玩转Spring Cloud之服务注册发现(eureka)及负载均衡消费(ribbon、feign)
如果说用Spring Boot+Spring MVC是开发单体应用(或单体服务)的利器,那么Spring Boot+Spring MVC+Spring Cloud将是开发分布式应用(快速构建微服务)的又一法宝,相信大家如果看到我近期总结的《JAVA WEB快速入门》系列文章,对Spring Boot+Spring MVC应该是比较熟悉了吧,从本文开始,一起来熟悉Spring Cloud、玩转Spring Cloud,至于什么是Spring Cloud?我这里就不再介绍了,网上资源太多了,比如:大话Spring Cloud、SpringCloud是什么?,当然介绍Spring Cloud系列文章也比较多(比如:https://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/70148833),大家也可以参考,我这里只是结合当前最新的Spring Boot、Spring MVC、Spring Cloud来重新演练一遍,把重要的知识点、遇到的一些坑分享出来,一来是为自己做记录(所谓“好记性不如烂笔头”),二来可以避免大家学习时走弯路,又因为介绍Spring Cloud文章实在太多了,故玩转Spring Cloud系列文章更多的是以把实现的DEMO代码一步步贴出来,一些组件名词我就不再详细解释了,然后对于涉及的重要知识点及踩坑点进行说明,以便大家可以:知其然还能知其所以然。(注:所有示例代码均采用IDEA IDE编写)
一、实现eureka server(注册中心)
1.1.通过IDEA来创建一个空的spring boot项目(类型是:maven-archtype-quickstart,这样最精简,当然如果你使用webapp项目也是可以,只是认为没有必要)。
创建步骤有2种,第一种是使用maven创建: maven->maven-archtype-quickstart,然后手动添加相关的spring boot依赖;第二种是使用spring initializer->填写项目参数->选择相关依赖(可直接选择spring cloud相关依赖,如:eureka,这样就一步到位,这里全部先不选),最终的初始POM XML如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>cn.zuowenjun.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>eurekaserver</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>eurekaserver</name> <!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --> <url>http://www.zuowenjun.cn</url> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
如上所示(如果不是请改成这样,如果只是多点依赖没关系,当然我认为此时只需要这么多的依赖即可,多了也无用),我们只是有spring boot的POM依赖,并没有spring cloud的相关依赖。
1.2添加spring cloud相关依赖,如下所示:(添加了dependencyManagement节点,并配置spring-cloud-dependencies pom import依赖,目的是:便于依赖继承,与parent节点功能类似,添加具体依赖时,若包含在parent中或pom import依赖中则无需版本号,能够保证组件的一致性,详见:https://blog.csdn.net/mn960mn/article/details/50894022,相反如果没有配置spring-cloud-dependencies pom import依赖,则添加具体依赖时需要指定version版本号,而且需要注意各依赖组件间的兼容性问题,如下面我把version注释掉)
<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>Greenwich.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependencies> ... ...其它原有依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter</artifactId> <!--<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>--> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId> <!--<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>--> </dependency> </dependencies>
1.3.在resouces目录下(若没有请创建,注意设为souces root目录,方法:右键文件夹->Mark directory as->souces root)创建application.yml(或application.properties,本文示例全部使用yml),添加如下配置:
server:
port: 8800
spring:
applcation:
name: demo-eurekaserver
# config detail:https://www.jianshu.com/p/98f4e5f6bca7 or https://blog.csdn.net/wo18237095579/article/details/83276352
eureka:
instance:
hostname: eurekaserver1 #实例主机名,集群时需要且唯一
server:
enable-self-preservation: true #自我保护,正式环境不要这么做
eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 5000 #定期清理失效节点,默认60s
peer-eureka-nodes-update-interval-ms: 6000 #同步更新节点频率,默认10min
renewal-percent-threshold: 0.49 #默认0.85
response-cache-auto-expiration-in-seconds: 30
client:
registerWithEureka: false
fetchRegistry: false
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:${server.port}/eureka/
1.4.在spring boot 启动类中添加@EnableEurekaServer即可,如下代码:

package cn.zuowenjun.cloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer; @EnableEurekaServer @SpringBootApplication public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); } }
整个项目结构如下图示,启动后浏览地址:http://localhost:8800/,会出现spring eureka的主页,就表明eureka server成功了。
二、实现service provider(含eureka client)--服务提供者
【即:具体微服务项目,注册服务信息,暴露API】,当然也有可能同时是service consumer【服务消费者】,需要远程调用其它服务
2.1.参照1.1方式创建一个空的spring boot项目,然后添加spring cloud 相关依赖(这里主要是:eureka-client【实现服务自动发现与注册】、web【即:springMVC,实现服务API】),POM XML添加配置如下:
<dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>Greenwich.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.11</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!--当.yml配置不生效时,应添加snakeyaml依赖,但一般spring-boot-starter中默认有此依赖,非spring boot项目需要添加--> <dependency> <groupId>org.yaml</groupId> <artifactId>snakeyaml</artifactId> <version>1.23</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
2.2.在application.yml文件中添加如下配置(若没有请参见1.3法创建):注意spring.application.name,这个是服务实例名,注册及服务消费时均需使用该名称
server:
port: 8801
spring:
application:
name: helloservice
ip: localhost #自定义配置,在demo代码中有用到
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8800/eureka/
3.3.编写controller 服务相关代码,在spring boot启动类上添加@EnableDiscoveryClient注解,具体完整实现代码如下:(除了@EnableDiscoveryClient注解,基余代码与普通的spring MVC项目代码均相同)

//controller: package cn.zuowenjun.cloud.controller; import cn.zuowenjun.cloud.model.Result; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class DemoController { @Value("${spring.application.name}") private String serviceName; @Value("${spring.application.ip}") private String address; @Value("${server.port}") private String port; @Autowired DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; @GetMapping(value = "/") public String index(){ return "demo service"; } @RequestMapping("/hello") public Object hello(){ return discoveryClient.getServices(); } @RequestMapping("/info") public Result info(){ Result result = new Result(); result.setServiceName(serviceName); result.setHost(String.format("%s:%s", address, port)); result.setMessage("hello"); return result; } @RequestMapping(value = "/multiply/{a}/{b}") public Result multiply(@PathVariable("a") int a,@PathVariable("b") int b){ Result result = new Result(); result.setServiceName(serviceName); result.setHost(String.format("%s:%s", address, port)); result.setMessage("ok"); result.setContent(a * b); return result; } } //model: package cn.zuowenjun.cloud.model; public class Result { private int code; private String message; private Object content; private String serviceName; private String host; public int getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(int code) { this.code = code; } public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } public Object getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(Object content) { this.content = content; } public String getServiceName() { return serviceName; } public void setServiceName(String serviceName) { this.serviceName = serviceName; } public String getHost() { return host; } public void setHost(String host) { this.host = host; } } //App spring boot启动类: package cn.zuowenjun.cloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; @EnableDiscoveryClient @SpringBootApplication public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { SpringApplication.run(App.class, args); } }
完成上述步骤后即实现了服务提供者项目,完整项目结构如下图示,启动运行http://localhost:8801/multiply/324/561(只需关注这个服务方法,后面服务消费会调用这个方法) ,可以看到正常响应出JSON结果,如:"code":0,"message":"ok","content":181764,"serviceName":"helloservice","host":"localhost:8801"}
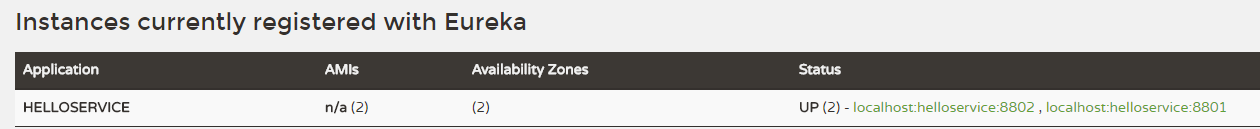
 为了后面服务消费者能体验出负载均衡的效果,可以把该项目再以另一个端口(server.port=8802)重新启动运行一个实例(IDEA启动多个实例的方法请参见:https://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/76408139,最后不一定要改yml中的port配置,也可以直接在Edit Configuration--> program argements中指定:--server.port=8802即可,原理与直接通过命令:java -jar xxx --server.port=8802类似),这样就会有两个服务提供者了,如果查看eureka server主页(http://localhost:8800/)会在Instances currently registered with Eureka列表中展示出2个服务实例信息,如下图示:
为了后面服务消费者能体验出负载均衡的效果,可以把该项目再以另一个端口(server.port=8802)重新启动运行一个实例(IDEA启动多个实例的方法请参见:https://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/76408139,最后不一定要改yml中的port配置,也可以直接在Edit Configuration--> program argements中指定:--server.port=8802即可,原理与直接通过命令:java -jar xxx --server.port=8802类似),这样就会有两个服务提供者了,如果查看eureka server主页(http://localhost:8800/)会在Instances currently registered with Eureka列表中展示出2个服务实例信息,如下图示:
三、实现service consumer(含eureka client)--服务消费者
【即:需要调用微服务API的项目,相对eureka,service provider来讲,就是客户端,消费方】,当然也有可能是service provider【服务提供者】,暴露服务API给其它微服务项目
3.0.参照1.1方式创建一个空的spring boot项目,然后添加spring cloud 相关依赖(这里仅先是:eureka-client【实现服务自动发现与注册】、web【即:springMVC,实现服务API】),POM XML添加配置如下:

<properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <spring-cloud.version>Greenwich.RELEASE</spring-cloud.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement>
3.1方式一:使用restTemplate+ribbon实现服务消费(负载均衡调用远程服务)
3.1.1.在POM XML中添加spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon依赖,如下:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon</artifactId> </dependency>
3.1.2.编写controller相关代码(含远程服务调用类HelloService),修改spring boot 启动类,具体完整实现代码如下:

//spring boot启动类: package cn.zuowenjun.cloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced; import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @EnableDiscoveryClient @SpringBootApplication class EurekaclientconsumerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaclientconsumerApplication.class, args); } @LoadBalanced @Bean public RestTemplate restTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); } } //controller: package cn.zuowenjun.cloud.controller; import cn.zuowenjun.cloud.service.HelloRemoteService; import cn.zuowenjun.cloud.service.HelloService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController { @Autowired private HelloService helloService; @RequestMapping("/x") public Object multiplyForRestTemplate(@RequestParam int a, @RequestParam int b) { return helloService.multiply(a,b); } } //HelloService(远程服务代理类) : package cn.zuowenjun.cloud.service; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @Service public class HelloService { @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate; @Value("${spring.application.helloServiceProvider}") private String helloServiceName; public Object multiply(int a,int b){ String url="http://"+ helloServiceName +"/multiply/" + a +"/" + b; return restTemplate.getForObject(url,String.class); } }
如上代码中最核心的是:HelloService类,通过这个类远程调用【消费】注册在eureka server上对应的服务API,而这个类中最核心的对象是:RestTemplate,而这个又是通过在spring boot启动类(EurekaclientconsumerApplication)中通过代码注入到Spring IOC容器中的(当然也可以自定义一个config类然后统一写BEAN注入的方法),重点请看这个restTemplate Bean注册方法上面的注解:@LoadBalanced,这个就是实现负载均衡(默认是采用轮询的负载均衡算法,还有其它的负载均衡Rule),就这么简单吗?是的,用起来简单,但内部实现还是非常复杂的,Ribbon的运行原理详见:深入理解Ribbon之源码解析,核心思路是:RestTemplate内部维护了一个被@LoadBalance注解的RestTemplate列表,而这些RestTemplate列表又被添加了LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截器,而LoadBalancerInterceptor内部又使用了LoadBalancerClient,而LoadBalancerClient(实现类:RibbonLoadBalancerClient)具体选择服务实例的逻辑又由ILoadBalancer来处理,ILoadBalancer通过配置IRule、IPing等信息,向EurekaClient获取注册列表的信息,并定时向EurekaClient发送“ping”心跳,进而检查是否更新了服务列表,最后得到注册服务实例列表后,ILoadBalancer根据IRule的策略进行负载均衡。
3.1.3.在application.yml文件中添加如下配置(若没有请参见1.3法创建):
server:
port: 8666
spring:
application:
name: ribbonclient
helloServiceProvider: helloservice #自定义配置,指定访问远程服务名称,当然也可以写死在代码中
eureka:
client:
serviceUrl:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8800/eureka/ #指向eureka server
完成上述步骤即实现了一个基于Ribbon的负载均衡服务消费者(客户端)项目。
3.2方式二:使用feign实现服务消费(负载均衡调用远程服务调用)
我们仍然基于3.1节原有项目基础上实现基于feign的负载均衡服务调用,注意feign的底层仍然使用了Ribbon。当然也可以单独创一个新的spring boot项目(参照第一节介绍)然后再按下文步骤操作即可。
3.2.1.在POM XML中添加spring-cloud-starter-openfeign依赖,配置如下:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
3.2.2.在spring boot启动类(EurekaclientconsumerApplication)上添加:@EnableFeignClients 注解,然后在cn.zuowenjun.cloud.service包中添加自定义HelloRemoteService,这个就是远程服务调用接口类(或称:客户端代理类【接口】),这个就是与3.1中定义的HelloService作用完全类似,只是实现方式不同而矣,最后在controller中添加一个新的API ACTION方法,以便可以调用HelloRemoteService中的服务方法,完整实现代码如下:

//spring boot启动类 package cn.zuowenjun.cloud; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced; import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerInterceptor; import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @EnableDiscoveryClient @SpringBootApplication @EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "cn.zuowenjun.cloud.service") // 如果启动类不在根目录需要指定basePackages,否则不需要 class EurekaclientconsumerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaclientconsumerApplication.class, args); } @LoadBalanced @Bean public RestTemplate restTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); } } //HelloRemoteService: package cn.zuowenjun.cloud.service; import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; /* * bug-refer https://blog.csdn.net/zlh313_01/article/details/80309144 * bug-refer https://blog.csdn.net/alinyua/article/details/80070890 */ @FeignClient(name= "helloservice") public interface HelloRemoteService { @RequestMapping("/multiply/{a}/{b}") Object multiply(@PathVariable("a") int a, @PathVariable("b") int b); } //controller: package cn.zuowenjun.cloud.controller; import cn.zuowenjun.cloud.service.HelloRemoteService; import cn.zuowenjun.cloud.service.HelloService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController { @Autowired private HelloService helloService; @Autowired private HelloRemoteService helloRemoteService; @RequestMapping("/x") public Object multiplyForRestTemplate(@RequestParam int a, @RequestParam int b) { return helloService.multiply(a,b); } @RequestMapping("/multiply/{a}/{b}") public Object multiplyForFeignClient(@PathVariable int a, @PathVariable int b) { return helloRemoteService.multiply(a,b); } }
如上代码HelloRemoteService是重点,需要注意:
a.必需是interface,因为@FeignClient注解只能用于interface中,而且很显然HelloRemoteService 是远程调用,本地不应有实现的,如果知道原理就更明白这个接口只是为了生成可供restTemplate调用的URL方法而矣;
b.@FeignClient注解的name(别名属性)或value必填,这个就是需要远程调用服务的应用名称【即:表明消费哪个服务】
c.接口中定义的方法应与远程服务的controller中的方法保持一致(方法签名,注解),同时注意方法上的一些映射请求的注解,如:@RequestMapping,这些与我们在spring MVC用法相同,但含义却不相同,spring MVC是指处理请求路径,而这里是调用请求路径,这个路径必需与服务提供者API 的对应的ACITON方法上的保持相同,否则将无法成功发送请求。常见问题及解决办法可参见:https://blog.csdn.net/zlh313_01/article/details/80309144
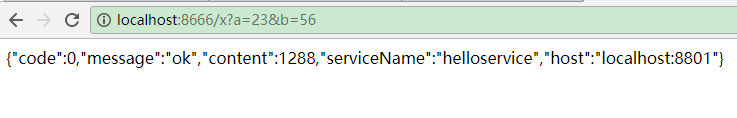
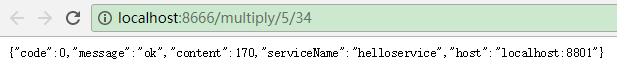
3.2.3.application.yml配置与3.1.3配置相同,即保持不变即可,最后启动项目即可(现在这个项目同时包含了Ribbon与Feign的负载均衡远程调用服务的方式),通过多次访问:http://localhost:8666/x?a=数字&b=数字 (基于Ribbon实现)、http://localhost:8666/multiply/数字/数字(基于Feign实现)可以看到远程调用服务成功(即:消费服务成功)。
FeignClient的运行原理详见:深入理解Feign之源码解析,核心思路是:spring boot项目启动时检查@EnableFeignClients,若有则扫描被@FeignClient注解接口并注入到spring IOC容器中,然后在请求被@ FeignCleint标注的接口方法时,会通过JDK动态代理来生成具体的RequesTemplate,RequesTemplate又会生成Request,Request交给Client去处理,最后Client被封装到LoadBalanceClient类,这个类Ribbon中的LoadBalancerClient相同,后面的负载均衡的处理请求相同。
项目结构及远程调用效果如下图所示:
 、
、
 、
、
四、下面分享相关可参考的博文资料链接:
Spring Cloud之Eureka服务注册与发现(概念原理篇)
Spring Cloud Netflix - Eureka Server源码阅读
提示:本文相关示例项目代码已上传GITHUB,地址如下:
https://github.com/zuowj/learning-demos/tree/master/java/demo-eurekaserver
https://github.com/zuowj/learning-demos/tree/master/java/demo-eurekaclient
https://github.com/zuowj/learning-demos/tree/master/java/demo-eurekaclientconsumer
说明:文中若有不足之处欢迎指出,码字不易,请多支持,谢谢!



