spring源码学习之路---IOC容器初始化要义之bean定义载入(五)
作者:zuoxiaolong8810(左潇龙),转载请注明出处,特别说明:本博文来自博主原博客,为保证新博客中博文的完整性,特复制到此留存,如需转载请注明新博客地址即可。
最近工作很忙,时间不多,研究spring的进度被严重拖下来,不过我会一直坚持写完。
上章说到要带各位去看看bean定义载入的要义,其实就是loadBeanDefinitions这个方法的具体实现步骤,下面我们跟随这个方法去看下它到底是如何载入bean定义的。
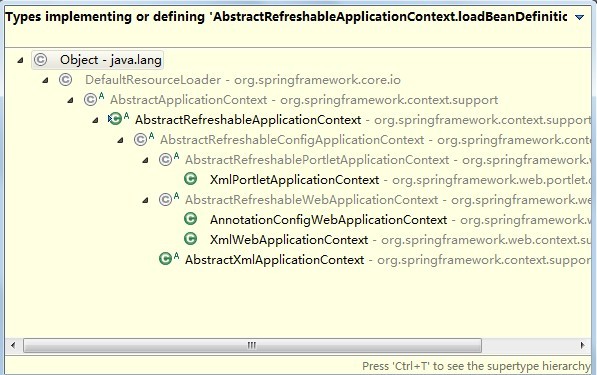

上面是我截取的实现了loadBeanDefinitions的类级别截图,loadBeanDefinitions方法是AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext抽象类的模板方法,而此次我们研究的FileSystemXmlApplicationContext中的loadBeanDefinitions方法是由AbstractXmlApplicationContext抽象类实现的。
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's // resource loading environment. beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); }
第一行首先定义了一个reader,很明显,这个就是spring为读取XML配置文件而定制的读取工具,这里AbstractXmlApplicationContext间接实现了ResourceLoader接口,所以该方法的第二行才得以成立,最后一行便是真正载入bean定义的过程。我们追踪其根源,可以发现最终的读取过程正是由reader完成的,代码如下。
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); } Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); if (currentResources == null) { currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4); this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); } if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); } try { InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); try { InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); } return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); } finally { inputStream.close(); } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); } finally { currentResources.remove(encodedResource); if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); } } }
这个方法中不难发现,try块中的代码才是载入bean定义的真正过程,我们一步一步的扒开bean定义的载入,spring将资源返回的输入流包装以后传给了doLoadBeanDefinitions方法,我们进去看看发生了什么。
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { try { int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource); Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument( inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware()); return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (SAXParseException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (SAXException ex) { throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); } catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); } }
可以看到,spring采用documentLoader将资源转换成了Document接口,这正是我们熟知的SAX对XML解析的重要接口之一,这下不难理解了,可以想象出spring一定是根据XSD文件规定的XML格式,解析了XML文件中的各个节点以及属性。尽管如此,我们还是跟着registerBeanDefinitions方法进去看看。此处该方法不再贴出代码,请各位自己跟踪进去看,这个方法里记录了一共注册了多少个bean定义。最终能看出端倪的地方在DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的parseBeanDefinitions方法中,如下代码。
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) { if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) { NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { Node node = nl.item(i); if (node instanceof Element) { Element ele = (Element) node; if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); } } } } else { delegate.parseCustomElement(root); } }
这里分了两种解析路线,一个是默认的,一个是自定义的,从这里我们可以看出,我们是可以在spring的配置文件中自定义节点的。
再往下走就基本上到了spring开始针对具体标签解析的过程,各位如果有兴趣可以自行跟进去看一下spring是如何对XML文件的各个节点和属性进行解析的,了解这个过程可以帮助你熟练的掌握spring中的XML配置文件的各个节点和属性的含义。
这里我要稍稍总结一下,spring对bean定义的载入有很多种方式,读取的过程是可插拔的,不论何种形式,spring的IOC容器只要获得了bean定义信息,都可以正常工作。而我们熟知的配置读取方式就是XML文件,如果你希望,可以自己定制配置信息的读取过程,有时间我会研究下spring留给我们扩展的接口在哪里。只要找到了这个入口,那么读取配置信息就任由我们宰割了。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号