python全栈闯关--19-python常用模块-time
表示时间的三种方式:
python表示时间有三种方式:
1、时间戳格式:通常来说,时间戳就是从1970年1月1日期,时间便宜的秒数,float格式
2、格式化时间:

%y 两位数的年份表示(00-99)
%Y 四位数的年份表示(000-9999)
%m 月份(01-12)
%d 月内中的一天(0-31)
%H 24小时制小时数(0-23)
%I 12小时制小时数(01-12)
%M 分钟数(00=59)
%S 秒(00-59)
%a 本地简化星期名称
%A 本地完整星期名称
%b 本地简化的月份名称
%B 本地完整的月份名称
%c 本地相应的日期表示和时间表示
%j 年内的一天(001-366)
%p 本地A.M.或P.M.的等价符
%U 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期天为星期的开始
%w 星期(0-6),星期天为星期的开始
%W 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期一为星期的开始
%x 本地相应的日期表示
%X 本地相应的时间表示
%Z 当前时区的名称
%% %号本身
3、元祖格式:
struct_time元组共有9个元素共九个元素:(年,月,日,时,分,秒,一年中第几周,一年中第几天等)
| 索引(Index) | 属性(Attribute) | 值(Values) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | tm_year(年) | 比如2011 |
| 1 | tm_mon(月) | 1 - 12 |
| 2 | tm_mday(日) | 1 - 31 |
| 3 | tm_hour(时) | 0 - 23 |
| 4 | tm_min(分) | 0 - 59 |
| 5 | tm_sec(秒) | 0 - 60 |
| 6 | tm_wday(weekday) | 0 - 6(0表示周一) |
| 7 | tm_yday(一年中的第几天) | 1 - 366 |
| 8 | tm_isdst(是否是夏令时) | 默认为0 |
print("时间戳格式!") print(time.time()) # 格式化时间 print("格式化时间:") print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %a %H:%M:%S")) #year month day HOUR MINUTE SECOND print(time.strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S")) #year month day HOUR MINUTE SECOND print(time.strftime("%m-%d %H:%M:%S")) #year month day HOUR MINUTE SECOND print(time.strftime("%H:%M:%S")) #year month day HOUR MINUTE SECOND print(time.strftime("%H:%M")) #year month day HOUR MINUTE SECOND print("元祖格式,struct_time") t = time.time() print(time.localtime(t)) print("格林威治时间下的struct_time") print(time.gmtime(t))
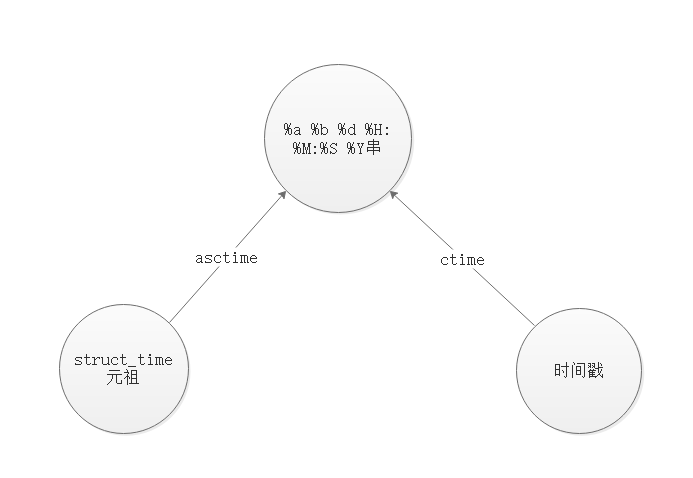
三种时间格式间的转换
时间戳→结构化时间:
localtime,gmtime
print("元祖格式,struct_time") t = time.time() print(time.localtime(t)) print("格林威治时间下的struct_time") print(time.gmtime(t))
结构化时间→时间戳
maketime
struct_time = time.localtime() print(struct_time) print(time.mktime(struct_time))
结构化时间→字符串格式时间
strtime
struct_time = time.localtime() print(struct_time) # print(time.mktime(struct_time)) str_time = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',struct_time) print(str_time)
字符串时间→结构化时间
strptime
struct_time = time.localtime() print(struct_time) # print(time.mktime(struct_time)) str_time = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',struct_time) print(str_time) struct_time = time.strptime(str_time,'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') print(struct_time)
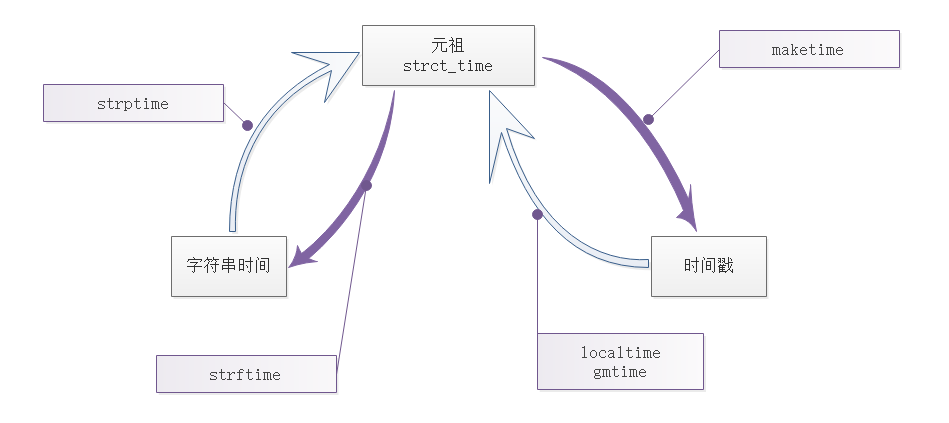
%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y串
结构化时间 --> %a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y串
# 结构化时间 --> %a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y串 # time.asctime(结构化时间) 如果不传参数,直接返回当前时间的格式化串 t1 = time.asctime(time.localtime(2000000000)) t2 = time.asctime() print(t1) # Wed May 18 11:33:20 2033 print(t2) # Wed Apr 1 16:48:08 2020
时间戳 --> %a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y串
# time.ctime(时间戳) 如果不传参数,直接返回当前时间的格式化串 t1 = time.ctime() t2 = time.ctime(2000000000) print(t1) # Wed Apr 1 16:48:53 2020 print(t2) # Wed May 18 11:33:20 2033