树结构存储表示
对于双亲表示法:我们先将双亲结点存入,我们每插入一个结点都是知道双亲结点位置的,数据可以直接插入。使用顺序存储结构更加方便
而对于孩子表示法,我们每次插入一个结点,对其子树的位置存放暂不确定,所有使用链式存储结构占主要(一)双亲表示法
以双亲作为索引的关键词的一种存储方式
每个结点只有一个双亲,所以选择顺序存储占主要
以一组连续空间存储树的结点,同时在每个结点中,附设一个指示其双亲结点位置的指针域
结点:

#include<iostream> #include<cstring> const int MAXN=100; using namespace std; struct node {//双亲表示法. char val;//值 int par;//父亲 }; node L[MAXN]; int length; bool vis[MAXN]; void print(int root) {//这个程序不用担心产生环. if(root<length) { cout<<L[root].val<<" "; vis[root]=true; for(int i=0;i<length;i++) if(!vis[i]&&L[i].par==root) print(i);
//这个地方是有瑕疵的,其实不必有vis的判断,因为树本身的性质决定了它不可能存在图的遍历中可能存在的环,也就排除了重复访问的可能性. } return ; } void init(int n) { for(int i=0;i<n;i++) L[i].par=-1,vis[i]=false; } int main() { int n; char chx,chy; cin>>n; length=n; init(n); for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++) { int x,y; cin>>x>>chx>>y>>chy; L[x].val=chx; L[y].val=chy; L[y].par=x; } print(0); return 0; } /* 10 0 a 1 b 0 a 2 c 1 b 3 d 3 d 6 g 3 d 7 h 3 d 8 i 2 c 4 e 2 c 5 f 4 e 9 j a b d g h i c e j f */
其实以上的双亲表示法虽然简单,但是也是有缺陷的,那就是在短时间内不容易快速写出.如何才能快速写出呢?
int par[maxn];//par[i]表示i结点的父亲下标 int val[maxn];//val[i]表示i结点对应的值.
以上代码即可.
二.孩子表示法.
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //孩子表示法; 6 //即每个树结点都有孩子索引域 7 8 struct node 9 {//degree=2 10 char val; 11 int left,right; 12 }a[1001]; 13 int n; 14 void init() 15 { 16 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) a[i].val=1,a[i].left=a[i].right=-1; 17 } 18 19 void print(int root) 20 { 21 if(root<n) 22 { 23 cout<<a[root].val<<" "; 24 if(a[root].left!=-1) print(a[root].left); 25 if(a[root].right!=-1) print(a[root].right); 26 } 27 return ; 28 } 29 30 31 int main() 32 { 33 int cnt=0,x,y; 34 char chx,chy; 35 cin>>n; 36 init(); 37 while(1) 38 { 39 if(cnt==n-1) break; 40 cin>>x>>chx>>y>>chy; 41 a[x].val=chx; a[y].val=chy; 42 if(a[x].left==-1) a[x].left=y; 43 else a[x].right=y; 44 cnt++; 45 } 46 print(0); 47 return 0; 48 }
以上就是孩子表示法,其实这是有很大瑕疵的,因为一个结点不容易找到它的爹,所以我们可以在结点的内部增加一个域用以表示其父亲也是可以的
正如:
1 struct node 2 {//degree=2 3 char val; 4 int par; 5 int left,right; 6 }
其实这样的改进也是不太好的.
为什么呢?
你怎么知道树的度是多少呢?
那如何呢?
看下面:
1 struct node 2 {//degree=2 3 char val;
4 int par; 5 int child[max_degree]; 6 }
看吧,儿子好找了,爹也好找了.但是我们看,这...是不是太浪费空间了?
如何优化呢?
不急,看图.
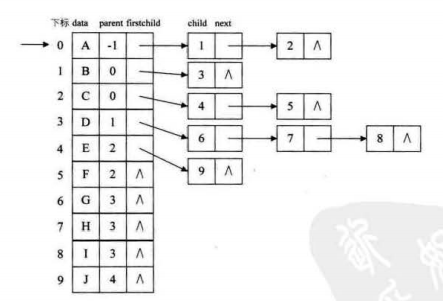
两种线性表的结合是不是很不错呢?
具体怎么运用呢?
自己琢磨去!
三.孩子兄弟法.
下面就是孩子兄弟法了,具体是:
1 struct node 2 { 3 char val; 4 node *firstchild,*next_sibling; 5 };
可以看出,结点的内容是存储每一个结点的第一个孩子以及此结点的兄弟.
可以看出,我们既优化了每个父亲对多个孩子的索引的简化,又能使得每个结点可以轻松的访问它的众多兄弟,
其实在xpath和dom树中对结点的兄弟的获取就是靠着这种结构而构造成的.
代码为:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstring> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //孩子表示法; 6 //即每个树结点都有孩子索引域 7 struct node 8 { 9 char val; 10 node *firstchild,*next_sibling; 11 }a[1001]; 12 int n; 13 void init() 14 { 15 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) a[i].val=1,a[i].firstchild=a[i].next_sibling=NULL; 16 } 17 18 void print(node *root) 19 { 20 if(root!=NULL) 21 { 22 cout<<root->val<<" "; 23 node* temp=root->firstchild; 24 while(temp) 25 { 26 print(temp); 27 temp=temp->next_sibling; 28 } 29 } 30 return ; 31 } 32 33 34 int main() 35 { 36 int cnt=0,x,y; 37 char chx,chy; 38 cin>>n; 39 init(); 40 while(1) 41 { 42 if(cnt==n-1) break; 43 cin>>x>>chx>>y>>chy; 44 a[x].val=chx; a[y].val=chy; 45 if(!a[x].firstchild) a[x].firstchild=&a[y]; 46 else 47 { 48 node * temp=a[x].firstchild,*fa=NULL; 49 while(temp) fa=temp,temp=temp->next_sibling; 50 fa->next_sibling=&a[y]; 51 } 52 cnt++; 53 } 54 print(&a[0]); 55 return 0; 56 }
以上就是这三种基本的树的存储结构,
里面还掺杂了一些优化缘由(无非是为了满足我们的某种需求而需要设计较好的数据结构)
以及优化后的结果.
其中三段大代码的输入数据都是一样的.
且结点的数据结构都是靠着数组来设计的.
好了,关于树的存储也告一段落了.
欢迎批评指正.
以下是两份我觉得写的很不错的博文.值得参考.
https://www.cnblogs.com/jpfss/p/10842521.html 梗概
https://www.cnblogs.com/ssyfj/p/9459887.html 优化.



