Java学习笔记 -Object类中常用的方法
1.toString方法:
public String toString()
- 返回对象的字符串表示形式。 一般来说, toString方法返回一个代表这个对象的字符串。
- 结果应该是一个简明扼要的表达,容易让人阅读。 建议所有子类覆盖此方法。
- 输出引用时默认自动调用toString方法
示例:
class MyTime{
private int year;
private int mouth;
private int second;
public MyTime(int year , int mouth , int second){
this.year = year;
this.mouth = mouth;
this.second = second;
}
public String toString(){
return year + "/" + mouth + "/" + second;
}
}
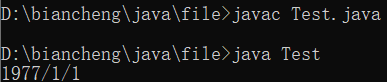
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
MyTime m = new MyTime(1977 , 1 , 1);
System.out.println(m);
}
}
2.equals 方法:
public boolean equals(Object obj){
return (this == obj);
}
以后编程的过程当中,通过equals方法来判断两个对象是否相等。
1.使用场景:
- 判断两个基本数据类型的数据是否相等 “==”
- == 判断内存中的值是否相等,而引用中保存的是内存地址,所有不能使用 == 判断两个对象是否相等
- 源代码中equals使用 == 判断,显然不够用,不能判断两个对象是否相等,所以需要方法覆盖
- 总结:
基本数据类型使用"=="
引用数据类型使用equals方法
示例:
- String也是一个类,重写了Object类中的toString equals方法
- equals用来判断两个字符串是否相等
- toString返回字符串的值
- 最好每新建一个类都要重写equals方法,模仿SUN的String类重写equals
class User{
String name;
Address addr;
public User(String name , Address addr){
this.name = name;
this.addr = addr;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj == null) return false;
if(obj == this) return true;
if(obj instanceof User){
User m = (User)obj;
return name.equals(m.name) && addr.equals(m.equals);
}
return false;
}
}
class Address{
String city;
String street;
String zipcode;
public Address(String city, String street, String zipcode){
this.city = city;
this.street = street;
this.zipcode = zipcode;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj == null) return false;
if(obj == this) return true;
if(obj instanceof Address){
Address m = (Address)obj;
return city.equals(m.city) && street.equals(m.street) && zipcode.equals(m.zipcode);
}
return false;
}
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
User m1 = new User("Zhao yan", new Address("Xu Zhou" , "Zheng Ji", "111111"));
User m2 = new User("Zhao yan", new Address("Xu Zhou" , "Zheng Ji", "111111"));
System.out.println(m1.equals(m2));
}
}
3.finalize()方法 (了解)
protected void finalize() throws Throwable
1.GC:负责调用finalize()方法
2.finalize()方法只有一个方法体,里面没有代码,而且是protected修饰的
3.不需要程序员手动调用,JVM的垃圾回收器负责调用这个方法,不需要手动调用
4.finalize()是SUN公司为Java程序员准备的另一个时机(垃圾回收时机),类似于静态代码块和实例代码块。
5.垃圾回收器不是轻易启动的,垃圾太少或者时间未到,种种条件下,才可能启动
示例:
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p = new Person();
//将对象变成垃圾
p = null;
//建议启动垃圾回收器(只是建议)
System.gc();
}
}
class Person{
//重写
protected void finalize() throws Throwable{
System.out.println("对象被销毁");
}
}
4.hashCode方法:
public native int hashCode();
1.带有native关键字,底层调用C++程序
2.返回哈希码,可以等同看作对象的内存地址
示例:
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Object o = new Object();
System.out.println(o.hashCode());
}
}

