链表之循环链表
上期文章介绍了单链表的一些基本功能函数,本次主要介绍循环链表的一些基本功能函数。循环链表其实就是将单链表的最后一个结点指向单链表的头结点,从而构成一个循环结构。本次函数功能主要包括链表创建函数(头插法和尾插法)、链表打印函数和两种链表是否有环的判定函数,以及最后的一个链表清除函数。
- 博文链接:http://haoyuanliu.github.io/2016/04/12/sieve/
- 对,我是来骗访问量的!O(∩_∩)O~~
函数运行如下图所示:
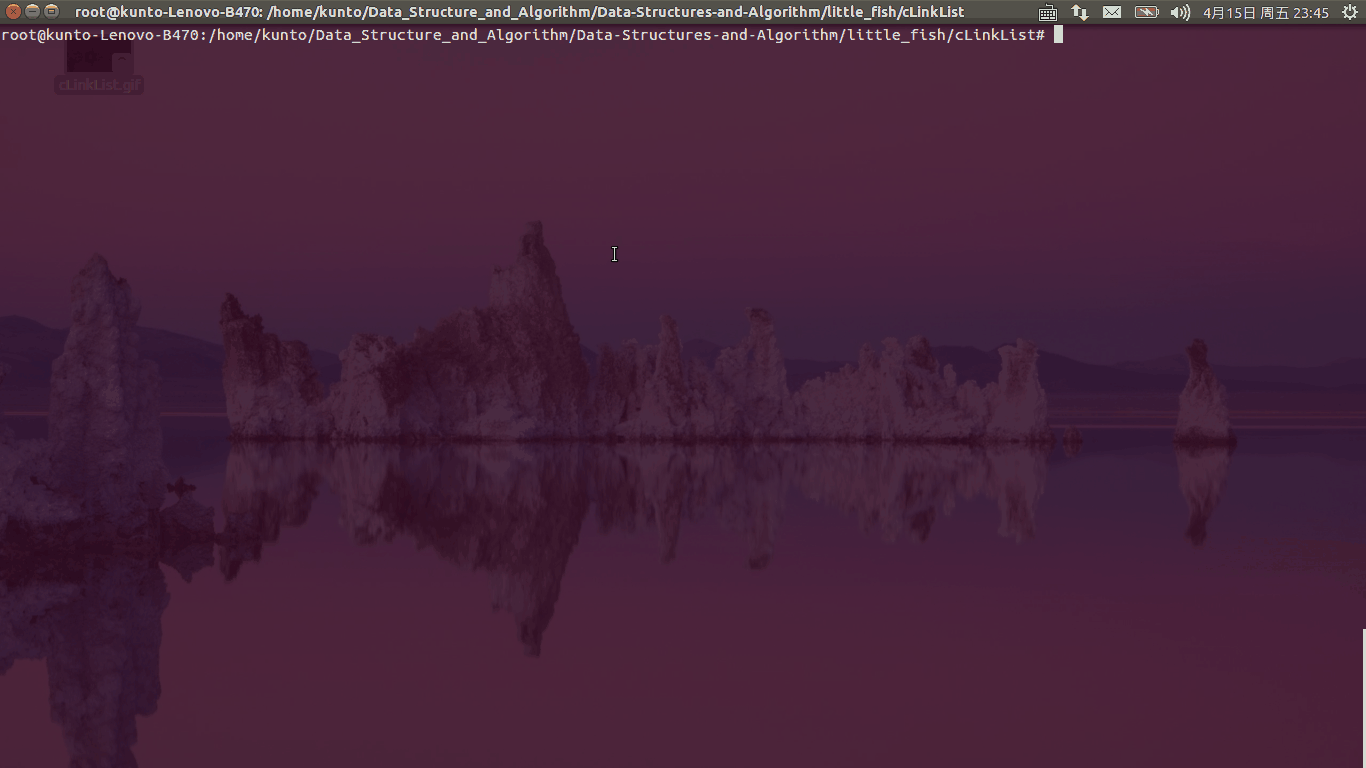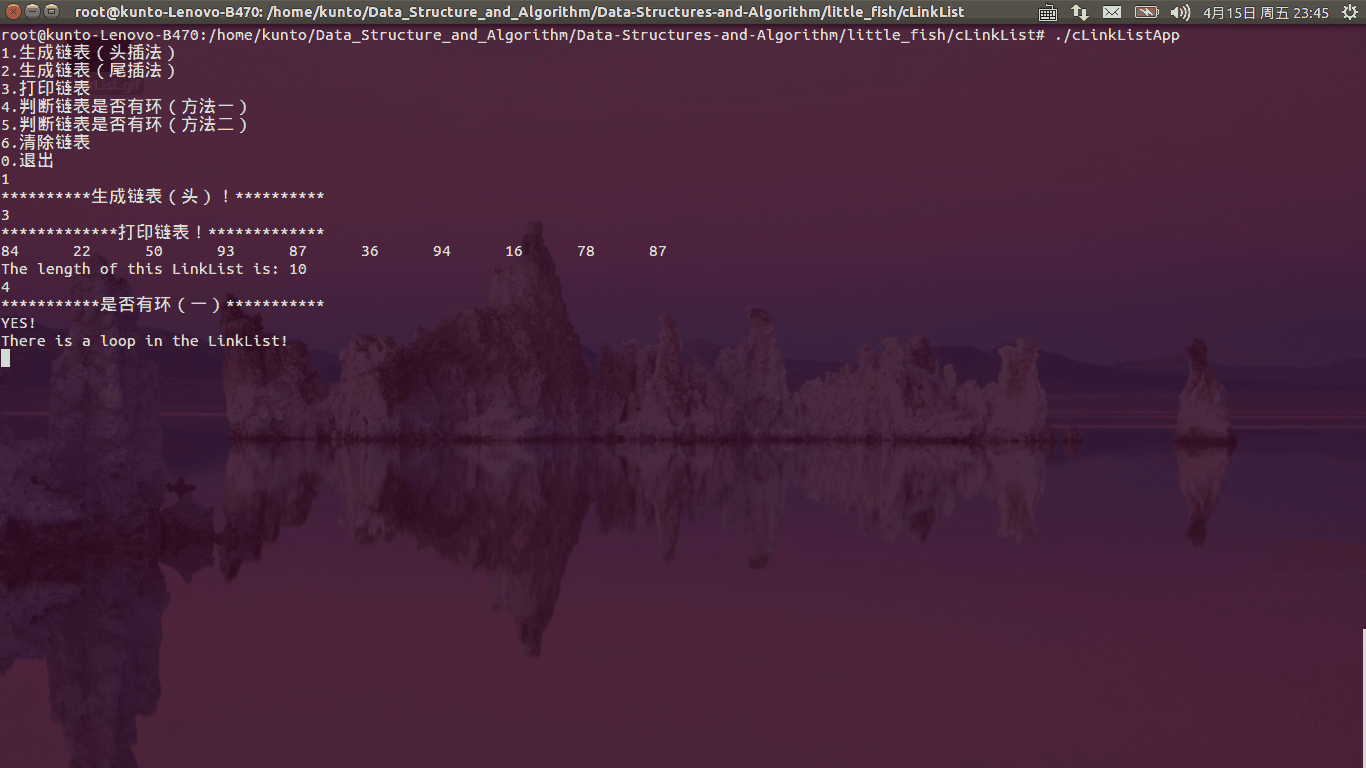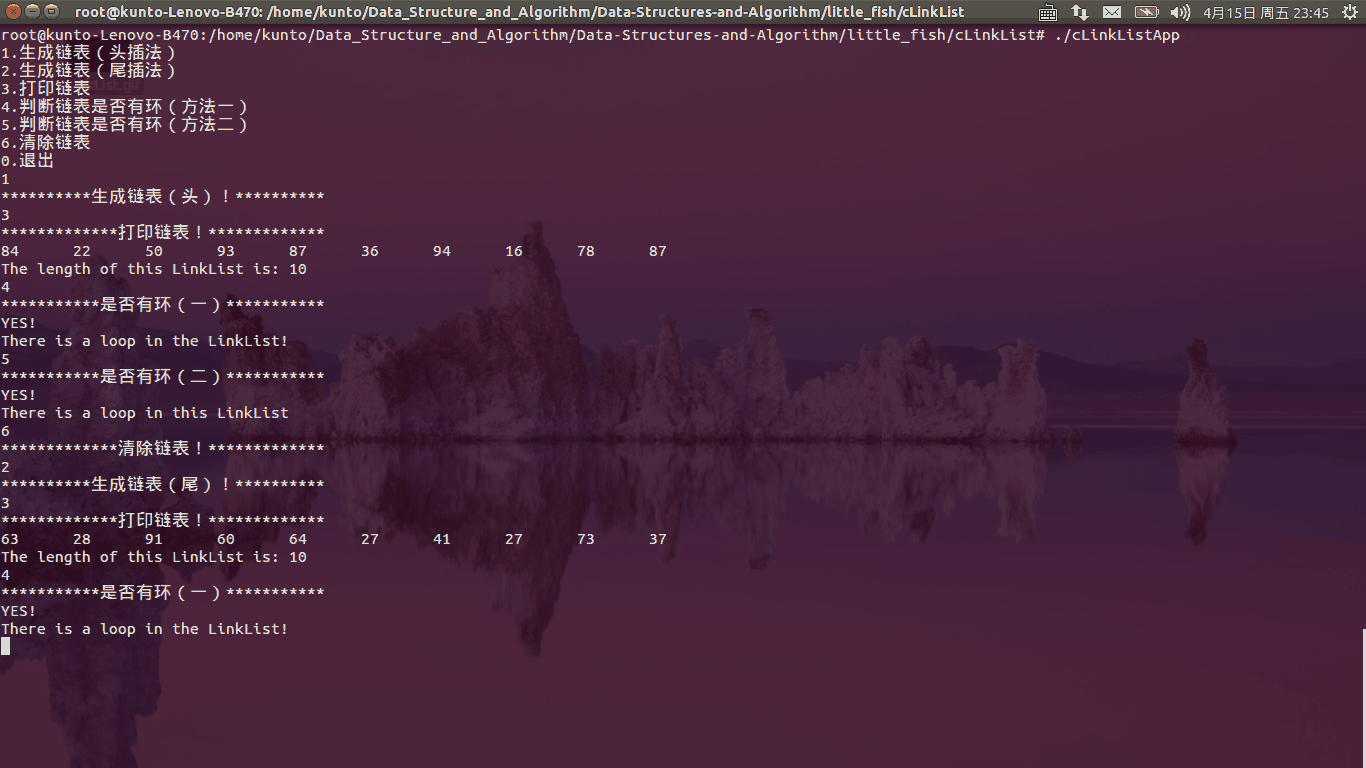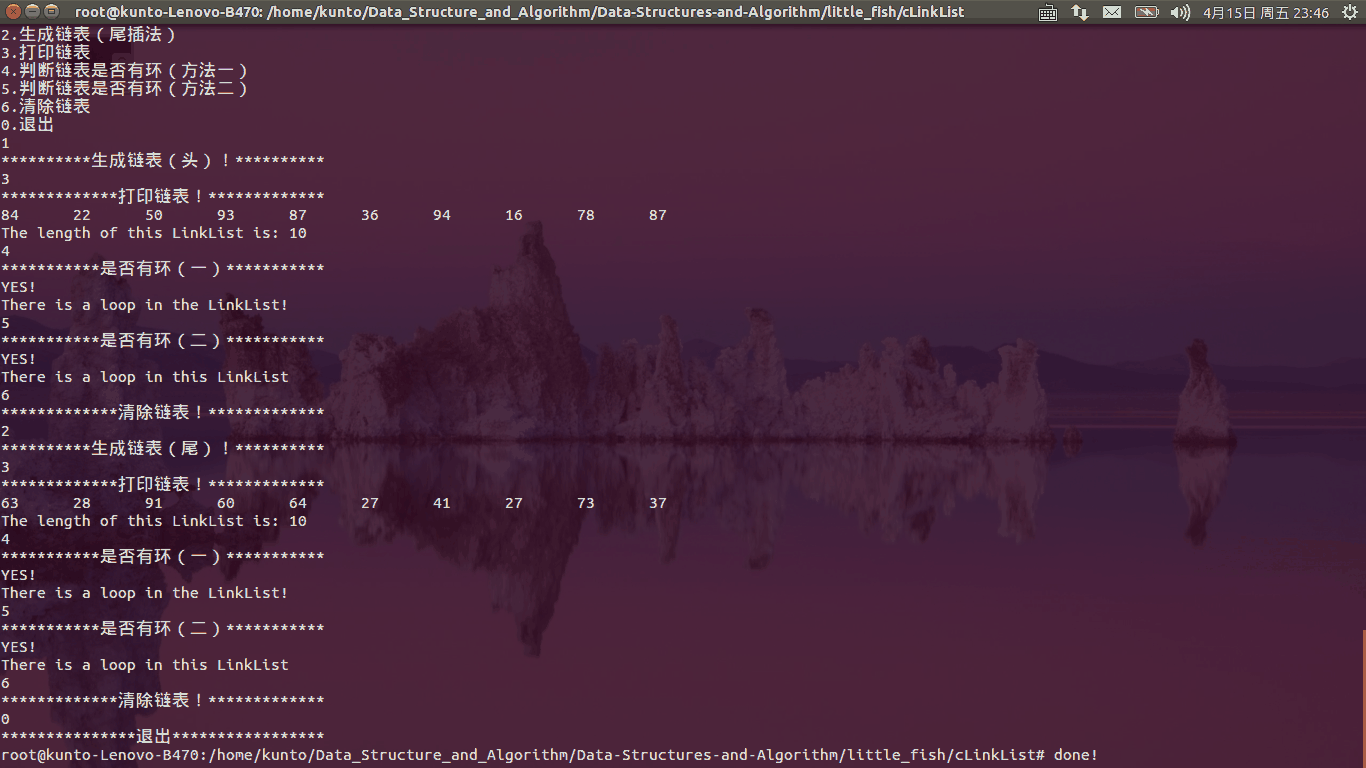
功能函数
链表创建函数(头插法)
//定义循环链表生成函数(头插法)
void cListCreatHead(cLinkList *L, int n)
{
int i;
cLinkList *p, *r;
p = L;
p->data = rand() % 100 + 1;
for(i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
r = (cLinkList *)malloc(sizeof(cLinkList));
r->data = rand() % 100 + 1;
r->next = p;
p = r;
}
L->next = p;
}
这里使用了头插法对链表进行生成操作,L作为cLinkList的一个指针,指向链表的最后一个结点,这里注意最后要将L指向p构建循环。
链表创建函数(尾插法)
//定义循环链表生成函数(尾插法)
void cListCreatTail(cLinkList *L, int n)
{
int i;
cLinkList *head, *p;
head = L;
L->data = rand() % 100 + 1;
for(i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
p = (cLinkList *)malloc(sizeof(cLinkList));
p->data = rand() % 100 + 1;
L->next = p;
L = p;
}
L->next = head;
}
这里使用了尾插法对链表进行生成操作,L作为cLinkList的一个指针,在创建过程中不断向后移动,最后指向链表的最后一个结点,这里注意最后要将L指向头结点指针head构建循环。
链表打印函数
void cListPrint(cLinkList *L)
{
cLinkList *head, *p;
head = L;
p = L;
int count = 1;
while(p->next != head)
{
printf("%d\t", p->data);
p = p->next;
count++;
}
printf("%d\n", p->data);
printf("The length of this LinkList is: %d\n", count);
}
通过判定p->next != head为条件对链表进行遍历打印,在遍历过程中计算链表的长度并打印输出。
检测是否有环(方法一)
//检查是否有环(方法一)
int cListCheckLoop1(cLinkList *L)
{
cLinkList *head, *p, *q;
head = p = q = L;
int countp, countq;
countp = 1;
while(1)
{
p=p->next;
countp++;
countq = 1;
q = head;
while(q != p)
{
q = q->next;
countq++;
}
if(++countq != countp)
{
printf("YES!\nThere is a loop in the LinkList!\n");
return 1;
}
if(p->next == NULL)
{
printf("NO!\nThere is no loop in the LinkLis!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
设置指针变量p对链表进行遍历,同时使用q对p之前的结点进行遍历,如果发现到达p所在结点的更短路径,则判定链表存在环。比如,p走了6步到达结点A,而q只需要3步即可到达结点A,则此时链表中必定存在环,换言之,此前p已经经过结点A了。
检测是否有环(方法二)
//检测链表是否有环(方法二)
int cListCheckLoop2(cLinkList *L)
{
cLinkList *p, *q;
p = q = L;
while(p->next != NULL && p->next->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next->next;
q = q->next;
if(p == q)
{
printf("YES!\nThere is a loop in this LinkList\n");
return 1;
}
}
printf("NO!\nThere is no loop in the LinkList\n");
return 0;
}
设置p的步长为2,q的步长为1,同时对链表进行遍历,如果在某个时刻p == q,则就可以断定链表中存在环。
链表清除
//链表清除函数
void cListClear(cLinkList *L)
{
cLinkList *p, *temp;
p = L->next;
while(p != L)
{
temp = p;
p = p->next;
free(temp);
}
}
使用free()函数对我们生成的链表空间进行遍历删除。
总体代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//定义循环链表结构
typedef struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
}cLinkList;
//定义循环链表生成函数(头插法)
void cListCreatHead(cLinkList *L, int n)
{
int i;
cLinkList *p, *r;
p = L;
p->data = rand() % 100 + 1;
for(i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
r = (cLinkList *)malloc(sizeof(cLinkList));
r->data = rand() % 100 + 1;
r->next = p;
p = r;
}
L->next = p;
}
//定义循环链表生成函数(尾插法)
void cListCreatTail(cLinkList *L, int n)
{
int i;
cLinkList *head, *p;
head = L;
L->data = rand() % 100 + 1;
for(i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
p = (cLinkList *)malloc(sizeof(cLinkList));
p->data = rand() % 100 + 1;
L->next = p;
L = p;
}
L->next = head;
}
//打印链表
void cListPrint(cLinkList *L)
{
cLinkList *head, *p;
head = L;
p = L;
int count = 1;
while(p->next != head)
{
printf("%d\t", p->data);
p = p->next;
count++;
}
printf("%d\n", p->data);
printf("The length of this LinkList is: %d\n", count);
}
//检查是否有环(方法一)
int cListCheckLoop1(cLinkList *L)
{
cLinkList *head, *p, *q;
head = p = q = L;
int countp, countq;
countp = 1;
while(1)
{
p=p->next;
countp++;
countq = 1;
q = head;
while(q != p)
{
q = q->next;
countq++;
}
if(++countq != countp)
{
printf("YES!\nThere is a loop in the LinkList!\n");
return 1;
}
if(p->next == NULL)
{
printf("NO!\nThere is no loop in the LinkLis!\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
//检测链表是否有环(方法二)
int cListCheckLoop2(cLinkList *L)
{
cLinkList *p, *q;
p = q = L;
while(p->next != NULL && p->next->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next->next;
q = q->next;
if(p == q)
{
printf("YES!\nThere is a loop in this LinkList\n");
return 1;
}
}
printf("NO!\nThere is no loop in the LinkList\n");
return 0;
}
//清除链表
void cListClear(cLinkList *L)
{
cLinkList *p, *temp;
p = L->next;
while(p != L)
{
temp = p;
p = p->next;
free(temp);
}
}
//主函数
int main()
{
int length = 10;
cLinkList *L;
L = (cLinkList *)malloc(sizeof(cLinkList));
char operator;
printf("1.生成链表(头插法)\n");
printf("2.生成链表(尾插法)\n");
printf("3.打印链表\n");
printf("4.判断链表是否有环(方法一)\n");
printf("5.判断链表是否有环(方法二)\n");
printf("6.清除链表\n");
printf("0.退出\n");
while(1)
{
scanf("%c", &operator);
switch(operator)
{
case '1':
cListCreatHead(L, length);
printf("**********生成链表(头)!**********\n");
break;
case '2':
cListCreatTail(L, length);
printf("**********生成链表(尾)!**********\n");
break;
case '3':
printf("*************打印链表!*************\n");
cListPrint(L);
break;
case '4':
printf("***********是否有环(一)***********\n");
cListCheckLoop1(L);
break;
case '5':
printf("***********是否有环(二)***********\n");
cListCheckLoop2(L);
break;
case '6':
printf("*************清除链表!*************\n");
cListClear(L);
break;
case '0':
printf("***************退出*****************\n");
free(L);
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
 Github: https://github.com/haoyuanliu
Github: https://github.com/haoyuanliu
 个人博客: http://haoyuanliu.github.io/
个人博客: http://haoyuanliu.github.io/
个人站点,欢迎访问,欢迎评论!



