实验4 类的组合、继承、模板类、标准库
1. 实验任务1

1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using std::cout; 4 using std::endl; 5 6 // 类A的定义 7 class A { 8 public: 9 A(int x0, int y0); 10 void display() const; 11 12 private: 13 int x, y; 14 }; 15 16 A::A(int x0, int y0) : x{ x0 }, y{ y0 } { 17 } 18 19 void A::display() const { 20 cout << x << ", " << y << endl; 21 } 22 23 // 类B的定义 24 class B { 25 public: 26 B(double x0, double y0); 27 void display() const; 28 29 private: 30 double x, y; 31 }; 32 33 B::B(double x0, double y0) : x{ x0 }, y{ y0 } { 34 } 35 36 void B::display() const { 37 cout << x << ", " << y << endl; 38 } 39 40 void test() { 41 cout << "测试类A: " << endl; 42 A a(3, 4); 43 a.display(); 44 45 cout << "\n测试类B: " << endl; 46 B b(3.2, 5.6); 47 b.display(); 48 } 49 50 int main() { 51 test(); 52 }

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 using std::string; 7 8 // 定义类模板 9 template<typename T> 10 class X { 11 public: 12 X(T x0, T y0); 13 void display(); 14 15 private: 16 T x, y; 17 }; 18 19 template<typename T> 20 X<T>::X(T x0, T y0) : x{ x0 }, y{ y0 } { 21 } 22 23 template<typename T> 24 void X<T>::display() { 25 cout << x << ", " << y << endl; 26 } 27 28 29 void test() { 30 cout << "测试1: 类模板X中的抽象类型T用int实例化" << endl; 31 X<int> x1(3, 4); 32 x1.display(); 33 34 cout << endl; 35 36 cout << "测试2: 类模板X中的抽象类型T用double实例化" << endl; 37 X<double> x2(3.2, 5.6); 38 x2.display(); 39 40 cout << endl; 41 42 cout << "测试3: 类模板X中的抽象类型T用string实例化" << endl; 43 X<string> x3("hello", "oop"); 44 x3.display(); 45 } 46 47 int main() { 48 test(); 49 }


2. 实验任务2

1 #pragma once 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <numeric> 7 #include <iomanip> 8 9 using std::vector; 10 using std::string; 11 using std::cin; 12 using std::cout; 13 using std::endl; 14 15 class GradeCalc : public vector<int> { 16 public: 17 GradeCalc(const string& cname, int size); 18 void input(); // 录入成绩 19 void output() const; // 输出成绩 20 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 21 int min() const; // 返回最低分 22 int max() const; // 返回最高分 23 float average() const; // 返回平均分 24 void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息 25 26 private: 27 void compute(); // 成绩统计 28 29 private: 30 string course_name; // 课程名 31 int n; // 课程人数 32 vector<int> counts = vector<int>(5, 0); // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100] 33 vector<double> rates = vector<double>(5, 0); // 保存各分数段比例 34 }; 35 36 GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const string& cname, int size) : course_name{ cname }, n{ size } {} 37 38 void GradeCalc::input() { 39 int grade; 40 41 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 42 cin >> grade; 43 this->push_back(grade); 44 } 45 } 46 47 void GradeCalc::output() const { 48 for (auto ptr = this->begin(); ptr != this->end(); ++ptr) 49 cout << *ptr << " "; 50 cout << endl; 51 } 52 53 void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { 54 if (ascending) 55 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end()); 56 else 57 std::sort(this->begin(), this->end(), std::greater<int>()); 58 } 59 60 int GradeCalc::min() const { 61 return *std::min_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 62 } 63 64 int GradeCalc::max() const { 65 return *std::max_element(this->begin(), this->end()); 66 } 67 68 float GradeCalc::average() const { 69 return std::accumulate(this->begin(), this->end(), 0) * 1.0 / n; 70 } 71 72 void GradeCalc::compute() { 73 for (int grade : *this) { 74 if (grade < 60) 75 counts.at(0)++; 76 else if (grade >= 60 && grade < 70) 77 counts.at(1)++; 78 else if (grade >= 70 && grade < 80) 79 counts.at(2)++; 80 else if (grade >= 80 && grade < 90) 81 counts.at(3)++; 82 else if (grade >= 90) 83 counts.at(4)++; 84 } 85 86 for (int i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) 87 rates.at(i) = counts.at(i) * 1.0 / n; 88 } 89 90 void GradeCalc::info() { 91 cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << endl; 92 cout << "排序后成绩: \t"; 93 sort(); output(); 94 cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << endl; 95 cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << endl; 96 cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << endl; 97 98 compute(); // 统计各分数段人数、比例 99 100 vector<string> tmp{ "[0, 60) ", "[60, 70)", "[70, 80)","[80, 90)", "[90, 100]" }; 101 for (int i = tmp.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) 102 cout << tmp[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" 103 << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i] * 100 << "%" << endl; 104 }

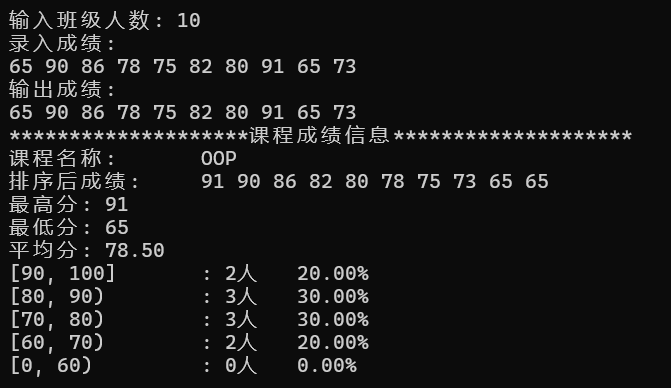
1 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 2 #include <iomanip> 3 4 void test() { 5 int n; 6 cout << "输入班级人数: "; 7 cin >> n; 8 9 GradeCalc c1("OOP", n); 10 11 cout << "录入成绩: " << endl;; 12 c1.input(); 13 cout << "输出成绩: " << endl; 14 c1.output(); 15 16 cout << string(20, '*') + "课程成绩信息" + string(20, '*') << endl; 17 c1.info(); 18 } 19 20 int main() { 21 test(); 22 }
问题一
派生类 GradeCalc 继承自 std::vector<int>,因此成绩存储在 GradeCalc 对象内部的 std::vector<int> 中。所有的成绩通过 vector<int> 的功能进行存取。接口访问成绩的方法:sort、min、max 和 average 这些方法都是直接利用 std::vector 提供的接口来访问和操作存储在内部的成绩。例如:min() 使用 std::min_element 来找到最低分,max() 使用 std::max_element 来找到最高分,average() 使用 std::accumulate 计算总分,然后除以人数 n 来得到平均分。input() 方法通过 push_back 接口将用户输入的成绩数据添加到对象的 std::vector<int> 中。push_back 是 std::vector 的成员函数,可以在向量的末尾插入新元素。
问题二l
ine 68 中的分母 n 表示参加考试的学生总人数。它用于计算平均分,确保在计算时按总人数取平均。如果去掉乘以 1.0,就会产生整型除法。在 C++ 中,两个整数相除的结果仍然是整数,任何小数部分都会被丢弃。因此,移除 1.0 后可能会导致平均分计算的结果不准确。例如,若总和是 7,总人数是 3,整型除法会得到 2,而正确的平均数应是 2.33。乘以 1.0 将其转换为浮点数,从而返回一个准确的浮点平均数。
问题三
设计及代码实现细节上,GradeCalc类尚未考虑的地方:
-
输入验证:当前的
input()方法没有对用户输入进行有效性检查。例如,输入的成绩是否在合理范围(0-100)内,并且主要检查是否为整型。 -
异常处理:在读取输入部分如果发生异常(例如输入格式错误),程序会崩溃。需要添加异常处理机制。
-
多样性和兼容性:考虑支持其他类型的数值,比如浮点数成绩,允许更灵活的输入。
3. 实验任务3

1 #pragma once 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <numeric> 7 #include <iomanip> 8 9 using std::vector; 10 using std::string; 11 using std::cin; 12 using std::cout; 13 using std::endl; 14 15 class GradeCalc { 16 public: 17 GradeCalc(const string& cname, int size); 18 void input(); // 录入成绩 19 void output() const; // 输出成绩 20 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 21 int min() const; // 返回最低分 22 int max() const; // 返回最高分 23 float average() const; // 返回平均分 24 void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息 25 26 private: 27 void compute(); // 成绩统计 28 29 private: 30 string course_name; // 课程名 31 int n; // 课程人数 32 vector<int> grades; // 课程成绩 33 vector<int> counts = vector<int>(5, 0); // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100] 34 vector<double> rates = vector<double>(5, 0); // 保存各分数段比例 35 }; 36 37 GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const string& cname, int size) : course_name{ cname }, n{ size } {} 38 39 void GradeCalc::input() { 40 int grade; 41 42 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 43 cin >> grade; 44 grades.push_back(grade); 45 } 46 } 47 48 void GradeCalc::output() const { 49 for (int grade : grades) 50 cout << grade << " "; 51 cout << endl; 52 } 53 54 void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { 55 if (ascending) 56 std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end()); 57 else 58 std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end(), std::greater<int>()); 59 60 } 61 62 int GradeCalc::min() const { 63 return *std::min_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); 64 } 65 66 int GradeCalc::max() const { 67 return *std::max_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); 68 } 69 70 float GradeCalc::average() const { 71 return std::accumulate(grades.begin(), grades.end(), 0) * 1.0 / n; 72 } 73 74 void GradeCalc::compute() { 75 for (int grade : grades) { 76 if (grade < 60) 77 counts.at(0)++; 78 else if (grade >= 60 && grade < 70) 79 counts.at(1)++; 80 else if (grade >= 70 && grade < 80) 81 counts.at(2)++; 82 else if (grade >= 80 && grade < 90) 83 counts.at(3)++; 84 else if (grade >= 90) 85 counts.at(4)++; 86 } 87 88 for (int i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) 89 rates.at(i) = counts.at(i) * 1.0 / n; 90 } 91 92 void GradeCalc::info() { 93 cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << endl; 94 cout << "排序后成绩: \t"; 95 sort(); output(); 96 cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << endl; 97 cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << endl; 98 cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << endl; 99 100 compute(); // 统计各分数段人数、比例 101 102 vector<string> tmp{ "[0, 60) ", "[60, 70)", "[70, 80)","[80, 90)", "[90, 100]" }; 103 for (int i = tmp.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) 104 cout << tmp[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" 105 << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i] * 100 << "%" << endl; 106 }

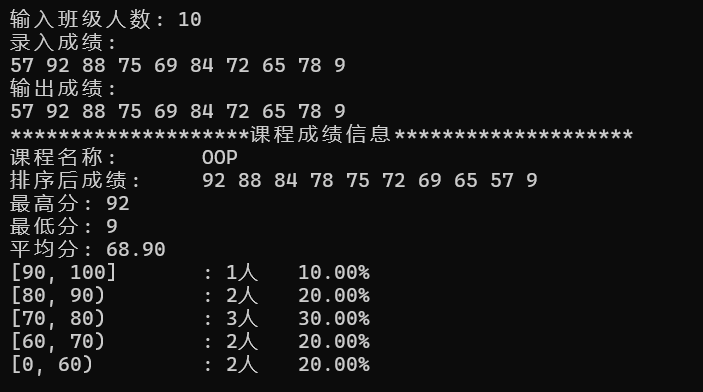
1 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 2 #include <iomanip> 3 4 void test() { 5 int n; 6 cout << "输入班级人数: "; 7 cin >> n; 8 9 GradeCalc c1("OOP", n); 10 11 cout << "录入成绩: " << endl;; 12 c1.input(); 13 cout << "输出成绩: " << endl; 14 c1.output(); 15 16 cout << string(20, '*') + "课程成绩信息" + string(20, '*') << endl; 17 c1.info(); 18 } 19 20 int main() { 21 test(); 22 }
问题一
在组合类 GradeCalc 中,成绩存储在私有成员变量 vector<int> grades 中。这个 grades 向量用于保存所有学生的成绩。
接口访问每个成绩的方法:sort():通过 std::sort 对 grades 进行排序。min():使用 std::min_element 查找 grades 中的最小值。max():使用 std::max_element 查找 grades 中的最大值。average():使用 std::accumulate 计算所有成绩的总和,然后平均。output():通过遍历 grades 向量输出所有成绩。
问题二
通过观察这两次任务的变化,我们可以看到面向对象编程允许我们以一种结构和层次化的方式来构建复杂系统,逐步改进和迭代设计,以提高代码的质量、可读性和可维护性。这有助于开发出更加健壮和灵活的应用程序。
4. 实验任务4

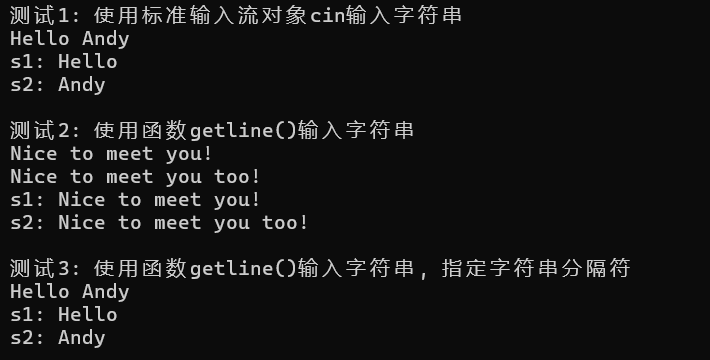
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <limits> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 void test1() { 8 string s1, s2; 9 cin >> s1 >> s2; // cin: 从输入流读取字符串, 碰到空白符(空格/回车/Tab)即结束 10 cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl; 11 cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl; 12 } 13 14 void test2() { 15 string s1, s2; 16 getline(cin, s1); // getline(): 从输入流中提取字符串,直到遇到换行符 17 getline(cin, s2); 18 cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl; 19 cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl; 20 } 21 22 void test3() { 23 string s1, s2; 24 getline(cin, s1, ' '); //从输入流中提取字符串,直到遇到指定分隔符 25 getline(cin, s2); 26 cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl; 27 cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl; 28 } 29 30 int main() { 31 cout << "测试1: 使用标准输入流对象cin输入字符串" << endl; 32 test1(); 33 cout << endl; 34 35 cin.ignore(numeric_limits<streamsize>::max(), '\n'); 36 37 cout << "测试2: 使用函数getline()输入字符串" << endl; 38 test2(); 39 cout << endl; 40 41 cout << "测试3: 使用函数getline()输入字符串, 指定字符串分隔符" << endl; 42 test3(); 43 }

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <limits> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void output(const vector<string>& v) { 9 for (auto& s : v) 10 cout << s << endl; 11 } 12 13 void test() { 14 int n; 15 while (cout << "Enter n: ", cin >> n) { 16 vector<string> v1; 17 18 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 19 string s; 20 cin >> s; 21 v1.push_back(s); 22 } 23 24 cout << "output v1: " << endl; 25 output(v1); 26 cout << endl; 27 } 28 } 29 30 int main() { 31 cout << "测试: 使用cin多组输入字符串" << endl; 32 test(); 33 }

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <limits> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void output(const vector<string>& v) { 9 for (auto& s : v) 10 cout << s << endl; 11 } 12 13 void test() { 14 int n; 15 while (cout << "Enter n: ", cin >> n) { 16 cin.ignore(numeric_limits<streamsize>::max(), '\n'); 17 18 vector<string> v2; 19 20 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 21 string s; 22 getline(cin, s); 23 v2.push_back(s); 24 } 25 cout << "output v2: " << endl; 26 output(v2); 27 cout << endl; 28 } 29 } 30 31 int main() { 32 cout << "测试: 使用函数getline()多组输入字符串" << endl; 33 test(); 34 }
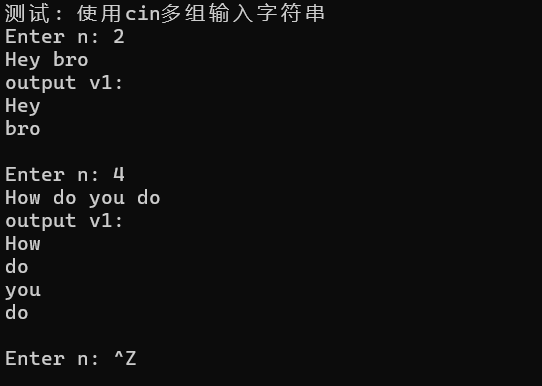
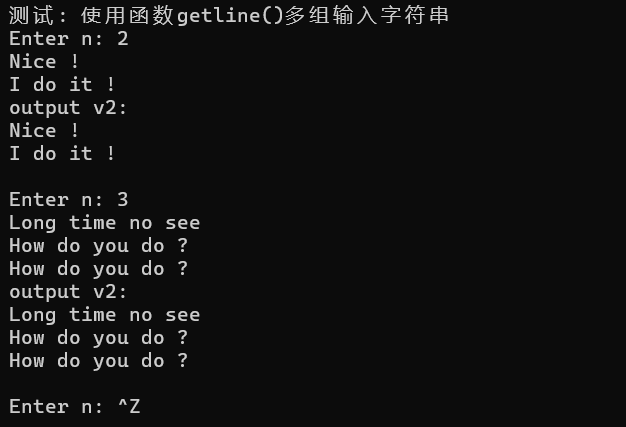
问题一
cin.ignore() 会忽略输入流中的下一个字符,直到指定的分隔符(在这里是换行符 '\n')被发现或者到达指定的字符数上限。在这种情况下,numeric_limits<streamsize>::max() 表示忽略最多一个非常大的字符数,实际上意味着它会一直忽略,直到找到换行符。
问题二
使用这种结构能够有效管理用户输入,确保后续输入不受前一条输入影响,提高代码的健壮性和用户体验。对于输入的错误处理和清理操作的结合,使得程序在处理多次交互时更为流畅。
5. 实验任务5

1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 template<typename T> 7 class GameResourceManager 8 { 9 private: 10 T resource; 11 public: 12 GameResourceManager(T); 13 T get() const; 14 void update(T); 15 }; 16 template<typename T> 17 GameResourceManager<T>::GameResourceManager(T a) :resource{ a } {} 18 19 template<typename T> 20 T GameResourceManager<T>::get() const 21 { 22 return resource; 23 } 24 template<typename T> 25 void GameResourceManager<T>::update(T a) 26 { 27 resource += a; 28 if (resource < 0) 29 resource = 0; 30 }

1 #include "grm.hpp" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 7 void test1() { 8 GameResourceManager<float> HP_manager(99.99); 9 cout << "当前生命值: " << HP_manager.get() << endl; 10 HP_manager.update(9.99); 11 cout << "增加9.99生命值后, 当前生命值: " << HP_manager.get() << endl; 12 HP_manager.update(-999.99); 13 cout << "减少999.99生命值后, 当前生命值: " << HP_manager.get() << endl; 14 } 15 16 void test2() { 17 GameResourceManager<int> Gold_manager(100); 18 cout << "当前金币数量: " << Gold_manager.get() << endl; 19 Gold_manager.update(50); 20 cout << "增加50个金币后, 当前金币数量: " << Gold_manager.get() << endl; 21 Gold_manager.update(-99); 22 cout << "减少99个金币后, 当前金币数量: " << Gold_manager.get() << endl; 23 } 24 25 26 int main() { 27 cout << "测试1: 用float类型对类模板GameResourceManager实例化" << endl; 28 test1(); 29 cout << endl; 30 31 cout << "测试2: 用int类型对类模板GameResourceManager实例化" << endl; 32 test2(); 33 }
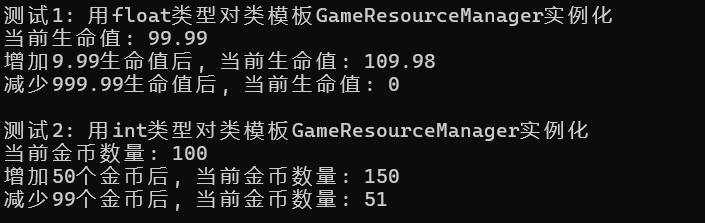
6. 实验任务6

1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class info 7 { 8 private: 9 string nickname; 10 string contact; 11 string city; 12 int n; 13 public: 14 info(string a, string b, string c, int d); 15 void display() const; 16 }; 17 18 info::info(string a, string b, string c, int d) :nickname{ a }, contact{ b }, city{ c }, n{ d } {}; 19 20 void info::display() const 21 { 22 cout << "昵称:" << "\t" << nickname << endl; 23 cout << "联系方式:" << "\t" << contact << endl; 24 cout << "所在城市:" << "\t" << city << endl; 25 cout << "预定人数:" << "\t" << n << endl; 26 int i = 40; 27 while (i--)cout << "-"; 28 cout << endl; 29 }

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<string> 3 #include<vector> 4 #include"info.hpp" 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int capacity = 100; 8 vector<info> audience_lst; 9 int main() 10 { 11 int s = 0;//当前人数 12 string a, b, c; 13 int d; 14 cout << "录入用户预约信息:" << "\n" << endl; 15 cout << "昵称" << "\t" << "联系方式" << "\t" << "所在城市" << "\t" << "预定参加人数" << endl; 16 while (cin >> a >> b >> c >> d) 17 { 18 info member(a, b, c, d); 19 audience_lst.push_back(member); 20 s += d; 21 if (s == 100) 22 break; 23 if (s > 100) 24 { 25 s -= d; 26 audience_lst.pop_back(); 27 cout << "对不起,只剩" << capacity - s << "个位置" << endl; 28 cout << "1.输入u,更新预定信息" << endl; 29 cout << "2.输入q,退出预定" << endl; 30 cout << "你的选择:"; 31 char choice; 32 cin >> choice; 33 if (choice == 'q') 34 break; 35 else if (choice == 'u') 36 continue; 37 } 38 } 39 cout << "截至目前,一共有" << s << "位听众预约。预约听众信息如下:" << endl; 40 int i = 40; 41 while (i--)cout << "-"; 42 cout << endl; 43 for (auto i : audience_lst) 44 i.display(); 45 return 0; 46 }
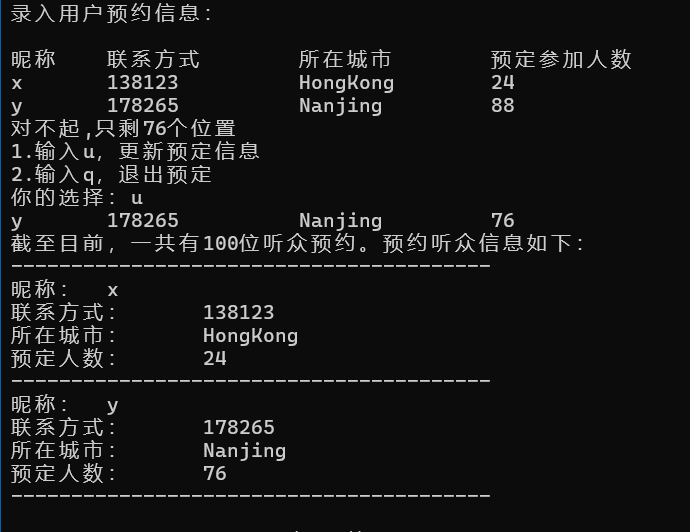
7. 实验任务7

#pragma once #ifndef DATE_H #define DATE_H class Date { private: int year; int month; int day; int totalDays; public: Date(int year, int month, int day); int getYear()const { return year; } int getMonth()const { return month; } int getDay()const { return day; } int getMaxDay()const; bool isLeapYear()const { return year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0; } void show()const; int distance(const Date& date)const { return totalDays - date.totalDays; } }; #endif // DATE_H

#include "date.h" #include <iostream> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; namespace { const int DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[] = { 0, 31, 59, 90, 120, 151, 181, 212, 243, 273, 304, 334, 365 }; } Date::Date(int year, int month, int day) : year{ year }, month{ month }, day{ day } { if (day <= 0 || day > getMaxDay()) { cout << "Invalid date:"; show(); cout << endl; exit(1); } int years = year - 1; totalDays = years * 365 + years / 4 - years / 100 + years / 400 + DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[month - 1] + day; if (isLeapYear() && month > 2) totalDays++; } int Date::getMaxDay()const { if (isLeapYear() && month == 2) return 29; else return DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[month] - DAYS_BEFORE_MONTH[month - 1]; } void Date::show()const { cout << getYear() << "-" << getMonth() << "-" << getDay(); }

#pragma once #ifndef ACCUMULATOR_H #define ACCUMULATOR_H #include "date.h" class Accumulator { private: Date lastDate; double value; double sum; public: Accumulator(const Date& date, double value) : lastDate(date), value(value), sum{ 0 } { } double getSum(const Date& date) const { return sum + value * date.distance(lastDate); } void change(const Date& date, double value) { sum = getSum(date); lastDate = date; this->value = value; } void reset(const Date& date, double value) { lastDate = date; this->value = value; sum = 0; } }; #endif // ACCUMULATOR_H

#pragma once #ifndef ACCUMULATOR_H #define ACCUMULATOR_H #include "date.h" class Accumulator { private: Date lastDate; double value; double sum; public: Accumulator(const Date& date, double value) : lastDate(date), value(value), sum{ 0 } { } double getSum(const Date& date) const { return sum + value * date.distance(lastDate); } void change(const Date& date, double value) { sum = getSum(date); lastDate = date; this->value = value; } void reset(const Date& date, double value) { lastDate = date; this->value = value; sum = 0; } }; #endif // ACCUMULATOR_H

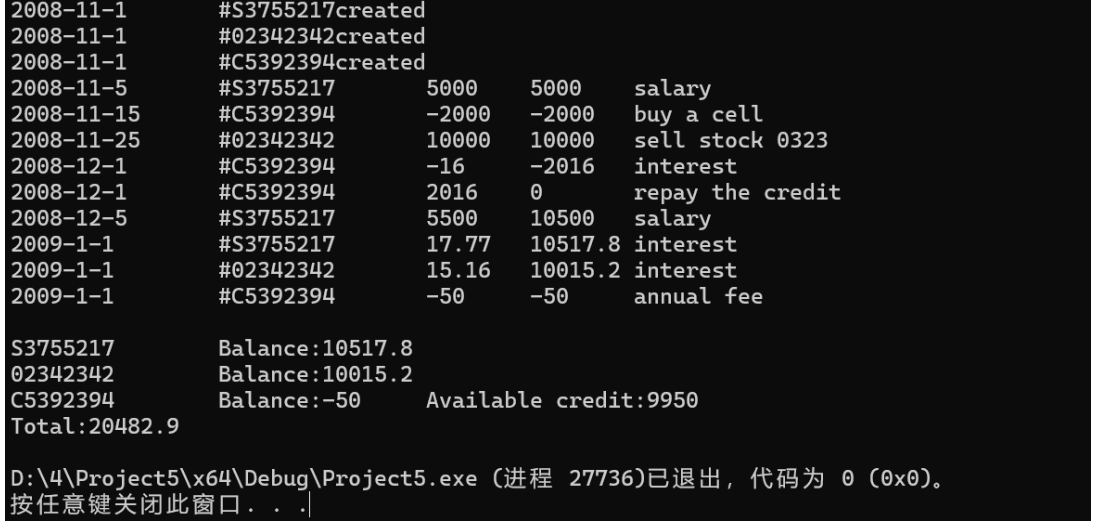
#include "account.h" #include <cmath> #include <iostream> using namespace std; double Account::total = 0; Account::Account(const Date& date, const string& id) : id{ id }, balance{ 0 } { date.show(); cout << "\t#" << id << " created" << endl; } void Account::record(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { amount = floor(amount * 100 + 0.5) / 100; // Rounding to two decimal places balance += amount; total += amount; date.show(); cout << "\t#" << id << "\t" << amount << "\t" << balance << "\t" << desc << endl; } void Account::show() const { cout << id << "\tBalance: " << balance; } void Account::error(const string& msg) const { cout << "Error (#" << id << "): " << msg << endl; } SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double rate) : Account(date, id), rate(rate), acc(date, 0) {} void SavingsAccount::deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { record(date, amount, desc); acc.change(date, getBalance()); } void SavingsAccount::withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { if (amount > getBalance()) { error("not enough money"); } else { record(date, -amount, desc); acc.change(date, getBalance()); } } void SavingsAccount::settle(const Date& date) { double interest = acc.getSum(date) * rate / date.distance(Date(date.getYear() - 1, 1, 1)); if (interest != 0) { record(date, interest, "interest"); } acc.reset(date, getBalance()); } CreditAccount::CreditAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double credit, double rate, double fee) : Account(date, id), credit(credit), rate(rate), fee(fee), acc(date, 0) {} void CreditAccount::deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { record(date, amount, desc); acc.change(date, getDebt()); } void CreditAccount::withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { if (amount - getBalance() > credit) { error("not enough credit"); } else { record(date, -amount, desc); acc.change(date, getDebt()); } } void CreditAccount::settle(const Date& date) { double interest = acc.getSum(date) * rate; if (interest != 0) { record(date, interest, "interest"); } if (date.getMonth() == 1) { record(date, -fee, "annual fee"); } acc.reset(date, getDebt()); } void CreditAccount::show() const { Account::show(); cout << "\tAvailable credit: " << getAvailableCredit(); }

#include "account.h" #include <cmath> #include <iostream> using namespace std; double Account::total = 0; Account::Account(const Date& date, const string& id) : id{ id }, balance{ 0 } { date.show(); cout << "\t#" << id << " created" << endl; } void Account::record(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { amount = floor(amount * 100 + 0.5) / 100; // Rounding to two decimal places balance += amount; total += amount; date.show(); cout << "\t#" << id << "\t" << amount << "\t" << balance << "\t" << desc << endl; } void Account::show() const { cout << id << "\tBalance: " << balance; } void Account::error(const string& msg) const { cout << "Error (#" << id << "): " << msg << endl; } SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double rate) : Account(date, id), rate(rate), acc(date, 0) {} void SavingsAccount::deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { record(date, amount, desc); acc.change(date, getBalance()); } void SavingsAccount::withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { if (amount > getBalance()) { error("not enough money"); } else { record(date, -amount, desc); acc.change(date, getBalance()); } } void SavingsAccount::settle(const Date& date) { double interest = acc.getSum(date) * rate / date.distance(Date(date.getYear() - 1, 1, 1)); if (interest != 0) { record(date, interest, "interest"); } acc.reset(date, getBalance()); } CreditAccount::CreditAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double credit, double rate, double fee) : Account(date, id), credit(credit), rate(rate), fee(fee), acc(date, 0) {} void CreditAccount::deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { record(date, amount, desc); acc.change(date, getDebt()); } void CreditAccount::withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc) { if (amount - getBalance() > credit) { error("not enough credit"); } else { record(date, -amount, desc); acc.change(date, getDebt()); } } void CreditAccount::settle(const Date& date) { double interest = acc.getSum(date) * rate; if (interest != 0) { record(date, interest, "interest"); } if (date.getMonth() == 1) { record(date, -fee, "annual fee"); } acc.reset(date, getDebt()); } void CreditAccount::show() const { Account::show(); cout << "\tAvailable credit: " << getAvailableCredit(); }