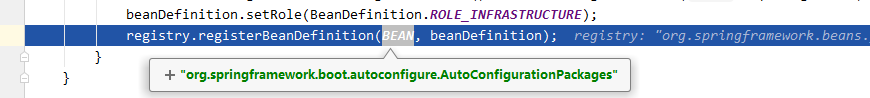
最后就是将这个包名保存至 BasePackages 类中,然后通过 BeanDefinitionRegistry 将其注册,进行后续处理,至此该流程结束。
参考文章:
[3]SpringBoot(二)自动装配正文 - @SpringBootApplication、@EnableAutoConfiguration


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号