自定义频率类、频率功能源码解析、分页功能、排序功能、过滤功能
自定义频率类
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle
class MyThrottle(BaseThrottle):
VISIT_RECORD = {}
def __init__(self):
self.history = None
def allow_request(self, request, view):
ip = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
import time
ctime = time.time()
if ip not in self.VISIT_RECORD:
self.VISIT_RECORD[ip] = [ctime, ]
return True
self.history = self.VISIT_RECORD.get(ip)
while self.history and -ctime + self.history[-1] < 60:
self.history.pop()
if len(self.history) < 3:
self.history.insert(0, ctime)
return True
else:
return False
def wait(self):
import time
ctime = time.time()
return 60 - (ctime - self.history[-1])
频率功能源码解析
# SimpleRateThrottle
-源码里执行的频率类的allow_request,读SimpleRateThrottle的allow_request
class SimpleRateThrottle(BaseThrottle):
cache = default_cache
timer = time.time
cache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'
scope = None
THROTTLE_RATES = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES
def __init__(self): # 只要类实例化得到对象就会执行,一执行,self.rate就有值了,而且self.num_requests和self.duration
if not getattr(self, 'rate', None): # 去频率类中反射rate属性或方法,发现没有,返回了None,这个if判断就符合,执行下面的代码
self.rate = self.get_rate() #返回了 '3/m'
# self.num_requests=3
# self.duration=60
self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate)
def get_rate(self):
return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope] # 字典取值,配置文件中咱们配置的字典{'ss': '3/m',},根据ss取到了 '3/m'
def parse_rate(self, rate):
if rate is None:
return (None, None)
# rate:字符串'3/m' 根据 / 切分,切成了 ['3','m']
# num=3,period=m
num, period = rate.split('/')
# num_requests=3 数字3
num_requests = int(num)
# period='m' ---->period[0]--->'m'
# {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
# duration=60
duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
# 3 60
return (num_requests, duration)
def allow_request(self, request, view):
if self.rate is None:
return True
# 咱们自己写的,返回什么就以什么做限制 咱们返回的是ip地址
# self.key=当前访问者的ip地址
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)
if self.key is None:
return True
# self.history 访问者的时间列表,从缓存中拿到,如果拿不到就是空列表,如果之前有 [时间2,时间1]
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
# 当前时间
self.now = self.timer()
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:
self.history.pop()
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
return self.throttle_failure()
return self.throttle_success()
# 总结:以后要再写频率类,只需要继承SimpleRateThrottle,重写get_cache_key,配置类属性scope,配置文件中配置一下就可以了
为什么要使用分页?
我们数据表中可能会有成千上万条数据,当我们访问某张表的所有数据时,我们不太可能需要一次把所有的数据都展示出来,因为数据量很大,对服务端的内存压力比较大还有就是网络传输过程中耗时也会比较大。
通常我们会希望一部分一部分去请求数据,也就是我们常说的一页一页获取数据并展示出来。
分页的三种方式
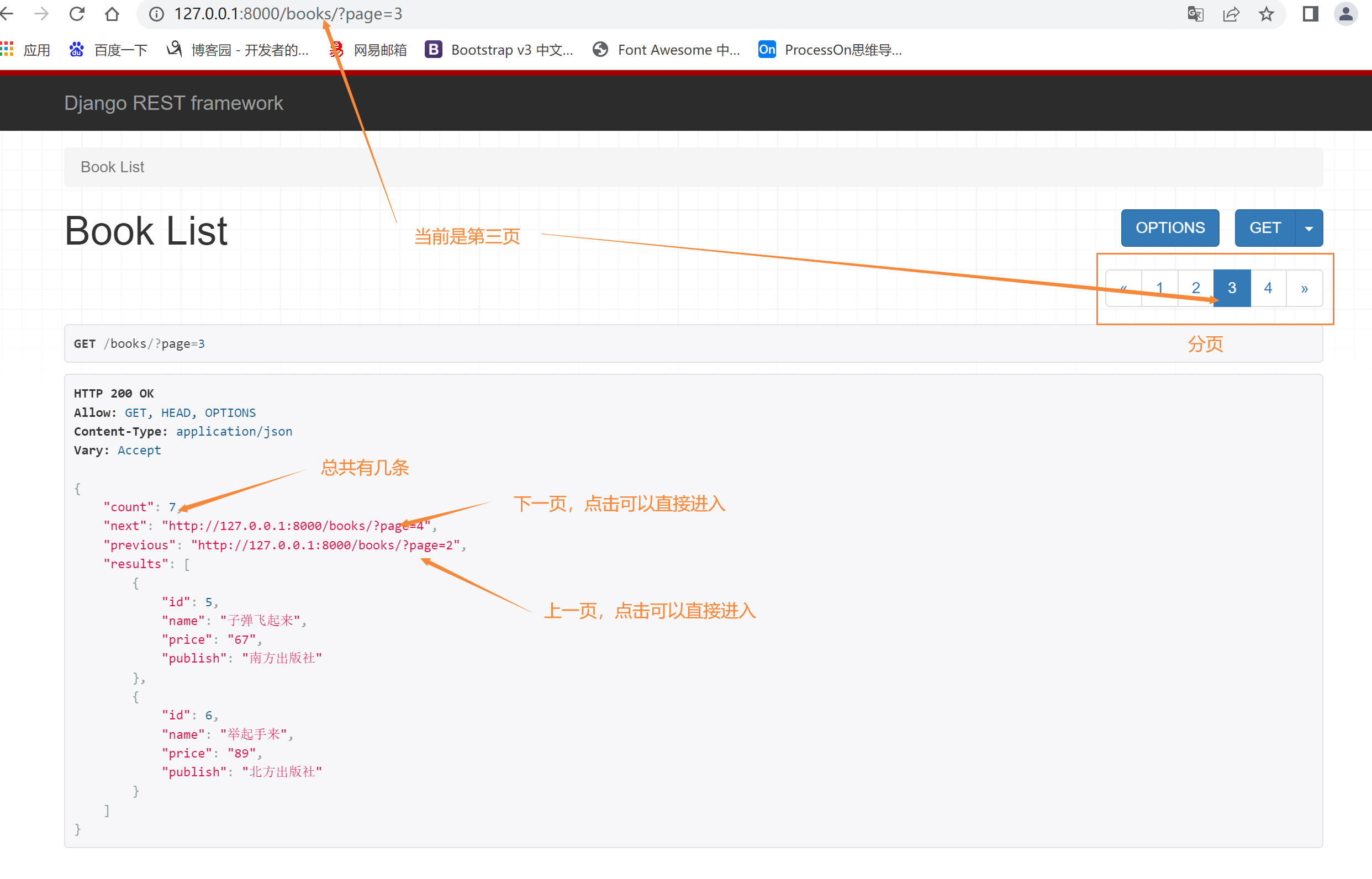
方式一:基本的分页,就是正常的查第几页每页显示多少条
model.py
from django.db import models
# Create your models here.
from django.db import models
class Book(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=32)
price = models.CharField(max_length=32)
publish = models.CharField(max_length=32)
def __str__(self):
return self.name
serializer.py
from rest_framework import serializers
from .models import Book, Publish
class BookSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Book
fields = '__all__'
page.py
from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination, LimitOffsetPagination, CursorPagination
class CommonPageNumberPagination(PageNumberPagination):
# 有4个类属性
# 每页显示条数
page_size = 2
# 分页查询的那个参数 ?page=10
page_query_param = 'page'
# ?page=3&size=3 查询3页,每页查询3条
page_size_query_param = 'size'
# 可以通过size控制每页显示的条数,但是通过这个参数控制最多显示多少条
max_page_size = 3
view.py
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
from rest_framework.generics import GenericAPIView
from rest_framework.mixins import ListModelMixin
from rest_framework.viewsets import ViewSetMixin
from app01.models import Book
from app01.serializer import BookSerializer
from rest_framework.pagination import PageNumberPagination, LimitOffsetPagination, CursorPagination
# as 后面是起的别名,将我们写的类导入进来
from .page import CommonPageNumberPagination as PageNumberPagination
class BookView(ViewSetMixin, GenericAPIView, ListModelMixin):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookSerializer
# pagination_class后面是我们自己写的类,只不过在导入的时候我们重新命名了
pagination_class = PageNumberPagination
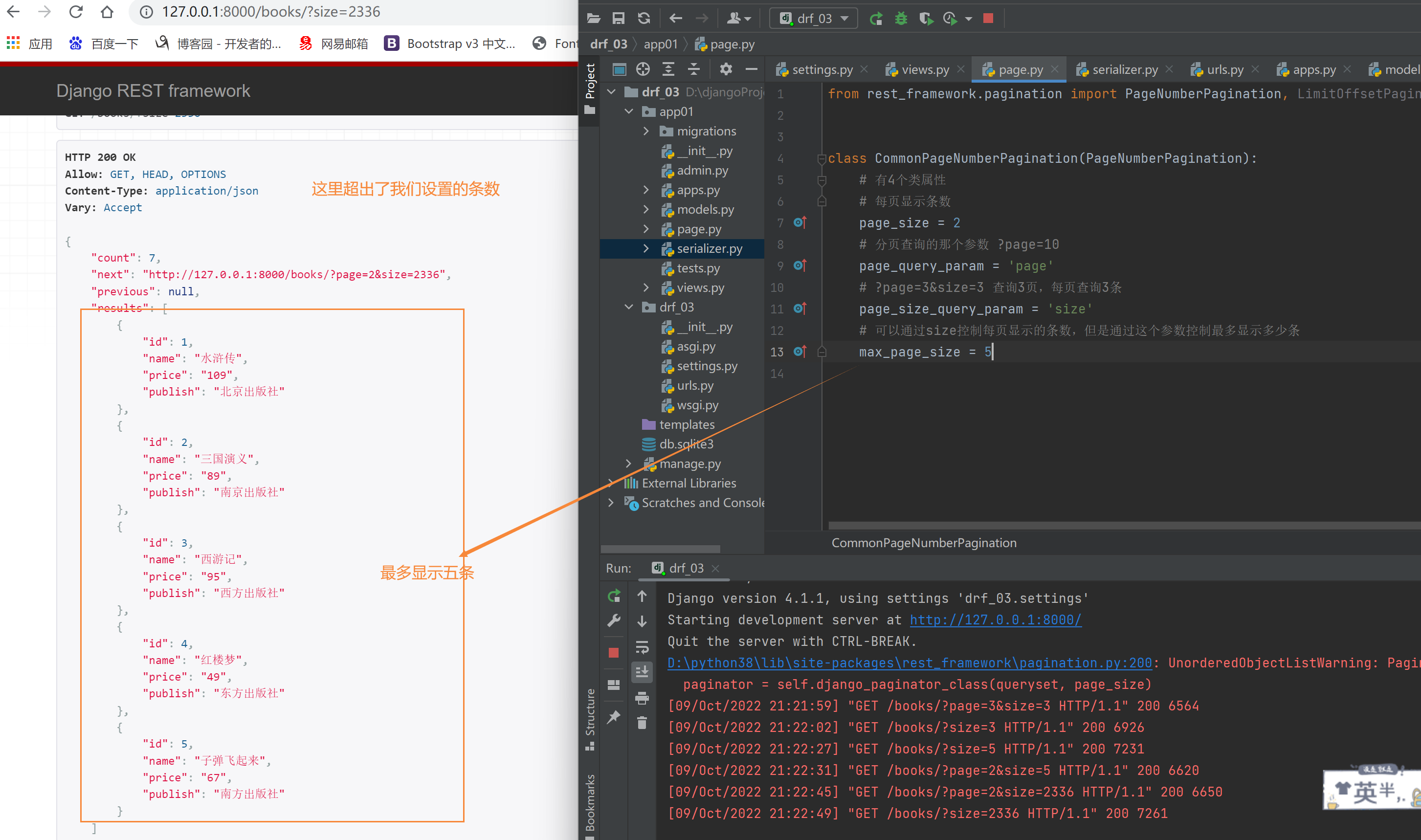
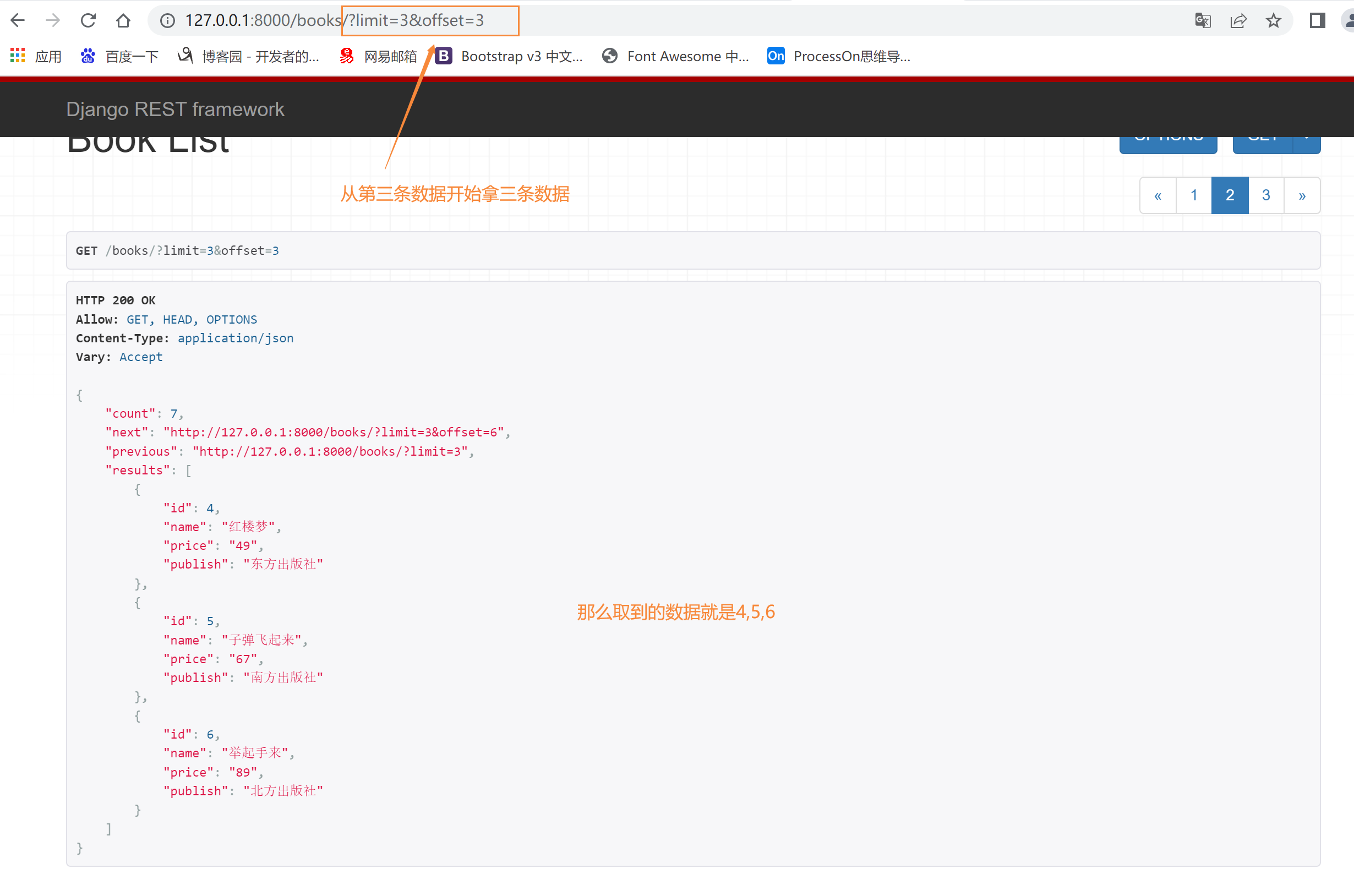
方式二:偏移分页:可以直接从第几页第几个位置开始拿数据 offset=6&limit=2
page.py
class CommonLimitOffsetPagination(LimitOffsetPagination):
# 每页显示多少条
default_limit = 2
# 可以直接从第几页第几个位置开始拿数据 offset=6&limit=2
limit_query_param = 'limit' # 取多少条
# 从第0个位置偏移多少开始取数据
offset_query_param = 'offset'
# 最大限制条数
max_limit = 5
view.py
from .page import CommonLimitOffsetPagination
class BookView(ViewSetMixin, GenericAPIView, ListModelMixin):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookSerializer
pagination_class = CommonLimitOffsetPagination
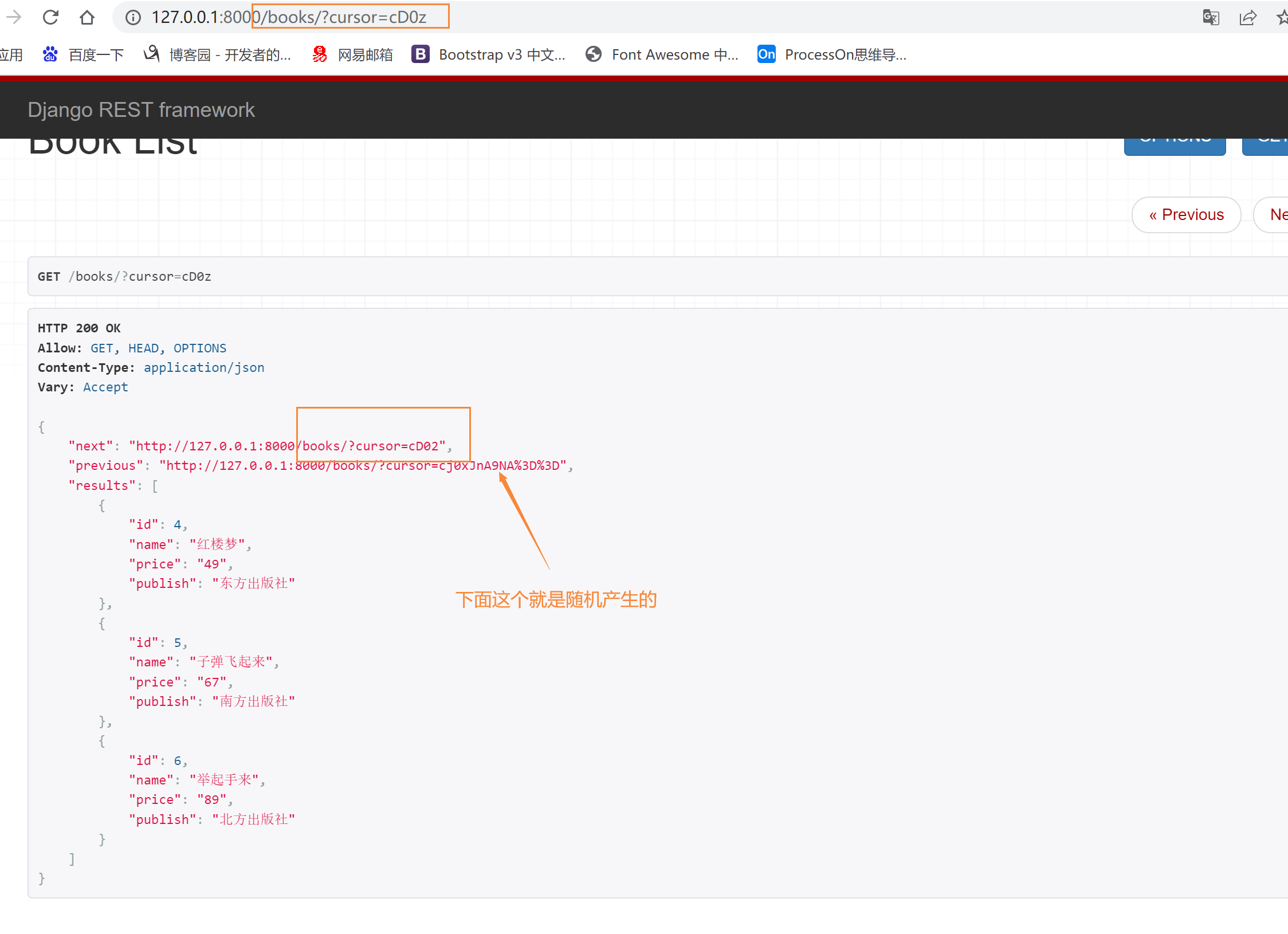
方式三:游标分页式分页
效率高,但是可控性差,只能选择上一页与下一页,不能直接跳转到某一页,这种针对于大数据
page.py
class CommonCursorPagination(CursorPagination):
# 查询的名字
cursor_query_param = 'cursor'
# 每页显示多少条
page_size = 3
# 必须是表中有的字段,一般用id
ordering = 'id'
view.py
from .page import CommonCursorPagination
class BookView(ViewSetMixin, GenericAPIView, ListModelMixin):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookSerializer
pagination_class = CommonCursorPagination
排序功能
排序功能只针对于所有接口,继承了GenericAPIView的视图类,只要加入,俩个类属性就可以了
from rest_framework.filters import OrderingFilter
# 查询所有,按照价格排序,必须继承GenericAPIView及其子类
class BookView(ViewSetMixin, GenericAPIView, ListModelMixin):
queryset = Book.objects.all()
serializer_class = BookSerializer
filter_backends = [OrderingFilter, ]
ordering_fields = ['price',]
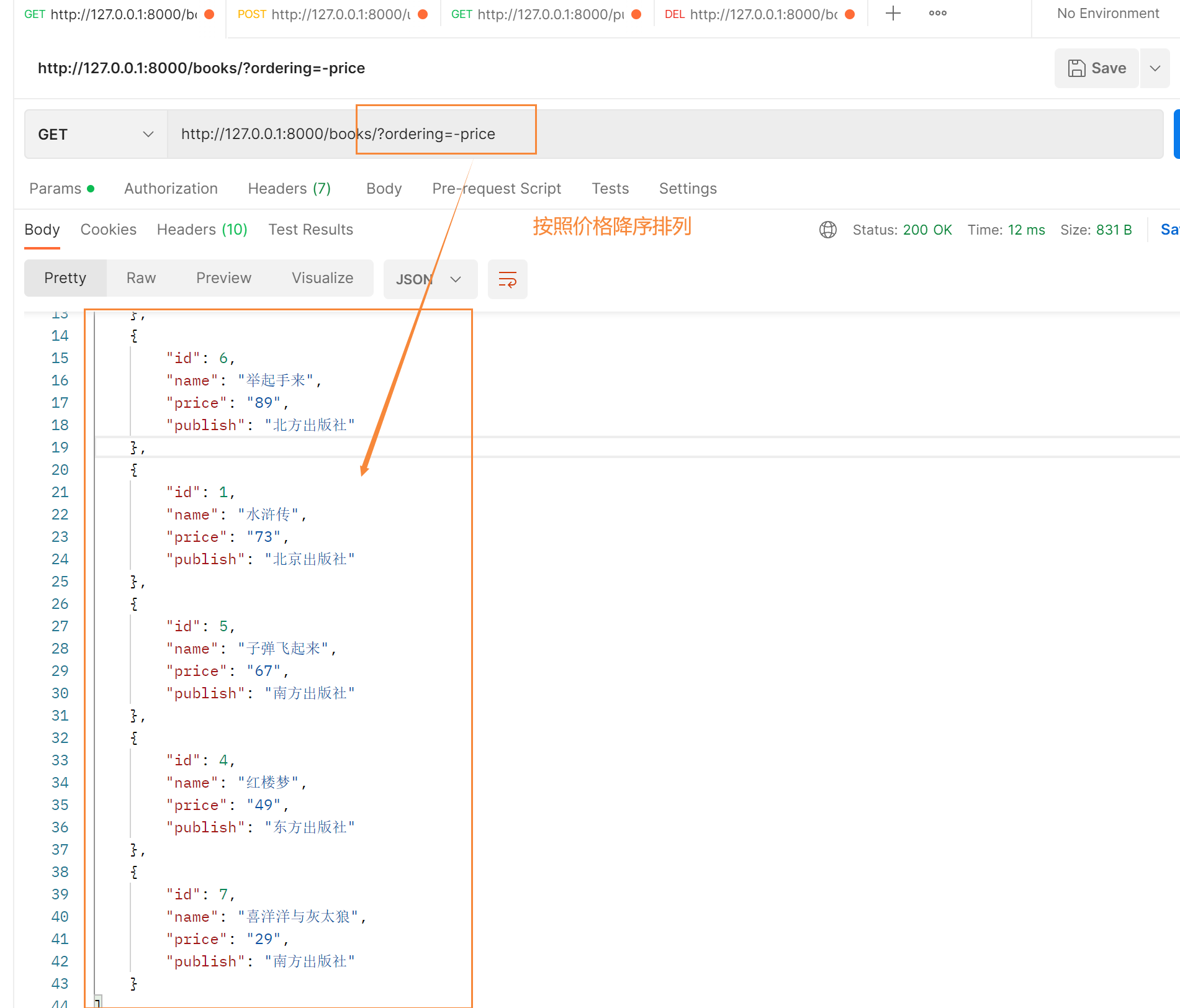
访问地址:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?ordering=-price # 按照price降序
http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?ordering=price # 按照price升序
http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?ordering=price,id # 先按价格升序排,价格一样再按id升序排
注意:
ordering后面跟的必须要在ordering_fields = ['price','id']先注册好
过滤功能
查询所有才涉及到过滤,其他接口都不需要
restful规范中有一条,请求地址中带过滤条件:分页、排序、过滤统称为过滤
内置过滤类
使用内置过滤类的步骤
必须是继承GenericAPIView+ListModelMixin的之类视图上
1.配置过滤类
filter_backends=[SearchFilter,]
2.配置过滤类的字段
search_fields = ['name', ]
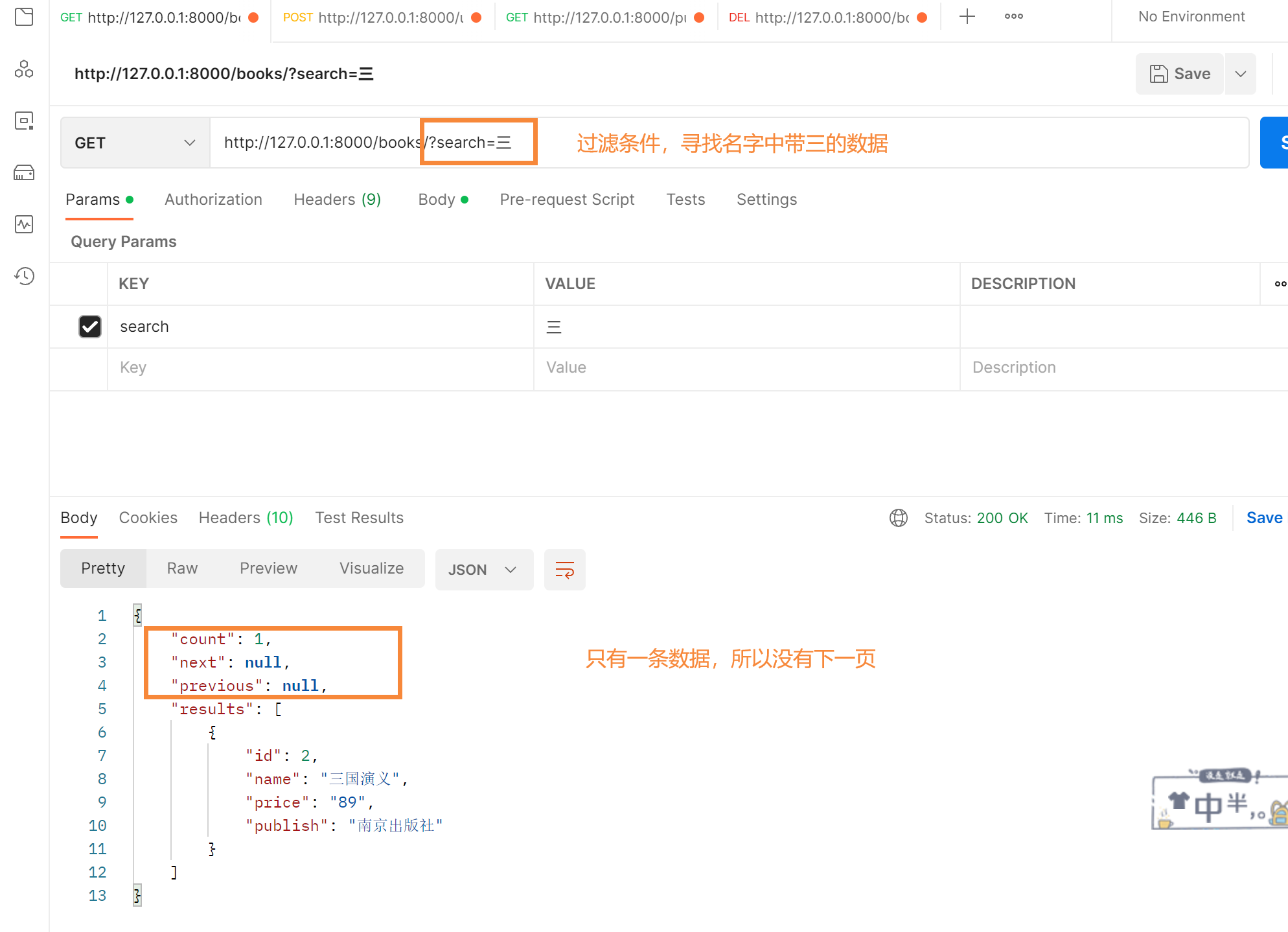
3.支持前端的访问形式
http://127.0.0.1:8000/books/?search=三 # 只要name中或publish中有三都能搜出来
内置过滤类只能通过search写条件,如果配置了多个过滤字段,是或者的条件
作业
继承APIView,实现分页
views.py
class BookView1(APIView):
def get(self, request):
qs = Book.objects.all()
page = CommonPageNumberPagination()
res = page.paginate_queryset(qs, request) # 会返回一个结果: return list(self.page),这个结果就是分页后的数据
# 分完页的数据序列化数据
ser = BookSerializer(instance=res, many=True)
# return Response(ser.data)
# return page.get_paginated_response(ser.data)
return Response({
'count': qs.count(),
'next': page.get_next_link(),
'previous': page.get_previous_link(),
'results': ser.data
})
路由的配置
path('books1/', views.BookView1.as_view()),





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步