Spring Security -- 自定义用户认证(转载)
在Spring Security -- Spring Boot中开启Spring Security一节中我们简单搭建了个Spring Boot + Spring Security的项目,认证的用户名和密码都是由Spring Security生成。Spring Security支持我们自定义认证的过程,如处理用户信息获取逻辑,使用我们自定义的登录页面替换Spring Security默认的登录页及自定义登录成功或失败后的处理逻辑等。这里将在上一节的源码基础上进行改造。
一、自定义认证过程
1、UserDetailService接口和UserDetails接口
自定义认证的过程需要实现Spring Security提供的UserDetailService接口,该接口只有一个抽象方法loadUserByUsername,源码如下:
package org.springframework.security.core.userdetails;
/**
* Core interface which loads user-specific data.
* <p>
* It is used throughout the framework as a user DAO and is the strategy used by the
* {@link org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider
* DaoAuthenticationProvider}.
*
* <p>
* The interface requires only one read-only method, which simplifies support for new
* data-access strategies.
*
* @see org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider
* @see UserDetails
*
* @author Ben Alex
*/
public interface UserDetailsService {
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
/**
* Locates the user based on the username. In the actual implementation, the search
* may possibly be case sensitive, or case insensitive depending on how the
* implementation instance is configured. In this case, the <code>UserDetails</code>
* object that comes back may have a username that is of a different case than what
* was actually requested..
*
* @param username the username identifying the user whose data is required.
*
* @return a fully populated user record (never <code>null</code>)
*
* @throws UsernameNotFoundException if the user could not be found or the user has no
* GrantedAuthority
*/
UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;
}
loadUserByUsername方法返回一个UserDetails对象,UserDetails也是一个接口,包含一些用于描述用户信息的方法,源码如下:
/**
* Provides core user information.
*
* <p>
* Implementations are not used directly by Spring Security for security purposes. They
* simply store user information which is later encapsulated into {@link Authentication}
* objects. This allows non-security related user information (such as email addresses,
* telephone numbers etc) to be stored in a convenient location.
* <p>
* Concrete implementations must take particular care to ensure the non-null contract
* detailed for each method is enforced. See
* {@link org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User} for a reference
* implementation (which you might like to extend or use in your code).
*
* @see UserDetailsService
* @see UserCache
*
* @author Ben Alex
*/
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
/**
* Returns the authorities granted to the user. Cannot return <code>null</code>.
*
* @return the authorities, sorted by natural key (never <code>null</code>)
*/
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
/**
* Returns the password used to authenticate the user.
*
* @return the password
*/
String getPassword();
/**
* Returns the username used to authenticate the user. Cannot return <code>null</code>.
*
* @return the username (never <code>null</code>)
*/
String getUsername();
/**
* Indicates whether the user's account has expired. An expired account cannot be
* authenticated.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the user's account is valid (ie non-expired),
* <code>false</code> if no longer valid (ie expired)
*/
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
/**
* Indicates whether the user is locked or unlocked. A locked user cannot be
* authenticated.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the user is not locked, <code>false</code> otherwise
*/
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
/**
* Indicates whether the user's credentials (password) has expired. Expired
* credentials prevent authentication.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the user's credentials are valid (ie non-expired),
* <code>false</code> if no longer valid (ie expired)
*/
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
/**
* Indicates whether the user is enabled or disabled. A disabled user cannot be
* authenticated.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the user is enabled, <code>false</code> otherwise
*/
boolean isEnabled();
}
这些方法的含义如下:、
- getAuthorities获取用户包含的权限,返回权限集合,权限是一个继承了GrantedAuthority的对象;
- getPassword和getUsername用于获取密码和用户名;
- isAccountNonExpired方法返回boolean类型,用于判断账户是否未过期,未过期返回true反之返回false;
- isAccountNonLocked方法用于判断账户是否未锁定;
- isCredentialsNonExpired用于判断用户凭证是否没过期,即密码是否未过期;
- isEnabled方法用于判断用户是否可用;
实际中我们可以自定义UserDetails接口的实现类,也可以直接使用Spring Security提供的UserDetails接口实现类org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User。
2、自定义CustomUserDetailService和User
说了那么多,下面我们来开始实现UserDetailService接口的loadUserByUsername方法。
首先创建UserDetails接口的实现类User,用于存放模拟的用户数据(实际中一般从数据库获取,这里为了方便直接模拟):
package com.zy.example.entity;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @Author: zy
* @Description: 用户实体类
* Spring Security框架提供了一个基础用户接口UserDetails,该接口提供了基本的用户相关的操作,比如获取用户名/密码、
* 用户账号是否过期和用户认证是否过期等,我们定义自己的User类时需要实现该接口。
* @Date: 2020-2-9
*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User implements UserDetails {
private static final PasswordEncoder PASSWORD_ENCODER = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
private String id;
/**
* 用户登录名
*/
private String username;
/**
* 用户真实姓名
*/
private String realName;
/**
* 用户登录密码,用户的密码不应该暴露给客户端
*/
@JsonIgnore
private String password;
/**
* 用户创建者
*/
private int createdBy;
/**
* 创建时间
*/
private Long createdTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
/**
* 该用户关联的企业/区块id
*/
private Map<String, Object> associatedResources = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 用户关注的企业列表
*/
private List<String> favourite = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 用户在系统中的角色列表,将根据角色对用户操作权限进行限制
*/
private List<String> roles = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 设置密码
* @param password
*/
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = PASSWORD_ENCODER.encode(password);
}
/**
* 权限集合
*/
private Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = null;
/**
* 账户是否未过期
*/
private boolean accountNonExpired = true;
/**
* 账户是否未锁定
*/
private boolean accountNonLocked= true;
/**
* 用户凭证是否没过期,即密码是否未过期
*/
private boolean credentialsNonExpired= true;
/**
* 用户是否可用
*/
private boolean enabled= true;
}
PasswordEncoder是一个密码加密接口,而BCryptPasswordEncoder是Spring Security提供的一个实现方法,我们也可以自己实现PasswordEncoder。不过Spring Security实现的BCryptPasswordEncoder已经足够强大,它对相同的密码进行加密后可以生成不同的结果。
此外,我们在com.zy.example.config下创建一个bean配置类,配置加密方式:
package com.zy.example.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
/**
* @Author: zy
* @Description: 定义一些bean
* @Date: 2020-2-9
*/
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
/**
* 密码加密
* @return
*/
@Bean
public static PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
接着创建类CustomUserDetailService实现UserDetailService接口:
package com.zy.example.service; import com.zy.example.entity.User; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.core.authority.AuthorityUtils; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * @Author: zy * @Description: 自定义用户信息Service配置类 * @Date: 2020-2-9 */ @Service public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { /** * 点击登录时会调用该函数、并传入登录名 根据用户名查询数据库获取用户信息 * @param username:登录用户名 * @return: 返回用户信息 * @throws UsernameNotFoundException */ @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { //模拟一个用户 替代数据库获取逻辑 User user = new User(); user.setUsername(username); user.setPassword("123456"); // 输出加密后的密码 System.out.println(user.getPassword()); return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), user.isEnabled(), user.isAccountNonExpired(), user.isCredentialsNonExpired(), user.isAccountNonLocked(), AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin")); } }
这里我们使用了org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User类包含7个参数的构造器,其还包含一个三个参数的构造器User(String username, String password,Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities),由于权限参数不能为空,所以这里先使用AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList方法模拟一个admin的权限,该方法可以将逗号分隔的字符串转换为权限集合。
这时候重启项目,访问http://localhost:8080/login,便可以使用任意用户名以及123456作为密码登录系统。我们多次进行登录操作,可以看到控制台输出的加密后的密码如下:
$2a$10$QWhO2OtA6/o0c6P2/KIwzOIlS5xGpPHrYxbeVc8AvAf0LfmZaLCfq
$2a$10$3A6L/hDeb9OeM/5KzUMfHufwZtqTuV5gyi2vHN6N2w8U7TrA9GQa2
$2a$10$gWzh2cqGqYg4qzH8lmYlUeHWc8epTyh6.gMyVdW4xZDJLNU4s1pnW
可以看到,BCryptPasswordEncoder对相同的密码生成的结果每次都是不一样的。
二、替换默认表单页面
默认的登录页面过于简陋,我们可以自己定义一个登录页面。
1、使用Freemarker模板引擎渲染Web视图
pom文件引入依赖包:
<!-- 引入freemarker的依赖包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId>
</dependency>
在src/main/resources/创建一个templates文件夹,并创建login.ftl文件:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
margin: 0px;
}
#content {
margin: 150px auto;
width: 100%;
height: 460px;
border: 1px transparent solid;
background-color: #21D4FD;
background-image: linear-gradient(243deg, #21D4FD 0%, #B721FF 100%);
background-image: -webkit-linear-gradient(243deg, #21D4FD 0%, #B721FF 100%);
background-image: -moz-linear-gradient(243deg, #21D4FD 0%, #B721FF 100%);
background-image: -o-linear-gradient(243deg, #21D4FD 0%, #B721FF 100%);
}
#box {
margin: 50px auto;
width: 30%;
height: 360px;
background-color: #fff;
text-align: center;
border-radius: 15px;
border: 2px #fff solid;
box-shadow: 10px 10px 5px #000000;
}
.title {
line-height: 58px;
margin-top: 20px;
font-size: 36px;
color: #000;
height: 58px;
}
#box:hover {
border: 2px #fff solid;
}
.input {
margin-top: 20px;
}
input {
margin-top: 5px;
outline-style: none;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 3px;
padding: 13px 14px;
width: 70%;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 700;
font-family: "Microsoft soft";
}
button {
margin-top: 20px;
border: none;
color: #000;
padding: 15px 32px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
border-radius: 15px;
background-color: #CCCCCC;
}
button:hover{
background-color: #B721FF;
color: #fff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="content">
<div id="box">
<div class="title">Login</div>
<div class="input">
<form name="f" action="/login" method="post">
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" value="" placeholder="用户名" />
<br>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" placeholder="密码" />
<br>
<input type="submit" value="登录" onclick="getuser()"/>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function getuser() {
var username = document.getElementById("username").value;
var password = document.getElementById("password").value;
var password1 = document.getElementById("password1").value;
testing(username, password,password1)
//alert("username:"+username+"\n"+"password:"+password);
}
function testing(username, password, password1) {
var tmp = username && password;
if (tmp == "") {
alert("请填写完整信息");
return 0;
}
if (username.length < 6 || username.length > 16) {
alert("用户名长度为:6-16位")
return 0;
}
if (password<6)
{
alert("密码长度错误");
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
在src/main/resources下新建freemarker配置文件application.yml:
spring:
## Freemarker 配置
freemarker:
##模版存放路径(默认为 classpath:/templates/)
template-loader-path: classpath:/templates/
##是否生成缓存,生成环境建议开启(默认为true)
cache: false
##编码
charset: UTF-8
check-template-location: true
##content-type类型(默认为text/html)
content-type: text/html
## 设定所有request的属性在merge到模板的时候,是否要都添加到model中(默认为false)
expose-request-attributes: false
##设定所有HttpSession的属性在merge到模板的时候,是否要都添加到model中.(默认为false)
expose-session-attributes: false
##RequestContext属性的名称(默认为-)
request-context-attribute: request
##模板后缀(默认为.ftl)
suffix: .ftl
2、LoginController
在com.zy.example.controller包下创建LoginController.java:
package com.zy.example.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @Author: zy
* @Description: 登陆页面
* @Date: 2020-2-9
*/
@Controller
public class LoginController {
/**
* 自定义登录页面
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(){
return "/login";
}
}
3、修改BrowserSecurityConfig配置
要怎么做才能让Spring Security跳转到我们自己定义的登录页面呢?很简单,只需要在类BrowserSecurityConfig的configure中添加一些配置:
/**
* 配置拦截请求资源
* @param http:HTTP请求安全处理
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.anyRequest() // 任何请求
.authenticated() //都需要身份认证
.and()
.formLogin() // 或者httpBasic()
.loginPage("/login") // 指定登录页的路径
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 指定自定义form表单请求的路径
// 必须允许所有用户访问我们的登录页(例如未验证的用户,否则验证流程就会进入死循环)
// 这个formLogin().permitAll()方法允许所有用户基于表单登录访问/login这个page。
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.permitAll()
.and()
//默认都会产生一个hiden标签 里面有安全相关的验证 防止请求伪造 这边我们暂时不需要 可禁用掉
.csrf().disable();
面代码中.loginPage("/login")指定了跳转到登录页面的请求URL,.loginProcessingUrl("/login")对应登录页面form表单的action="/login",如果两者不一样,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器将不会生效,.permitAll()表示跳转到登录页面的请求不被拦截,否则会进入无限循环。
这时候启动系统,访问http://localhost:8080/hello,会看到页面已经被重定向到了http://localhost:8080/login:
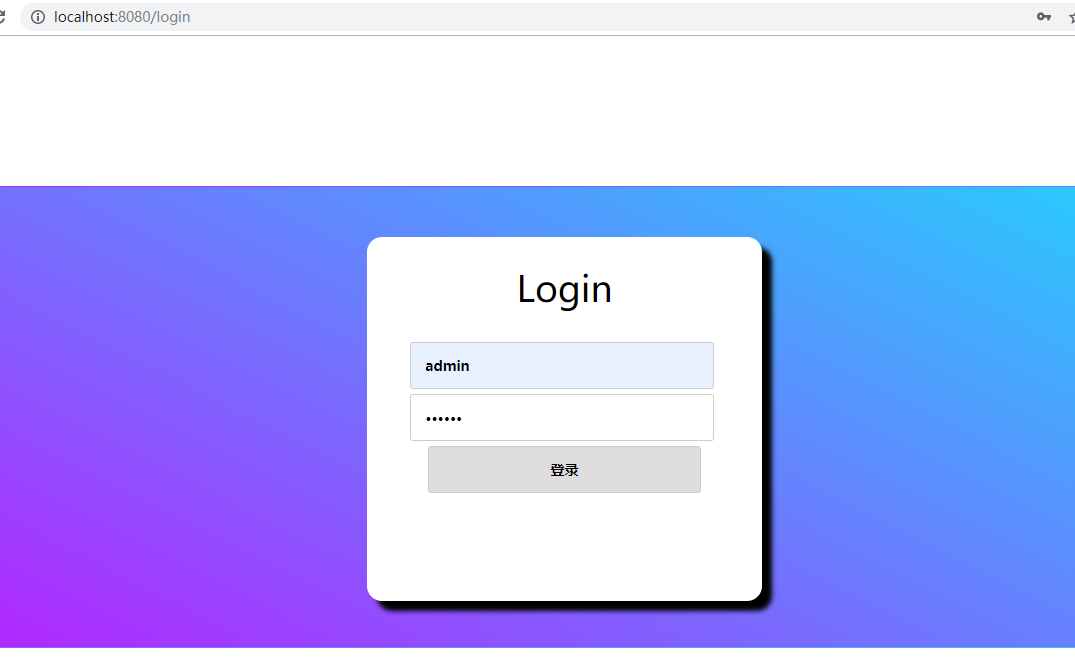
输入admin、123456,跳转到/hello页面:
![]()
三、处理登录成功和失败
Spring Security有一套默认的处理登录成功和失败的方法:当用户登录成功时,页面会跳转到引发登录的页面,比如在未登录的情况下访问http://localhost:8080/hello,页面会跳转到登录页,登录成功后再跳转回来;登录失败时则是跳转到Spring Security默认的错误提示页面。下面我们通过一些自定义配置来替换这套默认的处理机制。
1、自定义登录成功逻辑
要改变默认的处理成功逻辑很简单,只需要实现org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler接口的onAuthenticationSuccess方法即可:
首先添加jackson依赖:
<!-- 对象json转换 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.8.3</version>
</dependency>
创建包com.zy.example.handler,在包下创建CustomAuthenticationSucessHandler.java:
package com.zy.example.handler;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: zy
* @Description: 自定义登录成功逻辑
* @Date: 2020-2-9
*/
@Service
public class CustomAuthenticationSucessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper mapper;
/**
* 登录成功
* @param request:请求
* @param response:响应
* @param authentication:Authentication参数既包含了认证请求的一些信息,比如IP,请求的SessionId等,
* 也包含了用户信息
* @throws IOException
* @throws ServletException
*/
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(mapper.writeValueAsString(authentication));
}
}
其中Authentication参数既包含了认证请求的一些信息,比如IP,请求的SessionId等,也包含了用户信息,即前面提到的User对象。通过上面这个配置,用户登录成功后页面将打印出Authentication对象的信息。
此外我们注入了mapper对象,该对象用于将Authentication对象json序列化,注入前需要手动配置。我们在bean配置类配置它:
/**
* 对象Json序列化
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ObjectMapper mapper() {
return new ObjectMapper();
}
为了使CustomAuthenticationSucessHandler生效,我们还的在BrowserSecurityConfig的configure中配置:
@Autowired private AuthenticationSuccessHandler authenticationSucessHandler /** * 配置拦截请求资源 * @param http:HTTP请求安全处理 * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置 .anyRequest() // 任何请求 .authenticated() //都需要身份认证 .and() .formLogin() // 或者httpBasic() .loginPage("/login") // 指定登录页的路径 .loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 指定自定义form表单请求的路径 .successHandler(authenticationSucessHandler) // 处理登录成功 // 必须允许所有用户访问我们的登录页(例如未验证的用户,否则验证流程就会进入死循环) // 这个formLogin().permitAll()方法允许所有用户基于表单登录访问/login这个page。 .permitAll() .and() .logout() .permitAll() .and() //默认都会产生一个hiden标签 里面有安全相关的验证 防止请求伪造 这边我们暂时不需要 可禁用掉 .csrf().disable(); }
我们将CustomAuthenticationSucessHandler注入进来,并通过successHandler方法进行配置。
这时候重启项目登录后页面将会输出如下JSON信息:
{
"authorities": [{
"authority": "admin"
}],
"details": {
"remoteAddress": "127.0.0.1",
"sessionId": "8C6774C31B224228BCC19CE5F44DA432"
},
"authenticated": true,
"principal": {
"password": null,
"username": "admin",
"authorities": [{
"authority": "admin"
}],
"accountNonExpired": true,
"accountNonLocked": true,
"credentialsNonExpired": true,
"enabled": true
},
"credentials": null,
"name": "admin"
}
像password,credentials这些敏感信息,Spring Security已经将其屏蔽。
除此之外,我们也可以在登录成功后做页面的跳转,修改CustomAuthenticationSucessHandler:
package com.zy.example.handler;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.web.DefaultRedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.RedirectStrategy;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.HttpSessionRequestCache;
import org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.RequestCache;
import org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.SavedRequest;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: zy
* @Description: 自定义登录成功逻辑
* @Date: 2020-2-9
*/
@Service
public class CustomAuthenticationSucessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
private RequestCache requestCache = new HttpSessionRequestCache();
private RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy();
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper mapper;
/**
* 登录成功
* @param request:请求
* @param response:响应
* @param authentication:Authentication参数既包含了认证请求的一些信息,比如IP,请求的SessionId等,
* 也包含了用户信息
* @throws IOException
* @throws ServletException
*/
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
SavedRequest savedRequest = requestCache.getRequest(request, response);
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, savedRequest.getRedirectUrl());
}
}
其中HttpSessionRequestCache为Spring Security提供的用于缓存请求的对象,通过调用它的getRequest方法可以获取到本次请求的HTTP信息。DefaultRedirectStrategy的sendRedirect为Spring Security提供的用于处理重定向的方法。
通过上面配置,登录成功后页面将跳转回引发跳转的页面。如果想指定跳转的页面,比如跳转到/index,可以将savedRequest.getRedirectUrl()修改为/index,修改TestController类,添加如下方法:
@GetMapping("index")
public Object index(){
return SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
}
登录成功后,便可以使用SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()获取到Authentication对象信息。除了通过这种方式获取Authentication对象信息外,也可以使用下面这种方式:
@GetMapping("index")
public Object index(Authentication authentication) {
return authentication;
}
重启项目,登录成功后,页面将跳转到http://localhost:8080/index:
{
"authorities": [{
"authority": "admin"
}],
"details": {
"remoteAddress": "127.0.0.1",
"sessionId": "8C6774C31B224228BCC19CE5F44DA432"
},
"authenticated": true,
"principal": {
"password": null,
"username": "admin",
"authorities": [{
"authority": "admin"
}],
"accountNonExpired": true,
"accountNonLocked": true,
"credentialsNonExpired": true,
"enabled": true
},
"credentials": null,
"name": "admin"
}
2、自定义登录失败逻辑
和自定义登录成功处理逻辑类似,自定义登录失败处理逻辑需要实现org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler的onAuthenticationFailure方法::
@Service
public class MyAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException {
}
}
onAuthenticationFailure方法的AuthenticationException参数是一个抽象类,Spring Security根据登录失败的原因封装了许多对应的实现类,查看AuthenticationException的Hierarchy:

不同的失败原因对应不同的异常,比如用户名或密码错误对应的是BadCredentialsException,用户不存在对应的是UsernameNotFoundException,用户被锁定对应的是LockedException等。
假如我们需要在登录失败的时候返回失败信息,可以这样处理:
package com.zy.example.handler;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationFailureHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: zy
* @Description: 自定义登录失败逻辑
* @Date: 2020-2-9
*/
@Service
public class CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler implements AuthenticationFailureHandler {
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper mapper;
/**
* 登录失败 返回错误状态码
* @param request
* @param response
* @param exception
* @throws IOException
* @throws ServletException
*/
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value());
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.getWriter().write(mapper.writeValueAsString(exception.getMessage()));
}
}
状态码定义为500(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value()),即系统内部异常。
同样的,我们需要在BrowserSecurityConfig的configure中配置它:
@Autowired
private AuthenticationFailureHandler authenticationFailureHandler;
/**
* 配置拦截请求资源
* @param http:HTTP请求安全处理
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests() // 授权配置
.anyRequest() // 任何请求
.authenticated() //都需要身份认证
.and()
.formLogin() // 或者httpBasic()
.loginPage("/login") // 指定登录页的路径
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") // 指定自定义form表单请求的路径
.successHandler(authenticationSucessHandler) // 处理登录成功
.failureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler) // 处理登录失败
// 必须允许所有用户访问我们的登录页(例如未验证的用户,否则验证流程就会进入死循环)
// 这个formLogin().permitAll()方法允许所有用户基于表单登录访问/login这个page。
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.permitAll()
.and()
//默认都会产生一个hiden标签 里面有安全相关的验证 防止请求伪造 这边我们暂时不需要 可禁用掉
.csrf().disable();
}
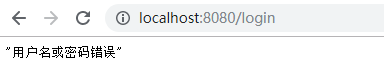
重启项目,当输入错误的密码时,页面输出如下:
四、修改错误页面
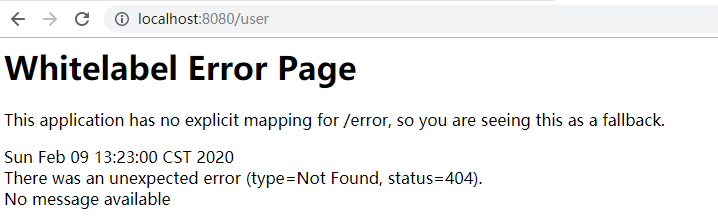
当我们登录一个不存在页面时,http://localhost:8080/user,将会抛出404错误,如何修改这些默认错误页面呢:
1、创建ErrorPageConfig配置类
在包com.zy.example.config下创建类ErrorPageConfig:
package com.zy.example.config;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPage;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPageRegistrar;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.ErrorPageRegistry;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
/**
* @Author: zy
* @Description: spring boot 错误页面配置
* @Date: 2020-2-8
*/
@Configuration
public class ErrorPageConfig implements ErrorPageRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry registry) {
ErrorPage errorPage400 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST,"/error/400");
ErrorPage errorPage401 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED,"/error/401");
ErrorPage errorPage403 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN,"/error/403");
ErrorPage errorPage404 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND,"/error/404");
ErrorPage errorPage415 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.UNSUPPORTED_MEDIA_TYPE,"/error/415");
ErrorPage errorPage500 = new ErrorPage(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,"/error/500");
registry.addErrorPages(errorPage400,errorPage401,errorPage403,errorPage404,errorPage415,errorPage500);
}
}
2、Controller
在com.zy.example.controller下创建类ErrorController:
package com.zy.example.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @Author: zy
* @Description: spring boot 错误页面配置
* @Date: 2020-2-8
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/error")
public class ErrorController {
@RequestMapping("/403")
public String error403(){
return "/error/403";
}
@RequestMapping("/404")
public String error404(){
return "/error/404";
}
}
3、新增ftl文件
在src/java/resource/templates/error新建错误页面:
403页面:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>403</title>
<style>
html, body {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
}
.box {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: wheat;
text-align: center; /*文本水平居中*/
line-height: 600px; /*文本垂直居中*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<h1 style="display: inline">Sorry, this page is Authorised by </h1>
<h1 style="display: inline"><a href="/login">zy</a></h1>
<h1 style="display: inline"> only.</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>
404页面:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>404</title>
<style>
html, body {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
}
.box {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: wheat;
text-align: center; /*文本水平居中*/
padding-top: 15%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<h1>404 您进入了无人区...</h1>
<span id="counter"></span>秒后 <a href="/login">返回登录首页</a>
</div>
<script>
var $counter = document.getElementById('counter');
function countDown(secs)
{
$counter.innerText=secs;
if(--secs>0)
{
setTimeout("countDown("+secs+")",1000);
}
if(secs==0)
{
location.href = '/login';
}
}
countDown(5);
</script>
</body>
</html>
四、代码下载
参考文章:
[1] Spring Security自定义用户认证



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号