Go从入门到精通——常见 strings 操作
常见 strings 操作
https://pkg.go.dev/strings
Go Version: 1.20.1
一、概要
Package strings implements simple functions to manipulate UTF-8 encoded strings.
(Package strings 实现简单的函数来操作 UTF-8 编码的字符串。)
For information about UTF-8 strings in Go, see https://blog.golang.org/strings.
有关 Go 中 UTF-8字符串的信息,请参见 https://blog.golang.org/strings。
二、常见的操作
2.1、判断字符串中是否含有某个字符串(func Contains)
https://pkg.go.dev/strings#Contains
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
// func Contains(s, substr string) bool
// 判断 subr 是否在 s 内,可用于判断字符串中是否含有某个指定的字符串
fmt.Println(strings.Contains("seafood", "foo")) // true
fmt.Println(strings.Contains("seafood", "bar")) // false
fmt.Println(strings.Contains("seafood", "")) // true
fmt.Println(strings.Contains("", "")) // ture
// func ContainsAny(s, chars string) bool
// 判断字符中的任何 Unicode 字符是否位于 s 内
fmt.Println(strings.ContainsAny("team", "i")) // false
fmt.Println(strings.ContainsAny("fail", "ui")) // true
fmt.Println(strings.ContainsAny("ure", "ui")) // true
fmt.Println(strings.ContainsAny("failure", "ui")) // true
fmt.Println(strings.ContainsAny("foo", "")) // false
fmt.Println(strings.ContainsAny("", "")) // false
// func ContainsRune(s string, r rune) bool
// 判断 Unicode字符 r 是否在 s 内,可用于判断是否含有某个指定 UTF-8 编码的字符
// Finds whether a string contains a particular Unicode code point.
// The code point for the lowercase letter "a", for example, is 97.
fmt.Println(strings.ContainsRune("aardvark", 97)) // true
fmt.Println(strings.ContainsRune("timeout", 97)) // false
}
2.2、获取字符串中子串的位置(func Index)
https://pkg.go.dev/strings#Index
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
"unicode"
)
func main() {
// func Index(s, substr string) int
// Index returns the index of the first instance of substr in s, or -1 if substr is not present in s.
fmt.Println(strings.Index("chicken", "ken")) // 4
fmt.Println(strings.Index("chicken", "dmr")) // -1
// func IndexAny(s, chars string) int
// IndexAny returns the index of the first instance of any Unicode code point from chars in s, or -1 if no Unicode code point from chars is present in s.
fmt.Println(strings.IndexAny("chicken", "aeiouy")) //2
fmt.Println(strings.IndexAny("crwth", "aeiouy")) //-1
// func IndexByte(s string, c byte) int
// IndexByte returns the index of the first instance of c in s, or -1 if c is not present in s.
fmt.Println(strings.IndexByte("golang", 'g')) // 0
fmt.Println(strings.IndexByte("gophers", 'h')) // 3
fmt.Println(strings.IndexByte("golang", 'x')) // -1
// func IndexFunc(s string, f func(rune) bool) int
// IndexFunc returns the index into s of the first Unicode code point satisfying f(c), or -1 if none do.
f := func(c rune) bool {
return unicode.Is(unicode.Han, c)
}
fmt.Println(strings.IndexFunc("Hello, 世界", f)) // 7
fmt.Println(strings.IndexFunc("Hello, world", f)) // -1
// func IndexRune(s string, r rune) int
// IndexRune returns the index of the first instance of the Unicode code point r, or -1 if rune is not present in s. If r is utf8.RuneError, it returns the first instance of any invalid UTF-8 byte sequence.
fmt.Println(strings.IndexRune("chicken", 'k')) // 4
fmt.Println(strings.IndexRune("chicken", 'd')) // -1
}
2.3、获取字符串中子串第 N 次出现的位置
2.3.1、循环切片法
每次使用 string.Index 函数获得子串出现位置后将原字符串进行切片去掉之前的部分(和子串该次出现的部分)。然后在新的切片中重复上述步骤,直到第 n 次发现该子串,然后将最后一次出现子串的位置加上之前去掉的部分的长度即可得到所求的位置。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
s := "上海中心气象台2023年3月13日5点钟发布今天和明天上海市天气预报:今天多云转晴,明天晴到多云。东北风,今天下午起东南风,风力都是3-4级,明天南到东南风4-5级。"
//将原字符串复制一份,进行循环切片,避免影响原来字符串s内容。
tempStr := s
count := 0
totalIndex := 0
strLen := len(s)
subLen := len("今天")
for {
// func Index(s, substr string) int
// Index returns the index of the first instance of substr in s, or -1 if substr is not present in s.
index := strings.Index(tempStr, "今天")
//如果 string 返回的index值0小于0次(-1 代表不存在),则退出
if index < 0 {
break
}
count++ //计数寻找多少次子串,每循环一次计数加1
totalIndex += index //记录至今为止实际去掉字符串的部分
if totalIndex >= strLen {
break
}
if count >= 3 {
break
}
totalIndex += subLen
tempStr = s[totalIndex:]
}
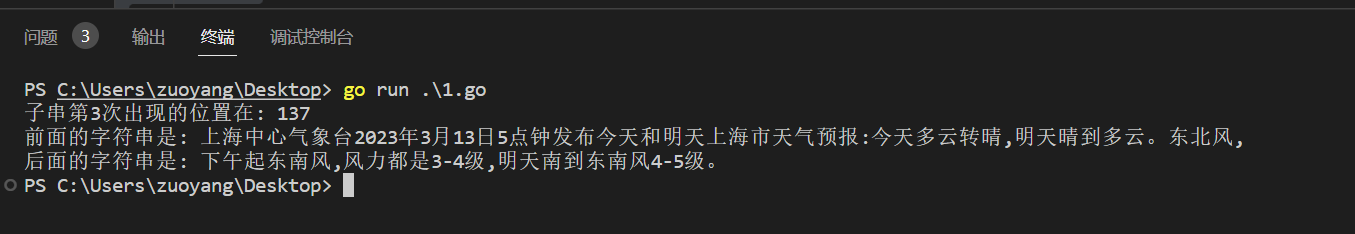
if count < 3 {
fmt.Println("Not found!")
} else {
fmt.Printf("子串第3次出现的位置在: %v \n前面的字符串是: %v \n后面的字符串是: %v\n", totalIndex, s[:totalIndex], s[totalIndex+subLen:])
}
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
2.3.2、使用 strings.SplitN 函数
第二种方法的思路是利用一个 strings.Split 函数,strings.Split 函数的作用是将某个字符串用某个子串分隔开成一个字符串切片。为了提高效率,我们使用 strings.SplitN hanshu ,这个函数多接受一个整数参数,表示分割字符串时最多分割成几个部分(或者说最多分割几次),多于这个指定次数后则不再分割。
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
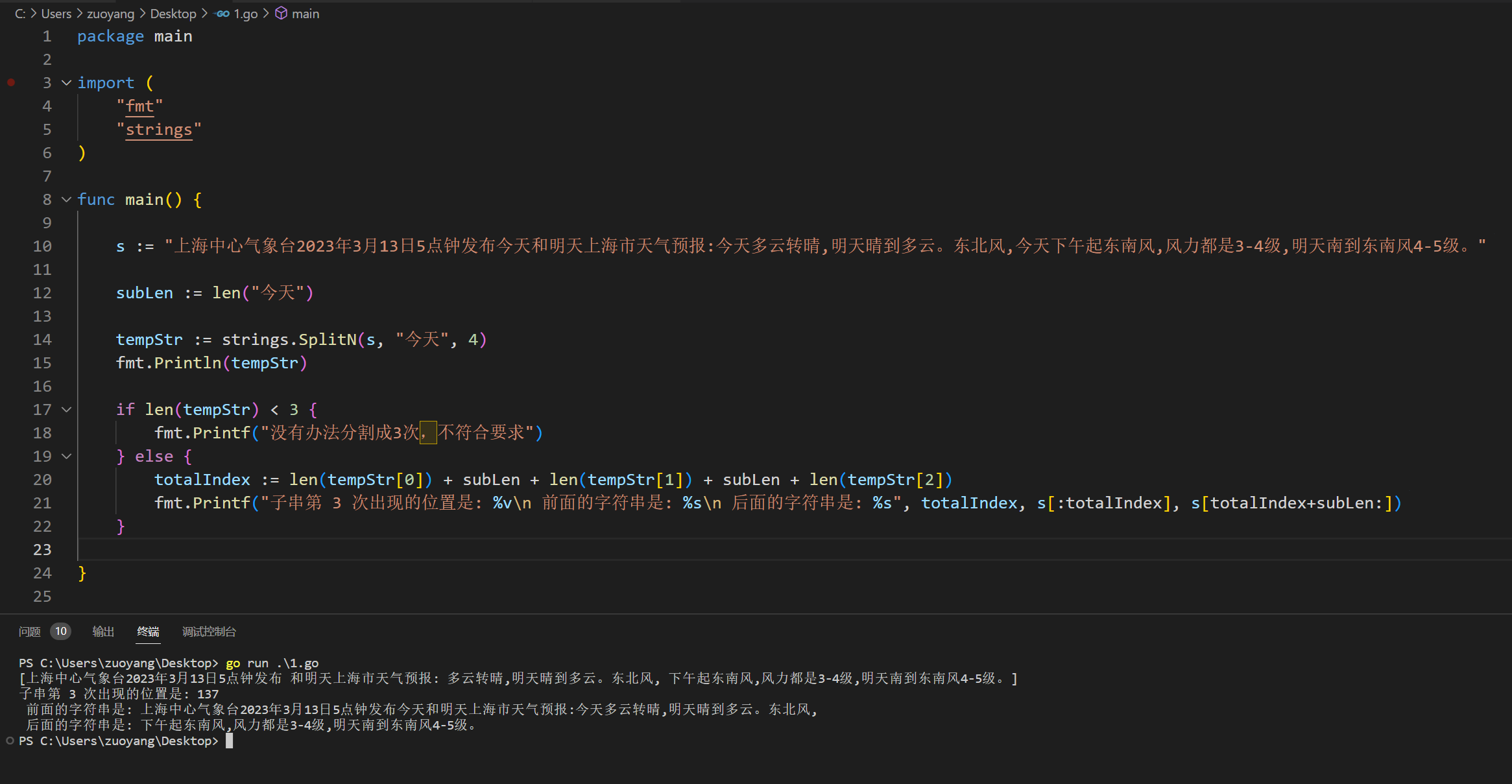
func main() {
s := "上海中心气象台2023年3月13日5点钟发布今天和明天上海市天气预报:今天多云转晴,明天晴到多云。东北风,今天下午起东南风,风力都是3-4级,明天南到东南风4-5级。"
subLen := len("今天")
tempStr := strings.SplitN(s, "今天", 4)
fmt.Println(tempStr)
if len(tempStr) < 3 {
fmt.Printf("没有办法分割成3次,不符合要求")
} else {
totalIndex := len(tempStr[0]) + subLen + len(tempStr[1]) + subLen + len(tempStr[2])
fmt.Printf("子串第 3 次出现的位置是: %v\n 前面的字符串是: %s\n 后面的字符串是: %s", totalIndex, s[:totalIndex], s[totalIndex+subLen:])
}
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
2.4、比较两个字符串
编程中经常会遇到字符串比较,比较字符串的目的一般是为了判断是否相等或用作排序,这些功能可以通过 "==" ">" "<" 等操作符就可以实现。
"=="操作符的含义:判读两个字符串是否相等(完全相同)。
">"操作符按字符串内每个字符的编码比大小顺序来比较两个字符串的 "大小",从大到小的顺序依次排列。
"<"操作符按字符串内每个字符的编码比大小顺序来比较两个字符串的 "大小",从小到大的顺序依次排列。
2.5、去除字符串首位空白或其他字符
https://pkg.go.dev/strings#Trim
所谓去除空白字符,指的:空格字符,tab字符(转义字符 \t 表示)、回车字符(转义字符是 \r)。
2.5.1、func Trim(s, cutset string) string
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
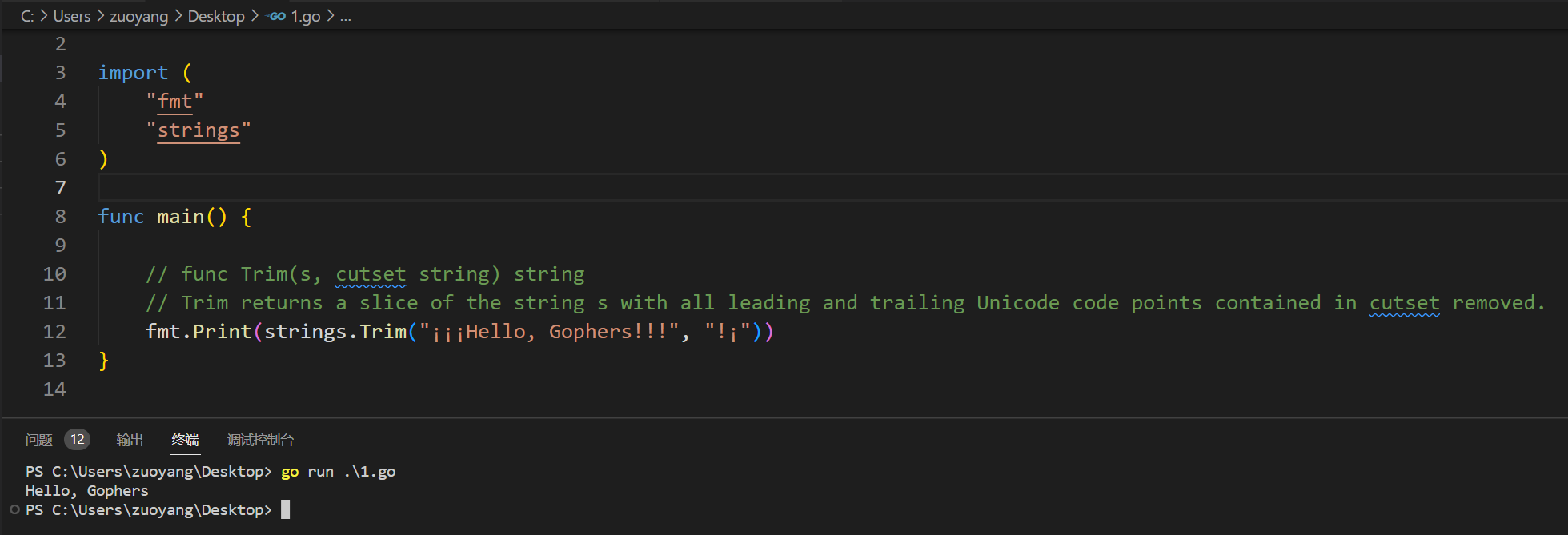
func main() {
// func Trim(s, cutset string) string
// Trim returns a slice of the string s with all leading and trailing Unicode code points contained in cutset removed.
fmt.Print(strings.Trim("¡¡¡Hello, Gophers!!!", "!¡"))
}
例代码运行结果如下:
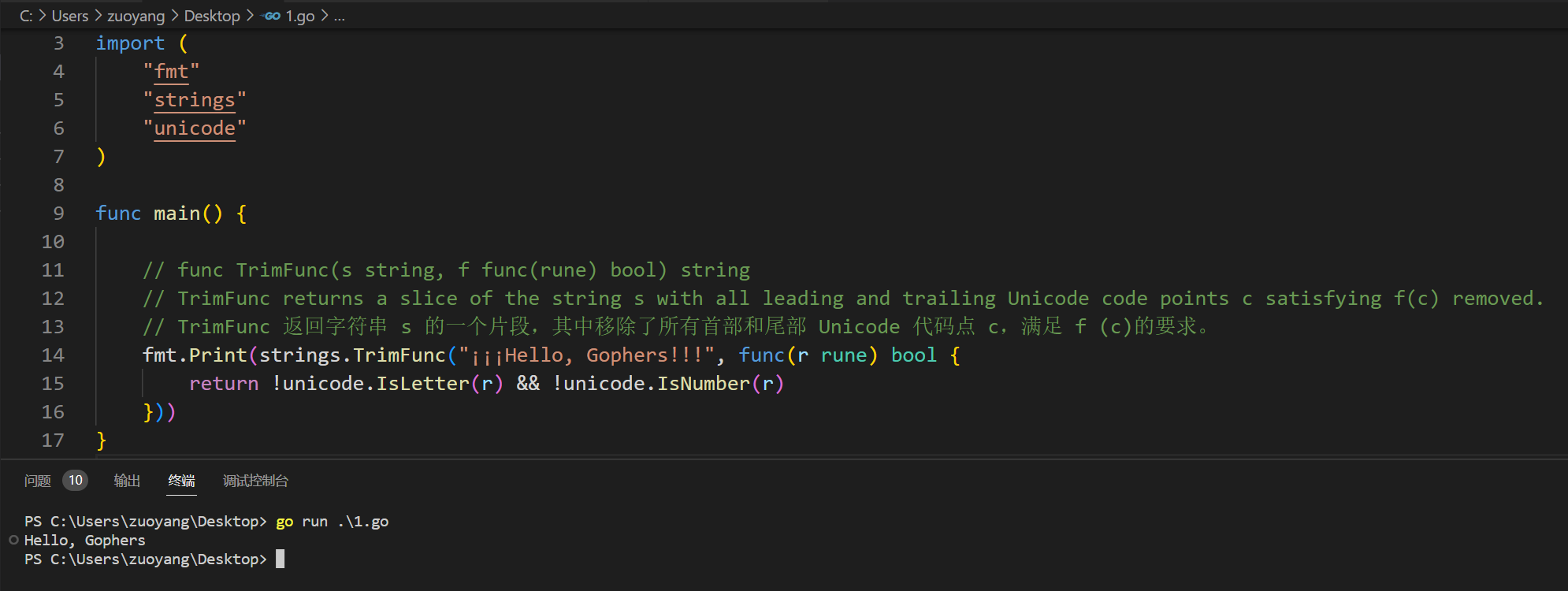
2.5.2、func TrimFunc(s string, f func(rune) bool) string
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
"unicode"
)
func main() {
// func TrimFunc(s string, f func(rune) bool) string
// TrimFunc returns a slice of the string s with all leading and trailing Unicode code points c satisfying f(c) removed.
// TrimFunc 返回字符串 s 的一个片段,其中移除了所有首部和尾部 Unicode 代码点 c,满足 f (c)的要求。
fmt.Print(strings.TrimFunc("¡¡¡Hello, Gophers!!!", func(r rune) bool {
return !unicode.IsLetter(r) && !unicode.IsNumber(r)
}))
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
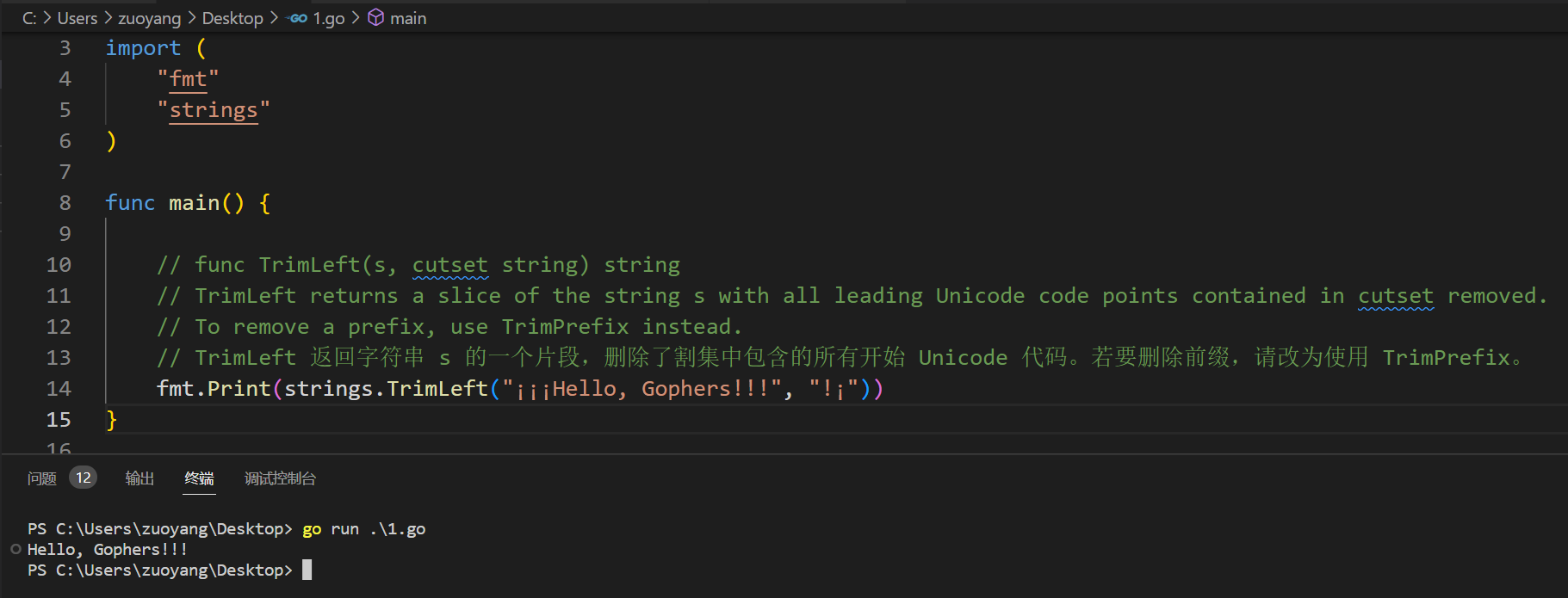
2.5.3、func TrimLeft(s, cutset string) string
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
// func TrimLeft(s, cutset string) string
// TrimLeft returns a slice of the string s with all leading Unicode code points contained in cutset removed.
// To remove a prefix, use TrimPrefix instead.
// TrimLeft 返回字符串 s 的一个片段,删除了割集中包含的所有开始 Unicode 代码。若要删除前缀,请改为使用 TrimPrefix。
fmt.Print(strings.TrimLeft("¡¡¡Hello, Gophers!!!", "!¡"))
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
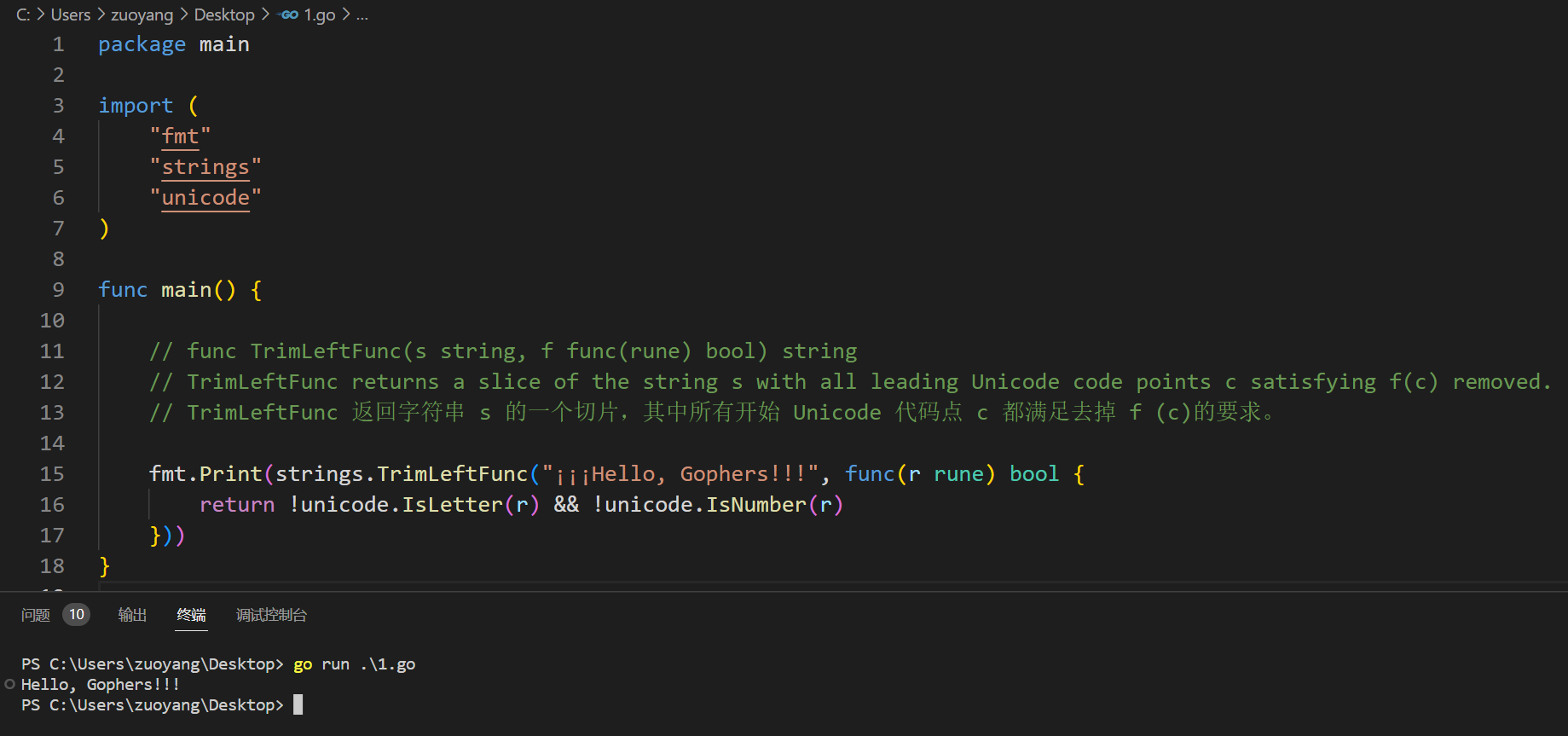
2.5.4、func TrimLeftFunc(s string, f func(rune) bool) string
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
"unicode"
)
func main() {
// func TrimLeftFunc(s string, f func(rune) bool) string
// TrimLeftFunc returns a slice of the string s with all leading Unicode code points c satisfying f(c) removed.
// TrimLeftFunc 返回字符串 s 的一个切片,其中所有开始 Unicode 代码点 c 都满足去掉 f (c)的要求。
fmt.Print(strings.TrimLeftFunc("¡¡¡Hello, Gophers!!!", func(r rune) bool {
return !unicode.IsLetter(r) && !unicode.IsNumber(r)
}))
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
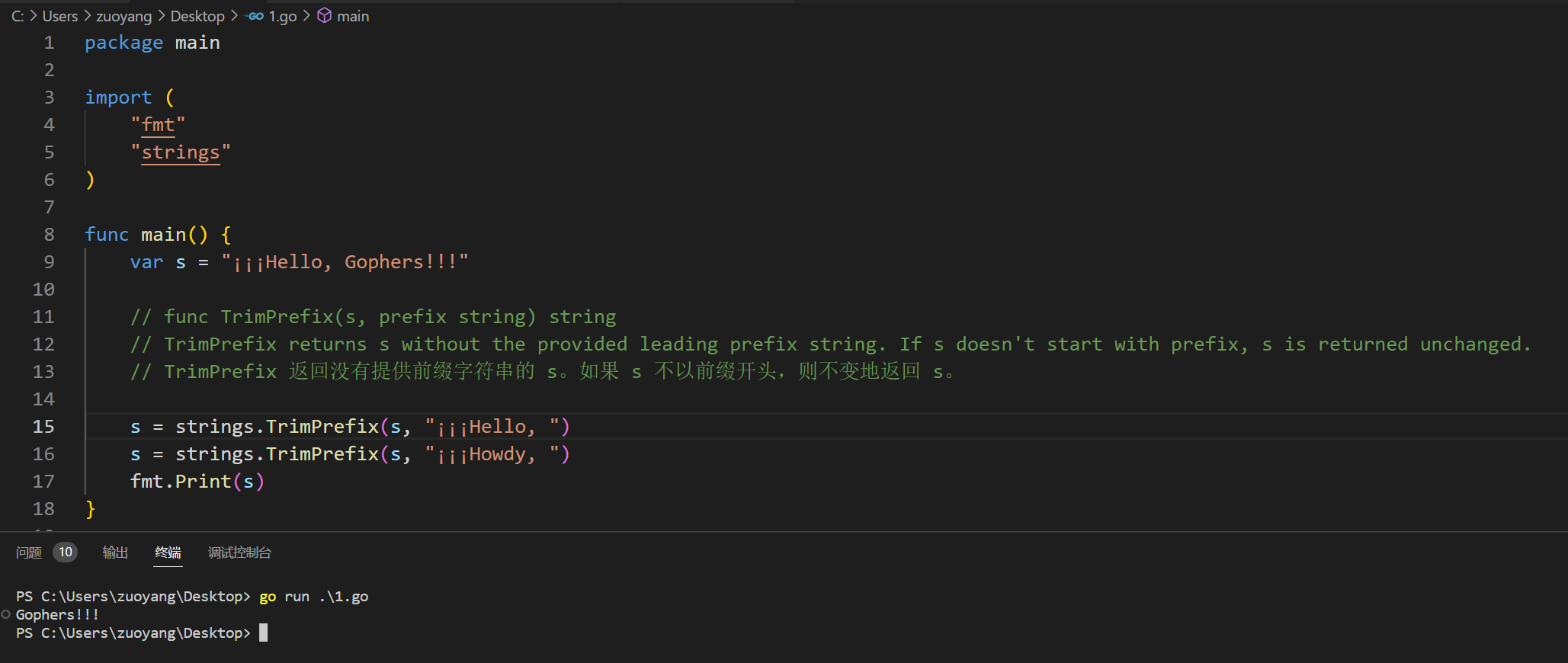
2.5.5、func TrimPrefix(s, prefix string) string
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
var s = "¡¡¡Hello, Gophers!!!"
// func TrimPrefix(s, prefix string) string
// TrimPrefix returns s without the provided leading prefix string. If s doesn't start with prefix, s is returned unchanged.
// TrimPrefix 返回没有提供前缀字符串的 s。如果 s 不以前缀开头,则不变地返回 s。
s = strings.TrimPrefix(s, "¡¡¡Hello, ")
s = strings.TrimPrefix(s, "¡¡¡Howdy, ")
fmt.Print(s)
}
示例代码结果运行如下:
2.5.6、func TrimRight(s, cutset string) string
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
// func TrimRight(s, cutset string) string
// TrimRight returns a slice of the string s, with all trailing Unicode code points contained in cutset removed.
// To remove a suffix, use TrimSuffix instead.
fmt.Print(strings.TrimRight("¡¡¡Hello, Gophers!!!", "!¡"))
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
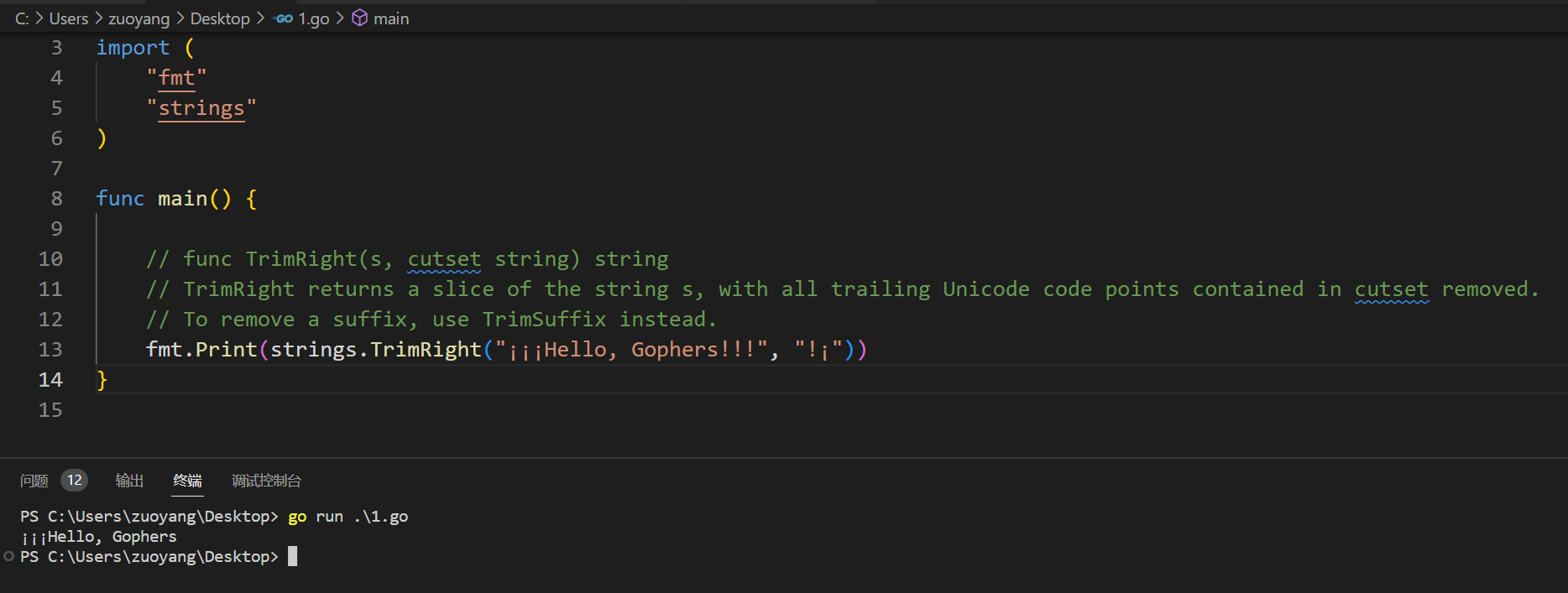
2.5.7、func TrimRightFunc(s string, f func(rune) bool) string
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
"unicode"
)
func main() {
//func TrimRightFunc(s string, f func(rune) bool) string
//TrimRightFunc returns a slice of the string s with all trailing Unicode code points c satisfying f(c) removed.
//TrimRightFunc 返回字符串 s 的一个片段,其中所有尾随的 Unicode 代码点 c 都满足删除 f (c)的要求。
fmt.Print(strings.TrimRightFunc("¡¡¡Hello, Gophers!!!", func(r rune) bool {
return !unicode.IsLetter(r) && !unicode.IsNumber(r)
}))
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
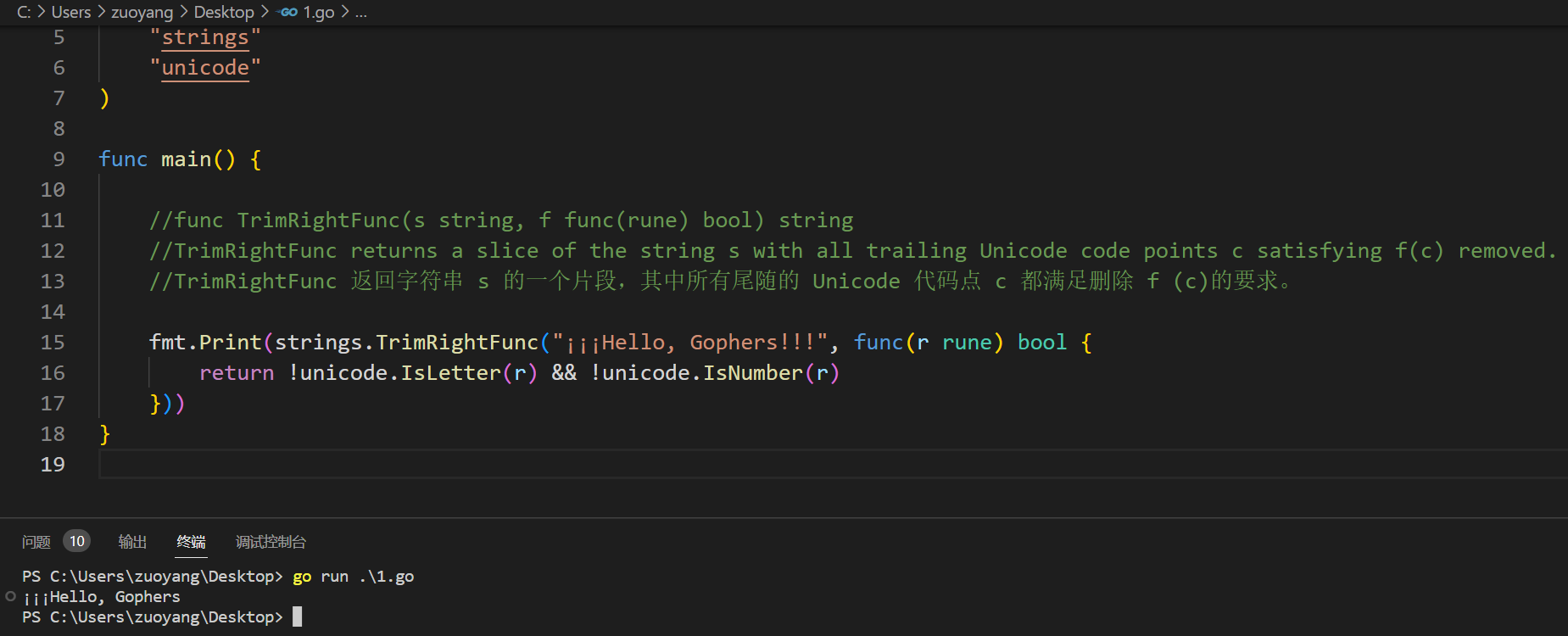
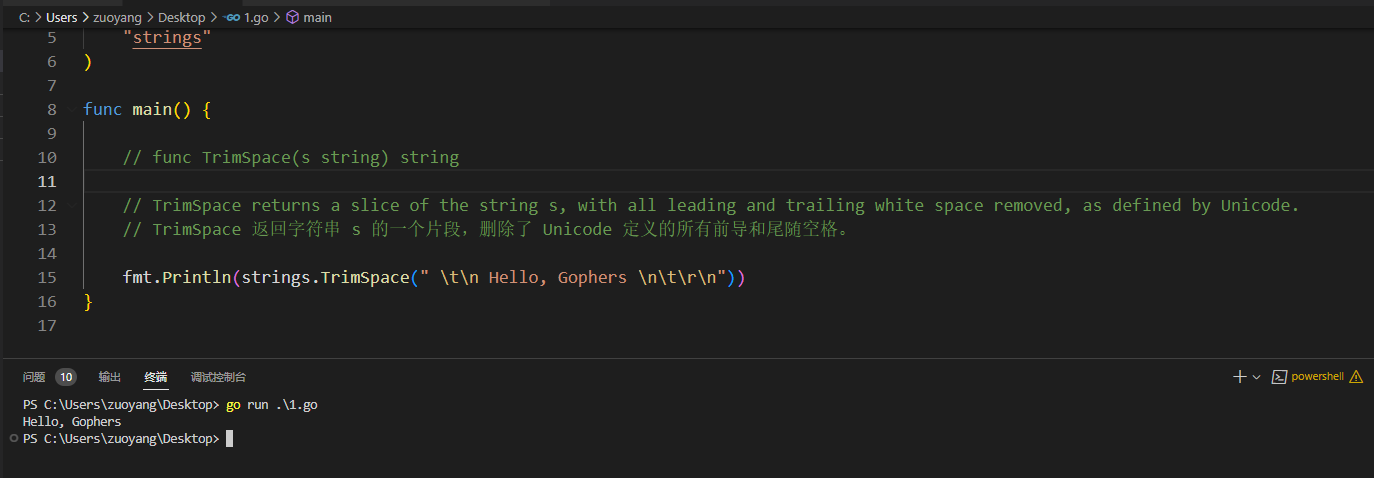
2.5.8、func TrimSpace(s string) string
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
// func TrimSpace(s string) string
// TrimSpace returns a slice of the string s, with all leading and trailing white space removed, as defined by Unicode.
// TrimSpace 返回字符串 s 的一个切片,删除了 Unicode 定义的所有前导和尾随空格。
fmt.Println(strings.TrimSpace(" \t\n Hello, Gophers \n\t\r\n"))
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
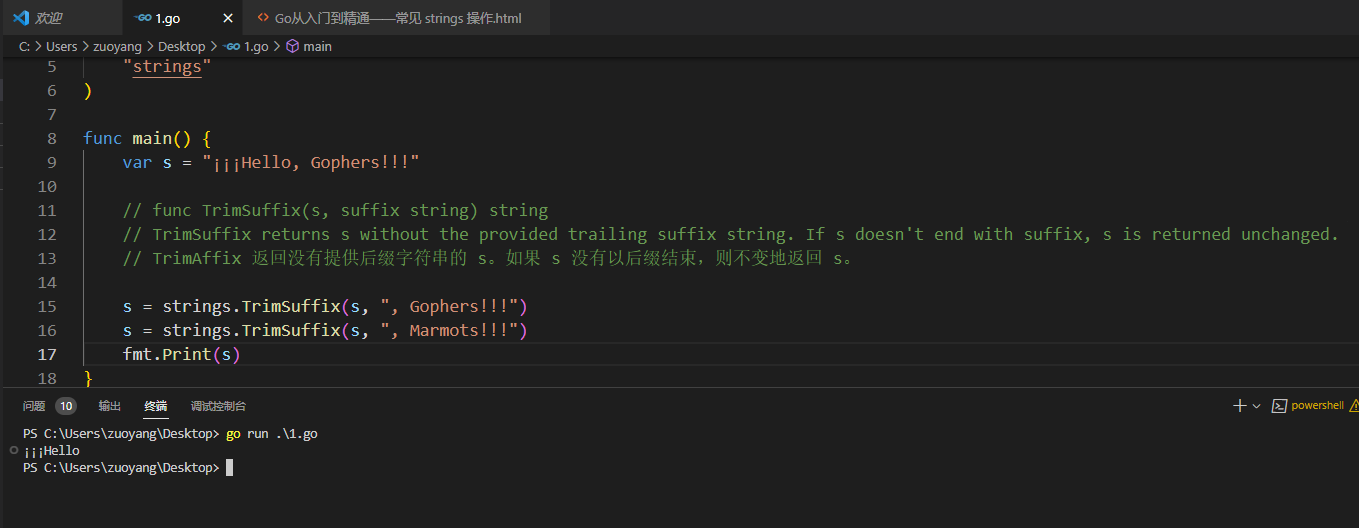
2.5.9、func TrimSuffix(s, suffix string) string
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
var s = "¡¡¡Hello, Gophers!!!"
// func TrimSuffix(s, suffix string) string
// TrimSuffix returns s without the provided trailing suffix string. If s doesn't end with suffix, s is returned unchanged.
// TrimAffix 返回没有提供后缀字符串的 s。如果 s 没有以后缀结束,则不变地返回 s。
s = strings.TrimSuffix(s, ", Gophers!!!")
s = strings.TrimSuffix(s, ", Marmots!!!")
fmt.Print(s)
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
2.6、替换字符串中的子串
https://pkg.go.dev/strings#Replace
2.6.1、func Replace(s, old, new string, n int) string
替换字符串中的子串可以使用 strings.Replace 函数。
func Replace(s, old, new string, n int) string
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
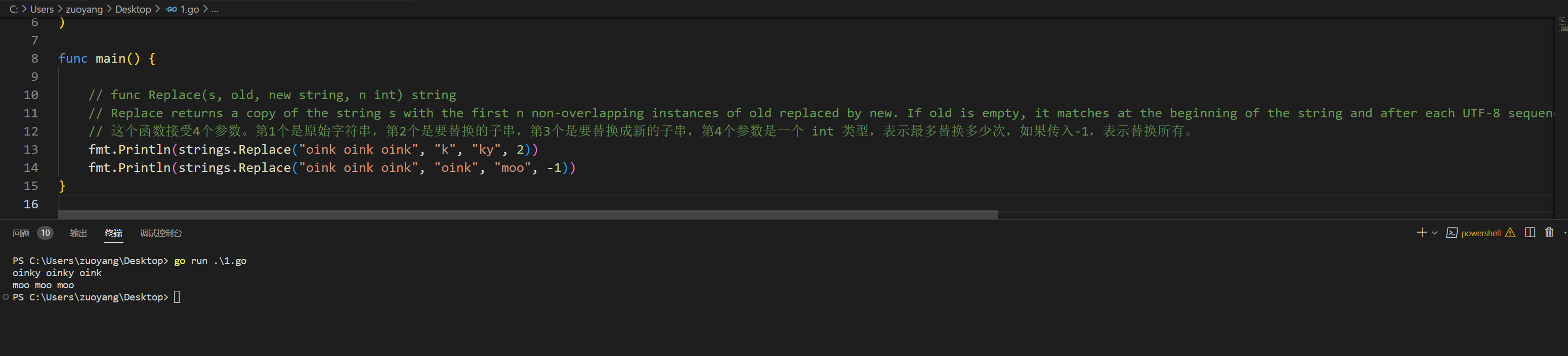
// func Replace(s, old, new string, n int) string
// Replace returns a copy of the string s with the first n non-overlapping instances of old replaced by new. If old is empty, it matches at the beginning of the string and after each UTF-8 sequence, yielding up to k+1 replacements for a k-rune string. If n < 0, there is no limit on the number of replacements.
// 这个函数接受4个参数。第1个是原始字符串,第2个是要替换的子串,第3个是要替换成新的子串,第4个参数是一个 int 类型,表示最多替换多少次,如果传入-1,表示替换所有。
fmt.Println(strings.Replace("oink oink oink", "k", "ky", 2))
fmt.Println(strings.Replace("oink oink oink", "oink", "moo", -1))
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
2.6.2、func ReplaceAll(s, old, new string) string
替换字符串中所有子串,可以使用 strings.replaceAll 函数。
func ReplaceAll(s, old, new string) string
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
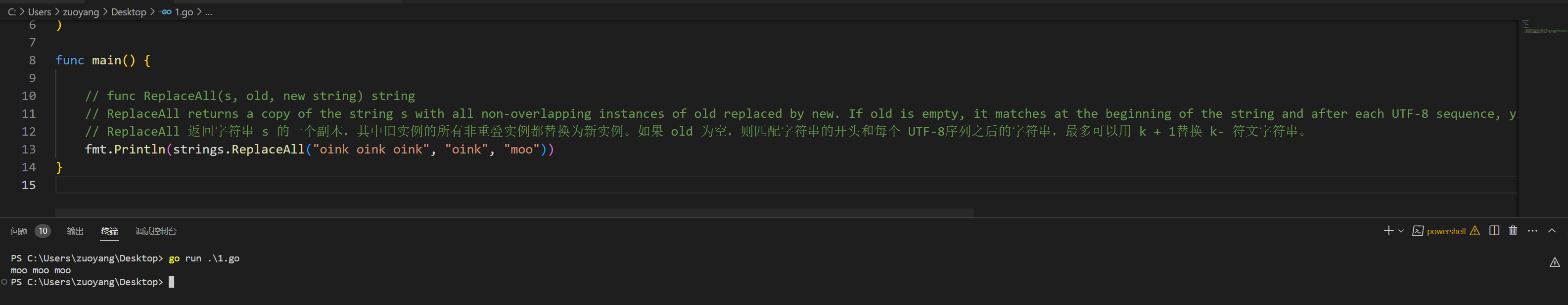
// func ReplaceAll(s, old, new string) string
// ReplaceAll returns a copy of the string s with all non-overlapping instances of old replaced by new. If old is empty, it matches at the beginning of the string and after each UTF-8 sequence, yielding up to k+1 replacements for a k-rune string.
// ReplaceAll 返回字符串 s 的一个副本,其中旧实例的所有非重叠实例都替换为新实例。如果 old 为空,则匹配字符串的开头和每个 UTF-8序列之后的字符串,最多可以用 k + 1替换 k- 符文字符串。
fmt.Println(strings.ReplaceAll("oink oink oink", "oink", "moo"))
}
2.7、字符串大小写的转换
https://pkg.go.dev/strings#ToLower
2.7.1、func ToLower(s string) string/
对字符串进行大小写转换,可以使用函数 strings.ToLower 和 strings.ToUpper 函数。
func ToLower(s string) string
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
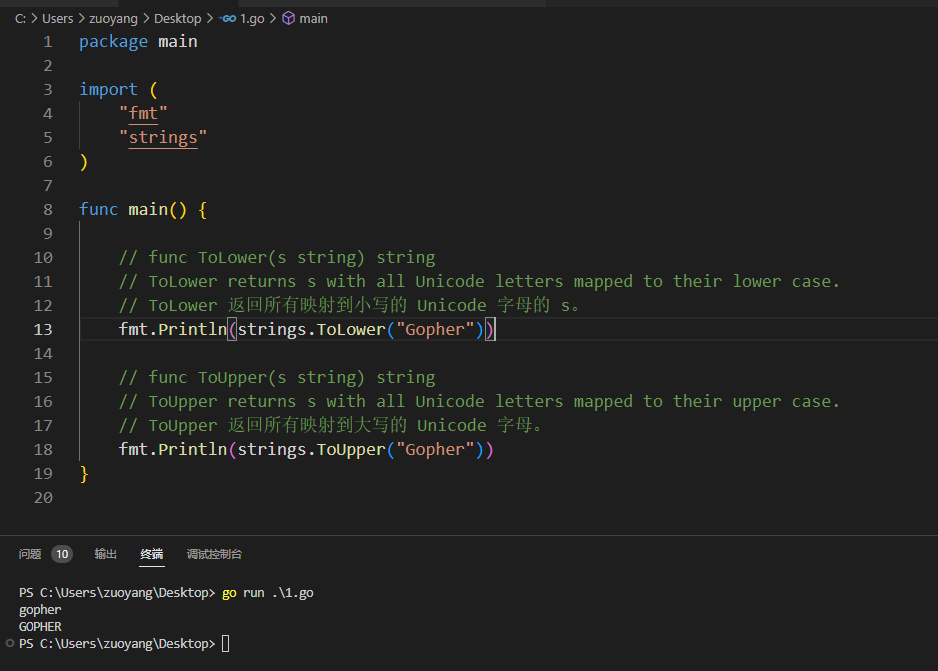
// func ToLower(s string) string
// ToLower returns s with all Unicode letters mapped to their lower case.
// ToLower 返回所有映射到小写的 Unicode 字母的 s。
fmt.Println(strings.ToLower("Gopher"))
// func ToUpper(s string) string
// ToUpper returns s with all Unicode letters mapped to their upper case.
// ToUpper 返回所有映射到大写的 Unicode 字母。
fmt.Println(strings.ToUpper("Gopher"))
}
示例代码运行结果如下:
2.8、切分字符串
https://pkg.go.dev/strings#Split
2.8.1、func Split(s, sep string) []string
切分字符串指的是将字符串以某个子串进行分割。
func Split(s, sep string) []string
示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
)
func main() {
// func Split(s, sep string) []string
// Split slices s into all substrings separated by sep and returns a slice of the substrings between those separators.
// If s does not contain sep and sep is not empty, Split returns a slice of length 1 whose only element is s.
// If sep is empty, Split splits after each UTF-8 sequence. If both s and sep are empty, Split returns an empty slice.
// It is equivalent to SplitN with a count of -1.
// To split around the first instance of a separator, see Cut.
// 将 s 分割成所有由 sep 分隔的子字符串,并返回这些分隔符之间的子字符串片。
// 如果 s 不包含 sep,并且 sep 不为空,Split 返回一个长度为1的片,其中唯一的元素是 s。
// 如果 sep 为空,Split 将在每个 UTF-8序列之后拆分。
// 如果 s 和 sep 都为空,Split 将返回一个空切片。它等效于计数为 -1的 SplitN。
// 若要围绕分隔符的第一个实例拆分,请参见 Cut。
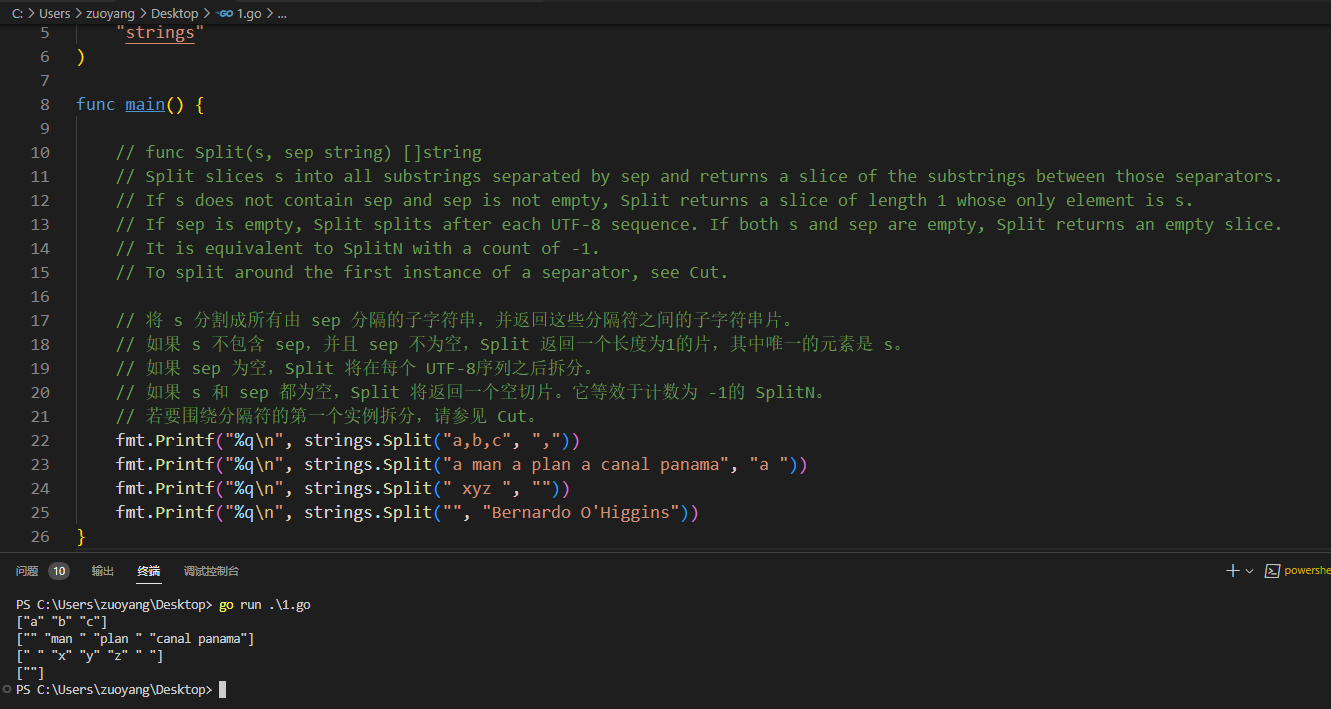
fmt.Printf("%q\n", strings.Split("a,b,c", ","))
fmt.Printf("%q\n", strings.Split("a man a plan a canal panama", "a "))
fmt.Printf("%q\n", strings.Split(" xyz ", ""))
fmt.Printf("%q\n", strings.Split("", "Bernardo O'Higgins"))
}
示例代码运行结果如下: