图的表示及遍历
1. 图的表示
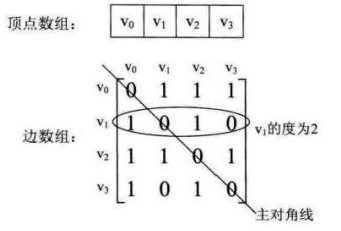
1)临接矩阵
使用二维数组arr[N][N]表示一个图。
a. N 为图的顶点个数,矩阵的对角线全为0。
b. 两个顶点连通的话,矩阵的值为1
c. 某一行的和表示该顶点的出度。某一列的和表示该顶点的入度
d. 有权值的图,矩阵元素不再是0,1表示是否连通,而是把元素值表示为权值。不存在的边,权值记录为∞;对角线上的权值为0
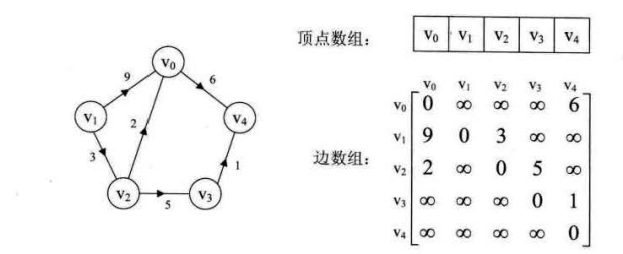
使用临接矩阵表示图,直观方便,缺点是占用空间大,因为需要 N*N 个空间。对于稀疏图来说,这比较浪费空间。
2) 临接表
a. 使用数组保存顶点
b. 每个顶点的所有临接点组成一个线性表,挂在数组后面。
这种方法类似散列表的开链法。
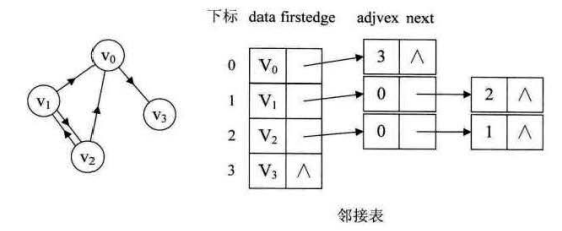
优点是节省空间,顶点的出度就在链表上,但是要查找入度的话,需要遍历整个图
2. 图的遍历
1)广度优先
先遍历图的所有临节点,再依次遍历临接点的临接点
2)深度优先
从某一个节点出发,一直走下去,直到找不到临接点。再从其他节点出发,继续一条道路走到黑
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
enum Ecolor
{
WHITE = 0,
GRAY,
BLACK
};
// 这里使用临接表表示图
struct graph_node_s
{
enum Ecolor color; // 节点颜色,用来标识该顶点是否别遍历过
int d;
int ftime; // 节点访问结束时间
int dtime; // 节点访问开始时间
struct graph_node_s *next;
};
typedef struct graph_node_s graph_node_t;
struct graph_s
{
int vertice; // 顶点数
int edge; // 边数
graph_node_t *bucket[1]; // 保存顶点节点
};
typedef struct graph_s graph_t;
// 广度优先遍历使用了队列保存临接点
struct queue_node_s
{
void *d;
struct queue_node_s *prev;
struct queue_node_s *next;
};
typedef struct queue_node_s queue_node_t;
struct queue_s
{
queue_node_t *sentinel;
};
typedef struct queue_s queue_t;
queue_t *queue_create(void)
{
queue_t *queue = (queue_t*)malloc(sizeof(queue_t));
assert(queue);
queue->sentinel = (queue_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(queue_node_t));
assert(queue->sentinel);
queue->sentinel->next = queue->sentinel;
queue->sentinel->prev = queue->sentinel;
return queue;
}
void queue_destroy(queue_t *q)
{
assert(q);
queue_node_t *nd = q->sentinel->next;
while (nd != q->sentinel)
{
queue_node_t *tmp = nd;
nd = nd->next;
free(tmp);
}
free(nd);
free(q);
}
void queue_push(queue_t *q, void *value)
{
assert(q);
assert(value);
queue_node_t* nd = (queue_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(queue_node_t));
assert(nd);
nd->d = value;
nd->next = q->sentinel;
nd->prev = q->sentinel->prev;
q->sentinel->prev->next = nd;
q->sentinel->prev = nd;
}
void queue_pop(queue_t *q)
{
assert(q);
queue_node_t *tmp = q->sentinel->next;
if (tmp != q->sentinel)
{
q->sentinel->next = q->sentinel->next->next;
q->sentinel->next->prev = q->sentinel;
free(tmp);
}
}
void *queue_front(queue_t *q)
{
assert(q);
return q->sentinel->next->d;
}
int queue_empty(queue_t *q)
{
assert(q);
return q->sentinel->next == q->sentinel;
}
graph_t *graph_create(int vertice)
{
graph_t *g = (graph_t*)malloc(sizeof(graph_t) + (vertice-1)*sizeof(graph_node_t*));
assert(g);
g->vertice = vertice;
g->edge = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vertice; ++i)
{
g->bucket[i] = (graph_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(graph_node_t));
assert(g->bucket[i]);
g->bucket[i]->d = i;
g->bucket[i]->color = WHITE;
g->bucket[i]->next = NULL;
}
return g;
}
void graph_destroy(graph_t *g)
{
assert(g);
for (int i = 0; i < g->vertice; ++i)
{
graph_node_t *head = g->bucket[i];
while (head)
{
graph_node_t *tmp = head;
head = head->next;
free(tmp);
}
}
free(g);
}
void graph_add_edge(graph_t *g, int src, int dst)
{
assert(g);
assert(src < g->vertice);
assert(dst < g->vertice);
graph_node_t *nd = (graph_node_t*)malloc(sizeof(graph_node_t));
assert(nd);
nd->d = dst;
nd->color = WHITE;
nd->next = g->bucket[src]->next;
g->bucket[src]->next = nd;
}
static void _graph_dfs(graph_t *g, int index, int *time)
{
assert(g);
assert(time);
assert(index < g->vertice);
(*time)++;
printf("%d ", g->bucket[index]->d);
g->bucket[index]->color = GRAY;
g->bucket[index]->dtime = *time;
graph_node_t *tmp = g->bucket[index]->next;
while (tmp)
{
if (g->bucket[tmp->d]->color == WHITE)
{
// 对临接点进行深度遍历
_graph_dfs(g, tmp->d, time);
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
g->bucket[index]->color = BLACK;
(*time)++;
g->bucket[index]->ftime = *time;
}
// 深度优先遍历
void graph_dfs(graph_t *g)
{
assert(g);
int time = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g->vertice; ++i)
{
if (g->bucket[i]->color == WHITE)
{
_graph_dfs(g, i, &time);
}
}
}
// 广度优先遍历
void graph_bfs(graph_t *g, int index)
{
assert(g);
assert(index < g->vertice);
queue_t *q = queue_create();
queue_push(q, g->bucket[index]);
while (!queue_empty(q))
{
graph_node_t *nd = queue_front(q);
if (g->bucket[nd->d]->color == WHITE)
{
printf("%d ", nd->d);
g->bucket[nd->d]->color = BLACK;
graph_node_t *head = g->bucket[nd->d]->next;
while (head)
{
// 所有临接点入队
queue_push(q, g->bucket[head->d]);
head = head->next;
}
}
queue_pop(q);
}
queue_destroy(q);
}
int main()
{
graph_t *g = graph_create(6);
graph_add_edge(g, 0, 1);
graph_add_edge(g, 2, 3);
graph_add_edge(g, 4, 5);
graph_add_edge(g, 3, 5);
graph_bfs(g, 0);
graph_destroy(g);
return 0;
}




