5.类与对象1
1. 类的定义:
【权限访问修饰符(public|default)】 class 类名 {
// 全局变量
// 方法
}
权限访问修饰符注意
类名: 首字母大写, 驼峰命名 标识符(字母、_、$开头)
2. 方法的定义
【权限访问修饰符】 【static】 返回修饰 方法名(参数列表) {
// 方法体
}
static: 违反面向对象: 静态的
方法名: 首字小写。
参数列表: (类型 参数名, 。。。)
3. OOP:Object Oriendted Programming :面向对象编程
面向过程的: 顺序写法
// 给一个圆的半径5,求周长
// Math.PI
int r = 5;
double zc = qiuzhouchang(r);
System.out.println(zc);
private static double qiuzhouchang(int i) {
return 2 * i * Math.PI;
}
面向对象的:复用性更好一些。
把事务抽象出来!!! 类 , 对象
所有的圆都有半径, 都能求周长。 圆类 属性 是 半角, 方法–行为 求周长。 对象就是每一圆。
// OOP
// 对象的实例化
Circle c1 = new Circle();
c1.r = 5; // 调用属性赋值
double zc2 = c1.qiuzhouchang(); // 调用方法
System.out.println(zc2);
class Circle {
int r; // 全局变量: 成员变量; 属性
// 求周长: 行为:方法
public double qiuzhouchang() {
return 2 * r * Math.PI;
}
public double qiumianji() {
return r * r * Math.PI;
}
}
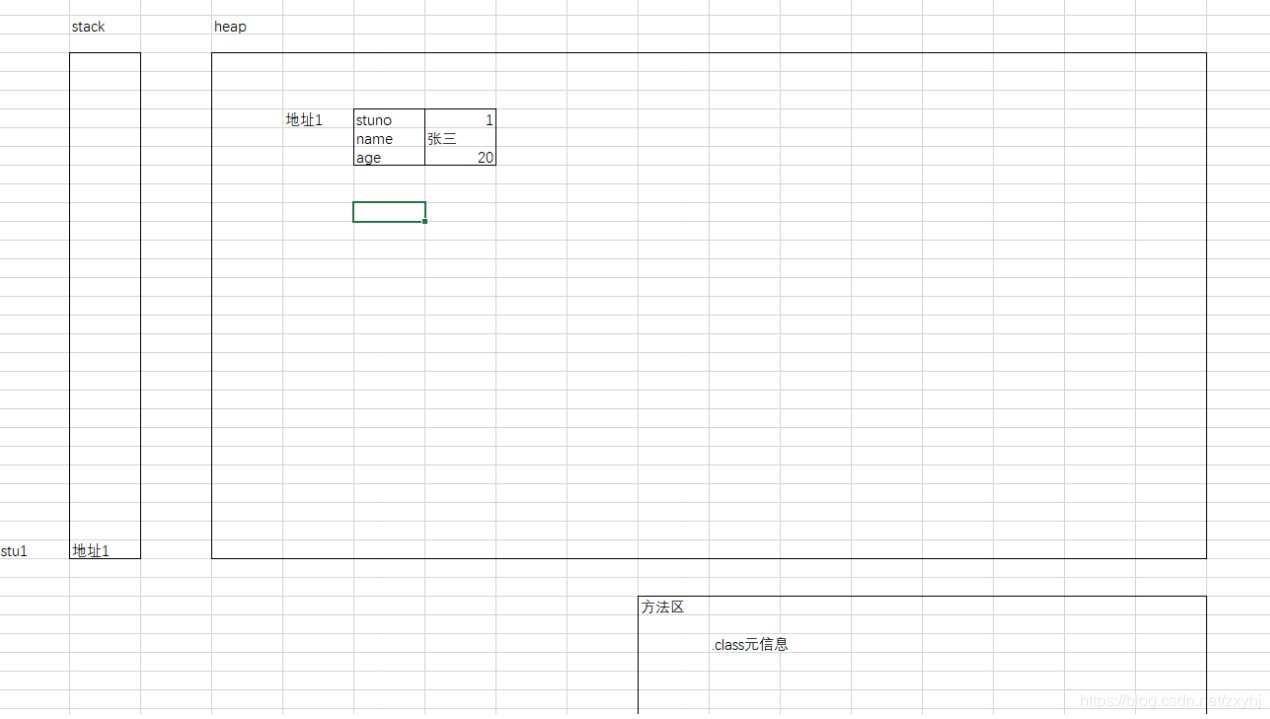
以学生为例:
类的属性: 学号,姓名,年龄
类的方法:行为: 学习,吃饭,打游戏。。。
对象: 每一个学生
package com.etc.lesson04;
public class Student {
int stuno;
String name;
int age;
public void study() {
System.out.println(stuno + "@" + name + "学习");
}
public void playGame() {
System.out.println(name + "游戏");
}
}
// 对象的实例化
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.stuno = 1;
stu1.name = "张三";
stu1.age = 20;
// com.etc.lesson04.Student@15db9742
System.out.println(stu1);
System.out.println(stu1.name);
stu1.study();
stu1.playGame();
// 对象的实例化
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.stuno = 2;
stu2.name = "李四";
stu2.age = 20;
// com.etc.lesson04.Student@15db9742
System.out.println(stu2);
System.out.println(stu2.name);
stu1.study();
stu1.playGame();
stu2.study();
stu2.playGame();
4. 对象实例化
类型 变量 = new 类型();类型===对象类型(除了8个基本类型)
变量===对象
new 开辟堆(heap)空间
类型() == 构造方法
5. 面向对象第二种理解:
boolean 1bit byte 8bit char 2byte short 2byte int 32bit float 32bit long 64bit double 64bit
复合的数据类型

6 static:
**静态不能调用非静态**
违反面向对象的:
静态是内存共享的。在方法区(元空间)中
静态是属于类的。
// Math.PI
// Arrays.sort();
//
7. 构造方法:
实例化的时候会调用构造方法: new 构造方法();
构造方法与类名相同,没有返回修饰符。
目的: 初始化属性
- 默认构造方法是无参数构造,编译生成
public Student() {
super(); // 默认第一行,可以不写。 调用父类构造方法
}
public Product(String proNO, String name, double price) {
super();
this.proNO = proNO;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
- 当有参数构造方法, 默认无参构造失效
- 规约: 有参数构造方法,就必须补无参数构造方法。
8: 方法传参数:
※:
值类型传参 : java八个基本类型 + String : 值的副本
对象类型传参:除了值类型: 地址的副本
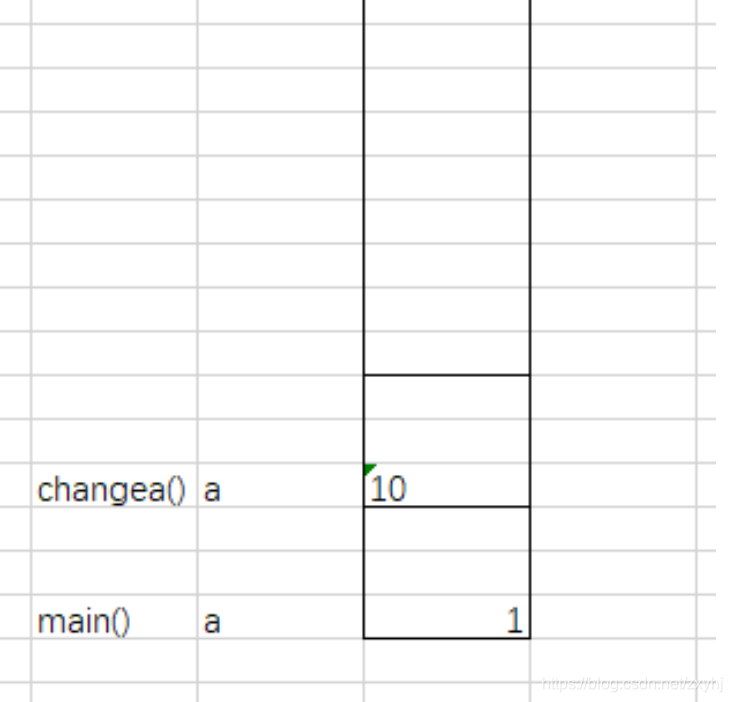
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 值类型传递
int a = 1;
changea(a);
System.out.println(a);
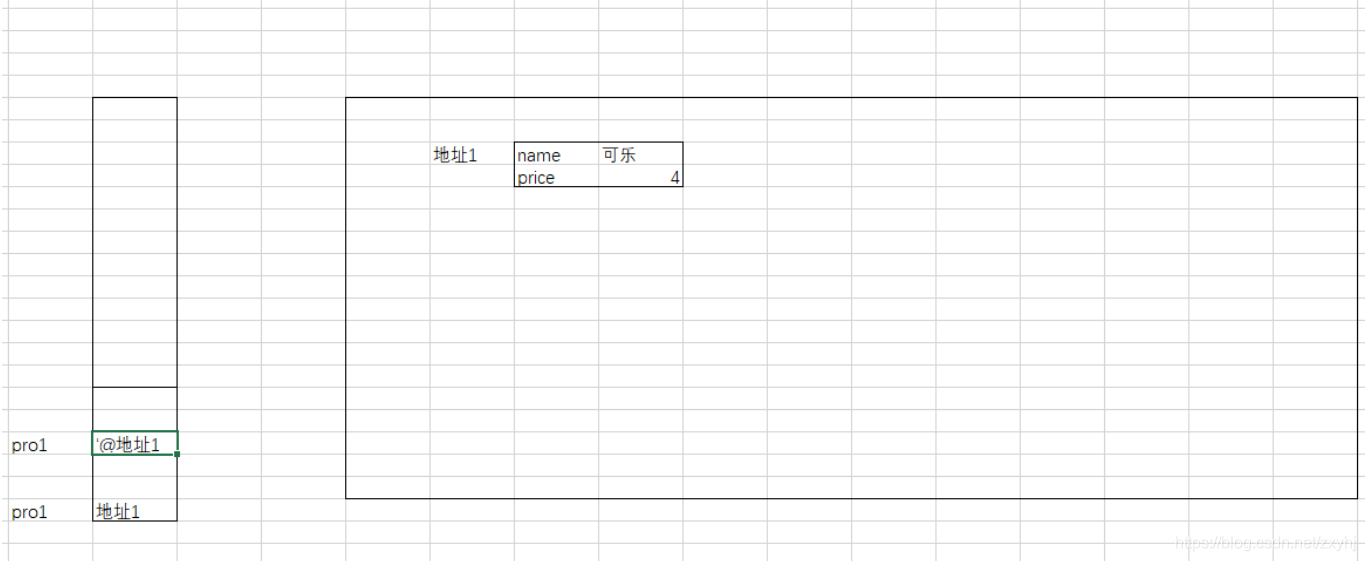
// 对象类型传值
Product pro1 = new Product("可乐", 3.0);
changeprice(pro1);
System.out.println(pro1.price);
}
private static void changeprice(Product pro1) {
// pro1 = new Product("雪碧", 4);
pro1.price = 6.0;
}
private static void changea(int a) {
a = 10;
System.out.println(a);
}
值传递:
对象传递:




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)