Android 服务组件
Android 服务组件
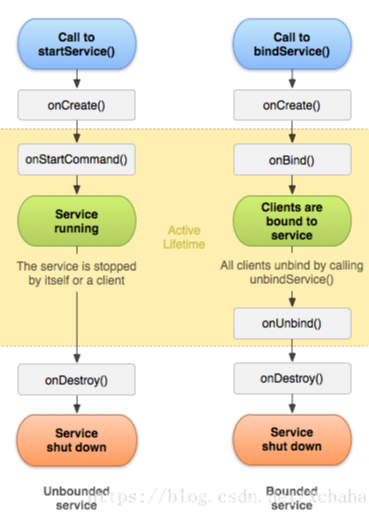
定义
服务是Android中实现程序后台运行的解决方案,不和用户交互而且要求长期运行的任务。
多线程编程
1.线程基本用法
// 继承Thread类
class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
// 处理逻辑
}
}
// 启动
new MyThread().start();
//实现Runnable接口
class MyThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
// 处理逻辑
}
}
// 启动
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
new Thread(myThread).start();
//常用写法
new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run() {
//处理逻辑
}
}).start();
//缩写为
new Thread(() -> {
//处理逻辑
}).start();
2.子线程中更新UI
因为活动的UI是在主线程中,通过子线程直接去修改UI的话,程序会报错,因此这里在子线程中调用下主线程的Handler对象中的handleMessage()来处理下
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final int UPDATE_TEXT = 1;
private TextView text;
@SuppressLint("MissingInflatedId")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
text = findViewById(R.id.text_view);
findViewById(R.id.button).setOnClickListener(v -> {
new Thread(() -> {
//处理发送信息逻辑
handler.sendEmptyMessage(UPDATE_TEXT);
}).start();
});
}
//不带参数的函数已经弃用,建议传入Looper
private Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
@Override
public void handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case UPDATE_TEXT:
text.setText("Nice to meet you!");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
};
}
3.异步消息处理机制
3.1 Message
线程之间传递的消息,内部可携带少量信息,用于不同线程之间交换数据
字段包含:what,arg1,arg2,Object
3.2 Handler
处理者
sendMessage() 发送消息
handleMessage() 处理消息
3.3 MessageQueue
消息队列
存储Handler发送的消息
每个线程只有一个MessageQueue
3.4 Looper
Looper 是每个线程中MessageQueue的管家
调用Looper 的loop()方法后,会进入一个无限循环中
发现一个消息,就取出交给Handler的handleMessage()方法处理,每个线程只有一个Looper对象。
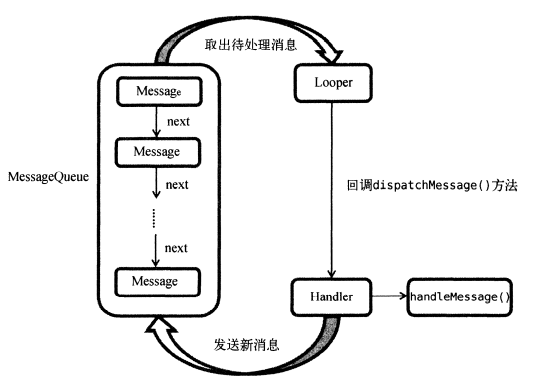
一条消息经过上面的流程后,子流程进入主流程中,从不能更新UI到可以更新,整个异步消息处理的核心思想就是如此。
之前我们有使用到runOnUiThread()方法,其实也是一个异步消息处理机制的接口封装,背后的原理和上图是一样的。
4.使用AsyncTask
AsyncTask背后的原理还是基于异步消息处理的,只是Android帮我们做了很好的封装,让我们可以十分简单的从子线程切换到主线程。
基本用法:
它是一个抽象类,想使用它,得去继承它,继承的时候, 有三个泛型参数
params 是执行AsyncTask时需要传入的参数,用于后台任务中使用
Progress 当前进度
Result 当前任务执行完毕后结果返回
class DownloadTask extends AsyncTask<Void,Integer,Boolean>{
....
}
//这三个泛型的参数和上面的一一对应
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final int UPDATE_TEXT = 1;
private TextView text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
DownloadTask task = new DownloadTask();
task.execute();
}
class DownloadTask extends AsyncTask<Void, Integer, Boolean> {
private ProgressDialog progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainActivity.this);
private int downloadPercent = 0;
@Override
protected Boolean doInBackground(Void... voids) {
try {
while (true) {
downloadPercent = doDownload();
publishProgress(downloadPercent);
if (downloadPercent >= 100) {
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
private int doDownload() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return downloadPercent + 10;
}
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
progressDialog.show();
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Boolean result) {
progressDialog.dismiss();//关闭对话框
//提示下载结果
if (result) {
Toast.makeText(progressDialog.getContext(), "Download succeeded", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} else {
Toast.makeText(progressDialog.getContext(), "Download failed", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) {
progressDialog.setMessage("Downloaded " + values[0] + "%");
}
}
}
服务的基本用法
1.定义一个服务
public class MyService extends Service {
public MyService() {
}
// 这里重写下onCreate,onStartCommand,onDestroy三个方法
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.d("MyService","onCreate executed");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.d("MyService","onStartCommand executed");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.d("MyService","onDestroy executed");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
}
在AndroidManifest.xml中自动生成了以下配置
<service
android:name=".MyService"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true"></service>
2.启动和停止服务
findViewById(R.id.start_service).setOnClickListener(v -> {
Intent startIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
startService(startIntent);
});
findViewById(R.id.stop_service).setOnClickListener(v -> {
Intent stopIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
stopService(stopIntent);
});
3.活动和服务进行通信
private DownloadBinder mBinder = new DownloadBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
class DownloadBinder extends Binder{
public void startDownload(){
Log.d("MyService","startDownload executed");
}
public int getProgress(){
Log.d("MyService","getProgress executed");
return 0;
}
}
服务的绑定和解绑
private MyService.DownloadBinder downloadBinder;
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
downloadBinder = (MyService.DownloadBinder) service;
downloadBinder.startDownload();
downloadBinder.getProgress();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
// 进行服务绑定
findViewById(R.id.bind_service).setOnClickListener(v -> {
Intent bindIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
bindService(bindIntent, connection , BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
});
// 解除服务绑定
findViewById(R.id.unbind_service).setOnClickListener(v -> {
Intent bindIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
unbindService(connection);
});
服务的生命周期
1.项目的任何位置调用Context的startService()方法,服务都可以启动起来,并回调onStartCommand()方法
2.服务之前没有创建过时,会先调用onCreate()方法
3.可调用Context的bindService()获取一个服务的持久连接,这时会回调服务中的onBind()方法。类似的,服务没有被创建的时候,onCreate()方法会在onBind()方法之前执行,调用onBind()的方法可获得IBinder对象实例
4.调用stopService()或stopSelf(),可终止服务运行状态,onDestory()执行销毁
更多服务技巧
1.使用前台服务
Intent intent = new Intent(this,MainActivity.class);
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getActivity(this, 0, intent, 0);
// new NotificationCompat.Builder(context) 过时
//取代方法new NotificationCompat.Builder(context,channelId)
Notification notification = new NotificationCompat.Builder(this, "001")
.setContentTitle("This is content title")
.setContentText("This is content text").setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher))
.setContentIntent(pi)
.build();
startForeground(1,notification);
本文来自博客园,作者:阿寳同學Zybao,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zybao/p/16902186.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步