【模板】最近公共祖先(LCA)
题目描述
如题,给定一棵有根多叉树,请求出指定两个点直接最近的公共祖先。
输入输出格式
输入格式:第一行包含三个正整数N、M、S,分别表示树的结点个数、询问的个数和树根结点的序号。
接下来N-1行每行包含两个正整数x、y,表示x结点和y结点之间有一条直接连接的边(数据保证可以构成树)。
接下来M行每行包含两个正整数a、b,表示询问a结点和b结点的最近公共祖先。
输出格式:输出包含M行,每行包含一个正整数,依次为每一个询问的结果。
输入输出样例
说明
时空限制:1000ms,128M
数据规模:
对于30%的数据:N<=10,M<=10
对于70%的数据:N<=10000,M<=10000
对于100%的数据:N<=500000,M<=500000
样例说明:
该树结构如下:
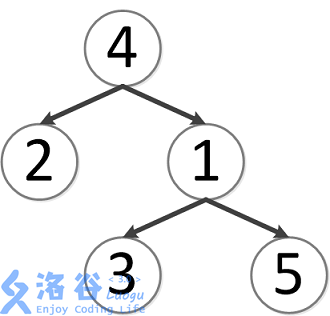
第一次询问:2、4的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第二次询问:3、2的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第三次询问:3、5的最近公共祖先,故为1。
第四次询问:1、2的最近公共祖先,故为4。
第五次询问:4、5的最近公共祖先,故为4。
故输出依次为4、4、1、4、4。
倍增就行了;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
using namespace std;
#define maxn 500005<<1
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define INF 9999999999
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9 + 7;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-3
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
//const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
inline ll rd() {
ll x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
}
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
ll sqr(ll x) { return x * x; }
/*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/
ll qpow(ll a, ll b, ll c) {
ll ans = 1;
a = a % c;
while (b) {
if (b % 2)ans = ans * a%c;
b /= 2; a = a * a%c;
}
return ans;
}
int head[maxn], nxt[maxn], ver[maxn];
int cnt;
int n, m, N;
void addedge(int x, int y) {
ver[++cnt] = y; nxt[cnt] = head[x]; head[x] = cnt;
}
int grand[maxn][20];
int dep[maxn];
int S;
void init() {
ms(head);
N = (int)(log(n) / log(2)) + 1;
dep[S] = 1; cnt = 0;
}
void dfs(int rt) {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)grand[rt][i] = grand[grand[rt][i - 1]][i - 1];
for (int i = head[rt]; i; i = nxt[i]) {
int v = ver[i];
if (v == grand[rt][0])continue;
grand[v][0] = rt; dep[v] = dep[rt] + 1; dfs(v);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (dep[x] > dep[y])swap(x, y);
for (int i = N; i >= 0; i--) {
if (dep[grand[y][i]] >= dep[x]) {
y = grand[y][i];
}
}
if (x == y)return x;
for (int i = N; i >= 0; i--) {
if (grand[x][i] != grand[y][i]) {
x = grand[x][i]; y = grand[y][i];
}
}
return grand[x][0];
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
rdint(n); rdint(m); rdint(S); init();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y; rdint(x); rdint(y); addedge(x, y); addedge(y, x);
}
dfs(S);
while (m--) {
int a, b; rdint(a); rdint(b); //cout << lca(a, b) << endl;
printf("%d\n", lca(a, b));
}
return 0;
}
EPFL - Fighting

