Spring Boot -- Spring Boot之热部署、性能优化、打包
一、热部署
所谓的热部署:比如项目的热部署,就是在应用程序在不停止的情况下,实现新的部署。
1.1、热部署原理
原理: 使用类加载器(classloader重新读取字节码文件到jvm内存)
如何纯手写一个热部署功能:
- 监听 class文件是否发生改变 版本号、修改时间 作对比;
- 如果发生改变就用classloader进行重新读取;
热部署可以用于在生产环境?
- 理论上可以(不推荐),热部署要是用在生产环境,性能很差了,不安全;
- 本地开发(eclipse、idea)、用来提高效率,不需要重启服务器;
1.2、devtools依赖
要想实现热部署,我们可以利用Spring Boot为我们提供了一个非常方便的工具spring-boot-devtools。
添加依赖:
<!-- 热部署 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional><!-- optional=true,依赖不会传递 -->
</dependency>
1.3、IDEA设置
如果使用idea,必须需要确保开启运行时编译才行,IDEA Settings->Build,Execution,Deployment->Compiler 开启Build project automatically:

快捷键 ctrl+shift+a,输入Registry,找到下面这行,开启:

以上即可实现热部署,前后台代码修改都可不用再次部署运行。
1.4、devtools原理
springboot-devtools模块能够实现热部署,添加类.添加方法,修改配置文件,修改页面等,都能实现热部署。
原理就是重启项目,但比手动重启快多了,其深层原理是使用了两个ClassLoder:
- 一个ClassLoader加载哪些不会改变的类(第三方jar包);
- 另一个ClassLoader加载会更改的类,称之为restart ClassLoader;
- 这样在有代码更改的时候,原来的restart Classloader被丢弃,重新创建一个restart ClassLoader,由于需要加载的类相比较少,所以实现了较快的重启时间(5秒以内);
二、性能优化
2.1、组件自动扫描带来的问题
默认情况下,我们会使用 @SpringBootApplication 注解来自动获取应用的配置信息,我们首先来看一下这个注解源代码:

/*
* Copyright 2012-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.TypeExcludeFilter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan.Filter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import org.springframework.data.repository.Repository;
/**
* Indicates a {@link Configuration configuration} class that declares one or more
* {@link Bean @Bean} methods and also triggers {@link EnableAutoConfiguration
* auto-configuration} and {@link ComponentScan component scanning}. This is a convenience
* annotation that is equivalent to declaring {@code @Configuration},
* {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} and {@code @ComponentScan}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @since 1.2.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
String[] excludeName() default {};
/**
* Base packages to scan for annotated components. Use {@link #scanBasePackageClasses}
* for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names.
* <p>
* <strong>Note:</strong> this setting is an alias for
* {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} only. It has no effect on {@code @Entity}
* scanning or Spring Data {@link Repository} scanning. For those you should add
* {@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan @EntityScan} and
* {@code @Enable...Repositories} annotations.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #scanBasePackages} for specifying the packages to
* scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned.
* <p>
* Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that
* serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
* <p>
* <strong>Note:</strong> this setting is an alias for
* {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} only. It has no effect on {@code @Entity}
* scanning or Spring Data {@link Repository} scanning. For those you should add
* {@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan @EntityScan} and
* {@code @Enable...Repositories} annotations.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses")
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
/**
* Specify whether {@link Bean @Bean} methods should get proxied in order to enforce
* bean lifecycle behavior, e.g. to return shared singleton bean instances even in
* case of direct {@code @Bean} method calls in user code. This feature requires
* method interception, implemented through a runtime-generated CGLIB subclass which
* comes with limitations such as the configuration class and its methods not being
* allowed to declare {@code final}.
* <p>
* The default is {@code true}, allowing for 'inter-bean references' within the
* configuration class as well as for external calls to this configuration's
* {@code @Bean} methods, e.g. from another configuration class. If this is not needed
* since each of this particular configuration's {@code @Bean} methods is
* self-contained and designed as a plain factory method for container use, switch
* this flag to {@code false} in order to avoid CGLIB subclass processing.
* <p>
* Turning off bean method interception effectively processes {@code @Bean} methods
* individually like when declared on non-{@code @Configuration} classes, a.k.a.
* "@Bean Lite Mode" (see {@link Bean @Bean's javadoc}). It is therefore behaviorally
* equivalent to removing the {@code @Configuration} stereotype.
* @since 2.2
* @return whether to proxy {@code @Bean} methods
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
使用这个注解后,会触发自动配置( auto-configuration )和 组件扫描 ( component scanning ),这跟使用 @Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration 和 @ComponentScan 三个注解的作用是一样的。但是由于@SpringBootApplication会扫描当前、以及子包下的所有文件,导致做给开发带来方便的同时,也会有三方面的影响:
- 会导致项目启动时间变长,当启动一个大的应用程序,或将做大量的集成测试启动应用程序时,影响会特别明显;
- 会加载一些不需要的多余的实例(beans);
- 会增加 CPU 消耗;
针对以上三个情况,我们可以移除 @SpringBootApplication,然后使用 @Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration 和 @ComponentScan注解来扫描特定的包。
2.2、Spring Boot JVM参数调优
关于Jvm调优Oracle官网有一份指导说明: Oracle官网对Jvm调优的说明, 有兴趣大家可以去看看。
调优策略:初始化堆内存与最大堆相同,减少垃圾回收次数。
两种方法:内部启动和外部启动
(1)、内部启动
实例参数-XX:+PrintGCDetails -Xmx32M -Xms1M
打印GC日志,设置最大堆内存32M,初始堆内存32M
-Xms :设置Java堆栈的初始化大小
-Xmx :设置最大的java堆大小
测试:
第一步,在项目运行,编辑结构中配置参数:

运行项目,查看回收次数:

这样配置后,GC回收次数非常多。
更改堆大小后,-XX:+PrintGCDetails -Xmx256M -Xms256M ,GC回收次数减少:

我们可以使用jconsole.exe工具查看堆内存使用情况:

(2)、外部启动
第一步,通过maven 项目打jar包,配置pom.xml:
<build> <plugins> <!-- 指定maven编译的jdk版本,如果不指定,maven3默认用jdk 1.5 maven2默认用jdk1.3 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> <!-- 使用maven-jar-plugin将指定包目录打成单独的jar包 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> <!-- SpringBoot 项目借由 spring-boot-maven-plugin 插件,通过 Maven 将项目打包成可执行的 JAR(Fat Jar) 或者 WAR,由此插件生成的 Jar 包 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
使用maven打包,如图:

最终生成spring-boot-helloworld-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar,执行如下命令:
java -server -Xms32m -Xmx232m -jar spring-boot-helloworld-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar

2.3、Spring Boot使用undertow代替tomcat
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<!-- 为什么不需要版本号,在parent里面已经封装好了版本号 -->
<exclusions>
<!-- 移除内嵌tomcat -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
然后,添加undertow依赖:
<!-- 引入undertow --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId> </dependency>
下面我们使用jMetter工具来测试udertow和tomcat的吞吐量,jMeter的使用可以参考博客:JMeter性能测试,完整入门篇;
|
服务器名称 |
第一次运行 |
第二次运行 |
第三次运行 |
平均值 |
|
tomcat |
8203 |
8190 |
7955 |
8116 |
|
undertow |
7097 |
7434 |
7462 |
7331 |
三、发布打包
目前,前后端分离的架构已成主流,因此使用springboot构建应用是非常快速的,项目发布到服务器上的时候,只需要打成一个jar包,然后通过命令 : java -server jar包名称即可启动服务了;
在2.3节中我们已经介绍了Jar类型打包方式,这里就不重复介绍了,这里主要介绍一下war类型打包方式。
3.1、修改pom文件
修改默认打包类型:
<groupId>com.zy.example</groupId> <artifactId>springboot-atomikos</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <packaging>war</packaging>
添加servlet-api依赖:
<!-- 添加servlet-api的依赖,用来打war包 --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>
3.2、排除Spring Boot内置tomcat
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <!-- 为什么不需要版本号,在parent里面已经封装好了版本号 --> <!-- 排除内置tomcat --> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency>
3.3、改造启动类
修改App.java:
package com.zy.example; import com.zy.example.config.DBConfig1; import com.zy.example.config.DBConfig2; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.support.SpringBootServletInitializer; /** * 启动代码 打包成war、使用外置tomcat启动 * * @author zy * @since 2020-2-2 */ @SpringBootApplication //开启读取配置文件 @EnableConfigurationProperties(value = { DBConfig1.class, DBConfig2.class }) public class App extends SpringBootServletInitializer { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(App.class,args); } @Override protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) { return builder.sources(App.class); } }
3.4、pom指定maven打包插件(不指定则使用默认的)
<build> <plugins> <!-- 指定maven编译的jdk版本,如果不指定,maven3默认用jdk 1.5 maven2默认用jdk1.3 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>1.8</source> <target>1.8</target> </configuration> </plugin> <!-- 使用maven-war-plugin将指定包目录打成单独的war包 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> <!-- SpringBoot 项目借由 spring-boot-maven-plugin 插件,通过 Maven 将项目打包成可执行的 JAR(Fat Jar) 或者 WAR --> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
3.5、打包
在idea环境下,依次执行clean、install:

执行完毕后,可以看到war包已经生成了,默认是在target目录下:

3.6、IDEA使用tomcat进行部署启动
IDEA编译器点击右上角Edit Configurations、新增tomcat server:
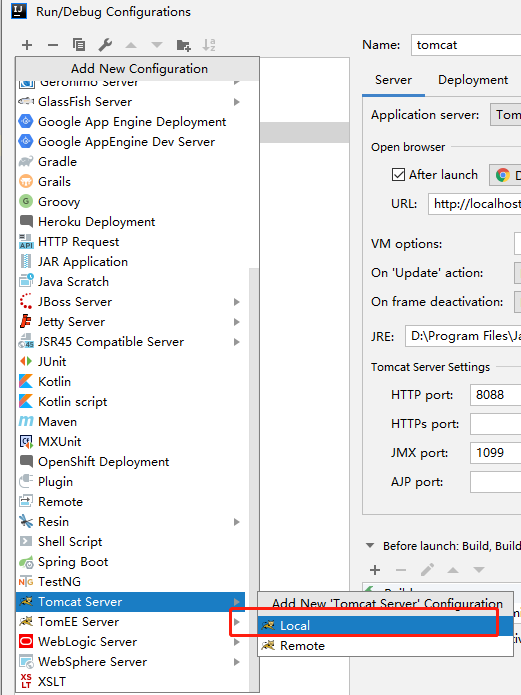
配置如下信息,指定启动端口和访问的路径:

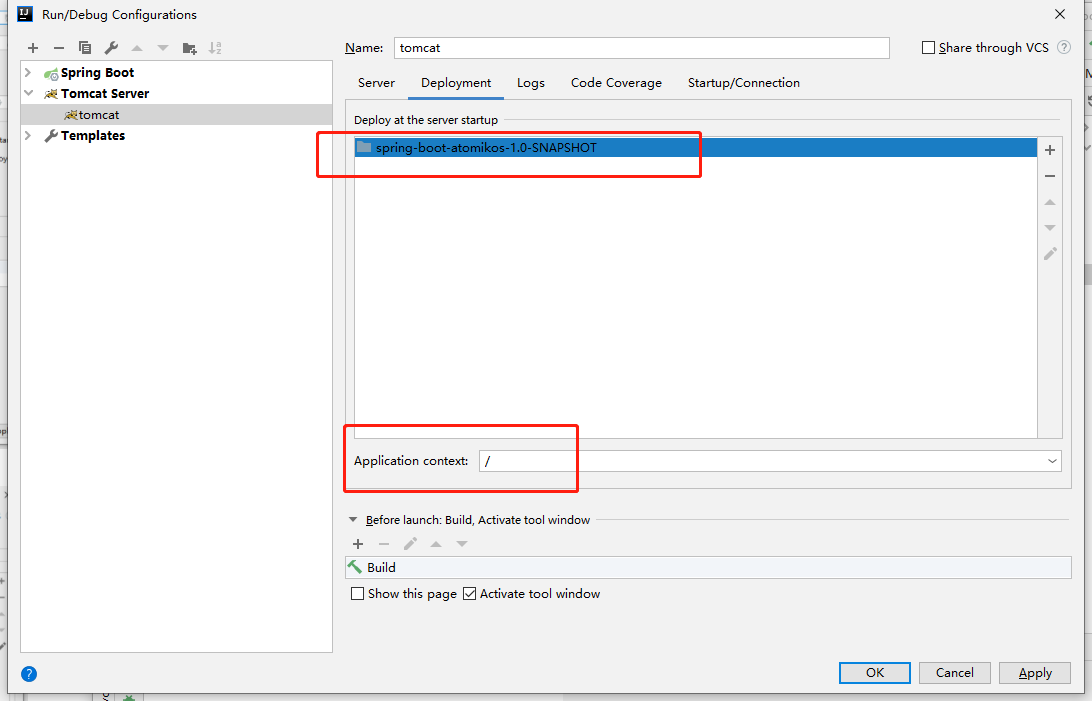
点击Deployment,添加war包:
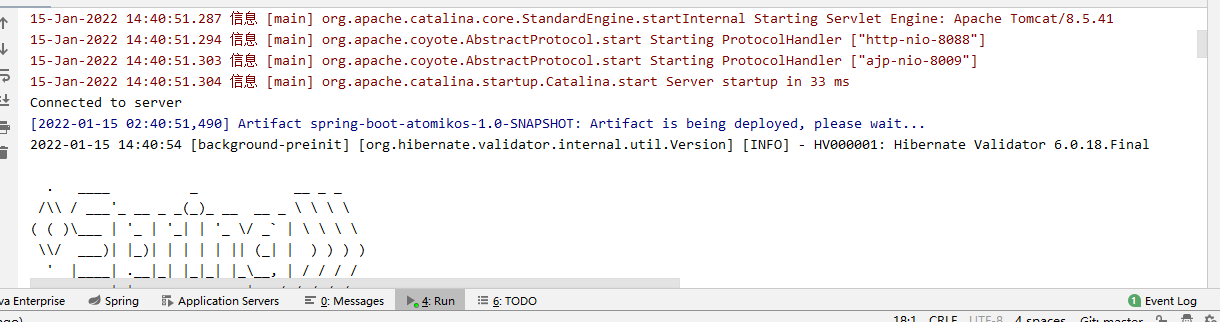
然后启动tomcat:
项目启动的时候出现了乱码,解决办法如下,添加配置,-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8即可:
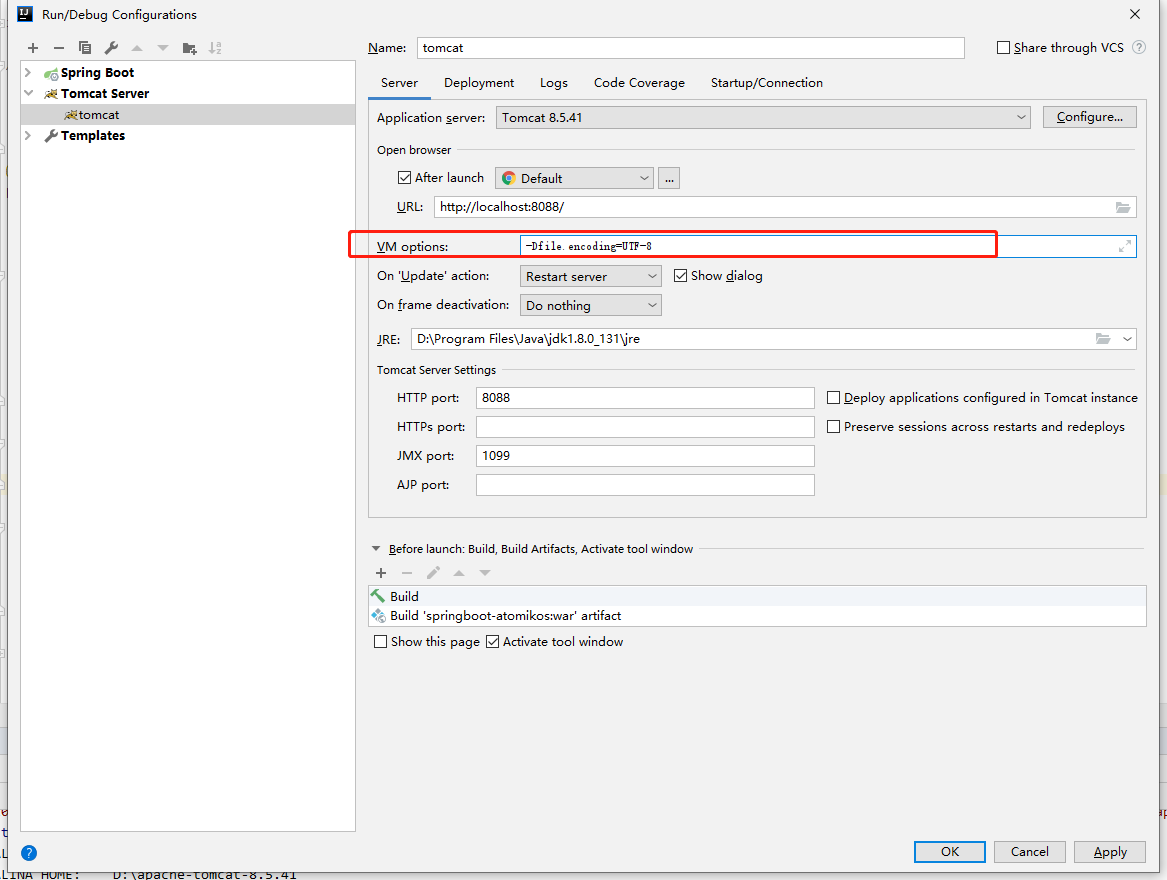
重新启动tomcat、访问http://localhost:8088/getStudent01?id=1即可。
3.7、直接使用tomcat部署
如果我们不想使用IDEA工具进行部署,我们可以将war直接拷贝到tomcat安装路径下的webapps下:
修改conf/server.xml文件,通过port修改端口号:
<!-- A "Connector" represents an endpoint by which requests are received
and responses are returned. Documentation at :
Java HTTP Connector: /docs/config/http.html
Java AJP Connector: /docs/config/ajp.html
APR (HTTP/AJP) Connector: /docs/apr.html
Define a non-SSL/TLS HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8080
-->
<Connector connectionTimeout="20000" port="8888" protocol="HTTP/1.1" redirectPort="8443"/>
然后我们需要定义上下文,通过在conf/server.xml文件中添加Context元素,每个Context元素代表了运行在虚拟主机上的单个Web应用,一个Host可以包含多个Context元素,每个Web应用有唯一的一个相对应的Context代表Web应用自身。
我们在Host元素下创建一个Context元素,并给上下文路径定义path属性,如下:
<Host appBase="webapps" autoDeploy="true" name="localhost" unpackWARs="true">
<!-- SingleSignOn valve, share authentication between web applications
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html -->
<!--
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.authenticator.SingleSignOn" />
-->
<!-- Access log processes all example.
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html
Note: The pattern used is equivalent to using pattern="common" -->
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs" pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".txt"/>
<Context docBase="D:\apache-tomcat-8.5.41\webapps\springboot-atomikos-1.0-SNAPSHOT.war" path="" reloadable="true"/>
</Host>
- appBase : 指 定虚拟主机的目录,可以指定绝对目录,也可以指定相对于<CATALINA_HOME>的相对目录.如果没有此项,默认 为<CATALINA_HOME>/webapps.,它将匹配请求URL和自己的Context的路径,并把请求转交给对应的Context来处理;
- path:指定访问该Web应用的URL入口;
- docBase:指定Web应用的文件路径,可以给定绝对路径,也可以给定相对于<Host>的appBase属性的相对路径,如果Web应用采用开放目录结构,则指定Web应用的根目录,如果Web应用是个war文件,则指定war文件的路径;
- reloadable:如果这个属性设为true,tomcat服务器在运行状态下会监视在WEB-INF/classes和WEB-INF/lib目录下class文件的改动,如果监测到有class文件被更新的,服务器会自动重新加载Web应用;
进入tomcat安装目录下bin文件,双击运行startup.bat文件(windows)或startup.sh文件(UNIX/Linux/Mac OS)来启动Tomcat:
然后访问http://localhost:8888/getStudent01?id=1即可:

四、源码下载
源码放置在gitee:
参考文章:
[1] IDEA新建springboot选择DevTools
[4] 简述GC回收机制



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号