Spring MVC -- Spring MVC入门
本篇博客首先介绍Spring MVC的优点,然后介绍Spring MVC的基本组件,包括DispatcherServlet,并学习如何开发一个“传统风格”的控制器,这是在Spring 2.5版本之前开发控制器的唯一方式。之所以介绍传统方式,是因为我们可能不得不在基于旧版Spring的遗留代码上工作。对于新的应用,我们可以采用基于注解的控制器。
此外,还会介绍Sping MVC配置,大部分的Spring MVC应用会采用一个XML文档来定义应用中所用到的bean(Spring管理的对象称为bean)。更多Spring MVC配置文件的信息可以参考博客Spring MVC -- Spring框架入门(IoC、DI以及XML配置文件)。
一 Spring MVC的优点
若采用Spring MVC框架开发一个应用程序,我们通常要负责编写一个DispatcherServlet(实际上就是一个Servlet控制器,实现了抽象类HttpServlet)和控制类(注意这里的控制类不是指的Servlet控制器,而是指实现了Controller接口的类,后面会详细介绍)。其中,DispatcherServlet必须能够做一下事情:
- 根据URL调用相应的action;
- 实例化正确的控制器类;
- 根据页面请求参数值来构造表单bean;
- 调用控制器对象的相应方法;
- 转到一个试图(jsp页面)。
幸运的是,Spring MVC是一个包含了DispatcherServlet的MVC框架。它调用控制器方法并转发到视图。使用Spring MVC的第一个好处是,不需要编写DispatcherServlet。以下是Spring MVC具有的能加速开发的功能的列表:
- Spring MVC提供了一个DispatcherServlet,无需额外开发;
- Spring MVC使用了基于XML的配置文件,可以编辑,而无需重新编译应用程序;
- Spring MVC实例化控制器,并根据用户输入来构造bean;
- Spring MVC可以自动绑定用户输入,并正确地转换数据类型。例如,Spring MVC能自动解析字符串,并设置float或decimal类型的属性;
- Spring MVC可以校验用户输入,若校验不通过,则重定向回输入表单。输入校验是可选的,支持编程方式及声明方式。关于这一点,Spring MVC内置了常见的校验器;
- Spring MVC是Spring框架的一部分,可以利用Spring提供的其它能力;
- Spring MVC支持国际化和本地化,支持根据用户区域显示多国语言;
- Spring MVC支持多种视图技术。最常见的jsp技术以及其他技术包括Velocity和FreeMarker。
二 Spring MVC基本组件
1、Spring MVC的DispatcherServlet
在Spring MVC -- MVC设计模式(演示4个基于MVC框架的案例)中我们创建了一个简单的基于MVC框架的Web应用,应用中包括一个充当调度员的控制器(servlet或者是filter)。基于Spring MVC,则无需如此。Spring MVC中自带了一个开箱即用的DispatcherServlet,该servlei全名是org.springframework.web.servlet.DispacterServlet。源码如下,有兴趣可以看一下:

/* * Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.web.servlet; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import javax.servlet.DispatcherType; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContext; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderUtils; import org.springframework.core.log.LogFormatUtils; import org.springframework.http.server.ServletServerHttpRequest; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.ui.context.ThemeSource; import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletWebRequest; import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManager; import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncUtils; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartException; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartHttpServletRequest; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartResolver; import org.springframework.web.util.NestedServletException; import org.springframework.web.util.WebUtils; /** * Central dispatcher for HTTP request handlers/controllers, e.g. for web UI controllers * or HTTP-based remote service exporters. Dispatches to registered handlers for processing * a web request, providing convenient mapping and exception handling facilities. * * <p>This servlet is very flexible: It can be used with just about any workflow, with the * installation of the appropriate adapter classes. It offers the following functionality * that distinguishes it from other request-driven web MVC frameworks: * * <ul> * <li>It is based around a JavaBeans configuration mechanism. * * <li>It can use any {@link HandlerMapping} implementation - pre-built or provided as part * of an application - to control the routing of requests to handler objects. Default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping} and * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping}. * HandlerMapping objects can be defined as beans in the servlet's application context, * implementing the HandlerMapping interface, overriding the default HandlerMapping if * present. HandlerMappings can be given any bean name (they are tested by type). * * <li>It can use any {@link HandlerAdapter}; this allows for using any handler interface. * Default adapters are {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter}, * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter}, for Spring's * {@link org.springframework.web.HttpRequestHandler} and * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller} interfaces, respectively. A default * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter} * will be registered as well. HandlerAdapter objects can be added as beans in the * application context, overriding the default HandlerAdapters. Like HandlerMappings, * HandlerAdapters can be given any bean name (they are tested by type). * * <li>The dispatcher's exception resolution strategy can be specified via a * {@link HandlerExceptionResolver}, for example mapping certain exceptions to error pages. * Default are * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver}, * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver}, and * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver}. * These HandlerExceptionResolvers can be overridden through the application context. * HandlerExceptionResolver can be given any bean name (they are tested by type). * * <li>Its view resolution strategy can be specified via a {@link ViewResolver} * implementation, resolving symbolic view names into View objects. Default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver}. * ViewResolver objects can be added as beans in the application context, overriding the * default ViewResolver. ViewResolvers can be given any bean name (they are tested by type). * * <li>If a {@link View} or view name is not supplied by the user, then the configured * {@link RequestToViewNameTranslator} will translate the current request into a view name. * The corresponding bean name is "viewNameTranslator"; the default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator}. * * <li>The dispatcher's strategy for resolving multipart requests is determined by a * {@link org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartResolver} implementation. * Implementations for Apache Commons FileUpload and Servlet 3 are included; the typical * choice is {@link org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver}. * The MultipartResolver bean name is "multipartResolver"; default is none. * * <li>Its locale resolution strategy is determined by a {@link LocaleResolver}. * Out-of-the-box implementations work via HTTP accept header, cookie, or session. * The LocaleResolver bean name is "localeResolver"; default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver}. * * <li>Its theme resolution strategy is determined by a {@link ThemeResolver}. * Implementations for a fixed theme and for cookie and session storage are included. * The ThemeResolver bean name is "themeResolver"; default is * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver}. * </ul> * * <p><b>NOTE: The {@code @RequestMapping} annotation will only be processed if a * corresponding {@code HandlerMapping} (for type-level annotations) and/or * {@code HandlerAdapter} (for method-level annotations) is present in the dispatcher.</b> * This is the case by default. However, if you are defining custom {@code HandlerMappings} * or {@code HandlerAdapters}, then you need to make sure that a corresponding custom * {@code RequestMappingHandlerMapping} and/or {@code RequestMappingHandlerAdapter} * is defined as well - provided that you intend to use {@code @RequestMapping}. * * <p><b>A web application can define any number of DispatcherServlets.</b> * Each servlet will operate in its own namespace, loading its own application context * with mappings, handlers, etc. Only the root application context as loaded by * {@link org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener}, if any, will be shared. * * <p>As of Spring 3.1, {@code DispatcherServlet} may now be injected with a web * application context, rather than creating its own internally. This is useful in Servlet * 3.0+ environments, which support programmatic registration of servlet instances. * See the {@link #DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext)} javadoc for details. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Rob Harrop * @author Chris Beams * @author Rossen Stoyanchev * @see org.springframework.web.HttpRequestHandler * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller * @see org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener */ @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet { /** Well-known name for the MultipartResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "multipartResolver"; /** Well-known name for the LocaleResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "localeResolver"; /** Well-known name for the ThemeResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "themeResolver"; /** * Well-known name for the HandlerMapping object in the bean factory for this namespace. * Only used when "detectAllHandlerMappings" is turned off. * @see #setDetectAllHandlerMappings */ public static final String HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME = "handlerMapping"; /** * Well-known name for the HandlerAdapter object in the bean factory for this namespace. * Only used when "detectAllHandlerAdapters" is turned off. * @see #setDetectAllHandlerAdapters */ public static final String HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME = "handlerAdapter"; /** * Well-known name for the HandlerExceptionResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. * Only used when "detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers" is turned off. * @see #setDetectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers */ public static final String HANDLER_EXCEPTION_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "handlerExceptionResolver"; /** * Well-known name for the RequestToViewNameTranslator object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME = "viewNameTranslator"; /** * Well-known name for the ViewResolver object in the bean factory for this namespace. * Only used when "detectAllViewResolvers" is turned off. * @see #setDetectAllViewResolvers */ public static final String VIEW_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME = "viewResolver"; /** * Well-known name for the FlashMapManager object in the bean factory for this namespace. */ public static final String FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME = "flashMapManager"; /** * Request attribute to hold the current web application context. * Otherwise only the global web app context is obtainable by tags etc. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#findWebApplicationContext */ public static final String WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".CONTEXT"; /** * Request attribute to hold the current LocaleResolver, retrievable by views. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getLocaleResolver */ public static final String LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".LOCALE_RESOLVER"; /** * Request attribute to hold the current ThemeResolver, retrievable by views. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getThemeResolver */ public static final String THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".THEME_RESOLVER"; /** * Request attribute to hold the current ThemeSource, retrievable by views. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getThemeSource */ public static final String THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".THEME_SOURCE"; /** * Name of request attribute that holds a read-only {@code Map<String,?>} * with "input" flash attributes saved by a previous request, if any. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getInputFlashMap(HttpServletRequest) */ public static final String INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".INPUT_FLASH_MAP"; /** * Name of request attribute that holds the "output" {@link FlashMap} with * attributes to save for a subsequent request. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getOutputFlashMap(HttpServletRequest) */ public static final String OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP"; /** * Name of request attribute that holds the {@link FlashMapManager}. * @see org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils#getFlashMapManager(HttpServletRequest) */ public static final String FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".FLASH_MAP_MANAGER"; /** * Name of request attribute that exposes an Exception resolved with an * {@link HandlerExceptionResolver} but where no view was rendered * (e.g. setting the status code). */ public static final String EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE = DispatcherServlet.class.getName() + ".EXCEPTION"; /** Log category to use when no mapped handler is found for a request. */ public static final String PAGE_NOT_FOUND_LOG_CATEGORY = "org.springframework.web.servlet.PageNotFound"; /** * Name of the class path resource (relative to the DispatcherServlet class) * that defines DispatcherServlet's default strategy names. */ private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "DispatcherServlet.properties"; /** * Common prefix that DispatcherServlet's default strategy attributes start with. */ private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX = "org.springframework.web.servlet"; /** Additional logger to use when no mapped handler is found for a request. */ protected static final Log pageNotFoundLogger = LogFactory.getLog(PAGE_NOT_FOUND_LOG_CATEGORY); private static final Properties defaultStrategies; static { // Load default strategy implementations from properties file. // This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized // by application developers. try { ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class); defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load '" + DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH + "': " + ex.getMessage()); } } /** Detect all HandlerMappings or just expect "handlerMapping" bean?. */ private boolean detectAllHandlerMappings = true; /** Detect all HandlerAdapters or just expect "handlerAdapter" bean?. */ private boolean detectAllHandlerAdapters = true; /** Detect all HandlerExceptionResolvers or just expect "handlerExceptionResolver" bean?. */ private boolean detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers = true; /** Detect all ViewResolvers or just expect "viewResolver" bean?. */ private boolean detectAllViewResolvers = true; /** Throw a NoHandlerFoundException if no Handler was found to process this request? *.*/ private boolean throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound = false; /** Perform cleanup of request attributes after include request?. */ private boolean cleanupAfterInclude = true; /** MultipartResolver used by this servlet. */ @Nullable private MultipartResolver multipartResolver; /** LocaleResolver used by this servlet. */ @Nullable private LocaleResolver localeResolver; /** ThemeResolver used by this servlet. */ @Nullable private ThemeResolver themeResolver; /** List of HandlerMappings used by this servlet. */ @Nullable private List<HandlerMapping> handlerMappings; /** List of HandlerAdapters used by this servlet. */ @Nullable private List<HandlerAdapter> handlerAdapters; /** List of HandlerExceptionResolvers used by this servlet. */ @Nullable private List<HandlerExceptionResolver> handlerExceptionResolvers; /** RequestToViewNameTranslator used by this servlet. */ @Nullable private RequestToViewNameTranslator viewNameTranslator; /** FlashMapManager used by this servlet. */ @Nullable private FlashMapManager flashMapManager; /** List of ViewResolvers used by this servlet. */ @Nullable private List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers; /** * Create a new {@code DispatcherServlet} that will create its own internal web * application context based on defaults and values provided through servlet * init-params. Typically used in Servlet 2.5 or earlier environments, where the only * option for servlet registration is through {@code web.xml} which requires the use * of a no-arg constructor. * <p>Calling {@link #setContextConfigLocation} (init-param 'contextConfigLocation') * will dictate which XML files will be loaded by the * {@linkplain #DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS default XmlWebApplicationContext} * <p>Calling {@link #setContextClass} (init-param 'contextClass') overrides the * default {@code XmlWebApplicationContext} and allows for specifying an alternative class, * such as {@code AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext}. * <p>Calling {@link #setContextInitializerClasses} (init-param 'contextInitializerClasses') * indicates which {@code ApplicationContextInitializer} classes should be used to * further configure the internal application context prior to refresh(). * @see #DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) */ public DispatcherServlet() { super(); setDispatchOptionsRequest(true); } /** * Create a new {@code DispatcherServlet} with the given web application context. This * constructor is useful in Servlet 3.0+ environments where instance-based registration * of servlets is possible through the {@link ServletContext#addServlet} API. * <p>Using this constructor indicates that the following properties / init-params * will be ignored: * <ul> * <li>{@link #setContextClass(Class)} / 'contextClass'</li> * <li>{@link #setContextConfigLocation(String)} / 'contextConfigLocation'</li> * <li>{@link #setContextAttribute(String)} / 'contextAttribute'</li> * <li>{@link #setNamespace(String)} / 'namespace'</li> * </ul> * <p>The given web application context may or may not yet be {@linkplain * ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh() refreshed}. If it has <strong>not</strong> * already been refreshed (the recommended approach), then the following will occur: * <ul> * <li>If the given context does not already have a {@linkplain * ConfigurableApplicationContext#setParent parent}, the root application context * will be set as the parent.</li> * <li>If the given context has not already been assigned an {@linkplain * ConfigurableApplicationContext#setId id}, one will be assigned to it</li> * <li>{@code ServletContext} and {@code ServletConfig} objects will be delegated to * the application context</li> * <li>{@link #postProcessWebApplicationContext} will be called</li> * <li>Any {@code ApplicationContextInitializer}s specified through the * "contextInitializerClasses" init-param or through the {@link * #setContextInitializers} property will be applied.</li> * <li>{@link ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh refresh()} will be called if the * context implements {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext}</li> * </ul> * If the context has already been refreshed, none of the above will occur, under the * assumption that the user has performed these actions (or not) per their specific * needs. * <p>See {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer} for usage examples. * @param webApplicationContext the context to use * @see #initWebApplicationContext * @see #configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext * @see org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer */ public DispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext) { super(webApplicationContext); setDispatchOptionsRequest(true); } /** * Set whether to detect all HandlerMapping beans in this servlet's context. Otherwise, * just a single bean with name "handlerMapping" will be expected. * <p>Default is "true". Turn this off if you want this servlet to use a single * HandlerMapping, despite multiple HandlerMapping beans being defined in the context. */ public void setDetectAllHandlerMappings(boolean detectAllHandlerMappings) { this.detectAllHandlerMappings = detectAllHandlerMappings; } /** * Set whether to detect all HandlerAdapter beans in this servlet's context. Otherwise, * just a single bean with name "handlerAdapter" will be expected. * <p>Default is "true". Turn this off if you want this servlet to use a single * HandlerAdapter, despite multiple HandlerAdapter beans being defined in the context. */ public void setDetectAllHandlerAdapters(boolean detectAllHandlerAdapters) { this.detectAllHandlerAdapters = detectAllHandlerAdapters; } /** * Set whether to detect all HandlerExceptionResolver beans in this servlet's context. Otherwise, * just a single bean with name "handlerExceptionResolver" will be expected. * <p>Default is "true". Turn this off if you want this servlet to use a single * HandlerExceptionResolver, despite multiple HandlerExceptionResolver beans being defined in the context. */ public void setDetectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers(boolean detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers) { this.detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers = detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers; } /** * Set whether to detect all ViewResolver beans in this servlet's context. Otherwise, * just a single bean with name "viewResolver" will be expected. * <p>Default is "true". Turn this off if you want this servlet to use a single * ViewResolver, despite multiple ViewResolver beans being defined in the context. */ public void setDetectAllViewResolvers(boolean detectAllViewResolvers) { this.detectAllViewResolvers = detectAllViewResolvers; } /** * Set whether to throw a NoHandlerFoundException when no Handler was found for this request. * This exception can then be caught with a HandlerExceptionResolver or an * {@code @ExceptionHandler} controller method. * <p>Note that if {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.DefaultServletHttpRequestHandler} * is used, then requests will always be forwarded to the default servlet and a * NoHandlerFoundException would never be thrown in that case. * <p>Default is "false", meaning the DispatcherServlet sends a NOT_FOUND error through the * Servlet response. * @since 4.0 */ public void setThrowExceptionIfNoHandlerFound(boolean throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound) { this.throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound = throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound; } /** * Set whether to perform cleanup of request attributes after an include request, that is, * whether to reset the original state of all request attributes after the DispatcherServlet * has processed within an include request. Otherwise, just the DispatcherServlet's own * request attributes will be reset, but not model attributes for JSPs or special attributes * set by views (for example, JSTL's). * <p>Default is "true", which is strongly recommended. Views should not rely on request attributes * having been set by (dynamic) includes. This allows JSP views rendered by an included controller * to use any model attributes, even with the same names as in the main JSP, without causing side * effects. Only turn this off for special needs, for example to deliberately allow main JSPs to * access attributes from JSP views rendered by an included controller. */ public void setCleanupAfterInclude(boolean cleanupAfterInclude) { this.cleanupAfterInclude = cleanupAfterInclude; } /** * This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}. */ @Override protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } /** * Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses. * <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects. */ protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); } /** * Initialize the MultipartResolver used by this class. * <p>If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * no multipart handling is provided. */ private void initMultipartResolver(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.multipartResolver = context.getBean(MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, MultipartResolver.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Detected " + this.multipartResolver); } else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Detected " + this.multipartResolver.getClass().getSimpleName()); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Default is no multipart resolver. this.multipartResolver = null; if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No MultipartResolver '" + MULTIPART_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME + "' declared"); } } } /** * Initialize the LocaleResolver used by this class. * <p>If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver. */ private void initLocaleResolver(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.localeResolver = context.getBean(LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, LocaleResolver.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Detected " + this.localeResolver); } else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Detected " + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName()); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // We need to use the default. this.localeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, LocaleResolver.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No LocaleResolver '" + LOCALE_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.localeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]"); } } } /** * Initialize the ThemeResolver used by this class. * <p>If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to a FixedThemeResolver. */ private void initThemeResolver(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.themeResolver = context.getBean(THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, ThemeResolver.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Detected " + this.themeResolver); } else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Detected " + this.themeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName()); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // We need to use the default. this.themeResolver = getDefaultStrategy(context, ThemeResolver.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No ThemeResolver '" + THEME_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.themeResolver.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]"); } } } /** * Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class. * <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping. */ private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { // Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later. } } // Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering // a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found. if (this.handlerMappings == null) { this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties"); } } } /** * Initialize the HandlerAdapters used by this class. * <p>If no HandlerAdapter beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter. */ private void initHandlerAdapters(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerAdapters = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerAdapters) { // Find all HandlerAdapters in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerAdapter> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerAdapter.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerAdapters = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerAdapters in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerAdapters); } } else { try { HandlerAdapter ha = context.getBean(HANDLER_ADAPTER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerAdapter.class); this.handlerAdapters = Collections.singletonList(ha); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerAdapter later. } } // Ensure we have at least some HandlerAdapters, by registering // default HandlerAdapters if no other adapters are found. if (this.handlerAdapters == null) { this.handlerAdapters = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerAdapter.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No HandlerAdapters declared for servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties"); } } } /** * Initialize the HandlerExceptionResolver used by this class. * <p>If no bean is defined with the given name in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to no exception resolver. */ private void initHandlerExceptionResolvers(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerExceptionResolvers = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerExceptionResolvers) { // Find all HandlerExceptionResolvers in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, HandlerExceptionResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils .beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerExceptionResolvers = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep HandlerExceptionResolvers in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerExceptionResolvers); } } else { try { HandlerExceptionResolver her = context.getBean(HANDLER_EXCEPTION_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, HandlerExceptionResolver.class); this.handlerExceptionResolvers = Collections.singletonList(her); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, no HandlerExceptionResolver is fine too. } } // Ensure we have at least some HandlerExceptionResolvers, by registering // default HandlerExceptionResolvers if no other resolvers are found. if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers == null) { this.handlerExceptionResolvers = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerExceptionResolver.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No HandlerExceptionResolvers declared in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties"); } } } /** * Initialize the RequestToViewNameTranslator used by this servlet instance. * <p>If no implementation is configured then we default to DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator. */ private void initRequestToViewNameTranslator(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.viewNameTranslator = context.getBean(REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Detected " + this.viewNameTranslator.getClass().getSimpleName()); } else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Detected " + this.viewNameTranslator); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // We need to use the default. this.viewNameTranslator = getDefaultStrategy(context, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No RequestToViewNameTranslator '" + REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.viewNameTranslator.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]"); } } } /** * Initialize the ViewResolvers used by this class. * <p>If no ViewResolver beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this * namespace, we default to InternalResourceViewResolver. */ private void initViewResolvers(ApplicationContext context) { this.viewResolvers = null; if (this.detectAllViewResolvers) { // Find all ViewResolvers in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts. Map<String, ViewResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, ViewResolver.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values()); // We keep ViewResolvers in sorted order. AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.viewResolvers); } } else { try { ViewResolver vr = context.getBean(VIEW_RESOLVER_BEAN_NAME, ViewResolver.class); this.viewResolvers = Collections.singletonList(vr); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default ViewResolver later. } } // Ensure we have at least one ViewResolver, by registering // a default ViewResolver if no other resolvers are found. if (this.viewResolvers == null) { this.viewResolvers = getDefaultStrategies(context, ViewResolver.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No ViewResolvers declared for servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties"); } } } /** * Initialize the {@link FlashMapManager} used by this servlet instance. * <p>If no implementation is configured then we default to * {@code org.springframework.web.servlet.support.DefaultFlashMapManager}. */ private void initFlashMapManager(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.flashMapManager = context.getBean(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME, FlashMapManager.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Detected " + this.flashMapManager.getClass().getSimpleName()); } else if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Detected " + this.flashMapManager); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // We need to use the default. this.flashMapManager = getDefaultStrategy(context, FlashMapManager.class); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No FlashMapManager '" + FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.flashMapManager.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]"); } } } /** * Return this servlet's ThemeSource, if any; else return {@code null}. * <p>Default is to return the WebApplicationContext as ThemeSource, * provided that it implements the ThemeSource interface. * @return the ThemeSource, if any * @see #getWebApplicationContext() */ @Nullable public final ThemeSource getThemeSource() { return (getWebApplicationContext() instanceof ThemeSource ? (ThemeSource) getWebApplicationContext() : null); } /** * Obtain this servlet's MultipartResolver, if any. * @return the MultipartResolver used by this servlet, or {@code null} if none * (indicating that no multipart support is available) */ @Nullable public final MultipartResolver getMultipartResolver() { return this.multipartResolver; } /** * Return the configured {@link HandlerMapping} beans that were detected by * type in the {@link WebApplicationContext} or initialized based on the * default set of strategies from {@literal DispatcherServlet.properties}. * <p><strong>Note:</strong> This method may return {@code null} if invoked * prior to {@link #onRefresh(ApplicationContext)}. * @return an immutable list with the configured mappings, or {@code null} * if not initialized yet * @since 5.0 */ @Nullable public final List<HandlerMapping> getHandlerMappings() { return (this.handlerMappings != null ? Collections.unmodifiableList(this.handlerMappings) : null); } /** * Return the default strategy object for the given strategy interface. * <p>The default implementation delegates to {@link #getDefaultStrategies}, * expecting a single object in the list. * @param context the current WebApplicationContext * @param strategyInterface the strategy interface * @return the corresponding strategy object * @see #getDefaultStrategies */ protected <T> T getDefaultStrategy(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { List<T> strategies = getDefaultStrategies(context, strategyInterface); if (strategies.size() != 1) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "DispatcherServlet needs exactly 1 strategy for interface [" + strategyInterface.getName() + "]"); } return strategies.get(0); } /** * Create a List of default strategy objects for the given strategy interface. * <p>The default implementation uses the "DispatcherServlet.properties" file (in the same * package as the DispatcherServlet class) to determine the class names. It instantiates * the strategy objects through the context's BeanFactory. * @param context the current WebApplicationContext * @param strategyInterface the strategy interface * @return the List of corresponding strategy objects */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies(ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { String key = strategyInterface.getName(); String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key); if (value != null) { String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value); List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<>(classNames.length); for (String className : classNames) { try { Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader()); Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz); strategies.add((T) strategy); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + "] for interface [" + key + "]", ex); } catch (LinkageError err) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "Unresolvable class definition for DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + "] for interface [" + key + "]", err); } } return strategies; } else { return new LinkedList<>(); } } /** * Create a default strategy. * <p>The default implementation uses * {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean}. * @param context the current WebApplicationContext * @param clazz the strategy implementation class to instantiate * @return the fully configured strategy instance * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext#getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean */ protected Object createDefaultStrategy(ApplicationContext context, Class<?> clazz) { return context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().createBean(clazz); } /** * Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch} * for the actual dispatching. */ @Override protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { logRequest(request); // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); if (this.flashMapManager != null) { FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); } try { doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } } } private void logRequest(HttpServletRequest request) { LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> { String params; if (isEnableLoggingRequestDetails()) { params = request.getParameterMap().entrySet().stream() .map(entry -> entry.getKey() + ":" + Arrays.toString(entry.getValue())) .collect(Collectors.joining(", ")); } else { params = (request.getParameterMap().isEmpty() ? "" : "masked"); } String query = StringUtils.isEmpty(request.getQueryString()) ? "" : "?" + request.getQueryString(); String dispatchType = (!request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.REQUEST) ? "\"" + request.getDispatcherType().name() + "\" dispatch for " : ""); String message = (dispatchType + request.getMethod() + " \"" + getRequestUri(request) + query + "\", parameters={" + params + "}"); if (traceOn) { List<String> values = Collections.list(request.getHeaderNames()); String headers = values.size() > 0 ? "masked" : ""; if (isEnableLoggingRequestDetails()) { headers = values.stream().map(name -> name + ":" + Collections.list(request.getHeaders(name))) .collect(Collectors.joining(", ")); } return message + ", headers={" + headers + "} in DispatcherServlet '" + getServletName() + "'"; } else { return message; } }); } /** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */ protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } } /** * Do we need view name translation? */ private void applyDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndView mv) throws Exception { if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) { String defaultViewName = getDefaultViewName(request); if (defaultViewName != null) { mv.setViewName(defaultViewName); } } } /** * Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is * either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView. */ private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } // Did the handler return a view to render? if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned."); } } if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Concurrent handling started during a forward return; } if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); } } /** * Build a LocaleContext for the given request, exposing the request's primary locale as current locale. * <p>The default implementation uses the dispatcher's LocaleResolver to obtain the current locale, * which might change during a request. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the corresponding LocaleContext */ @Override protected LocaleContext buildLocaleContext(final HttpServletRequest request) { LocaleResolver lr = this.localeResolver; if (lr instanceof LocaleContextResolver) { return ((LocaleContextResolver) lr).resolveLocaleContext(request); } else { return () -> (lr != null ? lr.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale()); } } /** * Convert the request into a multipart request, and make multipart resolver available. * <p>If no multipart resolver is set, simply use the existing request. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the processed request (multipart wrapper if necessary) * @see MultipartResolver#resolveMultipart */ protected HttpServletRequest checkMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException { if (this.multipartResolver != null && this.multipartResolver.isMultipart(request)) { if (WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class) != null) { if (request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.REQUEST)) { logger.trace("Request already resolved to MultipartHttpServletRequest, e.g. by MultipartFilter"); } } else if (hasMultipartException(request)) { logger.debug("Multipart resolution previously failed for current request - " + "skipping re-resolution for undisturbed error rendering"); } else { try { return this.multipartResolver.resolveMultipart(request); } catch (MultipartException ex) { if (request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) != null) { logger.debug("Multipart resolution failed for error dispatch", ex); // Keep processing error dispatch with regular request handle below } else { throw ex; } } } } // If not returned before: return original request. return request; } /** * Check "javax.servlet.error.exception" attribute for a multipart exception. */ private boolean hasMultipartException(HttpServletRequest request) { Throwable error = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE); while (error != null) { if (error instanceof MultipartException) { return true; } error = error.getCause(); } return false; } /** * Clean up any resources used by the given multipart request (if any). * @param request current HTTP request * @see MultipartResolver#cleanupMultipart */ protected void cleanupMultipart(HttpServletRequest request) { if (this.multipartResolver != null) { MultipartHttpServletRequest multipartRequest = WebUtils.getNativeRequest(request, MultipartHttpServletRequest.class); if (multipartRequest != null) { this.multipartResolver.cleanupMultipart(multipartRequest); } } } /** * Return the HandlerExecutionChain for this request. * <p>Tries all handler mappings in order. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the HandlerExecutionChain, or {@code null} if no handler could be found */ @Nullable protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.handlerMappings != null) { for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) { HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } } return null; } /** * No handler found -> set appropriate HTTP response status. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception if preparing the response failed */ protected void noHandlerFound(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (pageNotFoundLogger.isWarnEnabled()) { pageNotFoundLogger.warn("No mapping for " + request.getMethod() + " " + getRequestUri(request)); } if (this.throwExceptionIfNoHandlerFound) { throw new NoHandlerFoundException(request.getMethod(), getRequestUri(request), new ServletServerHttpRequest(request).getHeaders()); } else { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND); } } /** * Return the HandlerAdapter for this handler object. * @param handler the handler object to find an adapter for * @throws ServletException if no HandlerAdapter can be found for the handler. This is a fatal error. */ protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { if (this.handlerAdapters != null) { for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) { if (adapter.supports(handler)) { return adapter; } } } throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler"); } /** * Determine an error ModelAndView via the registered HandlerExceptionResolvers. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @param handler the executed handler, or {@code null} if none chosen at the time of the exception * (for example, if multipart resolution failed) * @param ex the exception that got thrown during handler execution * @return a corresponding ModelAndView to forward to * @throws Exception if no error ModelAndView found */ @Nullable protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { // Success and error responses may use different content types request.removeAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE); // Check registered HandlerExceptionResolvers... ModelAndView exMv = null; if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) { for (HandlerExceptionResolver resolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) { exMv = resolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex); if (exMv != null) { break; } } } if (exMv != null) { if (exMv.isEmpty()) { request.setAttribute(EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE, ex); return null; } // We might still need view name translation for a plain error model... if (!exMv.hasView()) { String defaultViewName = getDefaultViewName(request); if (defaultViewName != null) { exMv.setViewName(defaultViewName); } } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Using resolved error view: " + exMv, ex); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using resolved error view: " + exMv); } WebUtils.exposeErrorRequestAttributes(request, ex, getServletName()); return exMv; } throw ex; } /** * Render the given ModelAndView. * <p>This is the last stage in handling a request. It may involve resolving the view by name. * @param mv the ModelAndView to render * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @param response current HTTP servlet response * @throws ServletException if view is missing or cannot be resolved * @throws Exception if there's a problem rendering the view */ protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { // Determine locale for request and apply it to the response. Locale locale = (this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale()); response.setLocale(locale); View view; String viewName = mv.getViewName(); if (viewName != null) { // We need to resolve the view name. view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() + "' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } } else { // No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object. view = mv.getView(); if (view == null) { throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " + "View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } } // Delegate to the View object for rendering. if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Rendering view [" + view + "] "); } try { if (mv.getStatus() != null) { response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value()); } view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response); } catch (Exception ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "]", ex); } throw ex; } } /** * Translate the supplied request into a default view name. * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @return the view name (or {@code null} if no default found) * @throws Exception if view name translation failed */ @Nullable protected String getDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { return (this.viewNameTranslator != null ? this.viewNameTranslator.getViewName(request) : null); } /** * Resolve the given view name into a View object (to be rendered). * <p>The default implementations asks all ViewResolvers of this dispatcher. * Can be overridden for custom resolution strategies, potentially based on * specific model attributes or request parameters. * @param viewName the name of the view to resolve * @param model the model to be passed to the view * @param locale the current locale * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @return the View object, or {@code null} if none found * @throws Exception if the view cannot be resolved * (typically in case of problems creating an actual View object) * @see ViewResolver#resolveViewName */ @Nullable protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, @Nullable Map<String, Object> model, Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.viewResolvers != null) { for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) { View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale); if (view != null) { return view; } } } return null; } private void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, Exception ex) throws Exception { if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, ex); } throw ex; } /** * Restore the request attributes after an include. * @param request current HTTP request * @param attributesSnapshot the snapshot of the request attributes before the include */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void restoreAttributesAfterInclude(HttpServletRequest request, Map<?, ?> attributesSnapshot) { // Need to copy into separate Collection here, to avoid side effects // on the Enumeration when removing attributes. Set<String> attrsToCheck = new HashSet<>(); Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) { attrsToCheck.add(attrName); } } // Add attributes that may have been removed attrsToCheck.addAll((Set<String>) attributesSnapshot.keySet()); // Iterate over the attributes to check, restoring the original value // or removing the attribute, respectively, if appropriate. for (String attrName : attrsToCheck) { Object attrValue = attributesSnapshot.get(attrName); if (attrValue == null) { request.removeAttribute(attrName); } else if (attrValue != request.getAttribute(attrName)) { request.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue); } } } private static String getRequestUri(HttpServletRequest request) { String uri = (String) request.getAttribute(WebUtils.INCLUDE_REQUEST_URI_ATTRIBUTE); if (uri == null) { uri = request.getRequestURI(); } return uri; } }
要使用这个servlet,需要在部署描述符文件(web.xml)中使用servlet和servlet-mapping元素来配置它,如下所示:
<servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
servlet元素内的load-on-startup元素是可选的,如果它存在,则它将在应用程序启动时装载该servlet并调用它的init()方法。若它不存在,则在该servlet第一个请求时加载它。
DispatcherServlet将使用Spring MVC诸多默认的组件。此外,初始化时,它会寻找在应用程序的WEB-INF目录下的一个配置文件,该配置文件的命名规则如下:
servletName-servlet.xml
其中,servletName是部署描述符中的DispatcherServlet的名称(上面配置的 <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>)。如果这个servlet的名称是springmvc,则应在应用程序目录的WEB-INF下对应的文件时springmvc-servlet.xml。
此外,也可以把Spring MVC的配置文件放在应用程序目录中的任何地方,只要告诉DispatcherServlet在哪里可以找到该文件。我们使用servlet声明下的一个init-param元素来做到这一点。init-param元素拥有一个值为contextConfigLocation的param-name元素,其param-value元素则包含配置文件的路径。例如,可以利用init-param元素将默认的文件名和文件路径更改为/WEB-INF/config/simple-config.xml。
<servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/config/simple-config.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
2、Controller接口
在Spring 2.5之前,开发一个控制器的唯一方法是实现org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller接口。源码如下:

/* * Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; /** * Base Controller interface, representing a component that receives * {@code HttpServletRequest} and {@code HttpServletResponse} * instances just like a {@code HttpServlet} but is able to * participate in an MVC workflow. Controllers are comparable to the * notion of a Struts {@code Action}. * * <p>Any implementation of the Controller interface should be a * <i>reusable, thread-safe</i> class, capable of handling multiple * HTTP requests throughout the lifecycle of an application. To be able to * configure a Controller easily, Controller implementations are encouraged * to be (and usually are) JavaBeans. * * <h3><a name="workflow">Workflow</a></h3> * * <p>After a {@code DispatcherServlet} has received a request and has * done its work to resolve locales, themes, and suchlike, it then tries * to resolve a Controller, using a * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping HandlerMapping}. * When a Controller has been found to handle the request, the * {@link #handleRequest(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse) handleRequest} * method of the located Controller will be invoked; the located Controller * is then responsible for handling the actual request and — if applicable * — returning an appropriate * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView ModelAndView}. * So actually, this method is the main entry point for the * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet DispatcherServlet} * which delegates requests to controllers. * * <p>So basically any <i>direct</i> implementation of the {@code Controller} interface * just handles HttpServletRequests and should return a ModelAndView, to be further * interpreted by the DispatcherServlet. Any additional functionality such as * optional validation, form handling, etc. should be obtained through extending * {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.AbstractController AbstractController} * or one of its subclasses. * * <h3>Notes on design and testing</h3> * * <p>The Controller interface is explicitly designed to operate on HttpServletRequest * and HttpServletResponse objects, just like an HttpServlet. It does not aim to * decouple itself from the Servlet API, in contrast to, for example, WebWork, JSF or Tapestry. * Instead, the full power of the Servlet API is available, allowing Controllers to be * general-purpose: a Controller is able to not only handle web user interface * requests but also to process remoting protocols or to generate reports on demand. * * <p>Controllers can easily be tested by passing in mock objects for the * HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse objects as parameters to the * {@link #handleRequest(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse) handleRequest} * method. As a convenience, Spring ships with a set of Servlet API mocks * that are suitable for testing any kind of web components, but are particularly * suitable for testing Spring web controllers. In contrast to a Struts Action, * there is no need to mock the ActionServlet or any other infrastructure; * mocking HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse is sufficient. * * <p>If Controllers need to be aware of specific environment references, they can * choose to implement specific awareness interfaces, just like any other bean in a * Spring (web) application context can do, for example: * <ul> * <li>{@code org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware}</li> * <li>{@code org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware}</li> * <li>{@code org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware}</li> * </ul> * * <p>Such environment references can easily be passed in testing environments, * through the corresponding setters defined in the respective awareness interfaces. * In general, it is recommended to keep the dependencies as minimal as possible: * for example, if all you need is resource loading, implement ResourceLoaderAware only. * Alternatively, derive from the WebApplicationObjectSupport base class, which gives * you all those references through convenient accessors but requires an * ApplicationContext reference on initialization. * * <p>Controllers can optionally implement the {@link LastModified} interface. * * @author Rod Johnson * @author Juergen Hoeller * @see LastModified * @see SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter * @see AbstractController * @see org.springframework.mock.web.MockHttpServletRequest * @see org.springframework.mock.web.MockHttpServletResponse * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware * @see org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware * @see org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware * @see org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationObjectSupport */ @FunctionalInterface public interface Controller { /** * Process the request and return a ModelAndView object which the DispatcherServlet * will render. A {@code null} return value is not an error: it indicates that * this object completed request processing itself and that there is therefore no * ModelAndView to render. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @return a ModelAndView to render, or {@code null} if handled directly * @throws Exception in case of errors */ @Nullable ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception; }
这个接口公开了一个handleRequest()方法,下面是该方法的签名:
ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
其实现类可以访问对应请求的HttpServletRequest 和HttpServletResponse 还必须返回一个ModelAndView 对象,它包含视图路径或视图路径和模型。
Controller接口的实现类只能处理一个单一动作(action),而一个基于注解的控制器可以同时支持多个请求处理动作,并且无需实现任何接口(下一篇博客会介绍)。
三 第一个Spring MVC应用
本节的示例应用程序springmvc-intro1展示了基本的Spring MVC应用。该应用程序和Spring MVC -- MVC设计模式(演示4个基于MVC框架的案例)中的appdesign1应用非常相似,专用于展示Spring MVC是如何工作的。springmvc-intro1包含两个控制器类,类似于appdesign1中的控制器类。
1、目录结构
目录结构如下:
注意:WEB-INF/lib目录包含了Spring MVC所需要的所有jar文件。特别需要注意的是spring-webmvc-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar包含了DispacterServlet类。还要注意Spring MVC依赖于Apache Commons Logging组件,没有它,Spring MVC应用程序就无法正常工作。这些jar包的下载可以参考博客Spring MVC -- Spring框架入门(IoC、DI以及XML配置文件)。
该示例应用的所有jsp页面都存放在/WEB-INF/jsp目录下,这样就可以避免直接通过浏览器访问,但是控制器仍然可以转发请求到这些页面。
2、部署描述符(web.xml文件)和Spring MVC配置文件
部署描述符(web.xml文件):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="3.1" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
这里告诉了Servlet/JSP容器,我们将使用Spring MVC的DispatcherServlet,并通过url-pattern元素值配置为“/”,将所有的URL映射到该servlet。由于servlet元素下没有init-param元素,所以Spring MVC的配置文件在/WEB-INF文件夹下,并按照通常的命名约定:
Spring MVC配置文件(springmvc-servlet.xml):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean name="/input-product" class="controller.InputProductController"/> <bean name="/save-product" class="controller.SaveProductController"/> </beans>
这里声明了InputProductController和SaveProductController两个控制器,并分别映射到/input-product和/save-product。
3、Controller类
springmvc-intro1应用程序有InputProductController和SaveProductController这两个控制器,分别实现了Controller接口。
InputProductController类:
package controller; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller; public class InputProductController implements Controller { private static final Log logger = LogFactory .getLog(InputProductController.class); @Override public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { logger.info("InputProductController called"); return new ModelAndView("/WEB-INF/jsp/ProductForm.jsp"); } }
InputProductController类的handleRequest()方法只是返回一个ModelAndView ,包含一个视图,但没有模型。因此,该请求将被转发到/WEB-INF/jsp/ProductForm.jsp页面。
SaveProductController类:
package controller; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller; import domain.Product; import form.ProductForm; public class SaveProductController implements Controller { private static final Log logger = LogFactory .getLog(SaveProductController.class); @Override public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { logger.info("SaveProductController called"); //创建表单类 保存表单提交的信息 ProductForm productForm = new ProductForm(); // populate action properties productForm.setName(request.getParameter("name")); productForm.setDescription(request.getParameter("description")); productForm.setPrice(request.getParameter("price")); // create model 创建Product模型对象 Product product = new Product(); product.setName(productForm.getName()); product.setDescription(productForm.getDescription()); try { product.setPrice(Float.parseFloat(productForm.getPrice())); } catch (NumberFormatException e) { } // insert code to save Product return new ModelAndView("/WEB-INF/jsp/ProductDetails.jsp", "product", product); } }
SaveProductController类的handleRequest()方法中,首先用请求参数创建一个ProductForm对象,然后它根据ProductForm对象创建Product对象。由于ProductForm的price属性是一个字符串,而其在Product类对应的是一个float,此处类型转换是必要的。
SaveProductController类的handleRequest()方法最后返回的ModelAndView模型包含了视图的路径、模型名称以及模型(Product对象)。该模型将提供给目标视图,用于界面显示。
其中ProductForm类如下:

package form; public class ProductForm { private String name; private String description; private String price; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; } public String getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(String price) { this.price = price; } }
Product类如下:

package domain; import java.io.Serializable; public class Product implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 748392348L; private String name; private String description; private float price; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getDescription() { return description; } public void setDescription(String description) { this.description = description; } public float getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(float price) { this.price = price; } }
4、视图
springmvc-intro1应用程序包含两个jsp页面:ProductForm.jsp页面和ProductDetails页面:
ProductForm.jsp:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Add Product Form</title> <style type="text/css">@import url(css/main.css);</style> </head> <body> <div id="global"> <form action="save-product" method="post"> <fieldset> <legend>Add a product</legend> <p> <label for="name">Product Name: </label> <input type="text" id="name" name="name" tabindex="1"> </p> <p> <label for="description">Description: </label> <input type="text" id="description" name="description" tabindex="2"> </p> <p> <label for="price">Price: </label> <input type="text" id="price" name="price" tabindex="3"> </p> <p id="buttons"> <input id="reset" type="reset" tabindex="4"> <input id="submit" type="submit" tabindex="5" value="Add Product"> </p> </fieldset> </form> </div> </body> </html>
ProductDetails.jsp:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Save Product</title> <style type="text/css">@import url(css/main.css);</style> </head> <body> <div id="global"> <h4>The product has been saved.</h4> <p> <h5>Details:</h5> Product Name: ${product.name}<br/> Description: ${product.description}<br/> Price: $${product.price} </p> </div> </body> </html>
ProductDetails页面通过EL表达式语言访问product对象的各种属性。
main.css:

#global { text-align: left; border: 1px solid #dedede; background: #efefef; width: 560px; padding: 20px; margin: 100px auto; } form { font:100% verdana; min-width: 500px; max-width: 600px; width: 560px; } form fieldset { border-color: #bdbebf; border-width: 3px; margin: 0; } legend { font-size: 1.3em; } form label { width: 250px; display: block; float: left; text-align: right; padding: 2px; } #buttons { text-align: right; } #errors, li { color: red; }
5、测试应用
将项目部署到tomcat服务器,然后启动服务器,假设示例应用运行在本机的8000端口上,则可以通过如下URL访问应用:
http://localhost:8008/springmvc-intro1/input-product
会看到如下产品表单页面:
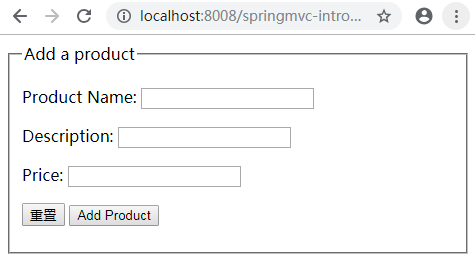
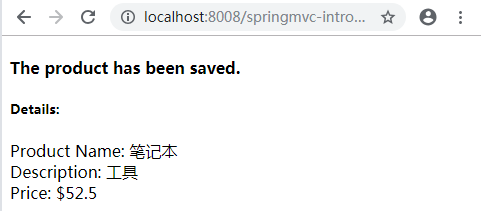
在表单中输入相应的值后单击Add Product按钮,会在下一页中看到产品属性:

注意:price应该输入一个合法数字,不然就会设置为float型默认值0.0。
四 视图解析器
Spring MVC中的视图解析器复制解析视图。可以通过在XML配置文件中定义一个ViewResolver来配置视图解析器,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean name="/input-product" class="controller.InputProductController"/> <bean name="/save-product" class="controller.SaveProductController"/> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> </beans>
视图解析器配置有前缀和后缀两个属性。这样一来,view路径将缩短。例如:仅需提供“myPage”,而不必再将视图路径设置为/WEB-INF/jsp/myPage.jsp,视图解析器将会自动增加前缀和后缀。
以springmvc-intro2应用为例,该例子和springmvc-intro1应用类似,只是调整了配置文件的名称和路径。此外,它还配置了默认的视图解析器,为所有视图路径增加前缀和后缀:
我们可以看一下InputProductController的代码:
package controller; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller; public class InputProductController implements Controller { private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(InputProductController.class); @Override public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { logger.info("InputProductController called"); return new ModelAndView("ProductForm"); } }
我们可以看到返回的视图名由springmvc-intro1中的/WEB-INF/jsp/ProductForm.jsp变成了ProductForm。
此外,在springmvc-intro2中,Spring MVC配置文件springmvc-config.xml被移动到/WEB-INF/config目录下。为了让Spring MVC可以正确加载到该配置文件,需要将文件路径配置到Spring MVC的DispatcherServlet。springmvc-intro2的web.xml配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="3.1" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd"> <servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/config/springmvc-config.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
需要特别注意的是web.xml文件中的init-param元素。如果要使用非默认配置文件的命名和路径,需要使用名为contextConfigLocation的init-param,其值应为配置文件在应用中的相对路径。
五 总结
下面我们来总结一下使用Spring MVC框架的Web应用,用户通过浏览器请求服务器的响应流程,我们以URL:http://localhost:8008/springmvc-intro1/input-product为例:
- 请求首先被应用程序的web.xml文件拦截,通过url-pattern元素值配置为“/”,将所有的URL映射到Spring MVC的DispatcherServlet;
<servlet> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
- DispatcherServlet在第一次加载时会调用init()方法进行初始化,会寻找Spring MVC配置文件;
- 通过配置文件中的bean元素,将URL映射到控制器类;
<bean name="/input-product" class="controller.InputProductController"/>
- 执行控制器的handleRequest方法,并返回一个ModelAndView。
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { logger.info("InputProductController called"); return new ModelAndView("/WEB-INF/jsp/ProductForm.jsp"); }
本篇博客是Spring MVC的入门介绍,我们学习了一个简单的Spring MVC应用。在Srping MVC中,我们无需编写自己的DispatcherServlet,并通过实现控制器接口来编写控制器,这是传统风格的控制器。从Spring 2.5版本开始,Spring提供了一个更好的开发控制器的方式,如采用注解。下一篇博客将会详细介绍。
参考文章
[1]Spring MVC学习指南



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号