【深度学习】Tensorflow学习(1)张量与常用函数
关于张量
张量可以表示0阶到N阶的数组
在TensorFlow中,张量(Tensor)表示某种相同数据类型的多维数据
因此张量有两个重要特征:
- 数据类型
- 数组形状(各个维度的大小)
张量的数据类型
tf.int,tf.float
tf.int32,tf.float32,tf.float64
tf.bool
tf.constant([True,False])
tf.string
tf.constant("Hello Wrold !")
创建Tensor
创建一个最简单的张量
tf.constant(张量内容,dtype=数据类型(可选))
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.constant([1,5],dtype=tf.int64)
print(a)
print(a.dtype)
print(a.shape)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor([1 5], shape=(2,), dtype=int64) <dtype: 'int64'> (2,)
将numpy数据类型转为tensor数据类型
tf.convert_to_tensor(a,dtype=tf.int64)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,5)
b = tf.convert_to_tensor(a,dtype=tf.int64)
print(a)
print(b)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
[0 1 2 3 4] tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3 4], shape=(5,), dtype=int64)
通过维度创建一个tensor
创建全为0的张量
tf.zeros(维度)
创建全为1的张量
tf.ones(维度)
创建全为指定值的张量
tf.fill(维度,指定值)
举例
import tensorflow as tf
a=tf.zeros([2,3])
b=tf.ones(4)
c=tf.fill([2,2],9)
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor( [[0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0.]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([1. 1. 1. 1.], shape=(4,), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor( [[9 9] [9 9]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=int32)
维度
一维 直接写个数
二维 用[行,列]
多维 用[n,m,j,k……]
生成随机数
生成正态分布的随机数
默认均值为0,标准差为1
tf.random.normal(维度,mean=均值,stddev=标准差)
生成截断式正态分布的随机数(生成的随机数更集中一些)
tf.ranodm.truncated_normal(维度,mean=均值,sttdev=标准差)

举例 对比
import tensorflow as tf
d = tf.random.normal([2,3],mean=0.5,stddev=1) # stddev 标准差
e = tf.random.truncated_normal([2,2],mean=0.5,stddev=1)
print(d)
print(e)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor( [[ 2.1269822 1.2042918 -0.28122586] [ 0.25896066 0.15369958 0.72224903]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor( [[ 1.900454 1.7232051 ] [-0.5688374 -0.36629975]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32)
生成指定维度的均匀分布的随机数[minval,maxval)
tf.random.uniform(维度,minval=最小值,maxval=最大值) # 前闭后开区间
import tensorflow as tf
f = tf.random.uniform([2,3],minval=0,maxval=1) # stddev 标准差
print(f)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor( [[0.29363596 0.731918 0.8976741 ] [0.13689423 0.53846407 0.23545396]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32)
常用函数
强制tensor转换为该数据类型
tf.cast(张量名称,dtype=数据类型)
计算张量维度上元素的最小值
tf.reduce_min(张量名)
计算张量维度上元素的最大值
tf.reduce_max(张量名)
import tensorflow as tf
x1=tf.constant([1.,2.,3.],dtype=tf.float64)
print(x1)
x2=tf.cast(x1,tf.int32)
print(x2)
print(tf.reduce_min(x2),'\n',tf.reduce_max(x2))
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor([1. 2. 3.], shape=(3,), dtype=float64) tf.Tensor([1 2 3], shape=(3,), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
axis
axis:用于指定操作方向
在一个二维张量或数组中,可以通过调整axis等于1或者0控制执行维度
- axis=0 代表跨行(经度,down)
- axis=1 代表跨列(维度,across)
- 不指定axis,则所有元素参与计算

计算张量沿着指定维度的平均值
tf.reduce_mean(张量名,axis=操作轴)
计算张量沿着指定维度的和
tf.reduce_sum(张量名,axis=操作轴)
import tensorflow as tf
x=tf.constant([
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6]
])
print(x)
print(tf.reduce_mean(x)) # 计算张量沿着指定维度的平均值 所有元素参与计算
print(tf.reduce_sum(x,axis=1)) #计算张量沿着指定维度的和 跨列操作
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor( [[1 2 3] [4 5 6]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor([ 6 15], shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
tf.Variable()
作用:将变量标记为“可训练”
被标记的变量会在反向传播中记录梯度信息。神经网络训练中,常用该函数标记待训练参数
tf.Variable(初始值)
import tensorflow as tf
# 神经网络初始化参数w
w = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=0,stddev=1)) # 生成正态分布的随机数 维度为[2,2] 均值为0 标准差为1
# 通过上述操作,就可以在反向传播中 通过梯度下降更新参数w
import tensorflow as tf w = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=0,stddev=1)) print(w)运行结果
<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2, 2) dtype=float32, numpy= array([[ 0.2049946 , 0.1968063 ], [-0.29070154, -0.02642607]], dtype=float32)>
tensorflow中的数学运算
对应元素的四则运算:tf.add,tf.subtract,tf.multiply,tf.divide(加减乘除)
平方:tf.square
次方:tf.pow
开方:tf.sqrt
矩阵乘:tf.matmul
重要:只有两个维度相同的张量才可以做四则运算
实现两个张量对应元素相加
tf.add(张量1,张量2)
实现两个张量对应元素相减
tf.subtract(张量1,张量2)
实现两个张量对应元素相乘
tf.multiply(张量1,张量2)
实现两个张量对应元素相除
tf.divide(张量1,张量2)
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.ones([1,3])
b = tf.fill([1,3],3.)
print(a)
print(b)
print(tf.add(a,b))
print(tf.subtract(a,b))
print(tf.multiply(a,b))
print(tf.divide(b,a))
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor([[1. 1. 1.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([[3. 3. 3.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([[4. 4. 4.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([[-2. -2. -2.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([[3. 3. 3.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([[3. 3. 3.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32)
计算某个张量的平方
ft.square(张量名)
计算某个张量的N次方
ft.pow(张量名,n次方数)
计算某个张量的开方
ft.sqrt(张量名)
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.fill([1,3],3.)
print(a)
print(tf.pow(a,3)) # 三次方
print(tf.square(a)) # 平方
print(tf.sqrt(a)) # 开方
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor([[3. 3. 3.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([[27. 27. 27.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([[9. 9. 9.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor([[1.7320508 1.7320508 1.7320508]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32)
矩阵乘
tf.matmul(矩阵1,矩阵2)
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.ones([3,2])
b = tf.fill([2,3],3.)
print(a)
print(b)
print(tf.matmul(a,b))
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor( [[1. 1.] [1. 1.] [1. 1.]], shape=(3, 2), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor( [[3. 3. 3.] [3. 3. 3.]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32) tf.Tensor( [[6. 6. 6.] [6. 6. 6.] [6. 6. 6.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices
切分传入张量的第一维度,生成输入 特征/标签 对,构建数据集
data =tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((输入特征,标签))
Numpy和Tensor格式都可以用该语句读入数据
import tensorflow as tf
features = tf.constant([12, 23, 10, 17])
labels = tf.constant([0, 1, 1, 0])
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((features, labels))
print(dataset)
for element in dataset:
print(element)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
<TensorSliceDataset element_spec=(TensorSpec(shape=(), dtype=tf.int32, name=None), TensorSpec(shape=(), dtype=tf.int32, name=None))> (<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=12>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=0>) (<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=23>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=1>) (<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=10>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=1>) (<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=17>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=0>)
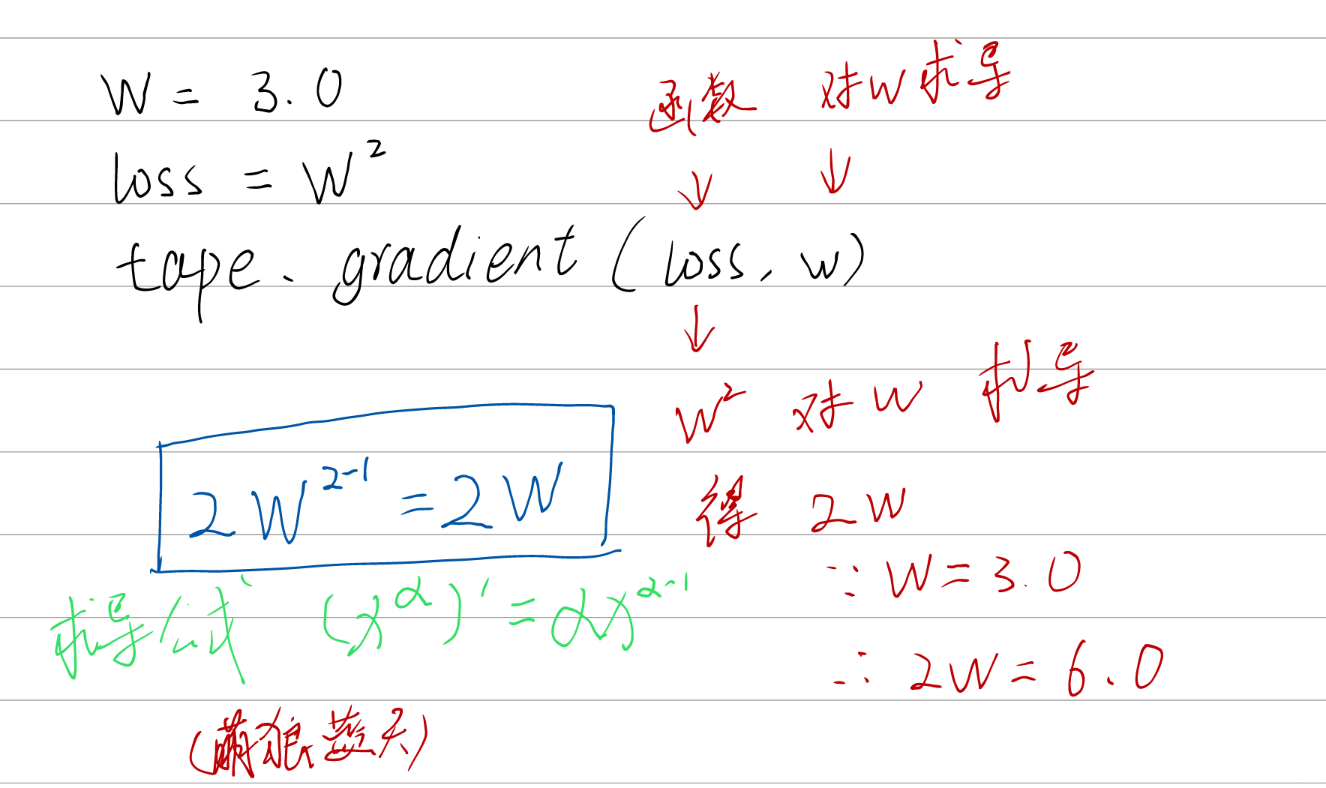
实现某个函数对指定参数的求导运算
tf.GradientTape
with结构计算过程,gradient求出张量的梯度
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
若干个计算过程
grad=tape.gradient(函数,对谁求导)
import tensorflow as tf
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
w = tf.Variable(tf.constant(3.0)) # 标记为“可训练”
loss = tf.pow(w, 2) # 求w的2次方
# 损失函数loss 对 参数w 的求导数运算
grad = tape.gradient(loss,w)
print(grad)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor(6.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
枚举 enumerate
enumerate是python的内建函数,它可以遍历每个元素(如列表、元组或者字符串),组合为 索引 元素。常在for循环中使用
enumerate 列表名
import tensorflow as tf
seq = ['one','two','three']
for i,element in enumerate(seq):
print(i,element)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
0 one 1 two 2 three
独热编码(one-hot encoding)
在分类问题中,常用独热编码做标签
标记类别:1表示是,0表示非
tf.one_hot()
该函数将待转换数据。转换为one-hot形式的数据输出
tf.one_hot(待转化数据,depth=几分类)
import tensorflow as tf
classes = 3
labels = tf.constant([1,0,2]) # 输入元素的最小值为0,最大值为2
output = tf.one_hot(labels,depth=classes)
print(output)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
tf.Tensor( [[0. 1. 0.] [1. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 1.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.nn.softmax(x)
作用:使输出符合概率分布
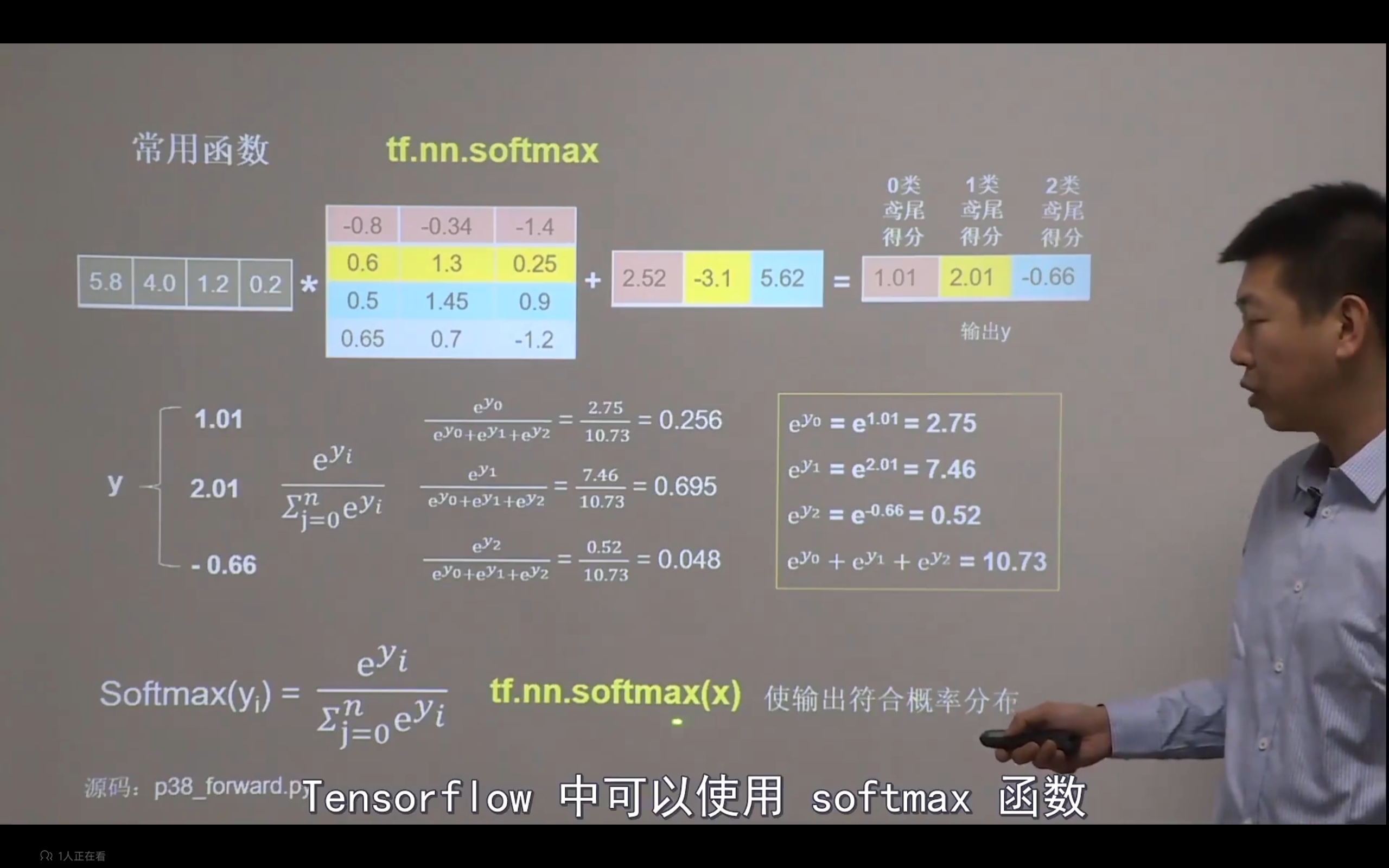
当n分类的n个输出(y0,y1 …… yn-1)通过softmax()函数
便符合概率分布了。
import tensorflow as tf
y = tf.constant([1.01,2.01,-0.66])
y_pro =tf.nn.softmax(y)
print("After softmax , y_pro is :",y_pro)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
After softmax , y_pro is : tf.Tensor([0.25598174 0.6958304 0.0481878 ], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
assign_sub
作用:常用于参数自更新
- 赋值操作,更新参数的返回值并返回
- 调用
assign_sub前,先使用tf.Variable定义变量w为可训练(可自更新)
w.assign_sub(w要自减的内容)
import tensorflow as tf
w = tf.Variable(4)
w.assign_sub(1) # w-=1 即是 w=w-1
print(w)
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=() dtype=int32, numpy=3>
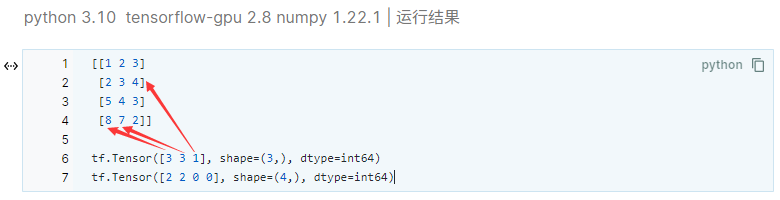
tf.argmax
作用:返回张量沿指定维度最大值的索引
tf.argmax(张量名,axis=操作轴)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
test = np.array([[1,2,3],[2,3,4],[5,4,3],[8,7,2]])
print(test)
print(tf.argmax(test,axis=0)) # 返回每一行(经度)最大值的索引
print(tf.argmax(test,axis=1)) # 返回每一行(维度)最大值的索引
python 3.10 tensorflow-gpu 2.8 numpy 1.22.1 | 运行结果
[[1 2 3] [2 3 4] [5 4 3] [8 7 2]] tf.Tensor([3 3 1], shape=(3,), dtype=int64) tf.Tensor([2 2 0 0], shape=(4,), dtype=int64)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号