Python学习笔记9—文件
在Python中,要对一个文件进行操作,只需用内置的open函数打开文件即可。
Signature: open(file, mode='r', buffering=-1, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None,closefd=True, opener=None)
Docstring:
Open file and return a stream. Raise IOError upon failure.
Python内置的open函数:
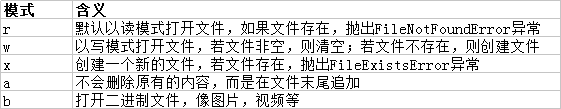
f = open('1.txt','w',encoding='GBK')
关闭文件:
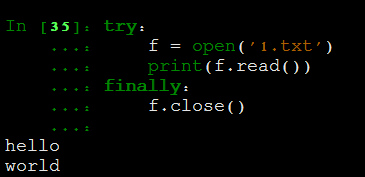
打开的文件要及时关闭,在Python中也可以使用finally语句来保证,但是却不够Pythonic。
使用finally的方法:
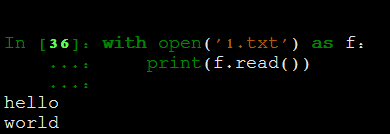
使用上下文管理器,会自动调用close()方法
常见的文件读取的函数:
- read read可以指定参数size,读取指定字节数
- readline 一次读取一行
- readlines 将文件读取到一个列表中,列表中的每一个成员代表一行
- seek 改变文件的读取偏移量
- tell 文件读取的偏移量
read:
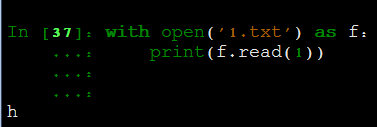
readline:
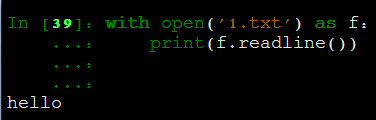
readlines:

seek

此时指针所在的位置,还可以用tell() 来显示,如
>>> f.tell()
17
读取大文件的几种方法:
while 循环和readlin() 来完成这个任务。
#/usr/bin/env python #coding=utf-8 f = open("/python/you.md") while True: line = f.readline() if not line: #到 EOF,返回空字符串,则终止循环 break print line, #注意后面的逗号,去掉 print 语句后面的 '\n',保留原文件中的换行 f.close()
还有一个方法:fileinput 模块
>>> import fileinput >>> for line in fileinput.input("you.md"): ... print line, ... You Raise Me Up When I am down and, oh my soul, so weary; Then troubles come and my heart burdened be;
但是使用迭代的方法是最好的:因为 file 是可迭代的数据类型

文件写的函数
- write 写字符串到文件中,并返回字符数
- writelines 写一个字符串列表到文件中
- print 比write和writelines更加灵活
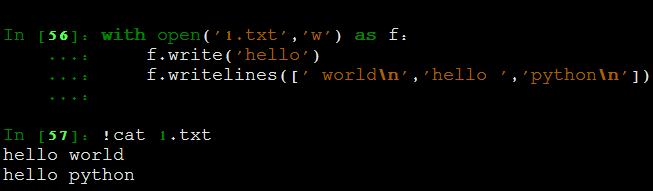
print:
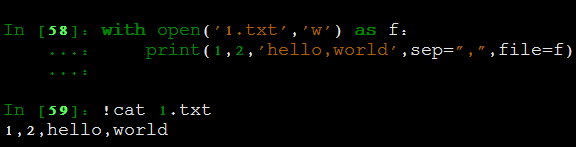
经典案列:
将所有单词首字母变为大写:
使用write:

使用print,更加简化:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号