Machine learning吴恩达第三周 Logistic Regression
1. Sigmoid function
function g = sigmoid(z) %SIGMOID Compute sigmoid function % g = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z. % You need to return the following variables correctly g = zeros(size(z)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix, % vector or scalar). g=1./(1+exp(-z)); % ============================================================= end

2. Logistic Regression Cost & Logistic Regression Gradient

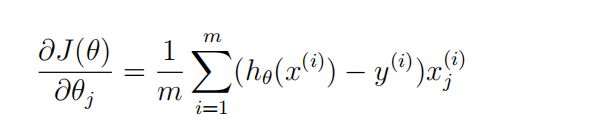
首先可以将h(x)表示出来----sigmoid函数
然后对于gredient(j)来说,
可以现在草稿纸上把矩阵画出来,然后观察,用向量来解决;
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y) %COSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression % J = COSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y) computes the cost of using theta as the % parameter for logistic regression and the gradient of the cost % w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly J = 0; grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta. % You should set J to the cost. % Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial % derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta % % Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta % h=sigmoid(X*theta); for i=1:m, J=J+1/m*(-y(i)*log(h(i))-(1-y(i))*log(1-h(i))); endfor grad=1/m*X'*(h.-y); % ============================================================= end
3. Predict
function p = predict(theta, X) %PREDICT Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic %regression parameters theta % p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a % threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1) m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly p = zeros(m, 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using % your learned logistic regression parameters. % You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's % p=sigmoid(X*theta); for i=1:m if(p(i)>=0.5)p(i)=1; else p(i)=0; end endfor % ========================================================================= end
4.Regularized Logistic Regression Cost & Regularized Logistic Regression Gradient

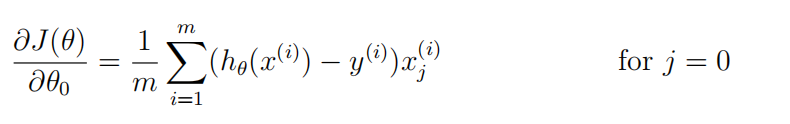

要注意的是:
Octave中,下标是从1开始的;
其次:
对于gradient(j)而言;
我们可以用X(:,j)的方式获取第j列的所有元素;
function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda) %COSTFUNCTIONREG Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with regularization % J = COSTFUNCTIONREG(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using % theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the % gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters. % Initialize some useful values m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly J = 0; grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta. % You should set J to the cost. % Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial % derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta h=sigmoid(X*theta); for i=1:m J=J+1/m*(-y(i)*log(h(i))-(1-y(i))*log(1-h(i))); endfor for i=2:length(theta) J=J+lambda/(2*m)*theta(i)^2; endfor grad(1)=1/m*(h-y)'*X(:,1); for i=2:length(theta) grad(i)=1/m*(h-y)'*X(:,i)+lambda/m*theta(i); endfor % ============================================================= end
EPFL - Fighting


