python源码阅读笔记
SWIG的python接口使用demo
主要准备三个文件,example.h, example.i, example.c,
example.i,
%module example
%{
#include "example.h"
%}
%include "example.h"
//exampe.h
int kernelProbe(long long x,long long y, int len);
//example.c
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int kernelProbe(uint64_t x_gm, uint64_t y_gm, int len) {
printf("real value in x tensor:\n");
uint8_t* x = (uint8_t*)x_gm;
uint8_t* y = (uint8_t*)y_gm;
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) {
printf("%d\n", x[i]);
}
return 0;
}
首先利用swig根据example.i生成example_wrap.c和example.py,
swig -python example.i
然后利用setup.py完成extension so的编译,
#setup.py
from distutils.core import setup, Extension
example_module = Extension('_example',
sources=['example_wrap.c', 'example.c'], extra_compile_args=['-g'])
setup(name='example',
version='0.1',
author='Your Name',
description='Example swig',
ext_modules=[example_module],
py_modules=["example"])
python setup.py build_ext --inplace
inplace表示替换原本的so
最后可以运行a.py来比较C中打印的tensor内容和python中print打印的tensor内容
#a.py
import example as ee
import torch
x = torch.randint(0, 10, [20,], dtype=torch.uint8)
y = torch.randint(0, 10, [20,], dtype=torch.uint8)
c = ee.kernelProbe(x.data_ptr(), y.data_ptr(), 10)
print(x)
python a.py
tensor.data_ptr()本质是个地址,接口中可以申明为long long, C里强转为不同的指针,接口中定义为int8_t* Py转的时候有问题。
example_wrap.c中解读
example_wrap.c主要做两个事,一是将C定义的函数进行挂载到模块中,二是将运行时python传递来的各种PyObject*的参数parse为C对应的参数。
python挂载C函数用的PyMethodDef定义如下,
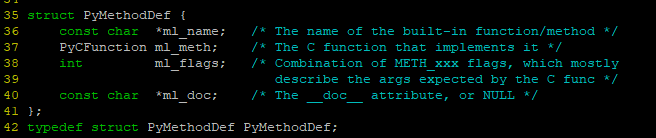
其中
在自定义的extension的C中使用示例如下,定义一个PyMethodDef的表,
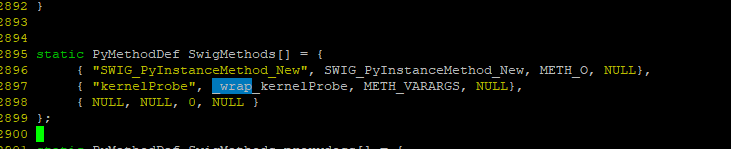
这个C函数接口表被挂到PyModuleDef的结构体中,
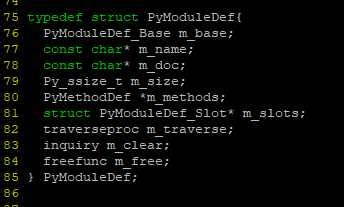
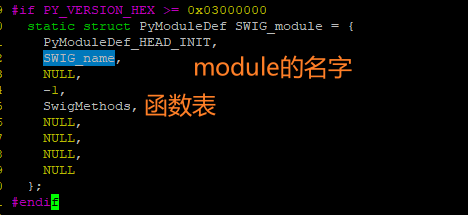
这个结构体对象被传给Python中的接口PyModule_Create(PyMethodDef*);注册到python的主进程中,从而可以被调用
m = PyModule_Create(&SWIG_module);
然后在PyInit_soName函数中完成m = PyModule_Create(&SWIG_module);操作,并返回生产的m这个PyObject*。
cfunction_call函数梳理
cfunction_call是python调用C extension中函数基本是必经之路。
其格式定义如下,第一个参数func本质是PyCFunctionObject*, 第二个参数
static PyObject *
cfunction_call(PyObject *func, PyObject *args, PyObject *kwargs) {
注意_wrap_kernelProbe第一个参数是self, 即example这个module, 后面是参数列表和keywords.
底层调用的时候,第一个参数传
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
PyMethodDef *m_ml; /* Description of the C function to call */
PyObject *m_self; /* Passed as 'self' arg to the C func, can be NULL */
PyObject *m_module; /* The __module__ attribute, can be anything */
PyObject *m_weakreflist; /* List of weak references */
vectorcallfunc vectorcall;
} PyCFunctionObject;
下图是cfunction_call中获取C函数句柄和module(self)的操作,
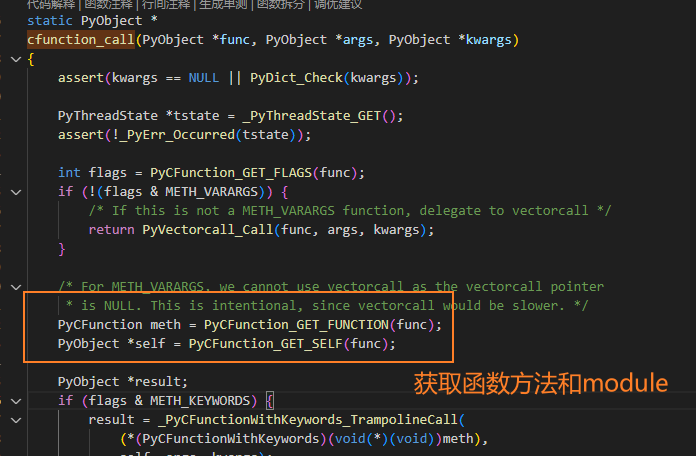

若关注某Python函数调用的底层C接口,可以使用下面定义的show_func,在gdb中break到cfunction_call查看具体调用的是什么c函数
#include <Python.h>
void show_func(PyCFunctionObject* func) {
printf("%s at %p called\n", func->m_ml->ml_name, func->m_ml->ml_meth);
}




