《HDU 2020 多校第二场》
Total Eclipse
思路:先考虑一种普遍解法。
对于每个极大连通块,一次次块上的全部点减去1,断开为子图后继续重复减1,显然是最优的减法。
但是减去后遍历边的复杂度过高,且b值也很大,所以考虑成加边的形式。
首先将点按权值降序。那么我们可以采取将最大的点减成第二大的点,然后两个点又一起减成第三大的点,然后三个点一起减成第四大.....
那么显然这中间能不能一起减去这个代价会是分界,当两个点可以从之前的点间接相连,或者他们可以直接相连时,那么显然可以一起减,
因为之前的点显然和他们已经减到了相同代价。如果不能直接或者间接相连,那么就是两个不同的连通块里的点,那么就要*连通块的个数。
那么每一次的代价就是 num(连通块) * (b[i] - b[i+1]).
所以,我们用并查集来维护连通块的个数,每次计算一个点时,先将这个点合并到和它相连的点且之前出现过的点的连通块中。
Code:

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef long double ld; typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int N = 1e5+5; const LL Mod = 1e9+9; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e8 #define INM INT_MIN #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { int x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9'){if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } struct Node{ int val,id; bool operator < (const Node &a)const{ return val > a.val; } }p[N]; int vis[N],fa[N]; vector<int> G[N]; int Find(int x) { return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = Find(fa[x]); } int main() { freopen("data1.in","r",stdin); freopen("data1.out","w",stdout); int t;t = read(); while(t--) { int n,m; n = read(),m = read(); for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) { p[i].val = read(); p[i].id = fa[i] = i; G[i].clear(); vis[i] = 0; } sort(p+1,p+n+1); p[n+1].val = 0; while(m--) { int u,v; u = read(),v = read(); G[u].push_back(v); G[v].push_back(u); } LL ans = 0; int cnt = 0;//连通块数量 for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) { int x = p[i].id; vis[x] = 1; cnt++; for(auto v : G[x]) { if(!vis[v]) continue; int xx = Find(x),yy = Find(v); if(xx != yy) { fa[xx] = yy; cnt--; } } ans += 1LL*(p[i].val-p[i+1].val)*cnt; } printf("%lld\n",ans); } system("pause"); return 0; }
Lead of Wisdom
思路:暴力搜素
如果直接搜索会超时。
考虑这样一种搜索树。
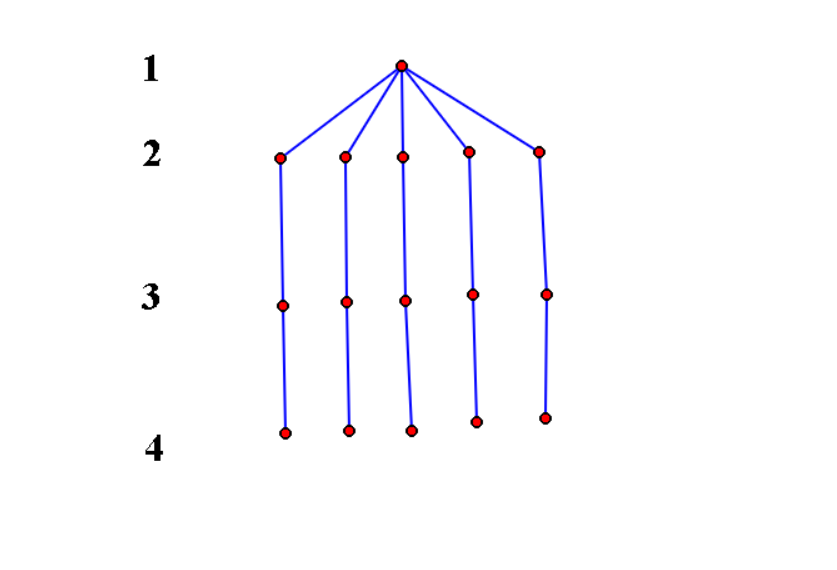
对于k = 3,4的情况,显然可以直接停止,但是还搜索会提高复杂度。
所以对于k种类的个数为0的种类,就不再存取。
那么对于每一层,对于剩下的k种,平均下每层大概$\frac{n}{k}$个数,那么复杂度就是$k^{\frac{n}{k}}$
最坏情况下n = 50,k为3的时候复杂度取到最高,还是能过。
Code:

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef long double ld; typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int N = 1e5+5; const LL Mod = 1e9+9; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e8 #define INM INT_MIN #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { int x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9'){if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } int n,k,cnt[55],tim; LL ans = 0; struct Node{int a,b,c,d;}; vector<Node> G[55]; LL cal(LL a,LL b,LL c,LL d) { return (100+a)*(100+b)*(100+c)*(100+d); } void dfs(int x,int a,int b,int c,int d) { if(x == tim+1) { ans = max(ans,cal(a,b,c,d)); return ; } for(auto v : G[x]) dfs(x+1,a+v.a,b+v.b,c+v.c,d+v.d); } int main() { int t;t = read(); while(t--) { n = read(),k = read(); ans = tim = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= k;++i) G[i].clear(); memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt)); for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) { int kk;kk = read(); int a,b,c,d; if(cnt[kk] == 0) cnt[kk] = ++tim; a = read(),b = read(),c = read(),d = read(); G[cnt[kk]].push_back(Node{a,b,c,d}); } dfs(1,0,0,0,0); printf("%lld\n",ans); } system("pause"); return 0; }
The Oculus
思路:需要注意一下这里的数据范围,代表的是长度。
那么显然直接处理出f[i]会爆longlong。
但是因为这里值涉及到了加法和乘法。那么取模显然不会影响结果。
所以先对f[i]进行hash,运用双模数,构建f1[i],f2[i]的键值对,这样基本就能保证数据与下标的对不重叠出现。
那么,显然我们要得到的就是A*B-C。对应的下标。
直接根据A*B-C对双模数取模后的键值来找到对应的下标即可。
但是这里map会T。所以要用到unorderedm_map.
但是unordered_map不支持pii的键值,所以只能放入<LL,int>形式。
但是可以通过构造一个比较单独型的LL值来继续保持下标对应的唯一性。
所以这里用了f1*mod+f2来构建hash的键值
Code:

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef long double ld; typedef pair<LL,LL> pii; const int N = 1e6+5; const LL Mod = 1e9+9; const LL mod = 1e9+7; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e8 #define INM INT_MIN #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline int read() { int x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9'){if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } LL f1[N<<1],f2[N<<1]; unordered_map<LL,int> mp; inline void init() { f1[1] = f2[1] = 1; f1[2] = f2[2] = 2; mp[f1[1]*mod+f2[1]] = 1; mp[f1[2]*mod+f2[2]] = 2; for(int i = 3;i < (N<<1);++i) { f1[i] = (f1[i-1]+f1[i-2])%Mod; f2[i] = (f2[i-1]+f2[i-2])%mod; mp[f1[i]*mod+f2[i]] = i; } } int main() { init(); /* freopen("data1.in","r",stdin); freopen("data1.out","w",stdout);*/ int t;t = read(); while(t--) { LL A1 = 0,A2 = 0; LL B1 = 0,B2 = 0; LL C1 = 0,C2 = 0; int n1;n1 = read(); for(int i = 1;i <= n1;++i) { int x;x = read(); if(x) { A1 = (A1+f1[i])%Mod; A2 = (A2+f2[i])%mod; } } int n2;n2 = read(); for(int i = 1;i <= n2;++i) { int x;x = read(); if(x) { B1 = (B1+f1[i])%Mod; B2 = (B2+f2[i])%mod; } } int n3;n3 = read(); for(int i = 1;i <= n3;++i) { int x;x = read(); if(x) { C1 = (C1+f1[i])%Mod; C2 = (C2+f2[i])%mod; } } LL tmp1 = ((A1*B1)%Mod-C1+Mod)%Mod; LL tmp2 = ((A2*B2)%mod-C2+mod)%mod; int ans = mp[tmp1*mod+tmp2]; printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0; }
New Equipments
思路:首先可以发现路径的代价是个二次函数,然后由于每个人只能匹配一个机器。
且一个机器只能对应一个人,那就是一个二分图的模型。
如果每个人去每个机器都建边,m是1e8的数据,显然会TLE。
但是可以发现的是n是只有50,而且一个人最多只会对应1个机器,那么我们让每个人和代价最小的n个机器连起来。
就能保证每个都能有匹配的对象。
同时由于这是个开口向上的二次函数,所以可以先利用二次函数的特性找到最小的点,然后向左右扩展连满n条边。
这里用了三分找最小点。
那么显然建立一个超级源点s和每个人都建立1的容量,0的费用。超级汇点和每个机器建立1的容量,0的费用。
对于每个人的费用就是之前的总费用+当前的费用流。
因为每条边都是1的容量,所以我们其实会spfa增广n次。
每次增广都将第i个点的费用流算出。
为什么当前的费用要加上之前的总费用。
我是这样理解的:之前的费用流算出后,残余网络上就会经过那些负边权的反向边,而反向边的总代价就是之前的费用流的总和。
中间算边的大小的时候,数据开小了,只算了人和机器的边数,调了蛮久..
Code:

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; typedef long double ld; typedef pair<int,int> pii; const int N = 1e5+5; const int M = 1e6+6; const LL Mod = 2505; #define pi acos(-1) #define INF 1e18 #define INM INT_MIN #define dbg(ax) cout << "now this num is " << ax << endl; inline LL read() { LL x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar(); while(c < '0' || c > '9'){if(c == '-') f = -1;c = getchar();} while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48);c = getchar();} return x*f; } /* work [1,n] equ [1+n,mp.size+n] s = 0,t = mp.size+n+1 */ int n,m,s,t,cnt = -1,tim = 0,num = 0; LL head[N],pre[N],cal[N],dis[N],vis[N],a[N],b[N],c[N],ans[N],ma; struct Node{int to,next;LL dis,flow;}e[N<<1]; map<int,int> mp; inline void add(int u,int v,LL f,LL w)//flow - cost { e[++cnt].to = v,e[cnt].dis = w,e[cnt].flow = f,e[cnt].next = head[u],head[u] = cnt; } void init() { cnt = -1,tim = 0,num = 0,ma = 0; mp.clear(); memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); memset(pre,0,sizeof(pre)); memset(cal,0,sizeof(cal)); } LL slove(LL a,LL b,LL c,int j) { return a*j*j+b*j+c; } bool spfa() { memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); for(int i = 0;i <= t;++i) dis[i] = INF; queue<int> Q; Q.push(s); dis[s] = 0,vis[s] = 1,cal[s] = INF; while(!Q.empty()) { int u = Q.front(); Q.pop(); vis[u] = 0; for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].next) { int v = e[i].to; LL d = e[i].dis,flow = e[i].flow; if(flow <= 0) continue; if(dis[v] > dis[u]+d) { dis[v] = dis[u]+d; cal[v] = min(cal[u],flow); pre[v] = i; if(!vis[v]) vis[v] = 1,Q.push(v); } } } if(dis[t] == INF) return false; return true; } void MCMF() { while(spfa()) { int x = t; ma += dis[t]*cal[t]; ans[++num] = ma; while(x != s) { int i = pre[x]; e[i].flow -= cal[t]; e[i^1].flow += cal[t]; x = e[i^1].to; } } } void check(int i) { int L = 1,r = m,tmp; while(L < r) { int mid = (L+r)>>1; int smid = (mid+r)>>1; if(slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],mid) > slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],smid)) L = mid,tmp = mid; else r = smid,tmp = smid; } if(mp[tmp] == 0) mp[tmp] = ++tim; add(i,n+mp[tmp],1,slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],L)); add(n+mp[tmp],i,0,-slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],L)); L = tmp-1,r = tmp+1; for(int j = 1;j < n;++j) { if(L >= 1 && (slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],L) <= slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],r))) { if(mp[L] == 0) mp[L] = ++tim; add(i,n+mp[L],1,slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],L)); add(n+mp[L],i,0,-slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],L)); L--; } else if(r <= m) { if(mp[r] == 0) mp[r] = ++tim; add(i,n+mp[r],1,slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],r)); add(n+mp[r],i,0,-slove(a[i],b[i],c[i],r)); r++; } } } int main() { freopen("data1.in","r",stdin); freopen("data1.out","w",stdout); int tt;tt = read(); while(tt--) { init(); n = read(),m = read(); for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) a[i] = read(),b[i] = read(),c[i] = read(); for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) check(i); s = 0,t = n+tim+1; for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) add(s,i,1,0),add(i,s,0,0); for(int i = 1;i <= tim;++i) add(i+n,t,1,0),add(t,i+n,0,0); MCMF(); for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i) printf("%lld%c",ans[i],i == n ? '\n' : ' '); } system("pause"); return 0; }


