java的异常
本文主要讲述java的异常体系图以及处理方法
一. java异常体系图
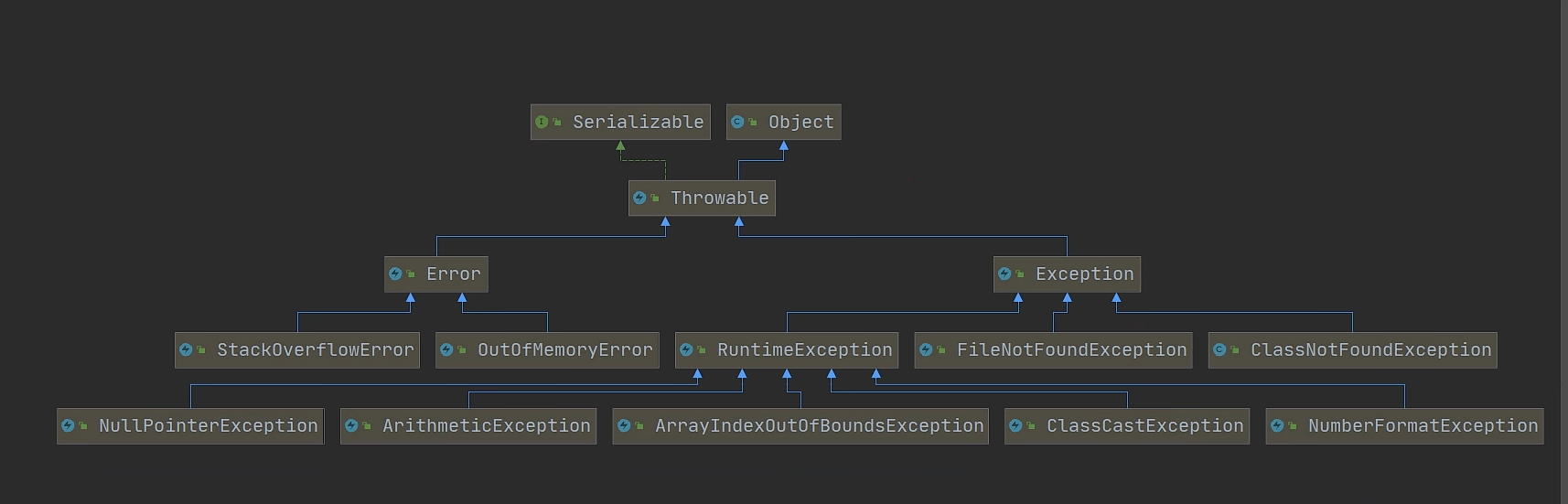
自己理解:
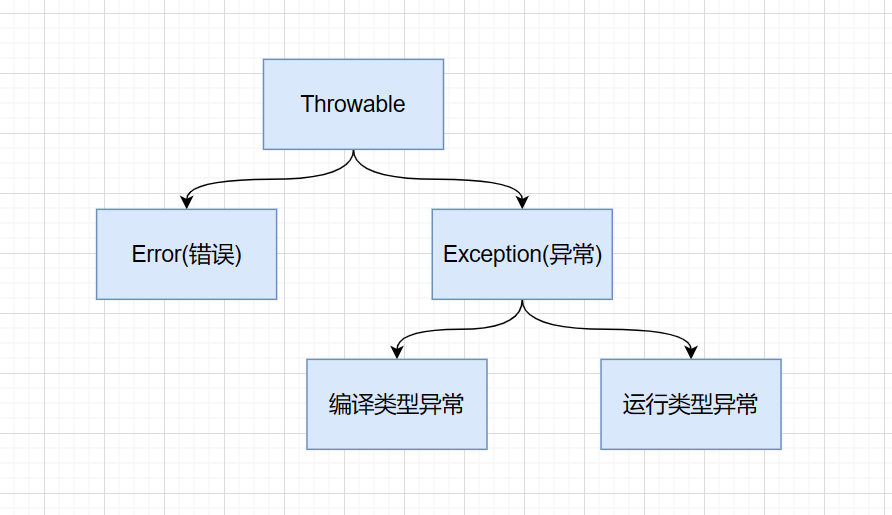
二. 编译异常与运行异常
注意:编译异常,程序员必须显示处理;运行异常,系统有默认处理机制。
示例代码如下:
1 public class ExceptionDetail { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 4 } 5 } 6 7 class CIA { 8 9 public void f1() throws FileNotFoundException { 10 11 } 12 13 // 编译异常,方法也要抛出编译异常,否则报错 14 public void f2() throws FileNotFoundException{ 15 f1(); 16 } 17 18 public void f3() throws RuntimeException{ 19 20 } 21 22 // 运行异常,系统有默认的处理机制【抛出】 23 public void f4() /*throws RuntimeException*/{ 24 f3(); 25 } 26 }
处理异常的两种方式:

(1)try-catch处理

(2)throws处理

异常处理的细节:

三. 自定义异常
public class ExceptionWork { public static void main(String[] args) { Person tom = null; try { tom = new Person("Tom", 101); } catch (AgeException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } } // 自定义异常 class AgeException extends RuntimeException { public AgeException(String message) { super(message); } } class Person { private String name; private int age; public Person(String name, int age) throws RuntimeException{ this.name = name; if(!(age >= 10 && age <= 80)){ throw new AgeException(name +"的年龄需要在10-80之间"); } this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号