实验2 类和对象_基础编程1
实验任务1
头文件
#pragma once
#include <string>
// 类T: 声明
class T {
// 对象属性、方法
public:
T(int x = 0, int y = 0); // 普通构造函数
T(const T& t); // 复制构造函数
T(T&& t);// 移动构造函数
~T();// 析构函数
void adjust(int ratio);
void display() const;
private:
int m1, m2;
// 类属性、方法
public:
static int get_cnt();
public:
static const std::string doc;
static const int max_cnt;
private:
static int cnt;
// 类T友元函数声明
friend void func();
};
// 普通函数声明
void func();实现文件
// 类T: 实现
// 普通函数实现
#include "t.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
// static成员数据类外初始化
const std::string T::doc{ "a simple class sample" };
const int T::max_cnt = 999;
int T::cnt = 0;
// 对象方法
T::T(int x, int y) : m1{ x }, m2{ y } {
++cnt;
cout << "T constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(const T& t) : m1{ t.m1 }, m2{ t.m2 } {
++cnt;
cout << "T copy constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(T&& t) : m1{ t.m1 }, m2{ t.m2 } {
++cnt;
cout << "T move constructor called.\n";
}
T::~T() {
--cnt;
cout << "T destructor called.\n";
}
void T::adjust(int ratio) {
m1 *= ratio;
m2 *= ratio;
}
void T::display() const {
cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")";
}
// 类方法
int T::get_cnt() {
return cnt;
}
// 友元
void func() {
T t5(42);
t5.m2 = 2049;
cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); cout << endl;
}主程序文件
// 类T: 实现
// 普通函数实现
#include "t.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
// static成员数据类外初始化
const std::string T::doc{ "a simple class sample" };
const int T::max_cnt = 999;
int T::cnt = 0;
// 对象方法
T::T(int x, int y) : m1{ x }, m2{ y } {
++cnt;
cout << "T constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(const T& t) : m1{ t.m1 }, m2{ t.m2 } {
++cnt;
cout << "T copy constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(T&& t) : m1{ t.m1 }, m2{ t.m2 } {
++cnt;
cout << "T move constructor called.\n";
}
T::~T() {
--cnt;
cout << "T destructor called.\n";
}
void T::adjust(int ratio) {
m1 *= ratio;
m2 *= ratio;
}
void T::display() const {
cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")";
}
// 类方法
int T::get_cnt() {
return cnt;
}
// 友元
void func() {
T t5(42);
t5.m2 = 2049;
cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); cout << endl;
}
问题1
t.h中,普通函数func 作为类X的友元,在类的内部声明了友元关系。在类外部,去掉line36,重
新编译,是否能正确运行。如果能,回答说明可以去掉line36。如果不能,以截图形式给出编译报
错信息,分析可能的原因
答:不能

声明友元关系的重点是“友元关系”。func是一个普通函数,又恰好它是一个类的友元,不过这两点要分别声明,而不是直接一步说完。
问题2
t.h中,line9-12给出了各种构造函数、析构函数。总结各种构造函数的功能,以及它们与析构函数
的调用时机
普通构造函数 用于初始化对象,可以接受两个整数参数,提供默认值(0,0)。
复制构造函数 用于通过已有对象创建新对象,复制该对象的状态。
移动构造函数 用于通过右值引用构造对象,能够高效地转移资源所有权,避免不必要的复制。
析构函数 用于在对象生命周期结束时释放资源,清理对象所持有的动态内存或其他资源。
实验任务2
头文件
#pragma once
#include<string>
class Complex
{
public:
Complex(double = 0, double = 0);
Complex(const Complex&);
double get_real() const;
double get_imag() const;
void add(const Complex&);
static std::string doc;
private:
double real;
double imag;
friend Complex& add(const Complex&, const Complex&);
friend bool is_equal(const Complex&, const Complex&);
friend bool is_not_equal(const Complex&, const Complex&);
friend double abs(const Complex&);
friend void output(const Complex&);
};
Complex& add(const Complex&, const Complex&);
bool is_equal(const Complex&, const Complex&);
bool is_not_equal(const Complex&, const Complex&);
double abs(const Complex&);
void output(const Complex&);实现文件
#include"Complex.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
std::string Complex::doc = "a simplified complex class";
Complex::Complex(double a,double b):real{a},imag{b}{}
Complex::Complex(const Complex& c):real{c.real},imag{c.imag}{}
double Complex::get_real() const
{
return real;
}
double Complex::get_imag() const
{
return imag;
}
void Complex::add(const Complex& c)
{
real += c.real;
imag += c.imag;
}
Complex& add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2)
{
Complex c3(c1.real + c2.real, c1.imag + c2.imag);
return c3;
}
bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2)
{
if (c1.real == c2.real && c1.imag == c2.imag)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2)
{
if (c1.real != c2.real || c1.imag != c2.imag)
return true;
else
return false;
}
double abs(const Complex& c)
{
double a = sqrt(pow(c.real, 2) + pow(c.imag, 2));
return a;
}
void output(const Complex& c)
{
cout << c.real << " + " << c.imag << "i" << endl;
}主程序文件
#include "Complex.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::boolalpha;
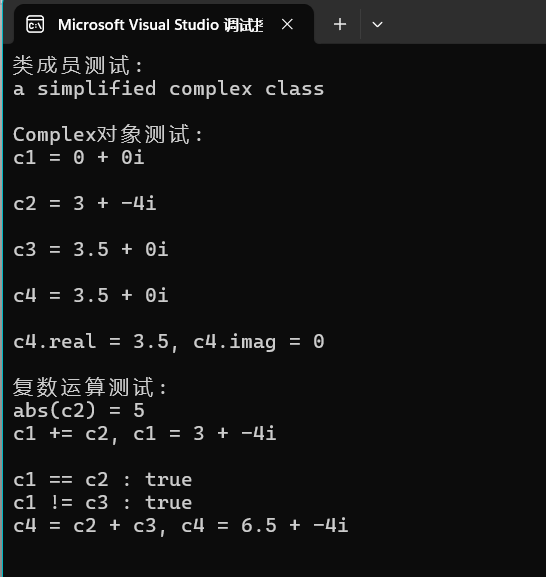
void test() {
cout << "类成员测试: " << endl;
cout << Complex::doc << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl;
Complex c1;
Complex c2(3, -4);
const Complex c3(3.5);
Complex c4(c3);
cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl;
cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl;
cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl;
cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl;
cout << "c4.real = " << c4.get_real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.get_imag() << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl;
cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl;
c1.add(c2);
cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl;
cout << "c1 != c3 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c3) << endl;
c4 = add(c2, c3);
cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
}
实验任务3
#include <iostream>
#include <complex>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::boolalpha;
using std::complex;
void test() {
cout << "标准库模板类comple测试: " << endl;
complex<double> c1;
complex<double> c2(3, -4);
const complex<double> c3(3.5);
complex<double> c4(c3);
cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl;
cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl;
cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl;
cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl;
cout << "c4.real = " << c4.real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.imag() << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl;
cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl;
c1 += c2;
cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2) << endl;
cout << "c1 != c3 : " << (c1 != c3) << endl;
c4 = c2 + c3;
cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
}
与我在实验任务2写的程序的区别:方法的使用更自然,用“+、-、*、/”即可;复数的表现形式为(x,y)。
实验任务4
头文件
#pragma once
#include<string>
class Fraction
{
public:
static std::string doc;
Fraction(int = 0, int = 1);
Fraction(Fraction&);
int get_up();
int get_down();
Fraction& negative();
private:
int up;
int down;
friend void output(Fraction&);
friend Fraction& add(Fraction&, Fraction&);
friend Fraction& sub(Fraction&, Fraction&);
friend Fraction& mul(Fraction&, Fraction&);
friend Fraction& div(Fraction&, Fraction&);
};
int fun(int, int);//求最大公因数
void output(Fraction&);
Fraction& add(Fraction&, Fraction&);
Fraction& sub(Fraction&, Fraction&);
Fraction& mul(Fraction&, Fraction&);
Fraction& div(Fraction&, Fraction&);实现文件
#include"Fraction.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int fun(int a, int b)
{
if (a == b)
return a;
else if (a > b)
{
while (b)
{
int t = a % b;
a = b; b = t;
}
return a;
}
else
{
while (a)
{
int t = b % a;
b = a; a = t;
}
return b;
}
}
std::string Fraction::doc = "Fraction类 v 0.01版.\n目前仅支持分数对象的构造、输出、加 / 减 / 乘 / 除运算.";
Fraction::Fraction(int a, int b) :up{ abs(a) }, down{ abs(b) }//这样在创造时分母一定大于0,负号只会在分子上
{
if (a * b < 0)
up *= -1;
}
Fraction::Fraction(Fraction& c) :up{ abs(c.up) }, down(abs(c.down))
{
if (c.up * c.down < 0)
up *= -1;
}
int Fraction::get_up()
{
return up;
}
int Fraction::get_down()
{
return down;
}
Fraction& Fraction::negative()
{
Fraction c(-up, down);
return c;
}
void output(Fraction& c)
{
if (c.down == 0)
{
cout << "分母不能为0" << endl;
}
else if (c.up == 0 || c.down == 1)//这种情况只有分子有用
{
cout << c.up << endl;
}
else
{
int t = fun(abs(c.up), abs(c.down));
int up = c.up, down = c.down;
if (t!= 1)
{
up /= t; down /= t;
}
cout << up << "/" << down << endl;
}
}
Fraction& add(Fraction& c1, Fraction& c2)
{
int down = c1.down * c2.down;
int up = c1.up * c2.down + c2.up * c1.down;
Fraction c3(up, down);//化简什么的就交给output吧!
return c3;
}
Fraction& sub(Fraction& c1, Fraction& c2)
{
int down = c1.down * c2.down;
int up = c1.up * c2.down - c2.up * c1.down;
Fraction c3(up, down);
return c3;
}
Fraction& mul(Fraction& c1, Fraction& c2)
{
int down = c1.down * c2.down;
int up = c1.up * c2.up;
Fraction c3(up, down);
return c3;
}
Fraction& div(Fraction& c1, Fraction& c2)
{
int down = c1.down * c2.up;
int up = c1.up * c2.down;
Fraction c3(up, down);
return c3;
}主程序文件
#include "Fraction.h"
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
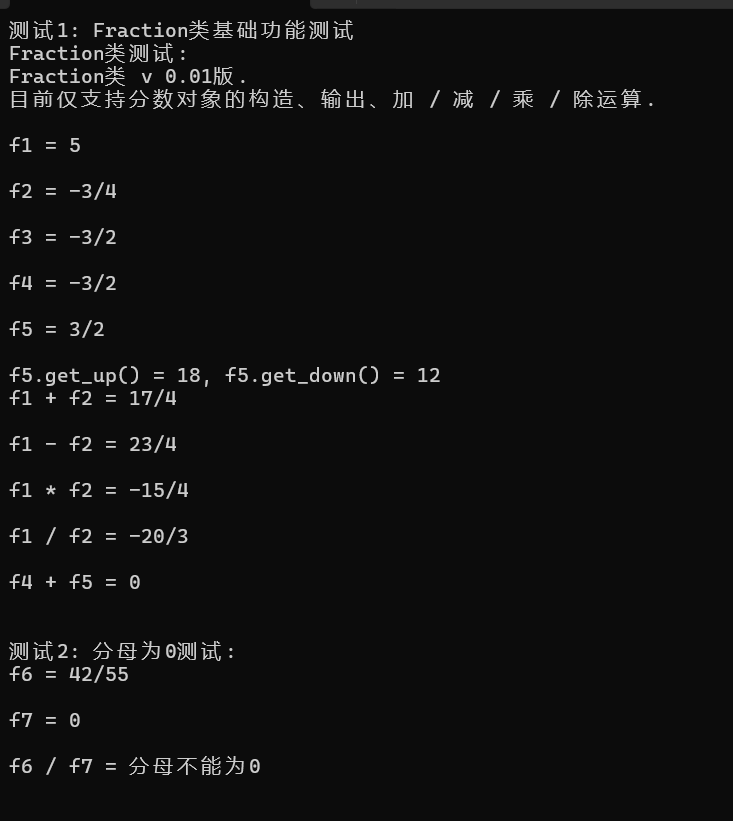
void test1() {
cout << "Fraction类测试: " << endl;
cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl;
Fraction f1(5);
Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12);
Fraction f4(f3);
cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl;
cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl;
cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl;
cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl;
Fraction f5(f4.negative());
cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl;
cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up() << ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl;
cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl;
}
void test2() {
Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3);
cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl;
cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl;
cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl;
}
int main() {
cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n";
test1();
cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试: \n";
test2();
}
实验任务5
头文件
#pragma once
#ifndef __ACCOUNT_H__
#define __ACCOUNT_H__
class SavingsAccount {
private:
int id;
double balance;
double rate;
int lastDate;
double accumulation;
static double total;
void record(int date, double account);
double accumulate(int date)const {
return accumulation + balance * (date - lastDate);
}
public:
SavingsAccount(int date, int id, double rate);
int getId()const { return id; }
double getBalance()const { return balance; }
double getRate()const { return rate; }
static double getTotal() { return total; }
void deposit(int date, double account);
void withdraw(int date, double account);
void settle(int date);
void show()const;
};
#endif实现文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "account.h"
#include<cmath>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
double SavingsAccount::total = 0;
SavingsAccount::SavingsAccount(int date, int id, double rate):id{ id }, balance{ 0 }, rate{ rate }, lastDate(date), accumulation{ 0 } {
cout << date << "\t#" << id << "is created" << endl;
}
void SavingsAccount::record(int date, double amount) {
accumulation = accumulate(date);
lastDate = date;
amount = floor(amount * 100 + 0.5) / 100;
balance += amount;
total += amount;
cout << date << "\t#" << id << "\t" << amount << "\t" << balance << endl;
}
void SavingsAccount::deposit(int date, double amount) {
record(date, amount);
}
void SavingsAccount::withdraw(int date, double amount) {
if (amount > getBalance()) {
cout << "Error: not enough money" << endl;
}
else {
record(date, -amount);
}
}
void SavingsAccount::settle(int date) {
double interst = accumulate(date) * rate / 365;
if (interst != 0) {
record(date, interst);
}
accumulation = 0;
}
void SavingsAccount::show()const {
cout << "#" << id << "/tBalance:" << balance;
}主程序文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "account.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
SavingsAccount sa0(1, 21325302, 0.015);
SavingsAccount sa1(1, 58320212, 0.015);
sa0.deposit(5, 5000);
sa1.deposit(25, 10000);
sa0.deposit(45, 5500);
sa1.withdraw(60, 4000);
sa0.settle(90);
sa1.settle(90);
sa0.show(); cout << endl;
sa1.show(); cout << endl;
cout << "Total:" << SavingsAccount::getTotal() << endl;
return 0;
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号