JAVA RPC(二)序列化协议杂谈
序列化和反序列化作为Java里一个较为基础的知识点,大家心里也有那么几句要说的,但我相信很多小伙伴掌握的也就是那么几句而已,如果再深究问一下Java如何实现序列化和反序列化的,就可能不知所措了!遥记当年也被问了这一个问题,自信满满的说了一大堆,什么是序列化、什么是反序列化、什么场景的时候才会用到等,然后面试官说:那你能说一下序列化和反序列化底层是如何实现的吗?一脸懵逼,然后回家等通知!
1、什么是序列化和反序列化
(1)Java序列化是指把Java对象转换为字节序列的过程,而Java反序列化是指把字节序列恢复为Java对象的过程;
(2)序列化:对象序列化的最主要的用处就是在传递和保存对象的时候,保证对象的完整性和可传递性。序列化是把对象转换成有序字节流,以便在网络上传输或者保存在本地文件中。序列化后的字节流保存了Java对象的状态以及相关的描述信息。序列化机制的核心作用就是对象状态的保存与重建。
(3)反序列化:客户端从文件中或网络上获得序列化后的对象字节流后,根据字节流中所保存的对象状态及描述信息,通过反序列化重建对象。
(4)本质上讲,序列化就是把实体对象状态按照一定的格式写入到有序字节流,反序列化就是从有序字节流重建对象,恢复对象状态。
2、为什么需要序列化与反序列化
我们知道,当两个进程进行远程通信时,可以相互发送各种类型的数据,包括文本、图片、音频、视频等, 而这些数据都会以二进制序列的形式在网络上传送。
那么当两个Java进程进行通信时,能否实现进程间的对象传送呢?答案是可以的!如何做到呢?这就需要Java序列化与反序列化了!
换句话说,一方面,发送方需要把这个Java对象转换为字节序列,然后在网络上传送;另一方面,接收方需要从字节序列中恢复出Java对象。
当我们明晰了为什么需要Java序列化和反序列化后,我们很自然地会想Java序列化的好处。其好处一是实现了数据的持久化,通过序列化可以把数据永久地保存到硬盘上(通常存放在文件里),二是,利用序列化实现远程通信,即在网络上传送对象的字节序列。
总的来说可以归结为以下几点:
(1)永久性保存对象,保存对象的字节序列到本地文件或者数据库中;
(2)通过序列化以字节流的形式使对象在网络中进行传递和接收;
(3)通过序列化在进程间传递对象;
3、序列化算法一般会按步骤做如下事情:
(1)将对象实例相关的类元数据输出。
(2)递归地输出类的超类描述直到不再有超类。
(3)类元数据完了以后,开始从最顶层的超类开始输出对象实例的实际数据值。
(4)从上至下递归输出实例的数据
4、各种 Java 的序列化库的性能比较测试结果
- 专门针对Java语言的:Kryo,FST等等
- 跨语言的:Protostuff,ProtoBuf,Thrift,Avro,MsgPack等等
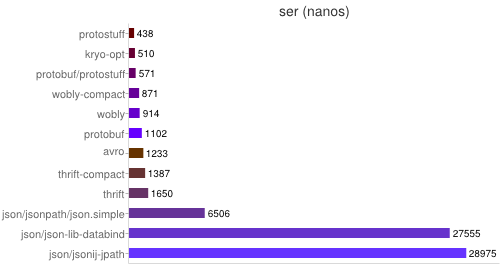
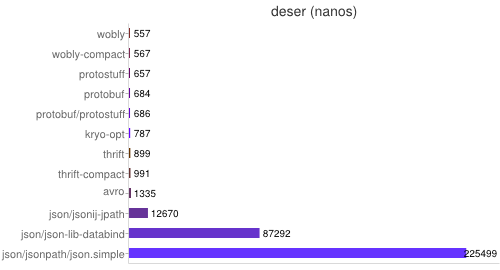
图片来源于网络,可以说明对原生序列化来讲,其他三方框架提供的序列化协议要快很多,所以我们做RPC技术选型的时候,序列化协议这块一定要摒弃原生序列化,去选择一款自己熟悉的序列化协议来传输IO流。下面选择做一个thrift序列化和原生序列化的对比结果。
原生序列化user类
package util.dto; import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable { private String name; private Integer integer; private String address; public User(String name, Integer integer, String address) { this.name = name; this.integer = integer; this.address = address; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getInteger() { return integer; } public void setInteger(Integer integer) { this.integer = integer; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } }
原生序列化工具类
1 package util; 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 import java.util.Arrays; 5 6 public class SerializeUtil { 7 8 /** 序列化对象 9 * @throws IOException */ 10 public static byte[] serializeObject(Object object) throws IOException { 11 ByteArrayOutputStream saos = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); 12 ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(saos); 13 oos.writeObject(object); 14 oos.flush(); 15 return saos.toByteArray(); 16 } 17 18 /** 反序列化对象 19 * @throws IOException 20 * @throws ClassNotFoundException */ 21 public static Object deserializeObject(byte[] buf) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{ 22 Object object=null; 23 ByteArrayInputStream sais=new ByteArrayInputStream(buf); 24 ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(sais); 25 object = ois.readObject(); 26 return object; 27 } 28 }
由thrift脚本生成的User类
1 /** 2 * Autogenerated by Thrift Compiler (0.8.0) 3 * 4 * DO NOT EDIT UNLESS YOU ARE SURE THAT YOU KNOW WHAT YOU ARE DOING 5 * @generated 6 */ 7 package util.dtothrift; 8 9 import org.apache.thrift.scheme.IScheme; 10 import org.apache.thrift.scheme.SchemeFactory; 11 import org.apache.thrift.scheme.StandardScheme; 12 13 import org.apache.thrift.scheme.TupleScheme; 14 import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TTupleProtocol; 15 import java.util.List; 16 import java.util.ArrayList; 17 import java.util.Map; 18 import java.util.HashMap; 19 import java.util.EnumMap; 20 import java.util.Set; 21 import java.util.HashSet; 22 import java.util.EnumSet; 23 import java.util.Collections; 24 import java.util.BitSet; 25 import java.nio.ByteBuffer; 26 import java.util.Arrays; 27 import org.slf4j.Logger; 28 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 29 30 public class User implements org.apache.thrift.TBase<User, User._Fields>, java.io.Serializable, Cloneable { 31 private static final org.apache.thrift.protocol.TStruct STRUCT_DESC = new org.apache.thrift.protocol.TStruct("User"); 32 33 private static final org.apache.thrift.protocol.TField STR_FIELD_DESC = new org.apache.thrift.protocol.TField("str", org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.STRING, (short)1); 34 private static final org.apache.thrift.protocol.TField AGE_FIELD_DESC = new org.apache.thrift.protocol.TField("age", org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.I32, (short)2); 35 private static final org.apache.thrift.protocol.TField ADDRESS_FIELD_DESC = new org.apache.thrift.protocol.TField("address", org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.STRING, (short)3); 36 37 private static final Map<Class<? extends IScheme>, SchemeFactory> schemes = new HashMap<Class<? extends IScheme>, SchemeFactory>(); 38 static { 39 schemes.put(StandardScheme.class, new UserStandardSchemeFactory()); 40 schemes.put(TupleScheme.class, new UserTupleSchemeFactory()); 41 } 42 43 public String str; // required 44 public int age; // required 45 public String address; // required 46 47 /** The set of fields this struct contains, along with convenience methods for finding and manipulating them. */ 48 public enum _Fields implements org.apache.thrift.TFieldIdEnum { 49 STR((short)1, "str"), 50 AGE((short)2, "age"), 51 ADDRESS((short)3, "address"); 52 53 private static final Map<String, _Fields> byName = new HashMap<String, _Fields>(); 54 55 static { 56 for (_Fields field : EnumSet.allOf(_Fields.class)) { 57 byName.put(field.getFieldName(), field); 58 } 59 } 60 61 /** 62 * Find the _Fields constant that matches fieldId, or null if its not found. 63 */ 64 public static _Fields findByThriftId(int fieldId) { 65 switch(fieldId) { 66 case 1: // STR 67 return STR; 68 case 2: // AGE 69 return AGE; 70 case 3: // ADDRESS 71 return ADDRESS; 72 default: 73 return null; 74 } 75 } 76 77 /** 78 * Find the _Fields constant that matches fieldId, throwing an exception 79 * if it is not found. 80 */ 81 public static _Fields findByThriftIdOrThrow(int fieldId) { 82 _Fields fields = findByThriftId(fieldId); 83 if (fields == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Field " + fieldId + " doesn't exist!"); 84 return fields; 85 } 86 87 /** 88 * Find the _Fields constant that matches name, or null if its not found. 89 */ 90 public static _Fields findByName(String name) { 91 return byName.get(name); 92 } 93 94 private final short _thriftId; 95 private final String _fieldName; 96 97 _Fields(short thriftId, String fieldName) { 98 _thriftId = thriftId; 99 _fieldName = fieldName; 100 } 101 102 public short getThriftFieldId() { 103 return _thriftId; 104 } 105 106 public String getFieldName() { 107 return _fieldName; 108 } 109 } 110 111 // isset id assignments 112 private static final int __AGE_ISSET_ID = 0; 113 private BitSet __isset_bit_vector = new BitSet(1); 114 public static final Map<_Fields, org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldMetaData> metaDataMap; 115 static { 116 Map<_Fields, org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldMetaData> tmpMap = new EnumMap<_Fields, org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldMetaData>(_Fields.class); 117 tmpMap.put(_Fields.STR, new org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldMetaData("str", org.apache.thrift.TFieldRequirementType.DEFAULT, 118 new org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldValueMetaData(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.STRING))); 119 tmpMap.put(_Fields.AGE, new org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldMetaData("age", org.apache.thrift.TFieldRequirementType.DEFAULT, 120 new org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldValueMetaData(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.I32))); 121 tmpMap.put(_Fields.ADDRESS, new org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldMetaData("address", org.apache.thrift.TFieldRequirementType.DEFAULT, 122 new org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldValueMetaData(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.STRING))); 123 metaDataMap = Collections.unmodifiableMap(tmpMap); 124 org.apache.thrift.meta_data.FieldMetaData.addStructMetaDataMap(User.class, metaDataMap); 125 } 126 127 public User() { 128 } 129 130 public User( 131 String str, 132 int age, 133 String address) 134 { 135 this(); 136 this.str = str; 137 this.age = age; 138 setAgeIsSet(true); 139 this.address = address; 140 } 141 142 /** 143 * Performs a deep copy on <i>other</i>. 144 */ 145 public User(User other) { 146 __isset_bit_vector.clear(); 147 __isset_bit_vector.or(other.__isset_bit_vector); 148 if (other.isSetStr()) { 149 this.str = other.str; 150 } 151 this.age = other.age; 152 if (other.isSetAddress()) { 153 this.address = other.address; 154 } 155 } 156 157 public User deepCopy() { 158 return new User(this); 159 } 160 161 @Override 162 public void clear() { 163 this.str = null; 164 setAgeIsSet(false); 165 this.age = 0; 166 this.address = null; 167 } 168 169 public String getStr() { 170 return this.str; 171 } 172 173 public User setStr(String str) { 174 this.str = str; 175 return this; 176 } 177 178 public void unsetStr() { 179 this.str = null; 180 } 181 182 /** Returns true if field str is set (has been assigned a value) and false otherwise */ 183 public boolean isSetStr() { 184 return this.str != null; 185 } 186 187 public void setStrIsSet(boolean value) { 188 if (!value) { 189 this.str = null; 190 } 191 } 192 193 public int getAge() { 194 return this.age; 195 } 196 197 public User setAge(int age) { 198 this.age = age; 199 setAgeIsSet(true); 200 return this; 201 } 202 203 public void unsetAge() { 204 __isset_bit_vector.clear(__AGE_ISSET_ID); 205 } 206 207 /** Returns true if field age is set (has been assigned a value) and false otherwise */ 208 public boolean isSetAge() { 209 return __isset_bit_vector.get(__AGE_ISSET_ID); 210 } 211 212 public void setAgeIsSet(boolean value) { 213 __isset_bit_vector.set(__AGE_ISSET_ID, value); 214 } 215 216 public String getAddress() { 217 return this.address; 218 } 219 220 public User setAddress(String address) { 221 this.address = address; 222 return this; 223 } 224 225 public void unsetAddress() { 226 this.address = null; 227 } 228 229 /** Returns true if field address is set (has been assigned a value) and false otherwise */ 230 public boolean isSetAddress() { 231 return this.address != null; 232 } 233 234 public void setAddressIsSet(boolean value) { 235 if (!value) { 236 this.address = null; 237 } 238 } 239 240 public void setFieldValue(_Fields field, Object value) { 241 switch (field) { 242 case STR: 243 if (value == null) { 244 unsetStr(); 245 } else { 246 setStr((String)value); 247 } 248 break; 249 250 case AGE: 251 if (value == null) { 252 unsetAge(); 253 } else { 254 setAge((Integer)value); 255 } 256 break; 257 258 case ADDRESS: 259 if (value == null) { 260 unsetAddress(); 261 } else { 262 setAddress((String)value); 263 } 264 break; 265 266 } 267 } 268 269 public Object getFieldValue(_Fields field) { 270 switch (field) { 271 case STR: 272 return getStr(); 273 274 case AGE: 275 return Integer.valueOf(getAge()); 276 277 case ADDRESS: 278 return getAddress(); 279 280 } 281 throw new IllegalStateException(); 282 } 283 284 /** Returns true if field corresponding to fieldID is set (has been assigned a value) and false otherwise */ 285 public boolean isSet(_Fields field) { 286 if (field == null) { 287 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 288 } 289 290 switch (field) { 291 case STR: 292 return isSetStr(); 293 case AGE: 294 return isSetAge(); 295 case ADDRESS: 296 return isSetAddress(); 297 } 298 throw new IllegalStateException(); 299 } 300 301 @Override 302 public boolean equals(Object that) { 303 if (that == null) 304 return false; 305 if (that instanceof User) 306 return this.equals((User)that); 307 return false; 308 } 309 310 public boolean equals(User that) { 311 if (that == null) 312 return false; 313 314 boolean this_present_str = true && this.isSetStr(); 315 boolean that_present_str = true && that.isSetStr(); 316 if (this_present_str || that_present_str) { 317 if (!(this_present_str && that_present_str)) 318 return false; 319 if (!this.str.equals(that.str)) 320 return false; 321 } 322 323 boolean this_present_age = true; 324 boolean that_present_age = true; 325 if (this_present_age || that_present_age) { 326 if (!(this_present_age && that_present_age)) 327 return false; 328 if (this.age != that.age) 329 return false; 330 } 331 332 boolean this_present_address = true && this.isSetAddress(); 333 boolean that_present_address = true && that.isSetAddress(); 334 if (this_present_address || that_present_address) { 335 if (!(this_present_address && that_present_address)) 336 return false; 337 if (!this.address.equals(that.address)) 338 return false; 339 } 340 341 return true; 342 } 343 344 @Override 345 public int hashCode() { 346 return 0; 347 } 348 349 public int compareTo(User other) { 350 if (!getClass().equals(other.getClass())) { 351 return getClass().getName().compareTo(other.getClass().getName()); 352 } 353 354 int lastComparison = 0; 355 User typedOther = (User)other; 356 357 lastComparison = Boolean.valueOf(isSetStr()).compareTo(typedOther.isSetStr()); 358 if (lastComparison != 0) { 359 return lastComparison; 360 } 361 if (isSetStr()) { 362 lastComparison = org.apache.thrift.TBaseHelper.compareTo(this.str, typedOther.str); 363 if (lastComparison != 0) { 364 return lastComparison; 365 } 366 } 367 lastComparison = Boolean.valueOf(isSetAge()).compareTo(typedOther.isSetAge()); 368 if (lastComparison != 0) { 369 return lastComparison; 370 } 371 if (isSetAge()) { 372 lastComparison = org.apache.thrift.TBaseHelper.compareTo(this.age, typedOther.age); 373 if (lastComparison != 0) { 374 return lastComparison; 375 } 376 } 377 lastComparison = Boolean.valueOf(isSetAddress()).compareTo(typedOther.isSetAddress()); 378 if (lastComparison != 0) { 379 return lastComparison; 380 } 381 if (isSetAddress()) { 382 lastComparison = org.apache.thrift.TBaseHelper.compareTo(this.address, typedOther.address); 383 if (lastComparison != 0) { 384 return lastComparison; 385 } 386 } 387 return 0; 388 } 389 390 public _Fields fieldForId(int fieldId) { 391 return _Fields.findByThriftId(fieldId); 392 } 393 394 public void read(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol iprot) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { 395 schemes.get(iprot.getScheme()).getScheme().read(iprot, this); 396 } 397 398 public void write(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol oprot) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { 399 schemes.get(oprot.getScheme()).getScheme().write(oprot, this); 400 } 401 402 @Override 403 public String toString() { 404 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("User("); 405 boolean first = true; 406 407 sb.append("str:"); 408 if (this.str == null) { 409 sb.append("null"); 410 } else { 411 sb.append(this.str); 412 } 413 first = false; 414 if (!first) sb.append(", "); 415 sb.append("age:"); 416 sb.append(this.age); 417 first = false; 418 if (!first) sb.append(", "); 419 sb.append("address:"); 420 if (this.address == null) { 421 sb.append("null"); 422 } else { 423 sb.append(this.address); 424 } 425 first = false; 426 sb.append(")"); 427 return sb.toString(); 428 } 429 430 public void validate() throws org.apache.thrift.TException { 431 // check for required fields 432 } 433 434 private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream out) throws java.io.IOException { 435 try { 436 write(new org.apache.thrift.protocol.TCompactProtocol(new org.apache.thrift.transport.TIOStreamTransport(out))); 437 } catch (org.apache.thrift.TException te) { 438 throw new java.io.IOException(te); 439 } 440 } 441 442 private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream in) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { 443 try { 444 // it doesn't seem like you should have to do this, but java serialization is wacky, and doesn't call the default constructor. 445 __isset_bit_vector = new BitSet(1); 446 read(new org.apache.thrift.protocol.TCompactProtocol(new org.apache.thrift.transport.TIOStreamTransport(in))); 447 } catch (org.apache.thrift.TException te) { 448 throw new java.io.IOException(te); 449 } 450 } 451 452 private static class UserStandardSchemeFactory implements SchemeFactory { 453 public UserStandardScheme getScheme() { 454 return new UserStandardScheme(); 455 } 456 } 457 458 private static class UserStandardScheme extends StandardScheme<User> { 459 460 public void read(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol iprot, User struct) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { 461 org.apache.thrift.protocol.TField schemeField; 462 iprot.readStructBegin(); 463 while (true) 464 { 465 schemeField = iprot.readFieldBegin(); 466 if (schemeField.type == org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.STOP) { 467 break; 468 } 469 switch (schemeField.id) { 470 case 1: // STR 471 if (schemeField.type == org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.STRING) { 472 struct.str = iprot.readString(); 473 struct.setStrIsSet(true); 474 } else { 475 org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolUtil.skip(iprot, schemeField.type); 476 } 477 break; 478 case 2: // AGE 479 if (schemeField.type == org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.I32) { 480 struct.age = iprot.readI32(); 481 struct.setAgeIsSet(true); 482 } else { 483 org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolUtil.skip(iprot, schemeField.type); 484 } 485 break; 486 case 3: // ADDRESS 487 if (schemeField.type == org.apache.thrift.protocol.TType.STRING) { 488 struct.address = iprot.readString(); 489 struct.setAddressIsSet(true); 490 } else { 491 org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolUtil.skip(iprot, schemeField.type); 492 } 493 break; 494 default: 495 org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocolUtil.skip(iprot, schemeField.type); 496 } 497 iprot.readFieldEnd(); 498 } 499 iprot.readStructEnd(); 500 501 // check for required fields of primitive type, which can't be checked in the validate method 502 struct.validate(); 503 } 504 505 public void write(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol oprot, User struct) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { 506 struct.validate(); 507 508 oprot.writeStructBegin(STRUCT_DESC); 509 if (struct.str != null) { 510 oprot.writeFieldBegin(STR_FIELD_DESC); 511 oprot.writeString(struct.str); 512 oprot.writeFieldEnd(); 513 } 514 oprot.writeFieldBegin(AGE_FIELD_DESC); 515 oprot.writeI32(struct.age); 516 oprot.writeFieldEnd(); 517 if (struct.address != null) { 518 oprot.writeFieldBegin(ADDRESS_FIELD_DESC); 519 oprot.writeString(struct.address); 520 oprot.writeFieldEnd(); 521 } 522 oprot.writeFieldStop(); 523 oprot.writeStructEnd(); 524 } 525 526 } 527 528 private static class UserTupleSchemeFactory implements SchemeFactory { 529 public UserTupleScheme getScheme() { 530 return new UserTupleScheme(); 531 } 532 } 533 534 private static class UserTupleScheme extends TupleScheme<User> { 535 536 @Override 537 public void write(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol prot, User struct) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { 538 TTupleProtocol oprot = (TTupleProtocol) prot; 539 BitSet optionals = new BitSet(); 540 if (struct.isSetStr()) { 541 optionals.set(0); 542 } 543 if (struct.isSetAge()) { 544 optionals.set(1); 545 } 546 if (struct.isSetAddress()) { 547 optionals.set(2); 548 } 549 oprot.writeBitSet(optionals, 3); 550 if (struct.isSetStr()) { 551 oprot.writeString(struct.str); 552 } 553 if (struct.isSetAge()) { 554 oprot.writeI32(struct.age); 555 } 556 if (struct.isSetAddress()) { 557 oprot.writeString(struct.address); 558 } 559 } 560 561 @Override 562 public void read(org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol prot, User struct) throws org.apache.thrift.TException { 563 TTupleProtocol iprot = (TTupleProtocol) prot; 564 BitSet incoming = iprot.readBitSet(3); 565 if (incoming.get(0)) { 566 struct.str = iprot.readString(); 567 struct.setStrIsSet(true); 568 } 569 if (incoming.get(1)) { 570 struct.age = iprot.readI32(); 571 struct.setAgeIsSet(true); 572 } 573 if (incoming.get(2)) { 574 struct.address = iprot.readString(); 575 struct.setAddressIsSet(true); 576 } 577 } 578 } 579 580 }
测试类
1 package util; 2 3 import org.apache.thrift.TException; 4 import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol; 5 import org.apache.thrift.transport.TIOStreamTransport; 6 import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket; 7 import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport; 8 import org.slf4j.Logger; 9 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 10 import util.dto.User; 11 12 import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; 13 import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; 14 import java.io.IOException; 15 import java.util.Arrays; 16 17 public class SerializeTest { 18 19 private final static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger ( SerializeTest.class ); 20 21 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, TException { 22 23 long a = System.currentTimeMillis (); 24 for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { 25 User user = new User("姓名"+i,i,"北京市海淀区中关村大厦"+i); 26 byte[] b = SerializeUtil.serializeObject ( user ); 27 //System.out.println (Arrays.toString ( b )); 28 User user1 = (User) SerializeUtil.deserializeObject ( b ); 29 } 30 System.out.println (System.currentTimeMillis ()-a); 31 32 long b = System.currentTimeMillis (); 33 34 for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { 35 util.dtothrift.User user = new util.dtothrift.User("姓名"+i,i,"北京市海淀区中关村大厦"+i); 36 ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 37 TTransport transport = new TIOStreamTransport (out); 38 TBinaryProtocol tp = new TBinaryProtocol(transport); 39 try { 40 user.write(tp); 41 } catch (TException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 byte[] bytes = out.toByteArray(); 45 //System.out.println ( Arrays.toString ( bytes )); 46 util.dtothrift.User user1 = new util.dtothrift.User(); 47 48 ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream ( bytes); 49 TTransport transport1 = new TIOStreamTransport(bis); 50 TBinaryProtocol tp1 = new TBinaryProtocol(transport1); 51 user1.read (tp1); 52 } 53 System.out.println (System.currentTimeMillis ()-b); 54 } 55 56 }
10万次序列化和反序列化的结果对比
由上图可以看出,采用facebook的序列化协议要比原生jdk序列化协议在10万次序列化和反序列化操作中的时间快很多,并且thrift没有原生序列化的那么多的要求,我们来看看原生序列化和thrift序列化的输入结果都是什么,打开 System.out.println ( Arrays.toString ( bytes ))代码后
jdk 输出流
[-84, -19, 0, 5, 115, 114, 0, 13, 117, 116, 105, 108, 46, 100, 116, 111, 46, 85, 115, 101, 114, -45, 124, 21, -36, 14, -39, -44, 35, 2, 0, 3, 76, 0, 7, 97, 100, 100, 114, 101, 115, 115, 116, 0, 18, 76, 106, 97, 118, 97, 47, 108, 97, 110, 103, 47, 83, 116, 114, 105, 110, 103, 59, 76, 0, 7, 105, 110, 116, 101, 103, 101, 114, 116, 0, 19, 76, 106, 97, 118, 97, 47, 108, 97, 110, 103, 47, 73, 110, 116, 101, 103, 101, 114, 59, 76, 0, 4, 110, 97, 109, 101, 113, 0, 126, 0, 1, 120, 112, 116, 0, 34, -27, -116, -105, -28, -70, -84, -27, -72, -126, -26, -75, -73, -26, -73, -128, -27, -116, -70, -28, -72, -83, -27, -123, -77, -26, -99, -111, -27, -92, -89, -27, -114, -90, 48, 115, 114, 0, 17, 106, 97, 118, 97, 46, 108, 97, 110, 103, 46, 73, 110, 116, 101, 103, 101, 114, 18, -30, -96, -92, -9, -127, -121, 56, 2, 0, 1, 73, 0, 5, 118, 97, 108, 117, 101, 120, 114, 0, 16, 106, 97, 118, 97, 46, 108, 97, 110, 103, 46, 78, 117, 109, 98, 101, 114, -122, -84, -107, 29, 11, -108, -32, -117, 2, 0, 0, 120, 112, 0, 0, 0, 0, 116, 0, 7, -27, -89, -109, -27, -112, -115, 48]
thrift输出流
[11, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 7, -27, -89, -109, -27, -112, -115, 48, 8, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 11, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 34, -27, -116, -105, -28, -70, -84, -27, -72, -126, -26, -75, -73, -26, -73, -128, -27, -116, -70, -28, -72, -83, -27, -123, -77, -26, -99, -111, -27, -92, -89, -27, -114, -90, 48, 0]
由此可以看出jdk的输出流比thrift的输出流多很多,因为jdk原生序列化对方法栈信息,类信息等做了详细的记录,其实这些信息对于RPC来说不是传输必要参数,所以精简序列化IO流大小在传输中十分关键
本章对序列化进行了简单的概述,大家可以针对我的上面代码进行测试。
高级java交流群:825199617
欢迎热爱源码志同道合的朋友加入。
koalas rpc源码地址https://gitee.com/a1234567891/koalas-rpc

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号