一、springboot整合tkMybatis
1、springboot整合tkMybatis
(1)、添加依赖:mapper-spring-boot-starter
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<mysql.version>8.0.11</mysql.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 通用Mapper启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
注意:tk.mybatis的版本为<version>2.0.4</version>,条件查询用的时ExamplerMapper。
mapper接口
@RegisterMapper public interface Mapper<T> extends BaseMapper<T>, ExampleMapper<T>, RowBoundsMapper<T>, Marker { }
(2)、配置连接数据库的四个参数
server.port=8081 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zwhxpp?serverTimezone=Hongkong&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.zwh.entity
因为用了Common Mapper,所以要指定别名包的扫描
(3)、编写启动类,在启动类中通过@MapperScan配置包扫描,扫描mapper包中的UserMapper接口
@SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.zwh.dao") public class UserApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(UserApplication.class, args); } }
注意:@MapperScan是tk.mybatis包下的。import tk.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
(4)、编写实体类
@Data @Table(name = "tab_user") public class User{ @Id @KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)//开启主键自动回填 private Integer uid; private String username;// 用户名 private String password;// 密码 private String name;// 姓名 private String sex;// 性别,1男性,2女性 private Date birthday; // 出生日期 }
由于是直接与数据库交互,所以要用到Common Mapper中的注解:@Table、@Id、@KeySQL
import tk.mybatis.mapper.annotation.KeySql;
@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)//开启主键自动回填
当主键是自增的情况下,添加一条记录的同时,其主键是不能使用的,但是有时我们需要该主键,我们设置useGeneratedKeys="true",这样在之后的java代码中我们就可以获取该主键对应的对象的属性值。useGeneratedKeys 取值范围true|false 默认值是:false。 含义:设置是否使用JDBC的getGenereatedKeys方法获取主键并赋值到keyProperty设置的领域模型属性中。
在springboot项目中相应的配置为:
#允许JDBC 生成主键。需要驱动器支持。如果设为了true,这个设置将强制使用被生成的主键,有一些驱动器不兼容不过仍然可以执行。 default:false
mybatis.configuration.use-generated-keys=true(5)、编写UserMapper接口,去操作数据库
import com.zwh.entity.User; import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper; public interface UserMapper extends Mapper<User> { }
(6)、编写UserService类,调用Mapper接口的方法进行数据库操作
@Service public class UserService { @Resource private UserMapper userMapper; public User queryById(Integer id){ User user = userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id); System.out.println(user); return user; } }
(7)、编写UserController
@RestController @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; @GetMapping("/{id}") public User queryById(@PathVariable Integer id){ User user = userService.queryById(id); return user; } }
(8)、启动项目,浏览器访问:http://localhost:8081/user/1,结果如下:
{"uid":1,"username":"zhangsan","password":"123456","name":"张三","sex":"男","birthday":"2020-11-10T16:00:00.000+0000"}
2、自定义通用基类
(1)、自定义通用基类
import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.ConditionMapper; import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper; import tk.mybatis.mapper.common.MySqlMapper; public interface MyMapper<T> extends Mapper<T>, MySqlMapper<T>, ConditionMapper<T>{ }
注意:自定义通用基类MyMapper不能被扫描到,否则会报错。
(2)、配置文件中指定通用基类MyMapper
mapper.mappers=com.zwh.config.mapper.MyMapper
(3)、dao接口使用自定义通用基类
import com.zwh.config.mapper.MyMapper; import com.zwh.entity.User; public interface UserMapper extends MyMapper<User> { }
二、插入数据后返回ID的方法(通用mapper主键策略)
通用Mapper还提供了序列(支持Oracle)、UUID(任意数据库,字段长度32)、主键自增(类似Mysql,Hsqldb)三种方式,其中序列和UUID可以配置多个,主键自增只能配置一个。
首先主键策略和数据库关系很大,有些数据库(如mysql、sqlserver)支持主键自增,而有些数据库(如oracle)只能通过序列来获得。
新增的@KeySql 注解用于替换 @GeneratedValue 注解
@KeySql 介绍
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface KeySql {
// 是否使用JDBC方式获取主键,优先级最高,设置为true后不对其他配置校验
boolean useGeneratedKeys() default false;
// 优先级第二,根据配置的数据库类型取回主键,忽略其他配置
IdentityDialect dialect() default IdentityDialect.NULL;
// 取主键的sql,序列或uuid,优先级第三
String sql() default "";
Class<? extends GenSql> genSql() default NULL.class;
// 和sql配合使用,默认使用全局配置中的ORDER
ORDER order() default ORDER.DEFAULT;
// java方式生成主键,优先级最低
Class<? extends GenId> genId() default tk.mybatis.mapper.genid.GenId.NULL.class;
}
通过上面的注释,大家可以看到主要的 3 个参数的优先级,useGeneratedKeys 优先级最高,其次是 dialect,最后是 sql。其中 order 只对 sql 方式有效。
useGeneratedKeys 和 dialect 相当于预设的基本用法,和数据库以及驱动紧密相关。sql 和 order 更灵活。
1、使用 JDBC 方式获取主键(优先级最高)
即配置@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)或@GeneratedValue(generator = "JDBC")
JDBC 支持通过 getGeneratedKeys 方法取回主键的情况。
常见的如 MySql,SqlServer 支持这种模式。
boolean useGeneratedKeys() default false;
是否使用 JDBC 方式获取主键,优先级最高,设置为 true 后,不对其他配置校验
这种情况下,配置主键策略最简单。
@Id @KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true) private Long id;
或
@Id @GeneratedValue(generator = "JDBC") private Long id;
为了让大家容易理解这里配置和 MyBatis 写法的关系,大家可以看看对应生成的 XML 代码:
<insert id="insert" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> insert into country (id, countryname, countrycode) values (#{id},#{countryname},#{countrycode}) </insert>
2、数据库支持自增(优先级第二)
支持自增数据库列表如下(共9种):
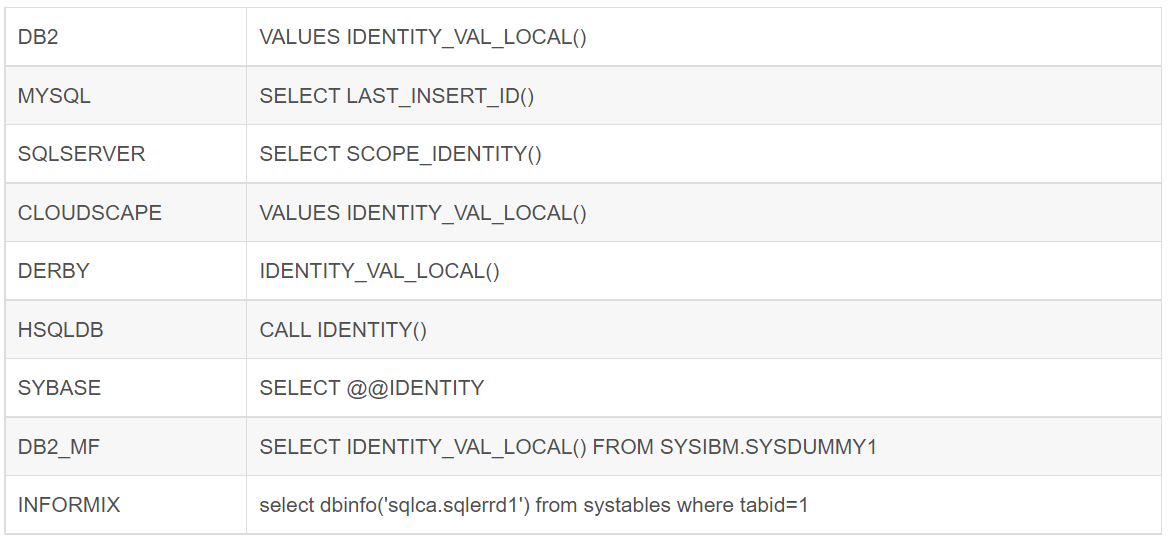
注意:没有oracle
@KeySql(dialect = IdentityDialect.MYSQL)或@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Id //DEFAULT 需要配合 IDENTITY 参数(ORDER默认AFTER) @KeySql(dialect = IdentityDialect.DEFAULT) private Integer id; //建议直接指定数据库 @Id @KeySql(dialect = IdentityDialect.MYSQL) private Integer id;
或:
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Integer id;
使用GenerationType.IDENTITY需要在全局配置中配置IDENTITY的参数值,并且需要根据数库配置ORDER属性。
mapper.identity=mysql mapper.order=AFTER //或者 #mapper.before=false
IDENTITY 参数以及 ORDER 参数会决定 selectKey 中的 SQL 和 order 属性的值(这里是 AFTER)。order="AFTER" mysql 自增长ID 先保存的数据 再生成的ID
对应的xml形式
<insert id="saveUser" parameterType="USER"> <!-- 配置保存时获取插入的 id -->
<selectKey keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" resultType="int"> select last_insert_id(); </selectKey> insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address}) </insert>
新增用户后,同时还要返回当前新增用户的 id 值,因为 id 是由数据库的自动增长来实现的,所以就相当于我们要在新增后将自动增长 auto_increment 的值返回。
3、通过 SQL 获取主键值(优先级第三)
(1)、oracle通过序列获取主键
像 Oracle 中通过序列获取主键就属于这种情况,除了类似序列获取值外,还可以是获取 UUID 的 SQL 语句,例如 select uuid()。
mapper.identity=select uuid() mapper.before=true
自增主键和非自增主键 的区别主要在于,自增主键 是插入表之后才有 id 的值(mapper.before=false),非自增主键是插入数据库前需要获取一个值作为主键(mapper.before=true)。
order()和取主键的 SQL配合使用
String sql() default "";
ORDER order() default ORDER.DEFAULT;
在 Oracle 中,我们可以用下面的方式进行配置:
@KeySql(sql = "select OUTPUT_SEQ.nextval from dual", order = ORDER.BEFORE)
或:
@Id @GeneratedValue( strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY, generator = "select SEQ_ID.nextval from dual") private Integer id;
使用 @GeneratedValue 时也要配置一个 ORDER 全局参数
xml的方式
<insert id="insertAuthor"> <selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="BEFORE"> select SEQ_ID.nextval from dual </selectKey> insert into country (id, countryname, countrycode) values (#{id},#{countryname},#{countrycode}) </insert>
order="BEFORE" oracle 自增长 UUID 先生成ID 再保存数据
(2)、获取mysql UUID 的 SQL 语句
order="BEFORE" mysql UUID 先生成ID 再保存数据
除了 Oracle 这种外,还有一种更普遍的用法,就是使用 UUID。
例如下面的配置:
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY,generator = "select uuid()") private String id;
注意: SQL 返回值类型和这里接收的类型(String)一致。
也可以自定义取回主键的方式:
CREATE DEFINER=`ip`@`%` FUNCTION `sys_guid`() RETURNS varchar(255) CHARSET utf8 BEGIN DECLARE uuid VARCHAR(32) DEFAULT ''; SET uuid = replace(uuid(),'-',''); RETURN uuid; END
对于主键类型为varchar的,可以通过预定义的默认生成策略来生成主键(推荐)
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private String id;
目前的生成策略为通过获得数据库生成的UUID来作为主键
mapper.identity=select sys_guid() from dual
同样对于varchar类型的主键,也可以直接使用系统生成的UUID,这个方式与GenerationType.IDENTITY的区别就是通过GenerationType.IDENTITY生成的主键能够在保存操作后,返回到实体中;而这种方式则不会
@GeneratedValue("UUID") private String id;
4、genId方式生成主键(优先级最低)
为了方便使用全局主键(例如:Vesta 是一款通用的ID产生器,互联网俗称统一发号器),通用 Mapper 4.0.2 版本增加了新的控制主键生成的策略。
@KeySql 注解增加了下面的方法:
/**
* Java 方式生成主键,可以和发号器一类的服务配合使用
*
* @return
*/
Class<? extends GenId> genId() default GenId.NULL.class;
使用该功能的时候,需要配置 genId 属性。 由于生成主键的方式通常和使用环境有关,因此通用 Mapper 没有提供默认的实现。
GenId 接口如下:
public interface GenId<T> { class NULL implements GenId { @Override public Object genId(String table, String column) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } } T genId(String table, String column); }
通过接口方法可以看出,在生成 Id 时,可以得到当前的表名和列名,我们可以使用这两个信息生成和表字段相关的 Id 信息。也可以完全不使用这两个信息,生成全局的 Id。
(1)、使用 UUID 方式
首先我们需要提供一个能产生 UUID 的实现类:
public class UUIdGenId implements GenId<String> { @Override public String genId(String table, String column) { return UUID.randomUUID().toString(); } }
使用:
public class User { @Id @KeySql(genId = UUIdGenId.class) private String id; }
注意:我们只需要在注解中配置 @KeySql(genId = UUIdGenId.class) 即可,需要注意的是,如果你使用了 @KeySql 提供的其他方式,genId 就不会生效,genId 是所有方式中优先级最低的。
(2)、简单的全局时序ID
public class SimpleGenId implements GenId<Long> { private Long time; private Integer seq; @Override public synchronized Long genId(String table, String column) { long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); if (time == null || time != current) { time = current; seq = 1; } else if (current == time) { seq++; } return (time << 20) | seq; } }
(3)、基于 Vesta 的实现
public class VestaGenId implement GenId<Long> { public Long genId(String table, String column){ //ApplicationUtil.getBean 需要自己实现 //IdService 是Vesta中的接口 IdService idService = ApplicationUtil.getBean(IdService.class); return idService.genId(); } } @Component @Lazy(false) public class ApplicationContextRegister implements ApplicationContextAware { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ApplicationContextRegister.class); private static ApplicationContext APPLICATION_CONTEXT; /** * 设置spring上下文 * * @param applicationContext spring上下文 * @throws BeansException */ @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { LOGGER.debug("ApplicationContext registed-->{}", applicationContext); APPLICATION_CONTEXT = applicationContext; } public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() { return APPLICATION_CONTEXT; } }
(4)、InsertListMapper 特殊支持
通用 Mapper 提供了好几个 InsertListMapper 接口,最早提供的都是和数据库相关的方法,所以在 Id 策略上都有和数据库相关的限制。
最新增加的 tk.mybatis.mapper.additional.insert.InsertListMapper 接口是一个和数据库无关的方法,他不支持任何的主键策略。但是有了 genId 方式后,这个接口增加了对 @KeySql 注解 genId 方法的支持。
import tk.mybatis.mapper.additional.insert.InsertListMapper; public interface UserMapper extends InsertListMapper<User> { } @Test public void testInsertList() { SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(); try { UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>(countries.length); for (int i = 0; i < countries.length; i++) { userList.add(new User(countries[i][0], countries[i][1])); } Assert.assertEquals(countries.length, mapper.insertList(userList)); for (User user : userList) { Assert.assertNotNull(user.getId()); System.out.println(user.getId()); } } finally { sqlSession.close(); } }
通过 genId 方式可以批量插入,并且可以回写 ID。
三、通用Mapper的方法
1、BaseMapper
@RegisterMapper public interface Mapper<T> extends BaseMapper<T>, ExampleMapper<T>, RowBoundsMapper<T>, Marker { }
@RegisterMapper
public interface BaseMapper<T> extends BaseSelectMapper<T>, BaseInsertMapper<T>, BaseUpdateMapper<T>, BaseDeleteMapper<T> {
}
@RegisterMapper
public interface BaseSelectMapper<T> extends SelectOneMapper<T>, SelectMapper<T>, SelectAllMapper<T>, 、SelectCountMapper<T>,
SelectByPrimaryKeyMapper<T>,ExistsWithPrimaryKeyMapper<T> {
}
在BaseMapper的增删改查方法中,insert和update时一般使用带selective的方法。select和delete可以根据主键进行查询或删除,也可以根据一个对象进行查询或删除。
(1)、BaseSelectMapper的方法:
Mapper继承BaseMapper(基础Mapper),BaseMapper继承BaseSelectMapper(基础selectMapper)
1)、接口:`SelectByPrimaryKeyMapper<T>`
方法:`T selectByPrimaryKey(Object key);`
说明:根据主键字段进行查询,方法参数必须包含完整的主键属性,查询条件使用等号(参数为主键,只能查出一条记录)
User _user = (User) _rs.getData(); Enterprise enterprise = enterpriseMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(u.getEnterpriseId());
2)、接口:`SelectMapper<T>`
方法:`List<T> select(T record);`
说明:根据实体中的属性值进行查询,查询条件使用等号(参数为对象,可以查出多条记录)
User user1 = new User(); user1.setEnterpriseId(user.getEnterpriseId()); user1.setDelFlag(0); List<User> list1 = userMapper.select(user1);
3)、接口:`SelectAllMapper<T>`
方法:`List<T> selectAll();`
说明:查询全部结果,select(null)方法能达到同样的效果(五参数,查询所有记录)
public List<User> getUsers() { return userMapper.selectAll(); }
4)、接口:`SelectOneMapper<T>`
方法:`T selectOne(T record);`
说明:根据实体中的属性进行查询,只能有一个返回值,有多个结果是抛出异常,查询条件使用等号(参数为对象,只能查出一条记录)
Output output = new Output(); output.setEnterpriseId(p.getEnterpriseId()); output.setMesNodeNo(materialType); Output selectOne = traceabilityOutputMapper.selectOne(output);
5)、接口:`SelectCountMapper<T>`
方法:`int selectCount(T record);`
说明:根据实体中的属性查询总数,查询条件使用等号(参数为对象)
ProductFeedBK checkExisted = new ProductFeedBK(); checkExisted.setTransactionId(productFeedERPDetailInfo.getTransactionId()); if (org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils.isNotBlank(productFeedERPDetailInfo.getInLotNum())) { checkExisted.setInLotNum(productFeedERPDetailInfo.getInLotNum()); } if (org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils.isNotBlank(productFeedERPDetailInfo.getOutLotNum())) { checkExisted.setOutLotNum(productFeedERPDetailInfo.getOutLotNum()); } int count = productFeedBKMapper.selectCount(checkExisted);
(2)、BaseInsertMapper的方法:
Mapper继承BaseMapper(基础Mapper),BaseMapper继承BaseInsertMapper(基础InsertMapper)
1)、接口:`InsertMapper<T>`
方法:`int insert(T record);`
说明:保存一个实体,null的属性也会保存,不会使用数据库默认值
2)、接口:`InsertSelectiveMapper<T>`
方法:`int insertSelective(T record);`(参数为对象)
UserRole userRole = new UserRole(); userRole.setDelFlag(0); userRole.setCreateBy(user.getUserName()); userRole.setCreateTime(new Date()); userRole.setRoleId(Integer.parseInt(list.get(i).toString())); userRole.setUserId(user.getUserId()); userRoleMapper.insertSelective(userRole);
说明:保存一个实体,null的属性不会保存,会使用数据库默认值。
(3)、BaseUpdateMapper的方法:
1)、接口:`UpdateByPrimaryKeyMapper<T>`
方法:`int updateByPrimaryKey(T record);`
说明:根据主键更新实体全部字段,null值会被更新
2)、接口:`UpdateByPrimaryKeySelectiveMapper<T>`
方法:`int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(T record);`
说明:根据主键更新属性不为null的值(参数为对象,除了有主键作为一个条件外,还需要其他属性作为条件)
public boolean changePassword(Integer userId) { User user = new User(); user.setUserId(userId); user.setPwdUpdateFlag("1"); int i = userMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(user); if (i != 0) { return true; } return false; }
(4)、BaseDeleteMapper的方法
1)、接口:`DeleteMapper<T>`
方法:`int delete(T record);`
说明:根据实体属性作为条件进行删除,查询条件使用等号
ExtractProduct tmp = new ExtractProduct(); tmp.setProductId(traceabilityProduct.getId()); extractProductMap.delete(tmp);
2)、接口:`DeleteByPrimaryKeyMapper<T>`
方法:`int deleteByPrimaryKey(Object key);`
说明:根据主键字段进行删除,方法参数必须包含完整的主键属性(参数为对象,主键作为唯一条件)
AtomicInteger a = new AtomicInteger(); String[] idArr = ids.split(","); for (int i = 0; i < idArr.length; i++) { ErpProductInfo productInfo = new ErpProductInfo(); productInfo.setProductId(Integer.parseInt(idArr[i])); a.set(productMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(productInfo)); }
2、ExampleMapper
@RegisterMapper public interface Mapper<T> extends BaseMapper<T>, ExampleMapper<T>, RowBoundsMapper<T>, Marker { }
@RegisterMapper
public interface ExampleMapper<T> extends SelectByExampleMapper<T>, SelectOneByExampleMapper<T>, SelectCountByExampleMapper<T>,
DeleteByExampleMapper<T>,UpdateByExampleMapper<T>, UpdateByExampleSelectiveMapper<T> {
}
示例:
Example placeExample = new Example(Place.class); Example.Criteria placeCriteria = placeExample.createCriteria(); placeCriteria.andEqualTo("delFlag", "0"); List<Place> places = placeMapper.selectByExample(placeExample);
常用selectByExample、updateByExampleSelective、deleteByExample这三个方法,没有insertByExample。
ExampleMapper的方法:
1)、接口:`SelectByExampleMapper<T>`
方法:`List<T> selectByExample(Object example);`
说明:根据Example条件进行查询
重点:这个查询支持通过`Example`类指定查询列,通过`selectProperties`方法指定查询列
Example example = new Example(IntelDrugStore.class); example.createCriteria().andEqualTo("equipmentCode", equipmentCode1) .andEqualTo("equipmentType",equipmentType) .andEqualTo("hospitalName",hospitalName); intelDrugStores = intelDrugStoreMapper.selectByExample(example);
2)、接口:`SelectOneByExampleMapper<T>`
方法:`T selectOneByExample(Object example);`
说明:根据Example条件进行查询一条记录
Example example = new Example(User.class); example.createCriteria() .andEqualTo("userName", user.getUserName()) .andEqualTo("delFlag", 0); User curUser = userMapper.selectOneByExample(example); if (null == curUser) { rs.setSuccess(false); rs.setMsg("用户名不存在!"); rs.setCode(ResultCode.SUCCESS); return rs; }
3)、接口:`SelectCountByExampleMapper<T>`
方法:`int selectCountByExample(Object example);`
说明:根据Example条件进行查询总数
public int queryCount(String enterpiseType, String enterpriseName, String enterpiseCode, String organizationCode) { Example example = new Example(Enterprise.class); Example.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); criteria.andEqualTo("delFlag", 0); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(enterpiseType)) { criteria.andEqualTo("enterpiseType", enterpiseType); } if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(enterpriseName)) { criteria.andLike("enterpriseName", "%" + enterpriseName + "%"); } if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(enterpiseCode)) { criteria.andLike("enterpiseCode", "%" + enterpiseCode + "%"); } if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(organizationCode)) { criteria.andLike("organizationCode", "%" + organizationCode + "%"); } return enterpriseMapper.selectCountByExample(example); }
4)、接口:`UpdateByExampleMapper<T>`
方法:`int updateByExample(@Param("record") T record, @Param("example") Object example);`
说明:根据Example条件更新实体`record`包含的全部属性,null值会被更新
5)、接口:`UpdateByExampleSelectiveMapper<T>`
方法:`int updateByExampleSelective(@Param("record") T record, @Param("example") Object example);`
说明:根据Example条件更新实体`record`包含的不是null的属性值
TraceabilityExtract traceabilityExtract = new TraceabilityExtract(); traceabilityExtract.setMaterialName(medSeed.getMaterialCommonName()); Example example = new Example(TraceabilityExtract.class); example.createCriteria().andEqualTo("materialCode", medSeed.getMaterialCode()); traceabilityExtractMapper.updateByExampleSelective(traceabilityExtract, example);
6)、接口:`DeleteByExampleMapper<T>`
方法:`int deleteByExample(Object example);`
说明:根据Example条件删除数据
//查询设备名称1是否存在,如果存在则删除,如果不存在则新增 List<IntelDrugStore> intelDrugStoreList1 = new ArrayList<>(); Example example = new Example(IntelDrugStore.class); example.createCriteria().andEqualTo("equipmentCode", equipmentCode1) .andEqualTo("equipmentType",equipmentType) .andEqualTo("hospitalName",hospitalName); intelDrugStoreList1 = intelDrugStoreMapper.selectByExample(example); if(CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(intelDrugStoreList1)){ intelDrugStoreMapper.deleteByExample(example); }
3、RowBoundsMapper
@RegisterMapper public interface Mapper<T> extends BaseMapper<T>, ExampleMapper<T>, RowBoundsMapper<T>, Marker { } @RegisterMapper public interface RowBoundsMapper<T> extends SelectByExampleRowBoundsMapper<T>, SelectRowBoundsMapper<T> { }
1)、接口:`SelectRowBoundsMapper<T>`
方法:`List<T> selectByRowBounds(T record, RowBounds rowBounds);`
说明:根据实体属性和RowBounds进行分页查询
2)、接口:`SelectByExampleRowBoundsMapper<T>`
方法:`List<T> selectByExampleAndRowBounds(Object example, RowBounds rowBounds);`
说明:根据example条件和RowBounds进行分页查询
控制返回条数(limit)
Example example = new Example(AppFeedback.class); Example.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); criteria.andEqualTo("userId", userId); example.orderBy("submitTime").desc(); RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(0, 3); // 每次查询3条 List<AppFeedback> appFeedbacks = appFeedbackMapper.selectByExampleAndRowBounds(example, rowBounds); return appFeedbacks;
4、CoditionMapper
当tk.mybatis的版本为2.0.1时,没有ExampleMapper,而是ConditionMapper
<dependency>
<groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>javax.persistence</groupId>
<artifactId>persistence-api</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
这个版本的条件查询使用的是CondtionMapper,不是ExampleMapper。
Mapper接口:
public interface Mapper<T> extends BaseMapper<T>, ConditionMapper<T>, IdsMapper<T>, InsertListMapper<T> { }
ConditionMapper
@RegisterMapper public interface ConditionMapper<T> extends SelectByConditionMapper<T>, SelectCountByConditionMapper<T>, DeleteByConditionMapper<T>, UpdateByConditionMapper<T>, UpdateByConditionSelectiveMapper<T> { }
Condition方法
接口:SelectByConditionMapper<T>
方法:List<T> selectByCondition(Object condition);
说明:根据Condition条件进行查询
接口:SelectCountByConditionMapper<T>
方法:int selectCountByCondition(Object condition);
说明:根据Condition条件进行查询总数
接口:UpdateByConditionMapper<T>
方法:int updateByCondition(@Param("record") T record, @Param("example") Object condition);
说明:根据Condition条件更新实体record包含的全部属性,null值会被更新。
接口:UpdateByConditionSelectiveMapper<T>
方法:int updateByConditionSelective(@Param("record") T record, @Param("example") Object condition);
说明:根据Condition条件更新实体record包含的不是null的属性值。
接口:DeleteByConditionMapper<T>
方法:int deleteByCondition(Object condition);
说明:根据Condition条件删除数据
代码示例:
controller
@PostMapping("/datalist") public Object datalist(ProduceEnterpriseyp produceEnterpriseyp) { Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>(); PageHelper.startPage(produceEnterpriseyp.getPageNumber(), produceEnterpriseyp.getPageSize()); List<ProduceEnterpriseyp> list = produceEnterpriseypService.selectByCon(produceEnterpriseyp); PageInfo<ProduceEnterpriseyp> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(list); if (list.size() > 0) { result.put("success", true); result.put("rows", list); result.put("total", pageInfo.getTotal()); } else { result.put("success", false); } return result; }
service接口
public interface ProduceEnterpriseypService extends Service<ProduceEnterpriseyp> { List<ProduceEnterpriseyp> selectByCon(ProduceEnterpriseyp produceEnterpriseyp); }
service实现类
@Service public class ProduceEnterpriseypServiceImpl extends AbstractService<ProduceEnterpriseyp> implements ProduceEnterpriseypService { @Resource private ProduceEnterpriseypMapper produceEnterpriseypMapper; @Override public List<ProduceEnterpriseyp> selectByCon(ProduceEnterpriseyp produceEnterpriseyp) { return produceEnterpriseypMapper.selectByCondition(getCondition(produceEnterpriseyp)); }
private Condition getCondition(ProduceEnterpriseyp produceEnterpriseyp){ Condition condition = new Condition(ProduceEnterpriseyp.class); Example.Criteria criteria = condition.createCriteria(); if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(produceEnterpriseyp.getCocode())){ criteria.andLike("cocode",produceEnterpriseyp.getCocode()); } if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(produceEnterpriseyp.getConame())){ criteria.andLike("coname",produceEnterpriseyp.getConame()); } return condition; } }
dao接口
public interface ProduceEnterpriseypMapper extends Mapper<ProduceEnterpriseyp> { }
感谢您的阅读,如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮。本文欢迎各位转载,但是转载文章之后必须在文章页面中给出作者和原文连接。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理