201871010135-张玉晶《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十周学习总结
| 项目 | 内容 |
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11778090.html |
| 作业的学习目标 |
1.掌握java异常处理技术; 2.了解断言的用法; 3.了解日志的用途; 4.掌握程序基础调试技巧。
|
1:总结第七章关于异常处理相关理论知识
1: 处理错误:
1)用户输入错误;2)设备错误;3)物理限制;4)代码错误
2: 异常分类:所有的异常都是由Throwable继承而来。 分为Error 类和 Exception类
Error类: 描述了Java运行时系统的内部错误和资源耗尽错误。应用程序不应该捕获这类异常,也不会抛出这种异常;
Exception类 : 是需重点掌握的异常类。Exception层次结构又分解为两个分支:1)一个分支派生于RuntimeException:2)另一个分支包含其他异常。
RuntimeException为运行时异常类,一般是程序错误产生;
派生于RuntimeException的异常包含下面几种情况:
1)错误的类型转换;
2)数组访问越界;
3)访问空指针;
不是派生于RuntimeException的异常包括:
1)试图在文件尾部后面读取数据;
2)试图打开一个不存在的文件;
3)试图根据给定的字符串查找class对象,而这个字符串表示的类并不存在。
Java将派生于Error类或RuntimeException类的所有异常称为未检查异常,编译器允许不对它们异常处理。
3. 声明受查异常
throws : 声明异常
throw : 抛出一个已检查异常
4. 捕获异常
若捕获一个异常,需要在程序中设置一个try/catch/finally块:
try语句 : 括住可能抛出异常的代码块;
catch语句: 指明要捕获的异常类及相应的处理代码;
catch块可以通过异常对象调用类Throwable所提供的方法。
---getMessage()用来得到有关异常事件的信息;
---printStackTrace()用来跟踪异常事件发生时执行堆栈的内容。
finally语句: 指明必须执行的代码块。
try 语句可以只有finally子句,而没有catch子句;也可以有多个catch子句。
可以在一个try块中不或多个异常类型,每个异常类型需要一个单独的catch子句;
5. 断言 : 是程序的开发和测试阶段用于插入一些代码错误检测语句的工具
a : assert 条件;
b : assert 条件 :表达式;
这两个形式都会对布尔“条件”进行判断,如果判断结果为假(false),说明程序已经处于不正确的状态下,系统则抛出AssertionError,给出警告并且退出。在第二种形式中,“ 表达式”会传入AssertionError的构造函数中并转成一个消息字符串。
c : -enableassertions 或 -ea 启用断言
d : -disableassertions 或 -da 禁用断言
2:实验内容和步骤
实验1:
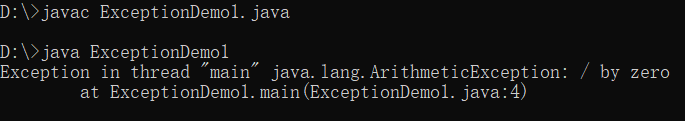
用命令行与IDE两种环境下编辑调试运行源程序ExceptionDemo1、ExceptionDemo2,结合程序运行结果理解程序,掌握未检查异常和已检查异常的区别。
1 //异常示例1 2 public class ExceptionDemo1 { 3 public static void main(String args[]) { 4 int a = 0; 5 System.out.println(5 / a); 6 } 7 }
IDE环境下:

命令行环境下:
1 import java.io.*; 2 3 public class ExceptionDemo2 { 4 public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException 5 { 6 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt");//JVM自动生成异常对象 7 int b; 8 while((b=fis.read())!=-1) 9 { 10 System.out.print(b); 11 } 12 fis.close(); 13 } 14 }
IDE环境下:
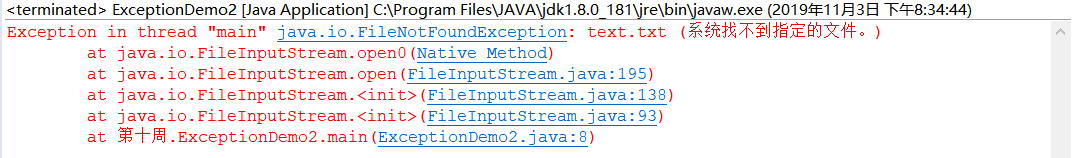
命令行环境下:
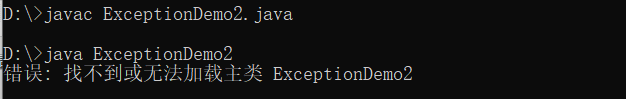
实验2: 导入以下示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
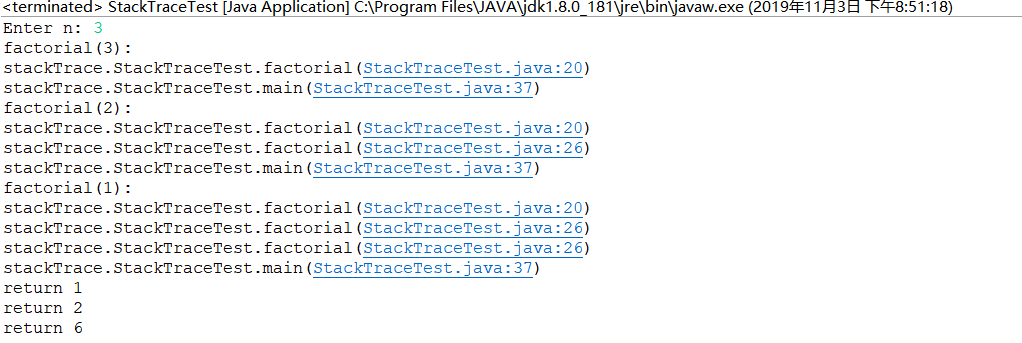
测试程序1:StackTraceTest.java:
1 package stackTrace; 2 3 import java.util.*; 4 5 /** 6 * A program that displays a trace feature of a recursive method call. 7 * @version 1.10 2017-12-14 8 * @author Cay Horstmann 9 */ 10 public class StackTraceTest 11 { 12 /** 13 * Computes the factorial of a number 14 * @param n a non-negative integer 15 * @return n! = 1 * 2 * . . . * n 16 */ 17 public static int factorial(int n) 18 { 19 System.out.println("factorial(" + n + "):"); 20 Throwable t = new Throwable(); 21 StackTraceElement[] frames=t.getStackTrace(); //调用堆栈的跟踪 22 for(StackTraceElement f : frames) 23 System.out.println(f); 24 int r; 25 if (n <= 1) r = 1; 26 else r = n * factorial(n - 1); //计算n的阶乘需要去调用n-1的阶乘 27 System.out.println("return " + r); 28 return r; 29 } 30 31 public static void main(String[] args) 32 { 33 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 34 35 System.out.print("Enter n: "); 36 int n = in.nextInt(); 37 factorial(n); 38 39 } 40 }
运行结果如下:
测试程序2:
Java语言的异常处理有积极处理方法和消极处理两种方式;
下列两个简单程序范例给出了两种异常处理的代码格式。在elipse IDE中编辑、调试运行源程序ExceptionTest.java,将程序中的text文件更换为身份证号.txt,要求将文件内容读入内容,并在控制台显示;
掌握两种异常处理技术的特点。
1 //积极处理方式 2 import java.io.*; 3 4 class ExceptionTest { 5 public static void main (string args[]) 6 { 7 try{ 8 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); 9 } 10 catch(FileNotFoundExcption e) 11 { …… } 12 …… 13 } 14 } 18 19 //消极处理方式 20 21 import java.io.*; 22 class ExceptionTest { 23 public static void main (string args[]) throws FileNotFoundExcption 24 { 25 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("text.txt"); 26 } 27 }
将程序中的text文件更换为身份证号.txt:
1 //积极的处理方式 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 5 class ExceptionTest { 6 public static void main (String args[]) 7 { 8 9 try{ 10 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("D://身份证号.txt"); 11 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); 12 String s = new String(); 13 while ((s = in.readLine()) != null) { 14 System.out.println(s); 15 } 16 in.close(); 17 fis.close(); 18 } 19 catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 20 System.out.println("文件未找到"); 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } catch (IOException e) { 23 System.out.println("文件读取错误"); 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 }

1 //消极的处理方式 2 3 import java.io.*; 4 5 public class ExceptionTest { 6 public static void main (String args[]) throws IOException 7 { 8 9 try{ 10 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("D:\\身份证号.txt"); 11 BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); 12 String s = new String(); 13 while ((s = in.readLine()) != null) { 14 System.out.println(s); 15 } 16 in.close(); 17 fis.close(); 18 } 19 finally { 20 21 } 22 23 } 24 }

实验3: 编程练习
编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作;
利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt;
在以上程序适当位置加入异常捕获代码。
1 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 2 import java.io.PrintWriter; 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class counter { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 8 number sf=new number(); 9 PrintWriter output = null; 10 try { 11 output = new PrintWriter("test.txt"); 12 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 int sum = 0; 16 17 for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) { 18 int a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 19 int b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 20 int num = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 4); 21 22 23 switch(num) 24 { 25 case 1: 26 System.out.println(i+": "+a+"/"+b+"="); 27 while(b==0){ 28 b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); 29 } 30 double c = in.nextDouble(); 31 output.println(a+"/"+b+"="+c); 32 if (c == sf.chu_fa(a, b)) { 33 sum += 10; 34 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); 35 } 36 else { 37 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); 38 } 39 break; 40 41 case 2: 42 System.out.println(i+": "+a+"*"+b+"="); 43 int c1 = in.nextInt(); 44 output.println(a+"*"+b+"="+c1); 45 if (c1 == sf.chen_fa(a, b)) { 46 sum += 10; 47 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); 48 } 49 else { 50 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); 51 }break; 52 case 3: 53 System.out.println(i+": "+a+"+"+b+"="); 54 int c2 = in.nextInt(); 55 output.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c2); 56 if (c2 == sf.jia_fa(a, b)) { 57 sum += 10; 58 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); 59 } 60 else { 61 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); 62 }break ; 63 case 4: 64 System.out.println(i+": "+a+"-"+b+"="); 65 int c3 = in.nextInt(); 66 output.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c3); 67 if (c3 == sf.jian_fa(a, b)) { 68 sum += 10; 69 System.out.println("恭喜答案正确"); 70 } 71 else { 72 System.out.println("抱歉,答案错误"); 73 }break ; 74 75 } 76 77 } 78 System.out.println("成绩"+sum); 79 output.println("成绩:"+sum); 80 output.close(); 81 82 } 83 }
1 public class number { 2 3 private int a; 4 private int b; 5 public int jia_fa(int a,int b) 6 { 7 return a+b; 8 } 9 public int jian_fa(int a,int b) 10 { 11 12 return a-b; 13 } 14 public int chen_fa(int a,int b) 15 { 16 return a*b; 17 } 18 public int chu_fa(int a,int b) 19 { 20 if(b!=0) 21 return a/b; 22 else 23 return 0; 24 } 25 26 27 }
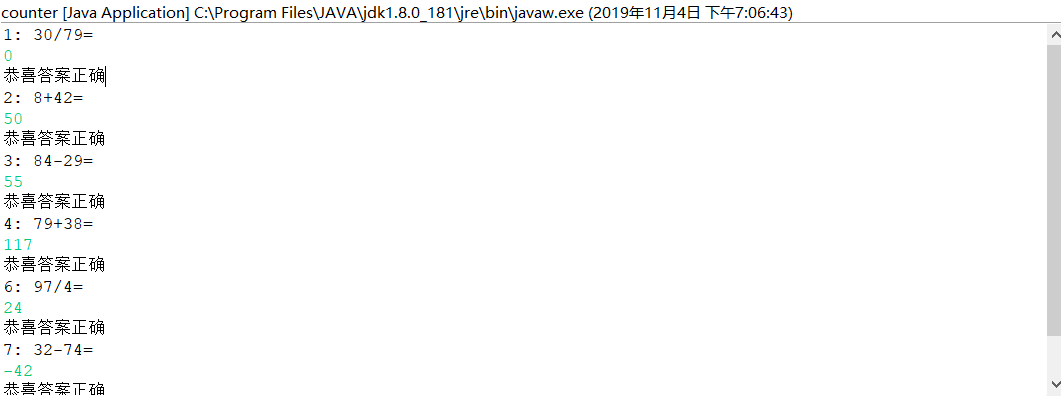
实验主要用到了两个类,主类和计算机类,在主类中创建计算机类对象,随机产生a,b及num,然后进行运算,并判断。最后在主类中将整个操作读入到文件中。
实验4:断言、日志、程序调试技巧验证实验。
实验程序1:
在elipse下调试程序AssertDemo,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
注释语句test1(-5);后重新运行程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
掌握断言的使用特点及用法。
1 //断言程序示例 2 public class AssertDemo { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 test1(-5); 5 test2(-3); 6 } 7 8 private static void test1(int a){ 9 assert a > 0; //引用assert关键字对条件进行检测 10 System.out.println(a); 11 } 12 private static void test2(int a){ 13 assert a > 0 : "something goes wrong here, a cannot be less than 0"; 14 System.out.println(a); 15 } 16 }
禁用断言时:

启用断言时:
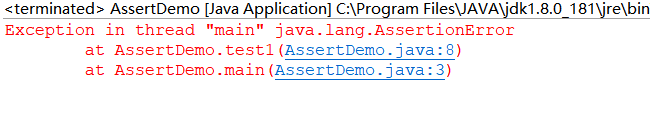
启用断言并注释语句test1(-5)后:

实验程序2:
用JDK命令调试运行教材298页-300页程序7-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
并掌握Java日志系统的用途及用法。
1 package logging; 2 3 import java.awt.*; 4 import java.awt.event.*; 5 import java.io.*; 6 import java.util.logging.*; 7 import javax.swing.*; 8 9 /** 10 * A modification of the image viewer program that logs various events. 11 * @version 1.03 2015-08-20 12 * @author Cay Horstmann 13 */ 14 public class LoggingImageViewer 15 { 16 public static void main(String[] args) 17 { 18 if (System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.class") == null 19 && System.getProperty("java.util.logging.config.file") == null) 20 { 21 try 22 { 23 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").setLevel(Level.ALL); 24 final int LOG_ROTATION_COUNT = 10; 25 FileHandler handler = new FileHandler("%h/LoggingImageViewer.log", 0, LOG_ROTATION_COUNT); 26 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(handler); 27 } 28 catch (IOException e) 29 { 30 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").log(Level.SEVERE, 31 "Can't create log file handler", e); 32 } 33 } 34 35 EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> 36 { 37 WindowHandler windowHandler = new WindowHandler(); 38 windowHandler.setLevel(Level.ALL); 39 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").addHandler(windowHandler); 40 41 ImageViewerFrame frame = new ImageViewerFrame(); 42 frame.setTitle("LoggingImageViewer"); 43 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 44 45 Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava").fine("Showing frame"); 46 frame.setVisible(true); 47 }); 48 } 49 } 50 51 /** 52 * The frame that shows the image. 53 */ 54 class ImageViewerFrame extends JFrame 55 { 56 private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300; 57 private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400; 58 59 private JLabel label; 60 private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("com.horstmann.corejava"); 61 62 public ImageViewerFrame() 63 { 64 logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); 65 setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); 66 67 // set up menu bar 68 JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar(); 69 setJMenuBar(menuBar); 70 71 JMenu menu = new JMenu("File"); 72 menuBar.add(menu); 73 74 JMenuItem openItem = new JMenuItem("Open"); 75 menu.add(openItem); 76 openItem.addActionListener(new FileOpenListener()); 77 78 JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit"); 79 menu.add(exitItem); 80 exitItem.addActionListener(new ActionListener() 81 { 82 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 83 { 84 logger.fine("Exiting."); 85 System.exit(0); 86 } 87 }); 88 89 // use a label to display the images 90 label = new JLabel(); 91 add(label); 92 logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame", "<init>"); 93 } 94 95 private class FileOpenListener implements ActionListener 96 { 97 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) 98 { 99 logger.entering("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed", event); 100 101 // set up file chooser 102 JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser(); 103 chooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File(".")); 104 105 // accept all files ending with .gif 106 chooser.setFileFilter(new javax.swing.filechooser.FileFilter() 107 { 108 public boolean accept(File f) 109 { 110 return f.getName().toLowerCase().endsWith(".gif") || f.isDirectory(); 111 } 112 113 public String getDescription() 114 { 115 return "GIF Images"; 116 } 117 }); 118 119 // show file chooser dialog 120 int r = chooser.showOpenDialog(ImageViewerFrame.this); 121 122 // if image file accepted, set it as icon of the label 123 if (r == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) 124 { 125 String name = chooser.getSelectedFile().getPath(); 126 logger.log(Level.FINE, "Reading file {0}", name); 127 label.setIcon(new ImageIcon(name)); 128 } 129 else logger.fine("File open dialog canceled."); 130 logger.exiting("ImageViewerFrame.FileOpenListener", "actionPerformed"); 131 } 132 } 133 } 134 135 /** 136 * A handler for displaying log records in a window. 137 */ 138 class WindowHandler extends StreamHandler 139 { 140 private JFrame frame; 141 142 public WindowHandler() 143 { 144 frame = new JFrame(); 145 JTextArea output = new JTextArea(); 146 output.setEditable(false); 147 frame.setSize(200, 200); 148 frame.add(new JScrollPane(output)); 149 frame.setFocusableWindowState(false); 150 frame.setVisible(true); 151 setOutputStream(new OutputStream() 152 { 153 public void write(int b) 154 { 155 } // not called 156 157 public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 158 { 159 output.append(new String(b, off, len)); 160 } 161 }); 162 } 163 164 public void publish(LogRecord record) 165 { 166 if (!frame.isVisible()) return; 167 super.publish(record); 168 flush(); 169 } 170 }
实验程序3:
用JDK命令调试运行教材298页-300页程序7-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
按课件66-77内容练习并掌握Elipse的常用调试技术。
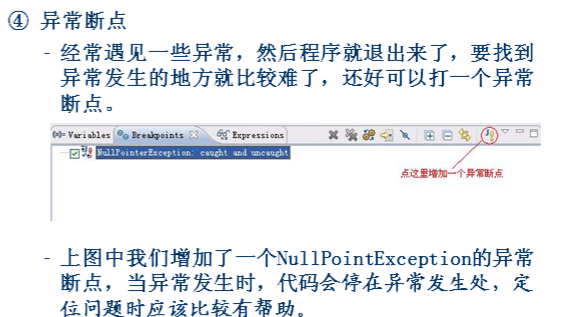
①条件断点 –在Eclipse Java 编辑区的行头双击就会得到一个断点, 代码会运行到此处时停止。



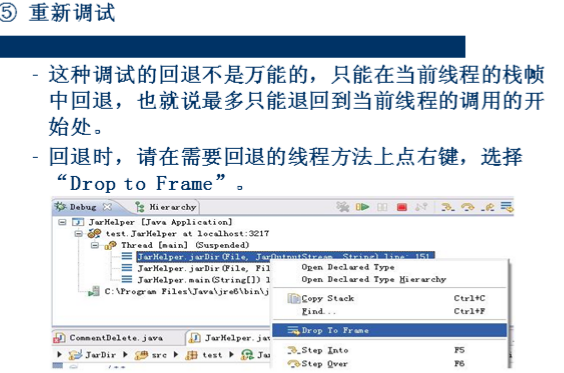

实验总结 : 在本次实验中我学到了 异常,断言及日志。所有的异常都是由Throwable继承而来。 分为Error 类和 Exception类。 Error类: 描述了Java运行时系统的内部错误和资源耗尽错误。应用程序不应该捕获这类异常,也不会抛出这种异常,Exception层次结构又分解为两个分支:1)一个分支派生于RuntimeException:2)另一个分支包含其他异常。 RuntimeException为运行时异常类,一般是程序错误产生; Java将派生于Error类或RuntimeException类的所有异常称为未检查异常,编译器允许不对它们异常处理。 throws : 声明异常, throw : 抛出一个已检查异常。 在捕获异常中, try 语句可以只有finally子句,而没有catch子句;也可以有多个catch子句。 断言 : assert 条件; assert 条件 :表达式; -enableassertions 或 -ea 启用断言 -disableassertions 或 -da 启用断言 。 本次实验相对来说还可以,比前面的简单一点点。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号