注解配置和XML配置要实现的功能都是一样的,都是要降低程序间的耦合,只是配置的形式不一样。XML是独立的写成一个配置文件,而注解的配置采用的是在类中添加一些注解来实现功能。
自己写的类如何使用注解:
一、 用于创建对象的注解:@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository。
他们的作用就和在XML配置文件中编写一个<bean>标签实现的功能是一样的。
@Controller、@Service、@Repository
这三个注解的作用和属性与@Component是一模一样的。那为什么要准备三个注解呢?他们三个是spring框架为我们提供明确的三层使用的注解,使我们的三层对象更加清晰。如果有些对象不属于三层中的任何一层,这时直接使用@Component
@Component:
在类上面加注解,用于把当前类反射创建对象并把对象存入spring容器中。Spring容器是Map结构,对象是value,key是通过该注解的value属性来指定bean的id。

如果一个注解中只有value属性,则value可以省略不写。如果同时有两个属性,则value必须写。
当我们不写value属性时,它的默认值是当前类名且首字母改小写,如AccountServiceImplement类对象的id为accountServiceImplement。
Spring是怎么发现@Configuration、@Controller、@Service这些注解修饰的类的?
原来@Configuration、@Controller、@Service这些注解其实都是@Component的派生注解,我们看这些注解的代码会发现,都有@Component注解修饰。而spring通过metadata.hasMetaAnnotation()方法获取到这些注解包含@Component,所以都可以扫描到。
虽然在类中加了注解@Component,但是在解析配置文件的时候不知道你在哪写了注解,于是我们在bean.xml中进行配置,告知spring在创建容器时要扫描的包,当扫描包的时候,就会扫描包中的注解。
配置所需要的标签不是在beans标签的约束中,而是一个名称为context的名称空间和约束中。

打开spring Framework Documentationà点击coreà拷贝下面的代码覆盖原先的代码

这时会多了一个context名称空间,有了context名称空间,就可以使用context:component-scan标签,该标签的base-package属性值为com.itheima这个包,这时就会扫描com.itheima包及其子包所有类上和接口上的注解.

注解相比于XML可能要简单一些,因为写了一个标签之后就再也不用再bean.xml中配置了。想创建对象就加@Component注解。
@Repository(使用在接口的实现类上)和@Mapper(使用在接口上)的区别:
@Repository注解便属于最先引入的一批,它用于将数据访问层 (DAO 层 ) 的类标识为 Spring Bean。具体只需将该注解标注在 DAO类上即可。为什么 @Repository 只能标注在 DAO 类上呢?这是因为该注解的作用不只是将类识别为Bean,同时它还能将所标注的类中抛出的数据访问异常封装为 Spring 的数据访问异常类型。 Spring本身提供了一个丰富的并且是与具体的数据访问技术无关的数据访问异常结构,用于封装不同的持久层框架抛出的异常,使得异常独立于底层的框架。
@Repository("accountDao") public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao { }
@Mapper: 这个注解一般使用在Dao层接口上,相当于一个mapper.xml文件,它的作用就是将接口生成一个动态代理类。加入了@Mapper注解,目的就是为了不再写mapper映射文件。这个注解就是用来映射mapper.xml文件的。使用@mapper后,不需要在spring配置中设置扫描地址,通过mapper.xml里面的namespace属性对应相关的mapper类,spring将动态的生成Bean后注入到ServiceImpl中.
@org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper public interface AreasMapper extends Mapper<Areas> { }
@MapperScan注解:
@MapperScan注解写在SpringBoot的启动类上。当我们的一个项目中存在多个Dao层接口的时候,此时我们需要对每个接口类都写上@Mapper注解,非常的麻烦,此时可以使用@MapperScan注解来解决这个问题。让这个接口进行一次性的注入,不需要在写@Mapper注解
@MapperScan({"com.xxxx.xxxx.dao"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class ServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
@ComponentScan 和 @MapperScan 的区别
@ComponentScan
这个注解导入的包为:import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;用来扫描spring容器下的带有注解为@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component的这些类。
@MapperScan
这个注解导入的包为:import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;通过添加这个注解,可以避免在许多mapper层上添加@Mapper,如果忽略添加@MapperScan,无法扫描mapper层,造成服务无法启动.
二、 用于注入数据的注解:@Autowired、@Qualifier、@Resource、@Value
他们的作用就和在XML配置文件中的bean标签中写一个<property>标签的作用是一样的。
@Autowired:
可以写在变量上,也可以写在方法上。自动按照类型注入,不能指定id。只要容器中有唯一的一个bean对象类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,就可以注入成功。 如果IOC容器中没有任何bean的类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,则报错。如果IOC容器中有多个bean对象的类型与要注入的变量类型匹配时,如果注入后的变量名称accountDao与容器中其中一个bean对象的id一致,也可以注入成功;如果两个bean对象的id与要注入的变量名称都不一样则报错。
解决方法:
1、 两个bean对象是相同类型时改id。
2、 使用@Qualifier注解

自动按照类型IAccountDao注入,由于AccountDaoImpl实现了IAccountDao接口,故可以注入成功。如果AccountDaoImpl没有实现IAccountDao,则容器中找不到IAccountDao类型的对象,则没有唯一的bean对象类型与要注入的变量类型匹配,故注入不成功。如果不注入就会报空指针异常。
@Qualifier:
在按照类型注入的基础之上(即同类型的bean对象有多个)再按照名称注入,它在给类成员注入时不能单独使用,因为@Qualifier仅指定id,而没有指定类型。但是在给方法参数注入时可以单独使用。@Qualifier注解的value属性用于指定注入bean的id。
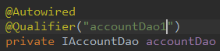
另外,在创建QueryRunner对象注入DataSource依赖时,spring自动为我们匹配一个数据源DataSource,因为此时容器中有一个DataSource类型的数据源,如果容器中有多个数据源,首先选择bean的id为形参dataSource的数据源,如果容器中没有数据源DataSource对象的id与形参dataSource相同,有两个方法:
1、 将形参dataSource的名称改为容器中DataSource对象的id,

2、@Qualifier注解在注入类成员时要与@Autowired注解一起使用,而给方法参数注入时可以单独使用

@Resource:
直接按照bean的id注入,它可以独立使用,不依托于@Autowired,即该注解既可以指定类型,又可以指定id。@Resource注解有name属性,用于指定bean的id。这样一个@Resource注解可以取代@Autowired和@Qualifier两个注解。

使用@Resource注入Mapper时不会出现红色的波浪线,使用@Autowired会出现红色的波浪线
@Autowired、@Qualifier、@Resource这三个注解都只能注入其他bean类型的数据,而基本类型和String类型无法使用上述注解实现。另外,集合类型的注入只能通过XML来实现。
@value:
用于注入基本类型和String类型的数据,该注解有一个value属性,用于指定数据的值,它可以使用spring中的SPEL(也就是spring的el表达式),SPEL的写法:
${表达式},mybatis中也能使用${}给参数赋值,如果${}写在JSP文件中,就是JSP的EL表达式,此时一定会去四大域中获取数据,如果写在spring的配置文件或注解中,就是spring的el表达式,则去spring指定的位置取数据。如果写在mybatis的配置文件中,则是mybatis的el表达式,则会去mybatis对应的位置获取数据。以后鉴别${}是什么时,看它在什么地方就可以了。
三、 用于改变作用范围的注解:仅@Scope一个
他们的作用就和在Bean标签中使用scope属性实现的功能是一样的。
@Scope:
用于指定bean的作用范围,@Scope注解的属性只用value一个,指定范围的取值,常用取值为singleton、prototype,不写是默认情况下是单例的。

四、 和生命周期相关的注解:(了解即可)@PreDestroy、@PostConstruct
他们的作用就和在Bean标签中使用init-method和destroy-method的作用是一样的
@PostConstruct:
用于指定初始化方法
@PreDestroy:
用于指定销毁方法。容器关闭才会执行销毁方法,

1、创建maven的jar工程,导入依赖,
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2、创建数据库eesy下的account1表
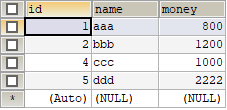
3、创建Account实体类
public class Account implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String name; private Float money; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Float getMoney() { return money; } public void setMoney(Float money) { this.money = money; } @Override public String toString() { return "Account{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", money=" + money + '}'; } }
4、写业务层接口IAccountService
public interface IAccountService { List<Account> findAllAccount(); Account findAccountById(Integer accountId); void saveAccount(Account account); void updateAccount(Account account); void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId); }
5、 写业务层接口的实现类,在类中添加注解注入依赖,之前在类中添加set方法以XML的方式注入依赖
@Service("accountService") public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService{ @Autowired private IAccountDao accountDao; @Override public List<Account> findAllAccount() { return accountDao.findAllAccount(); } @Override public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) { return accountDao.findAccountById(accountId); } @Override public void saveAccount(Account account) { accountDao.saveAccount(account); } @Override public void updateAccount(Account account) { accountDao.updateAccount(account); } @Override public void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId) { accountDao.deleteAccount(acccountId); } }
在AccountServiceImpl类上面添加@service注解并且命名id为accountService,即@Service(“AccountService”),由于AccountDao类型的对象在容器中只有一个,故可以用@Autowired,当我们用注解注入依赖的时候,set方法可以删除。
6、创建持久层接口IAccountDao
public interface IAccountDao { List<Account> findAllAccount(); Account findAccountById(Integer accountId); void saveAccount(Account account); void updateAccount(Account account); void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId); }
7、创建持久层实现类AccountDaoImpl
@Repository("accountDao") public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao { @Autowired private QueryRunner runner; @Override public List<Account> findAllAccount() { try{ return runner.query("select * from account",new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class)); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) { try{ return runner.query("select * from account where id = ? ",new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class),accountId); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void saveAccount(Account account) { try{ runner.update("insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney()); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void updateAccount(Account account) { try{ runner.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId()); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) { try{ runner.update("delete from account where id=?",accountId); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
在AccountDaoImpl类上添加@Repository注解并且命名id为accountDao,即@Repository(“accountDao”), 由于QueryRunner类型的对象在容器中只有一个,故可以用@Autowired,当我们用注解注入依赖的时候,set方法可以删除。
8、创建bean.xml文件,导入约束,配置bean对象
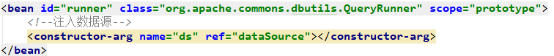
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 告知spring在创建容器时要扫描的包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan> <!--配置QueryRunner--> <bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype"> <!--注入数据源--> <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- 配置数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <!--连接数据库的必备信息--> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property> <property name="user" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="1234"></property> </bean> </beans>
删除service和dao的bean标签的配置。
将bean.xml的约束替换成带有context名称空间的约束,
一旦我们使用了注解开发,一定要告知spring在创建容器时要扫描的包。
9、使用Junit单元测试,测试我们的配置
以下代码是使用注解配置时的测试方法。
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:bean.xml") public class AccountServiceTest { @Autowired private IAccountService as; @Test public void testFindAll() { //3.执行方法 List<Account> accounts = as.findAllAccount(); for(Account account : accounts){ System.out.println(account); } } @Test public void testFindOne() { //3.执行方法 Account account = as.findAccountById(1); System.out.println(account); } @Test public void testSave() { Account account = new Account(); account.setName("test"); account.setMoney(12345f); //3.执行方法 as.saveAccount(account); } @Test public void testUpdate() { //3.执行方法 Account account = as.findAccountById(4); account.setMoney(23456f); as.updateAccount(account); } @Test public void testDelete() { //3.执行方法 as.deleteAccount(4); } }
总结:基于XML的配置和基于注解的配置并没有太大差异,同时,注解IOC中,配置文件bean.xml依然存在,那能不能把配置文件去掉呢?
另外创建容器时如何扫描包呢?使用@ComponentScan注解。
现在我们学的注解只能用到我们的类上,而QueryRunner是DBUtils的jar包中的一个类,而你想在QueryRunner类上面加注解是无法实现的。以上是基于注解和XML的IOC,下面改造成纯注解的IOC
jar包中的类如何使用注解
创建一个配置类,配置类的名称可以自定义,配置类的作用于bean.xml的作用是一样的。
@Configuration:
该注解的作用是指定当前类是一个配置类。只有在配置类上面加了@Configuration注解,配置类的作用才与bean.xml的作用一样。
细节:当配置类的字节码作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建时的参数时,该注解可以不写。
配置类应该配置一些公共的信息,而和spring连接数据库相关的bean对象(如QueryRunner和DataSource)的配置放到JdbcConfig类中,此时有两个配置类SpringConfiguration和JdbcConfig,此时如果JdbcConfig类的字节码没有作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建时的参数的话,则必须扫描配置类所在的包config,并且JdbcConfig类上要加@Configuration注解。
此时扫描时要扫描两个包:
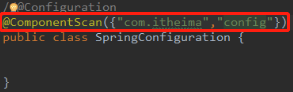
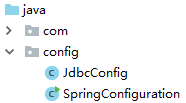
在扫描包的时候,会扫描包下所有的类,另外如果这个类是配置类,才会对类里面的注解进行扫描,此时@Configuration注解不能省略了。
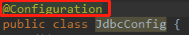
但是如果这个配置类JdbcConfig的字节码也作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建时的参数时,
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class, JdbcConfig.class);
JdbcConfig类上面的@Configuration注解也可以省略,此时也不用扫描config包,即:

总结:当存在两配置文件时,当两个类的字节码作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建时的参数是,两个类上的@Configuration注解可以都不写,且配置类所在的包(如config)也不用再@ComponentScan注解中进行配置;如果其中一个配置类的字节码没有作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建时的参数时,则必须在该配置类上加上@Configuration注解,且必须将配置类所在的包(如config)在@ComponentScan注解中进行配置。
当SpringConfiguration.class和JdbcConfig.class均作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建时的参数时,他们两个之间是兄弟关系,并列的,没有谁打谁小,而我们真正想实现的功能是:SpringConfiguration是一个综合的大配置类,里面包含若干个小配置类,我们不希望在创建对象时写很多字节码,可以将JdbcConfig.class删除,此时要么在JdbcConfig类上添加@Configuration注解并将配置类所在的包在@ComponentScan注解中配置,要么使用@Import注解
@Import
用于导入其他的配置类到主配置类(如SpringConfiguration),从而只用加载主配置类就可以将小配置类全都加载进来。相当于分配置文件编写配置。该注解中有一个value属性,作用是指定其他类的字节码。该属性的类型为字节码数组,如果有多个小的配置类,都可以在@Import注解中指定类的字节码。
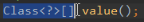
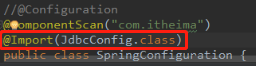
当我们使用@Import注解之后,有@Import注解的类就是主(父)配置类,而导入的都是子配置类。
Spring创建容器,显然父子关系的配置类更合理,也更清晰。
@ComponentScan
当我们使用了@ComponentScan注解,就等同于在XML中配置了context:component-scan标签。

用于通过注解指定spring在创建容器时要扫描的包,该注解有value属性和basePackage属性,
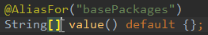
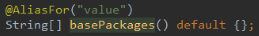
并且在这两个属性上面都使用了@AliasFor的注解,这样value属性和basePackage属性的作用是一样的,都是指定创建容器时要扫描的包。
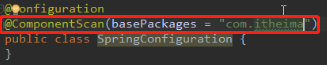
由于value属性和basePackage属性都是一个数组,所以标准写法应该要加上{},如下:

如果注解的属性有且只有一个值,如果是数组类型的,我们可以去掉大括号。如果只有一个属性,且属性名为value是,value可以省略。

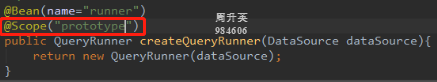
@Bean
将当前方法的返回值作为Bean对象存入spring容器中。该注解的name属性用于指定bean的id,当不写name属性时,默认id值是当前方法的名称createQueryRunner。

将通过构造函数注入依赖来创建bean对象,
改成在配置类中通过一个方法来创建bean对象,
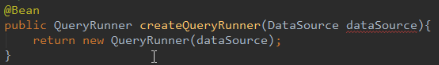
当我们使用注解配置方法时,如果方法有参数,如上面的DataSource,spring框架会去容器中查找有没有可用的bean对象,查找的方式和@Autowired注解是一样的,自动按照类型注入,如果有唯一的一个类型匹配的对象时,则自动注入,如果没有匹配的对象则报错。如果有多个对象匹配时,使用@Qualifier注解。
此时QueryRunner对象是单例对象,而QueryRunner应该是多例对象,否则会出现线程安全问题。在创建QueryRunner对象的方法上加@Scope注解
创建数据源对象如下所示:

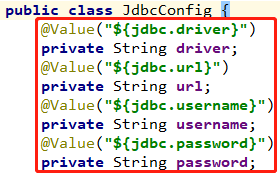
连接池的四个参数原来是写在配置文件中,现在又在代码中写死了,我们仍然可以将这四个参数在类路径下的配置文件JdbcConfig.properties中进行配置,现在读取配置文件,现在JdbcConfig配置文件中定义一些变量,然后通过@Value注解给这些变量赋值,
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=1234
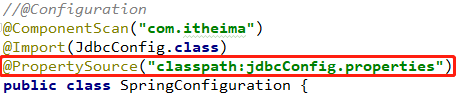
那么如何读取配置文件呢?使用@PropertySource注解,
@PropertySource
用于加载指定properties文件,不管是properties文件还是yml文件,都是把配置的数据放到spring容器中。
该注解@PropertySource的name和value属性,value属性用于指定文件的名称和文件的路径。关键字classpath表示类路径下
项目部署之后,src/main/resources目录下的配置文件都跑到C:\Users\miracle\IdeaProjects\day02_eesy_04account_annoioc_withoutxml\target\classes目录下,

即src/main/java目录下的代码和src/main/resources目录下的配置文件都会跑到target\classes类路径下,那如何识别类路径呢?在类路径前面加上一个classpath关键字,classpath:后面的路径是类路径。
如果类路径下有包config/spring则写包,没包就写文件名。

通过@Configuration、@ComponentScan、@Bean三个注解,我们实现了把配置文件中原来不能拿走的配置全都可以拿掉了。如下图所示:
此时可以将bean.xml配置文件删除,使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext实现类来获取容器。

注意AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建的参数为被@Configuration注解过的类的字节码,即配置类的字节码。
纯注解的方式和之前这种不是纯注解的方式(虽然用了一部分注解但是仍然保留XML的方式)比起来并没有省事,反而更费事,在实际开发中如何选择呢?首先在没有自主选择去权利的情况下,以公司为准,在能自己选择的情况下,纯XML有一些复杂性,纯注解的配置并没有很省事反而让我们更麻烦一些,
故选择有注解有XML的方式更合适一些,如果是jar包中的类用XML配置,如果是我们自己写的类,显然用注解
1、创建配置类SpringConfiguration和JdbcConfig
@ComponentScan("com.itheima") @Import(JdbcConfig.class) @PropertySource("classpath:jdbcConfig.properties") public class SpringConfiguration { public static void main(String[] args) { DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); String format = dateFormat.format(date); System.out.println(format); } } }
JdbcConfig
public class JdbcConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; /** * 用于创建一个QueryRunner对象 * @param dataSource * @return */ @Bean(name="runner") @Scope("prototype") public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(@Qualifier("ds2") DataSource dataSource){ return new QueryRunner(dataSource); } /** * 创建数据源对象 * @return */ @Bean(name="ds2") public DataSource createDataSource(){ try { ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource(); ds.setDriverClass(driver); ds.setJdbcUrl(url); ds.setUser(username); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; }catch (Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Bean(name="ds1") public DataSource createDataSource1(){ try { ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource(); ds.setDriverClass(driver); ds.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy02"); ds.setUser(username); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; }catch (Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
2、使用注解注入QueryRunner
@Repository("accountDao") public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao { @Autowired private QueryRunner runner; @Override public List<Account> findAllAccount() { try{ return runner.query("select * from account",new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class)); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) { try{ return runner.query("select * from account where id = ? ",new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class),accountId); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void saveAccount(Account account) { try{ runner.update("insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney()); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void updateAccount(Account account) { try{ runner.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId()); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) { try{ runner.update("delete from account where id=?",accountId); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }


