洛谷3829:信用卡凸包
洛谷3829:[SHOI2012]信用卡凸包
题目描述
- 有一种矩形,四个角做了圆滑处理,使他们都是与矩形的两边相切的\(\frac{1}{4}\)圆。现在平面上有一些这样规格相同的矩形,求凸包的周长。
输入格式
- 第一行输入一个正整数\(n\),表示有多少个矩形。第二行给出三个实数\(a,b,r\)表示矩形的竖直+水平方向上的长度以及\(\frac{1}{4}\)圆的半径。
- 之后\(n\)行,每行包三个实数\(x,y,θ\),表示一张矩形的中心(对角线交点)的横纵坐标以及绕中心逆时针旋转的弧度。
输出格式
- 输出一个实数表示凸包的周长,四舍五入精确到小数点后\(2\)位。
数据范围
- \(1\leq n\leq 10^5\)
思路
-
如果这一题四个角没有做圆滑处理的话,也就是\(r=0\)的情况,就会容易很多,直接提取矩形的四个角之后跑Graham即可。
-
但其实仔细观察之后发现,几个圆弧形的地方总合起来的角度等于360度,也就是说对于有圆滑处理的矩形来说,最后的结果就相当于把未圆滑处理的矩形组成的凸包加上一个圆的周长。
-
如图所示
-

-
就相当于红色部分加上最外一周圆周长。
-
于是这题就变成了二维凸包裸题。
-
绕中心旋转处理要怎么做
-
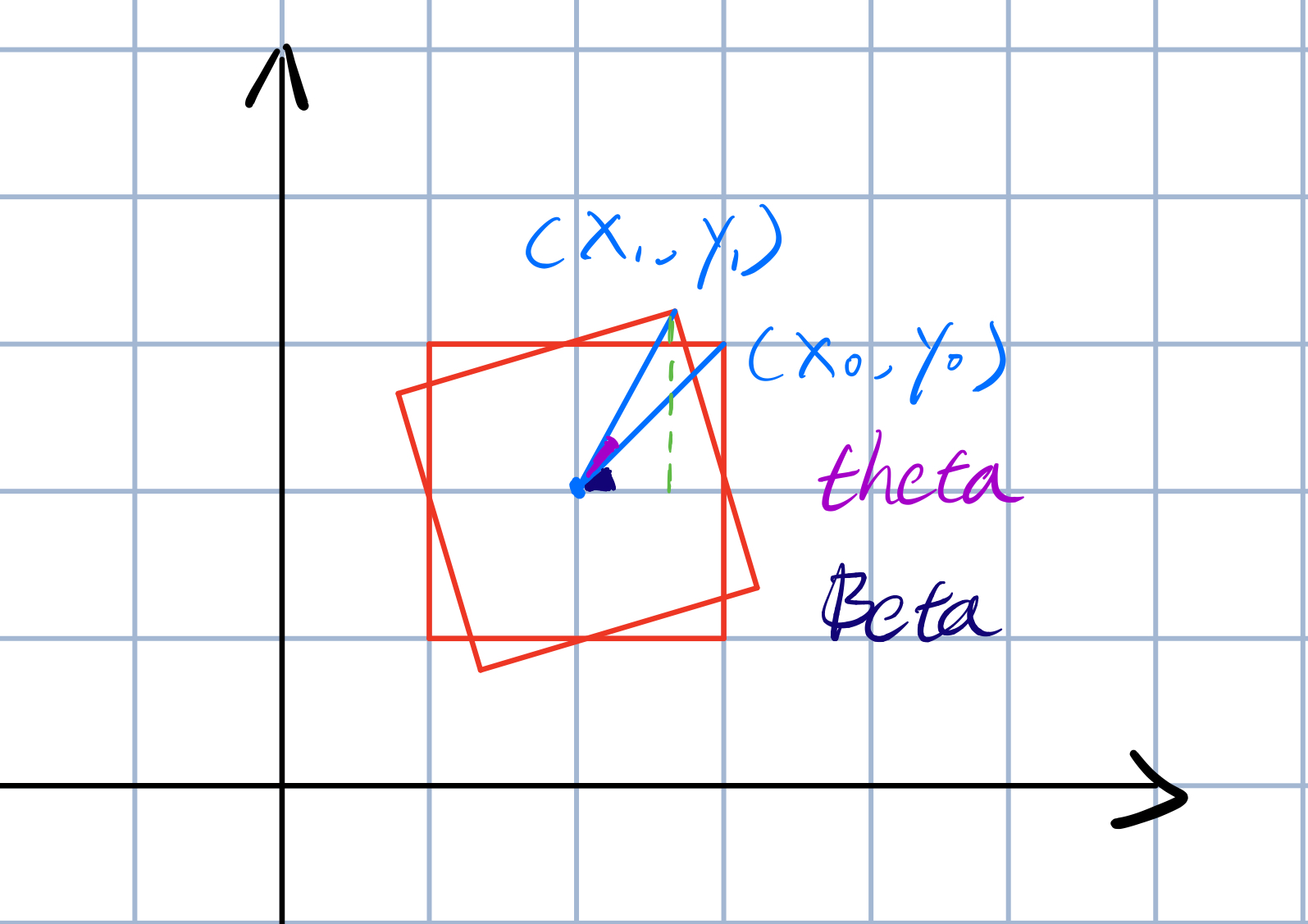
-
假设原先没旋转前,中心点为\((x,y)\),右上角的点是\((x_0,y_0)\),矩形绕中心旋转\(theta\),右上角的点变成了\((x_1,y_1)\)。假设对角线长度的一半为\(length\)。\(a\)为矩形竖直方向的长度的一半,\(b\)为矩形水平方向的长度的一半。
-
首先可以求得\(β=asin(\frac{a}{length})\)。
-
可以发现,旋转之后\((x_1,y_1)=(x+length*cos(β+θ),y+length*sin(β+θ))\)
-
剩下三个点同理,推一推就能明白了,这里给出公式:
- 右上角:\((x+length*cos(β+θ),y+length*sin(β+θ))\)
- 右下角:\((x+length*cos(β-θ),y-length*sin(β-θ))\)
- 左上角:\(((x-length*cos(β-θ),y+length*sin(β-θ)))\)
- 左下角:\((x-length*cos(β+θ),y-length*sin(β+θ))\)
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
const double PI = acos(-1);
int n, cnt, tot;
double a, b, r, x, y, theta, beta, length;
struct Node{
double x, y;
}p[maxn<<2], s[maxn<<2];
Node get_point(int op, double theta)
{
Node a;
if(op == 1) //右上角
a.x = x+length*cos(beta+theta), a.y = y+length*sin(beta+theta);
if(op == 2) //右下角
a.x = x+length*cos(beta-theta), a.y = y-length*sin(beta-theta);
if(op == 3) //左上角
a.x = x-length*cos(beta-theta), a.y = y+length*sin(beta-theta);
if(op == 4) //左下角
a.x = x-length*cos(beta+theta), a.y = y-length*sin(beta+theta);
return a;
}
double vp(Node a1, Node a2, Node b1, Node b2){
return (a2.x-a1.x)*(b2.y-b1.y) - (b2.x-b1.x)*(a2.y-a1.y);
}
double dis(Node a, Node b){
return sqrt((b.y-a.y)*(b.y-a.y)+(b.x-a.x)*(b.x-a.x));
}
bool cmp(Node a, Node b)
{
double tmp = vp(p[1], a, p[1], b);
if(tmp > 0) return 1;
if(tmp == 0 && dis(p[0], a) < dis(p[0], b)) return 1;
return 0;
}
void Graham()
{
for(int i = 2; i <= cnt; i++)
{
if(p[i].y < p[1].y)
{
double tmp;
tmp = p[1].y; p[1].y = p[i].y; p[i].y = tmp;
tmp = p[1].x; p[1].x = p[i].x; p[i].x = tmp;
}
}
sort(p+2, p+1+cnt, cmp);
tot = 1;
s[1] = p[1];
for(int i = 2; i <= cnt; i++)
{
while(tot > 1 && vp(s[tot-1], s[tot], s[tot], p[i]) <= 0)
tot--;
s[++tot] = p[i];
}
s[tot+1] = p[1];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &a, &b, &r);
a -= 2*r, b -= 2*r; a /= 2, b /= 2;
length = sqrt(a*a+b*b); //对角线长度的一半
beta = asin(a/length);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &x, &y, &theta);
p[++cnt] = get_point(1, theta); //右上角
p[++cnt] = get_point(2, theta); //右下角
p[++cnt] = get_point(3, theta); //左上角
p[++cnt] = get_point(4, theta); //左下角
}
Graham();
double ans = PI*2*r;
for(int i = 1; i <= tot; i++)
ans += dis(s[i], s[i+1]);
printf("%.2f\n", ans);
return 0;
}



