秋招-算法题
1、将字符串中的数字打上括号
1 //法一: 2 bool isNumber(const char& c) 3 { 4 if(c >= '0' && c <= '9') 5 return true; 6 return false; 7 } 8 int main() 9 { 10 std::string inStr = "b"; 11 std::string outStr = ""; 12 bool flag = false; //我还没有插 13 for (const char& c : inStr) 14 { 15 if(isNumber(c)) 16 { 17 if(flag == false) 18 { 19 outStr += '('; 20 flag = true; 21 } 22 } 23 else 24 { 25 if(flag == true) 26 { 27 outStr += ')'; 28 flag = false; 29 } 30 } 31 outStr += c; 32 } 33 if(flag) 34 outStr += ')'; 35 std::cout << outStr << std::endl; 36 } 37 //法二:双指针 38 std::string addBrackets(std::string s) 39 { 40 std::string res; 41 int left = 0; 42 for(int right = 0; right < s.size(); right++) 43 { 44 if(!isdigit(s[right])) res += s[right]; 45 else { 46 res += '('; 47 left = right; 48 while(right < s.size() && isdigit(s[right])) right++; 49 res += s.substr(left, right - left); 50 res += ')'; 51 right--; //这得自减 52 } 53 } 54 return res; 55 }
2、rand35实现rand47
class Solution {
public:
int rand47() {
while(true)
{
int x = (rand35()-1)*35 + rand35();//rand生成0-1225
if (x <= 47*26) //拒绝1223-1225
{return x % 47 + 1;}
}
};
3、实现字符串反转,以逗号作为切割符,切割的子串以单词作为单元反转
4、N个骰子出现和为m的概率(剑指offer 60)
5、判断两个矩形是否重叠
- 按照一般的思路,先列举出所有的矩形重叠的情况,然后,判断是否是其中一种,如图所示,共有四种重叠情况,我们使用紫色代表矩形A,红色代表矩形B,并分别用
p1,p2,p3,p4代表对应的左上角与右下角。如果依次判断,过于复杂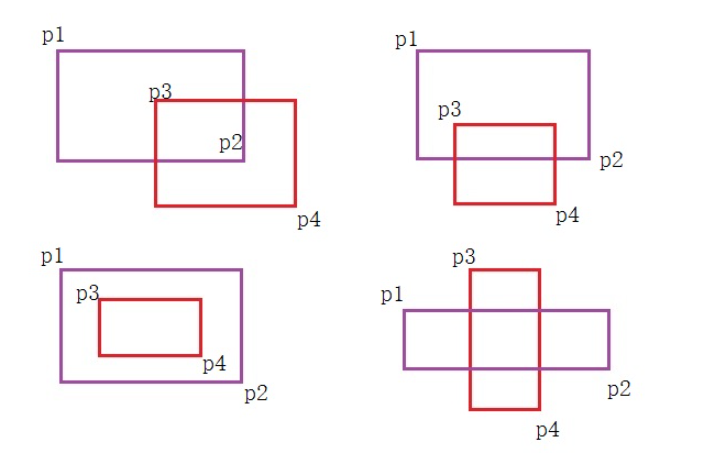
6、一数组有正有负,输出正负交替,多余的就全放在后面
思路:我思路就是用一个标记flag表示当前需要正数还是负数,遍历数字,如果当前是需要的数字就flag=!flag然后continue,如果不是就往后找一个需要的数字跟它交换位置,然后flag=!flag
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> a = {-1, 3, 2, 4, 5, -6, 7, -9};
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); ++i){
if (flag && a[i]>=0){
flag = !flag;
continue;
}
if (!flag && a[i]<0){
flag = !flag;
continue;
}
if (flag){
int j = i + 1;
while (j < a.size() && a[j] < 0) ++j;
if (j == a.size()) break;
swap(a[i], a[j]);
}
else {
int j = i + 1;
while (j < a.size() && a[j] >= 0) ++j;
if (j == a.size()) break;
swap(a[i], a[j]);
}
flag = !flag;
}
for (auto& num : a) cout << num << " " ;
return 0;
}
7、手撕代码:以概率p生成1、概率1-p生成0的rand函数,得到0-1等概率的rand函数,计算新的rand函数
int Rand()
{
int i1 = rand();
int i2 = rand();
if(i1==0 && i2==1)
return 1;
else if(i1==1 && i2==0)
return 0;
else
return Rand();
return -1;
}
8、给一个m*n的网格,返回网格里所有长方形的个数
9、n个数中随机选取m个,要求概率相等
- i=0时,rand()%(n-i)取值范围为0-n-1,共计n个数,此时如果输出0,只需要rand()%(n-i)小于m,因此,i=0被输出的概率为m/n
- i=1时,rand()%(n-i)取值范围为0-n-2,共计n-1个数,此时如果0已经输出了,则m已经自减,此时为m-1,则i=1被输出的概率为(m-1)/(n-1);如果0没有被输出,则m未自减,此时,i=1被输出的概率为m/(n-1)。此时,i=1被输出的概率为(1-m/n)x(m/(n-1))+m/nx(m-1)/(n-1)=m/n。
-
#include<iostream> #include<time.h> using namespace std; void knuth(int n,int m) { srand((unsigned int)time(0)); for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) { if(rand()%(n-i)<m) { cout<<i<<endl; m--; } } } int main() { int n=100,m=10; knuth(n,m); }
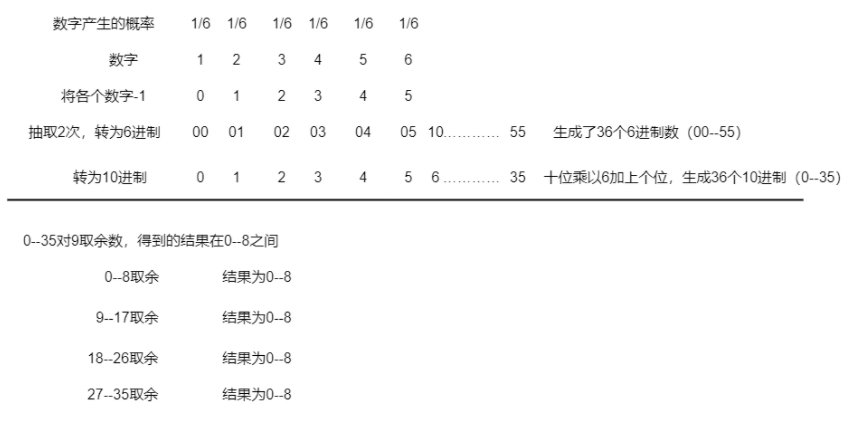
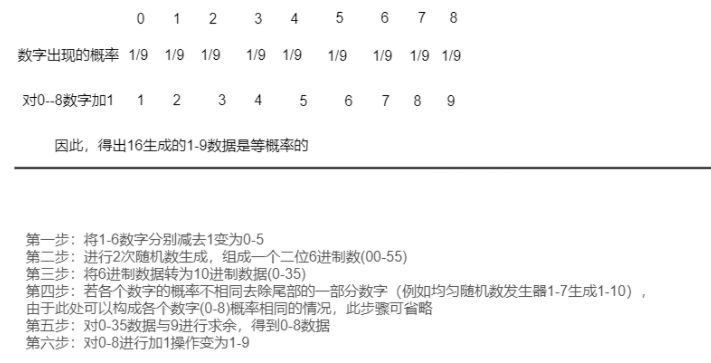
10、超长16进制转10进制
11、一个骰子,怎么等概率地从9个人中选出两个人
12、红黑树的实现
1、基本定义
enum RBTColor{RED, BLACK};
template <class T>
class RBTNode{
public:
RBTColor color; // 颜色
T key; // 关键字(键值)
RBTNode *left; // 左孩子
RBTNode *right; // 右孩子
RBTNode *parent; // 父结点
RBTNode(T value, RBTColor c, RBTNode *p, RBTNode *l, RBTNode *r):
key(value),color(c),parent(),left(l),right(r) {}
};
template <class T>
class RBTree {
private:
RBTNode<T> *mRoot; // 根结点
public:
RBTree();
~RBTree();
// 前序遍历"红黑树"
void preOrder();
// 中序遍历"红黑树"
void inOrder();
// 后序遍历"红黑树"
void postOrder();
// (递归实现)查找"红黑树"中键值为key的节点
RBTNode<T>* search(T key);
// (非递归实现)查找"红黑树"中键值为key的节点
RBTNode<T>* iterativeSearch(T key);
// 查找最小结点:返回最小结点的键值。
T minimum();
// 查找最大结点:返回最大结点的键值。
T maximum();
// 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"红黑树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。
RBTNode<T>* successor(RBTNode<T> *x);
// 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"红黑树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。
RBTNode<T>* predecessor(RBTNode<T> *x);
// 将结点(key为节点键值)插入到红黑树中
void insert(T key);
// 删除结点(key为节点键值)
void remove(T key);
// 销毁红黑树
void destroy();
// 打印红黑树
void print();
private:
// 前序遍历"红黑树"
void preOrder(RBTNode<T>* tree) const;
// 中序遍历"红黑树"
void inOrder(RBTNode<T>* tree) const;
// 后序遍历"红黑树"
void postOrder(RBTNode<T>* tree) const;
// (递归实现)查找"红黑树x"中键值为key的节点
RBTNode<T>* search(RBTNode<T>* x, T key) const;
// (非递归实现)查找"红黑树x"中键值为key的节点
RBTNode<T>* iterativeSearch(RBTNode<T>* x, T key) const;
// 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最小结点。
RBTNode<T>* minimum(RBTNode<T>* tree);
// 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最大结点。
RBTNode<T>* maximum(RBTNode<T>* tree);
// 左旋
void leftRotate(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T>* x);
// 右旋
void rightRotate(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T>* y);
// 插入函数
void insert(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T>* node);
// 插入修正函数
void insertFixUp(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T>* node);
// 删除函数
void remove(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T> *node);
// 删除修正函数
void removeFixUp(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T> *node, RBTNode<T> *parent);
// 销毁红黑树
void destroy(RBTNode<T>* &tree);
// 打印红黑树
void print(RBTNode<T>* tree, T key, int direction);
#define rb_parent(r) ((r)->parent)
#define rb_color(r) ((r)->color)
#define rb_is_red(r) ((r)->color==RED)
#define rb_is_black(r) ((r)->color==BLACK)
#define rb_set_black(r) do { (r)->color = BLACK; } while (0)
#define rb_set_red(r) do { (r)->color = RED; } while (0)
#define rb_set_parent(r,p) do { (r)->parent = (p); } while (0)
#define rb_set_color(r,c) do { (r)->color = (c); } while (0)
};
2、左旋
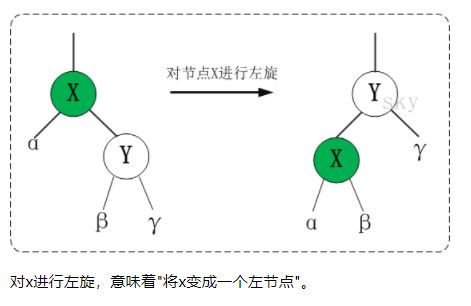
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转
*
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋):
* px px
* / /
* x y
* / \ --(左旋)--> / \ #
* lx y x ry
* / \ / \
* ly ry lx ly
*
*
*/
template <class T>
void RBTree<T>::leftRotate(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T>* x)
{
// 设置x的右孩子为y
RBTNode<T> *y = x->right;
// 将 “y的左孩子” 设为 “x的右孩子”;
// 如果y的左孩子非空,将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子的父亲”
x->right = y->left;
if (y->left != NULL)
y->left->parent = x;
// 将 “x的父亲” 设为 “y的父亲”
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == NULL)
{
root = y; // 如果 “x的父亲” 是空节点,则将y设为根节点
}
else
{
if (x->parent->left == x)
x->parent->left = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
else
x->parent->right = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
// 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子”
y->left = x;
// 将 “x的父节点” 设为 “y”
x->parent = y;
}
3、右旋
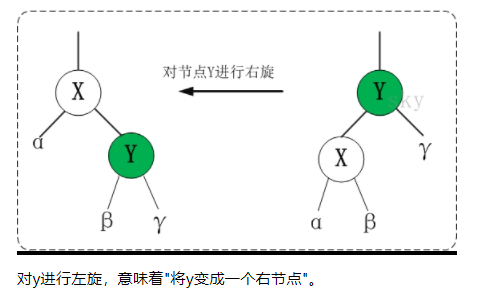
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(y)进行右旋转
*
* 右旋示意图(对节点y进行左旋):
* py py
* / /
* y x
* / \ --(右旋)--> / \ #
* x ry lx y
* / \ / \ #
* lx rx rx ry
*
*/
template <class T>
void RBTree<T>::rightRotate(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T>* y)
{
// 设置x是当前节点的左孩子。
RBTNode<T> *x = y->left;
// 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”;
// 如果"x的右孩子"不为空的话,将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子的父亲”
y->left = x->right;
if (x->right != NULL)
x->right->parent = y;
// 将 “y的父亲” 设为 “x的父亲”
x->parent = y->parent;
if (y->parent == NULL)
{
root = x; // 如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点
}
else
{
if (y == y->parent->right)
y->parent->right = x; // 如果 y是它父节点的右孩子,则将x设为“y的父节点的右孩子”
else
y->parent->left = x; // (y是它父节点的左孩子) 将x设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
// 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子”
x->right = y;
// 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”
y->parent = x;
}
4、添加
将一个节点插入到红黑树中,需要执行哪些步骤呢?首先,将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点插入;然后,将节点着色为红色;最后,通过"旋转和重新着色"等一系列操作来修正该树,使之重新成为一颗红黑树。详细描述如下:
第一步: 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点插入。
红黑树本身就是一颗二叉查找树,将节点插入后,该树仍然是一颗二叉查找树。也就意味着,树的键值仍然是有序的。此外,无论是左旋还是右旋,若旋转之前这棵树是二叉查找树,旋转之后它一定还是二叉查找树。这也就意味着,任何的旋转和重新着色操作,都不会改变它仍然是一颗二叉查找树的事实。
好吧?那接下来,我们就来想方设法的旋转以及重新着色,使这颗树重新成为红黑树!
第二步:将插入的节点着色为"红色"。
为什么着色成红色,而不是黑色呢?为什么呢?在回答之前,我们需要重新温习一下红黑树的特性:
(1) 每个节点或者是黑色,或者是红色。
(2) 根节点是黑色。
(3) 每个叶子节点是黑色。 [注意:这里叶子节点,是指为空的叶子节点!]
(4) 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
(5) 从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑节点。
将插入的节点着色为红色,不会违背"特性(5)"!少违背一条特性,就意味着我们需要处理的情况越少。接下来,就要努力的让这棵树满足其它性质即可;满足了的话,它就又是一颗红黑树了。o(∩∩)o...哈哈
第三步: 通过一系列的旋转或着色等操作,使之重新成为一颗红黑树。
第二步中,将插入节点着色为"红色"之后,不会违背"特性(5)"。那它到底会违背哪些特性呢?
对于"特性(1)",显然不会违背了。因为我们已经将它涂成红色了。
对于"特性(2)",显然也不会违背。在第一步中,我们是将红黑树当作二叉查找树,然后执行的插入操作。而根据二叉查找数的特点,插入操作不会改变根节点。所以,根节点仍然是黑色。
对于"特性(3)",显然不会违背了。这里的叶子节点是指的空叶子节点,插入非空节点并不会对它们造成影响。
对于"特性(4)",是有可能违背的!
那接下来,想办法使之"满足特性(4)",就可以将树重新构造成红黑树了。
/*
* 将结点插入到红黑树中
*
* 参数说明:
* root 红黑树的根结点
* node 插入的结点 // 对应《算法导论》中的node
*/
template <class T>
void RBTree<T>::insert(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T>* node)
{
RBTNode<T> *y = NULL;
RBTNode<T> *x = root;
// 1. 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点添加到二叉查找树中。
while (x != NULL)
{
y = x;
if (node->key < x->key)
x = x->left;
else
x = x->right;
}
node->parent = y;
if (y!=NULL)
{
if (node->key < y->key)
y->left = node;
else
y->right = node;
}
else
root = node;
// 2. 设置节点的颜色为红色
node->color = RED;
// 3. 将它重新修正为一颗二叉查找树
insertFixUp(root, node);
}
/*
* 将结点(key为节点键值)插入到红黑树中
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 红黑树的根结点
* key 插入结点的键值
*/
template <class T>
void RBTree<T>::insert(T key)
{
RBTNode<T> *z=NULL;
// 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if ((z=new RBTNode<T>(key,BLACK,NULL,NULL,NULL)) == NULL)
return ;
insert(mRoot, z);
}
内部接口 -- insert(root, node)的作用是将"node"节点插入到红黑树中。其中,root是根,node是被插入节点。
外部接口 -- insert(key)的作用是将"key"添加到红黑树中。
添加修正操作的实现代码(C++语言)
/*
* 红黑树插入修正函数
*
* 在向红黑树中插入节点之后(失去平衡),再调用该函数;
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一颗红黑树。
*
* 参数说明:
* root 红黑树的根
* node 插入的结点 // 对应《算法导论》中的z
*/
template <class T>
void RBTree<T>::insertFixUp(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T>* node)
{
RBTNode<T> *parent, *gparent;
// 若“父节点存在,并且父节点的颜色是红色”
while ((parent = rb_parent(node)) && rb_is_red(parent))
{
gparent = rb_parent(parent);
//若“父节点”是“祖父节点的左孩子”
if (parent == gparent->left)
{
// Case 1条件:叔叔节点是红色
{
RBTNode<T> *uncle = gparent->right;
if (uncle && rb_is_red(uncle))
{
rb_set_black(uncle);
rb_set_black(parent);
rb_set_red(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
}
// Case 2条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是右孩子
if (parent->right == node)
{
RBTNode<T> *tmp;
leftRotate(root, parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// Case 3条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是左孩子。
rb_set_black(parent);
rb_set_red(gparent);
rightRotate(root, gparent);
}
else//若“z的父节点”是“z的祖父节点的右孩子”
{
// Case 1条件:叔叔节点是红色
{
RBTNode<T> *uncle = gparent->left;
if (uncle && rb_is_red(uncle))
{
rb_set_black(uncle);
rb_set_black(parent);
rb_set_red(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
}
// Case 2条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是左孩子
if (parent->left == node)
{
RBTNode<T> *tmp;
rightRotate(root, parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// Case 3条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是右孩子。
rb_set_black(parent);
rb_set_red(gparent);
leftRotate(root, gparent);
}
}
// 将根节点设为黑色
rb_set_black(root);
}
5. 删除操作
将红黑树内的某一个节点删除。需要执行的操作依次是:首先,将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将该节点从二叉查找树中删除;然后,通过"旋转和重新着色"等一系列来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。详细描述如下:
第一步:将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点删除。
这和"删除常规二叉查找树中删除节点的方法是一样的"。分3种情况:
① 被删除节点没有儿子,即为叶节点。那么,直接将该节点删除就OK了。
② 被删除节点只有一个儿子。那么,直接删除该节点,并用该节点的唯一子节点顶替它的位置。
③ 被删除节点有两个儿子。那么,先找出它的后继节点;然后把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。在这里,后继节点相当于替身,在将后继节点的内容复制给"被删除节点"之后,再将后继节点删除。这样就巧妙的将问题转换为"删除后继节点"的情况了,下面就考虑后继节点。 在"被删除节点"有两个非空子节点的情况下,它的后继节点不可能是双子非空。既然"的后继节点"不可能双子都非空,就意味着"该节点的后继节点"要么没有儿子,要么只有一个儿子。若没有儿子,则按"情况① "进行处理;若只有一个儿子,则按"情况② "进行处理。
第二步:通过"旋转和重新着色"等一系列来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。
因为"第一步"中删除节点之后,可能会违背红黑树的特性。所以需要通过"旋转和重新着色"来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。
/*
* 删除结点(node),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* root 红黑树的根结点
* node 删除的结点
*/
template <class T>
void RBTree<T>::remove(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T> *node)
{
RBTNode<T> *child, *parent;
RBTColor color;
// 被删除节点的"左右孩子都不为空"的情况。
if ( (node->left!=NULL) && (node->right!=NULL) )
{
// 被删节点的后继节点。(称为"取代节点")
// 用它来取代"被删节点"的位置,然后再将"被删节点"去掉。
RBTNode<T> *replace = node;
// 获取后继节点
replace = replace->right;
while (replace->left != NULL)
replace = replace->left;
// "node节点"不是根节点(只有根节点不存在父节点)
if (rb_parent(node))
{
if (rb_parent(node)->left == node)
rb_parent(node)->left = replace;
else
rb_parent(node)->right = replace;
}
else
// "node节点"是根节点,更新根节点。
root = replace;
// child是"取代节点"的右孩子,也是需要"调整的节点"。
// "取代节点"肯定不存在左孩子!因为它是一个后继节点。
child = replace->right;
parent = rb_parent(replace);
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = rb_color(replace);
// "被删除节点"是"它的后继节点的父节点"
if (parent == node)
{
parent = replace;
}
else
{
// child不为空
if (child)
rb_set_parent(child, parent);
parent->left = child;
replace->right = node->right;
rb_set_parent(node->right, replace);
}
replace->parent = node->parent;
replace->color = node->color;
replace->left = node->left;
node->left->parent = replace;
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(root, child, parent);
delete node;
return ;
}
if (node->left !=NULL)
child = node->left;
else
child = node->right;
parent = node->parent;
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = node->color;
if (child)
child->parent = parent;
// "node节点"不是根节点
if (parent)
{
if (parent->left == node)
parent->left = child;
else
parent->right = child;
}
else
root = child;
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(root, child, parent);
delete node;
}
/*
* 删除红黑树中键值为key的节点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 红黑树的根结点
*/
template <class T>
void RBTree<T>::remove(T key)
{
RBTNode<T> *node;
// 查找key对应的节点(node),找到的话就删除该节点
if ((node = search(mRoot, key)) != NULL)
remove(mRoot, node);
}
内部接口 -- remove(root, node)的作用是将"node"节点插入到红黑树中。其中,root是根,node是被插入节点。
外部接口 -- remove(key)删除红黑树中键值为key的节点。
删除修正操作的实现代码(C++语言)
/*
* 红黑树删除修正函数
*
* 在从红黑树中删除插入节点之后(红黑树失去平衡),再调用该函数;
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一颗红黑树。
*
* 参数说明:
* root 红黑树的根
* node 待修正的节点
*/
template <class T>
void RBTree<T>::removeFixUp(RBTNode<T>* &root, RBTNode<T> *node, RBTNode<T> *parent)
{
RBTNode<T> *other;
while ((!node || rb_is_black(node)) && node != root)
{
if (parent->left == node)
{
other = parent->right;
if (rb_is_red(other))
{
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
rb_set_black(other);
rb_set_red(parent);
leftRotate(root, parent);
other = parent->right;
}
if ((!other->left || rb_is_black(other->left)) &&
(!other->right || rb_is_black(other->right)))
{
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
rb_set_red(other);
node = parent;
parent = rb_parent(node);
}
else
{
if (!other->right || rb_is_black(other->right))
{
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
rb_set_black(other->left);
rb_set_red(other);
rightRotate(root, other);
other = parent->right;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
rb_set_color(other, rb_color(parent));
rb_set_black(parent);
rb_set_black(other->right);
leftRotate(root, parent);
node = root;
break;
}
}
else
{
other = parent->left;
if (rb_is_red(other))
{
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
rb_set_black(other);
rb_set_red(parent);
rightRotate(root, parent);
other = parent->left;
}
if ((!other->left || rb_is_black(other->left)) &&
(!other->right || rb_is_black(other->right)))
{
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
rb_set_red(other);
node = parent;
parent = rb_parent(node);
}
else
{
if (!other->left || rb_is_black(other->left))
{
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
rb_set_black(other->right);
rb_set_red(other);
leftRotate(root, other);
other = parent->left;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
rb_set_color(other, rb_color(parent));
rb_set_black(parent);
rb_set_black(other->left);
rightRotate(root, parent);
node = root;
break;
}
}
}
if (node)
rb_set_black(node);
}