常见的排序算法
一、归并排序
1、算法思想
该算法是采用分治法,将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
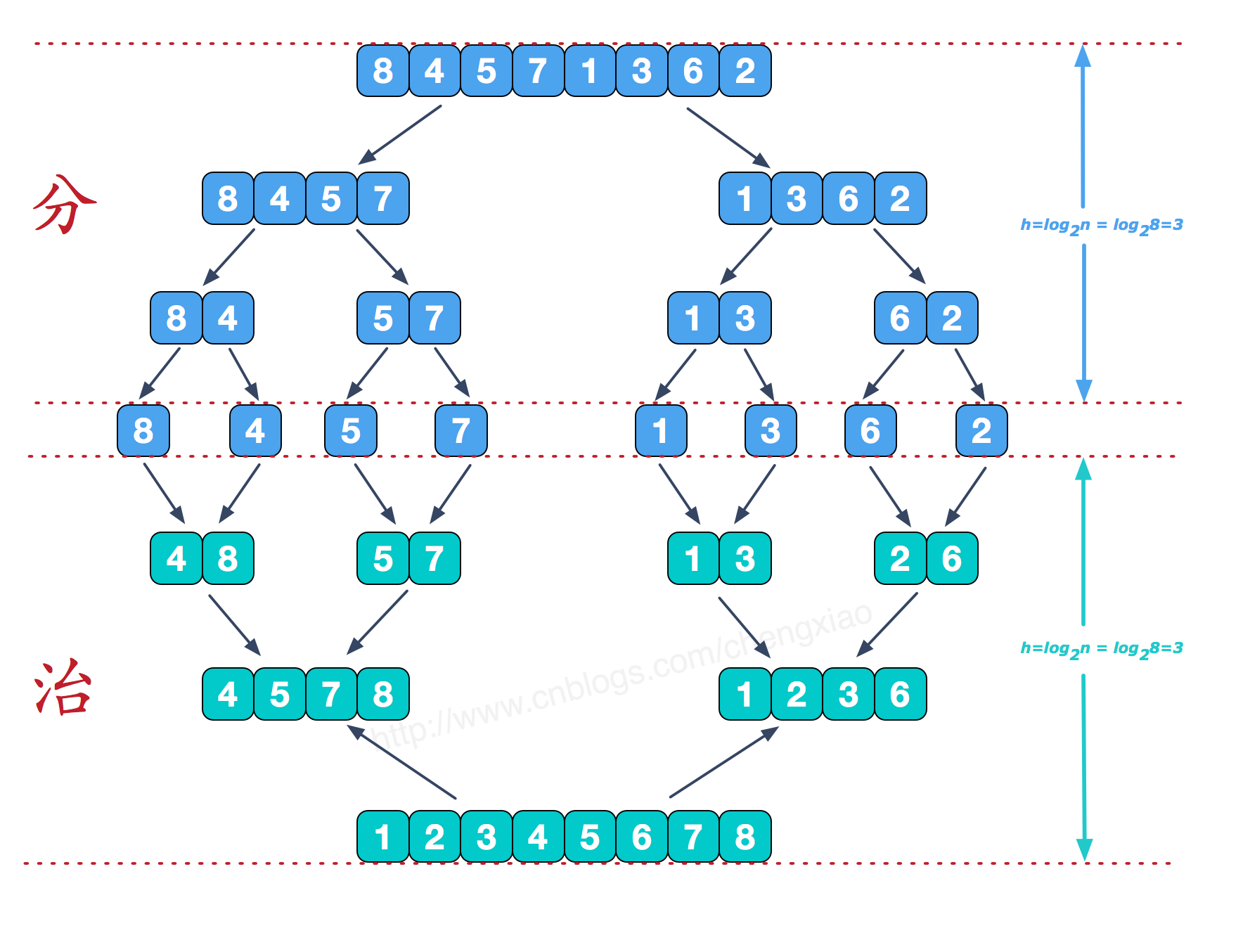
再来看看治阶段,我们需要将两个已经有序的子序列合并成一个有序序列,比如上图中的最后一次合并,要将[4,5,7,8]和[1,2,3,6]两个已经有序的子序列,合并为最终序列[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8],来看下实现步骤。
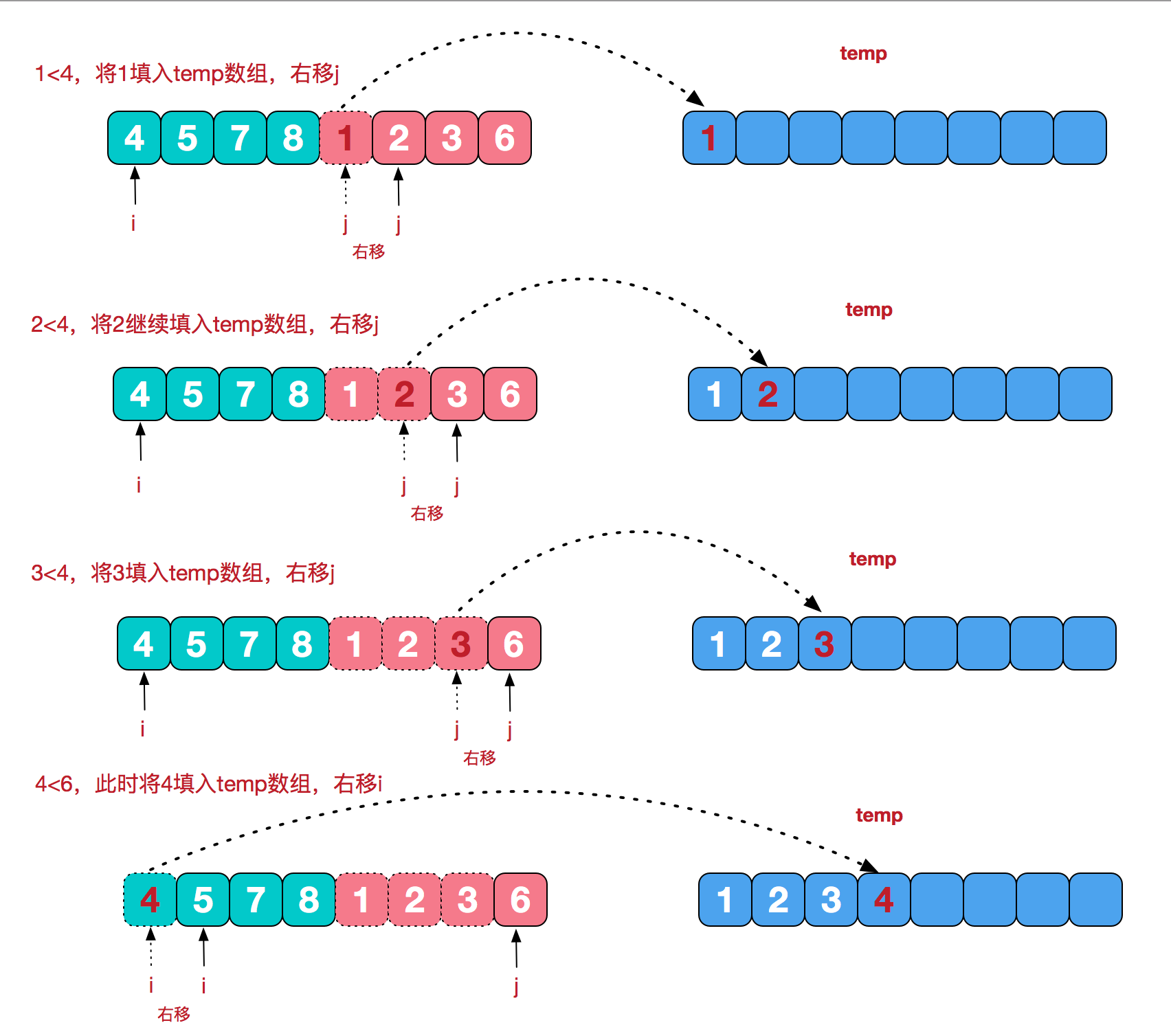
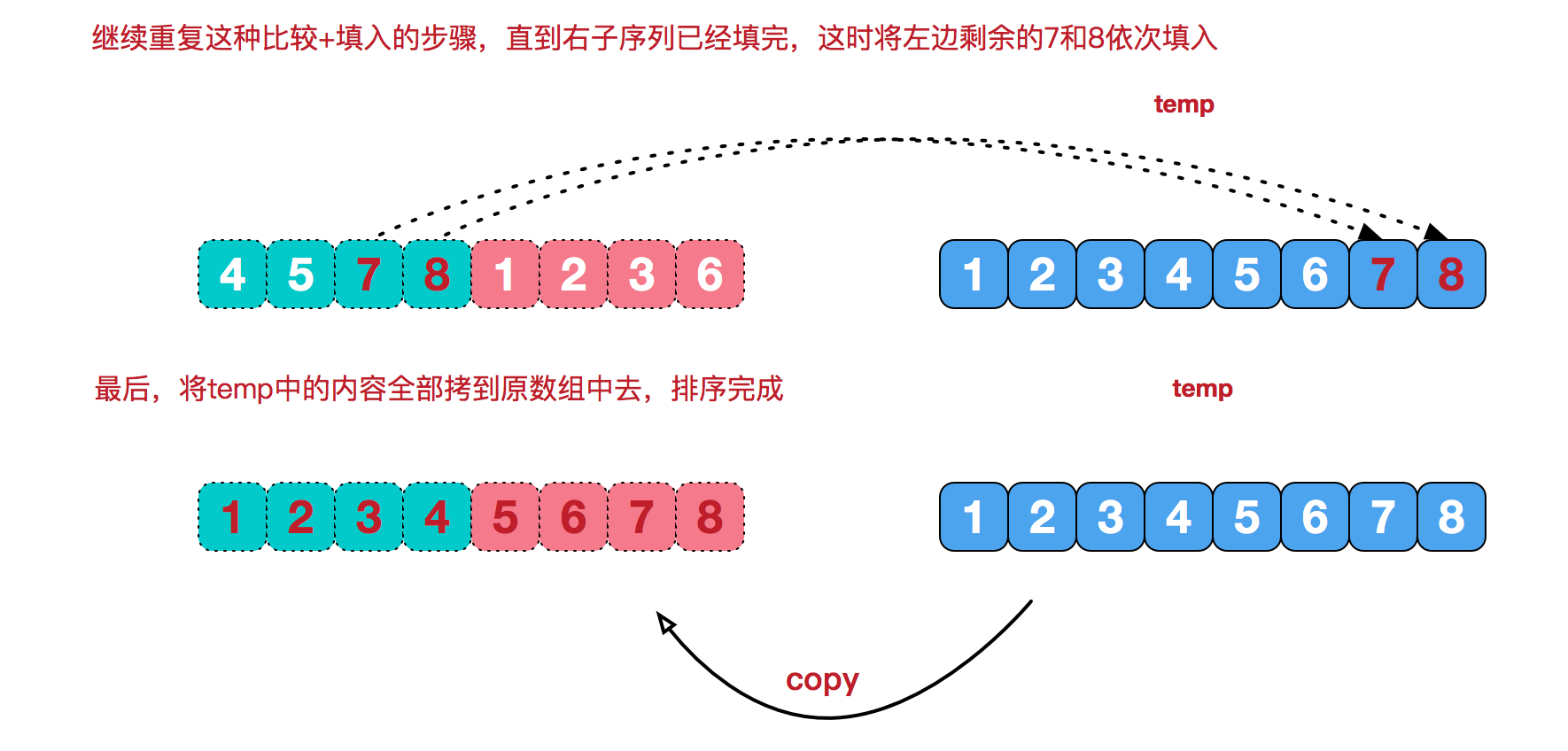
2、代码实现
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<algorithm>
3 using namespace std;
4
5 void merge(int *data,int start,int end,int *result)
6 {
7 int left_length = (end - start + 1) / 2 + 1;
8 int left_index = start;
9 int right_index = start + left_length;
10 int result_index = start;
11 while(left_index<start + left_length && right_index <end + 1) //store data into new array
12 {
13 if(data[left_index] <= data[right_index])
14 result[result_index++] = data[left_index++];
15 else
16 result[result_index++] = data[right_index++];
17 }
18 while(left_index < start + left_length)
19 result[result_index++] = data[left_index++];
20 while(right_index <end+1)
21 result[result_index++] = data[right_index++];
22 }
23
24 void merge_sort(int *data,int start,int end,int *result)
25 {
26 if(1 == end - start) //last only two elements
27 {
28 if(data[start] > data[end])
29 {
30 int temp = data[start];
31 data[start] = data[end];
32 data[end] = temp;
33 }
34 return;
35 }
36 else if (end == start)
37 return; //last one element then there is no need to sort;
38 else{
39 //continue to divide the interval
40 merge_sort(data, start, (end - start + 1) / 2 + start, result);
41 merge_sort(data, (end - start + 1) / 2 + start + 1, end, result);
42 //start to merge sorted data
43 merge(data, start, end, result);
44 for (int i = start; i <= end;++i)
45 {
46 data[i] = result[i];
47 }
48 }
49
50 }
51 //example
52 int main()
53 {
54 int data[] = {5,3,6,7,3,2,7,9,8,6,34,32,5,4,43,12,37};
55 int length = 17;
56 int result[length];
57 cout << "before sorted:"<<'\n';
58 for (int i = 0; i < length;i++)
59 cout << data[i]<<' ';
60 cout << '\n'
61 << "after sorted:"<<'\n';
62 merge_sort(data, 0, length - 1, result);
63 for (int i = 0; i < length;i++)
64 cout << result[i]<<' ';
65 return 0;
66 }
二、快排
1、基本思想
选取一个基准元素(pivot)
比pivot小的放到pivot左边,比pivot大的放到pivot右边
对pivot左边的序列和右边的序列分别递归的执行步骤1和步骤2
//快速排序采用的思想是分治思想
//时间复杂度为O(N*logN)
2、代码实现
1 void quicksort(vector<int>& nums,int startindex,int endindex)
2 {
3 if(startindex>=endindex) return;
4 int privo=partition(nums,startindex,endindex);
5 quicksort(nums,startindex,privo-1);
6 quicksort(nums,privo+1,endindex);
7 }
8 int partition(vector<int>& nums,int startindex,int endindex)
9 {
10 int pri=nums[startindex];
11 int left=startindex;
12 int right=endindex;
13 while(left!=right)
14 {
15 while(left<right&&nums[right]>pri)
16 right--;
17 while(left<right&&nums[left]<=pri)
18 left++;
19 if(left<right)
20 {
21 int p=nums[left];
22 nums[left]=nums[right];
23 nums[right]=p;
24 }
25 }
26 if(left == right && nums[right] > pri) right--;
27 nums[startindex]=nums[left]; //把基准值移到分界线出
28 nums[left]=pri;
29 return left; //返回基准值的下标
30 }
三、插入排序
插入排序的基本思想是每次将一个待排序的记录,按其关键字大小插入到前面已经排好序的子文件中的适当位置,直到全部记录插入完成为止。常见的插入排序有插入排序(Insertion Sort),希尔排序(Shell Sort)
1、直接插入排序
最差时间复杂度:O(n^2)
最优时间复杂度:O(n)
平均时间复杂度:O(n^2)
稳定性:稳定
直接插入排序(Insertion Sort),是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理是通过构建有序序列,对未排序的数据,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应位置并插入。
插入排序算法的一般步骤:
1.从第一个元素开始,该元素可以认为已被排序;
2.取出下一个元素,在已经排序的元素序列中从后向前扫描;
3.如果该元素(已排序)大于新元素,将该元素移到下一个位置;
4.重复步骤3,直到找到已排序的元素小于或者等于新元素的位置;
5.将新元素插入到该位置后,重复2~5
void InsertionSort(int *a, int len)
{
for (int j=1; j<len; j++)
{
int key = a[j];
int i = j-1;
while (i>=0 && a[i]>key)
{
a[i+1] = a[i];
i--;
}
a[i+1] = key;
}
}
(二)希尔排序
平均时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
稳定性:不稳定
希尔排序(Shell Sort),也称为递减增量排序算法,是插入排序的一种高速而稳定的改进版本。希尔排序是基于插入排序的以下两点性质而提出改进方法的:1.插入排序在对几乎已经排好序的数据操作时,效率高,即可以达到线性排序的效率;2.但插入排序一般来说是低效的, 因为插入排序每次只能将数据移动一位。
希尔排序的一般步骤为:
1.先取一个小于n的整数d1作为第一个增量,把文件的全部记录分成d1个组。所有距离为dl的倍数的记录放在同一个组中,在各组内进行直接插人排序。
2.取第二个增量d2<d1重复上述的分组和排序,直至所取的增量dt=1(dt<dt-l<…<d2<d1),即所有记录放在同一组中进行直接插入排序为止。
步长的选择是希尔排序的重要部分。只要最终步长为1任何步长串行都可以工作。算法最开始以一定的步长进行排序。然后会继续以一定步长进行排序,最终算法以步长为1进行排序。当步长为1时,算法变为插入排序,这就保证了数据一定会被排序。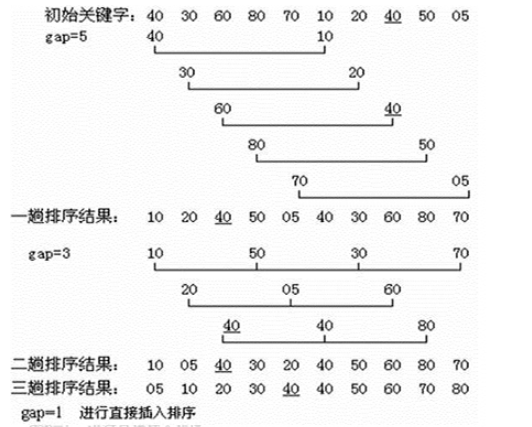
void ShellSort(int *a, int len)
{
int h = 1;
while( h<len )
h = 3*h + 1;
while( h>0 )
{
for (int j=h; j<len; j++)
{
int key = a[j];
int i = j-h;
while( i>=0 && a[i]>key )
{
a[i+h] = a[i];
i = i-h;
}
a[i+h] = key;
}
h = h/3;
}
}
————————————————
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/left_la/article/details/8656425



