黑匣子_NOI导刊2010提高(06) Splay Tree
题目描述
Black Box是一种原始的数据库。它可以储存一个整数数组,还有一个特别的变量i。最开始的时候Black Box是空的.而i等于0。这个Black Box要处理一串命令。
命令只有两种:
ADD(x):把x元素放进BlackBox;
GET:i加1,然后输出Blackhox中第i小的数。
记住:第i小的数,就是Black Box里的数的按从小到大的顺序排序后的第i个元素。例如:
我们来演示一下一个有11个命令的命令串。(如下图所示)
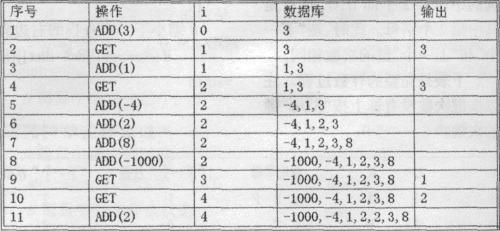
现在要求找出对于给定的命令串的最好的处理方法。ADD和GET命令分别最多200000个。现在用两个整数数组来表示命令串:
1.A(1),A(2),…A(M):一串将要被放进Black Box的元素。每个数都是绝对值不超过2000000000的整数,M$200000。例如上面的例子就是A=(3,1,一4,2,8,-1000,2)。
2.u(1),u(2),…u(N):表示第u(j)个元素被放进了Black Box里后就出现一个GET命令。例如上面的例子中u=(l,2,6,6)。输入数据不用判错。
输入输出格式
输入格式:第一行,两个整数,M,N。
第二行,M个整数,表示A(l)
……A(M)。
第三行,N个整数,表示u(l)
…u(N)。
输出格式:输出Black Box根据命令串所得出的输出串,一个数字一行。
输入输出样例
说明
对于30%的数据,M≤10000;
对于50%的数据,M≤100000:
对于100%的数据,M≤200000。
貌似比较简单的做法是对顶堆;
但是求区间kth , Splay Tree 是直接想到的;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define maxn 200005
#define inf 0x7fffffff
//#define INF 1e18
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9 + 7;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-3
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
inline ll rd() {
ll x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
}
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
int sqr(int x) { return x * x; }
/*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/
int rt, n, tot = 0;
struct node {
int ch[2];
int ff;
int cnt;
int val;
int son;
}e[maxn<<2];
void pushup(int u) {
e[u].son = e[e[u].ch[0]].son + e[e[u].ch[1]].son + e[u].cnt;
}
void rotate(int x) {
int y = e[x].ff;
int z = e[y].ff;
int k = (e[y].ch[1] == x);
e[z].ch[e[z].ch[1] == y] = x; e[x].ff = z;
e[y].ch[k] = e[x].ch[k ^ 1];
e[e[x].ch[k ^ 1]].ff = y;
e[x].ch[k ^ 1] = y; e[y].ff = x;
pushup(y); pushup(x);
}
void splay(int x, int aim) {
while (e[x].ff != aim) {
int y = e[x].ff;
int z = e[y].ff;
if (z != aim) {
(e[y].ch[0] == x) ^ (e[z].ch[0] == y) ? rotate(x) : rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
if (aim == 0)rt = x;
}
void ins(int x) {
int u = rt, ff = 0;
while (u&&e[u].val != x) {
ff = u; u = e[u].ch[x > e[u].val];
}
if (u)e[u].cnt++;
else {
u = ++tot;
if (ff)e[ff].ch[x > e[ff].val] = u;
e[tot].ch[0] = 0; e[tot].ch[1] = 0;
e[tot].ff = ff; e[tot].val = x;
e[tot].cnt = e[tot].son = 1;
}
splay(u, 0);
}
int k_th(int x) {
int u = rt;
if (e[u].son < x)return false;
while (1) {
int y = e[u].ch[0];
if (x > e[y].son + e[u].cnt) {
x -= e[y].son + e[u].cnt; u = e[u].ch[1];
}
else if (e[y].son >= x)u = y;
else return e[u].val;
}
}
int a[maxn];
int main() {
//ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
ins(inf); ins(-inf);
int m; cin >> m; cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
rdint(a[i]);
}
int j = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int tmp; rdint(tmp);
for (; j <= tmp; j++)ins(a[j]);
cout << k_th(i + 1) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
EPFL - Fighting


