Control Plane vs Data Plane – Difference b/w Control and Data Plane
https://ipwithease.com/difference-between-control-plane-and-data-plane/
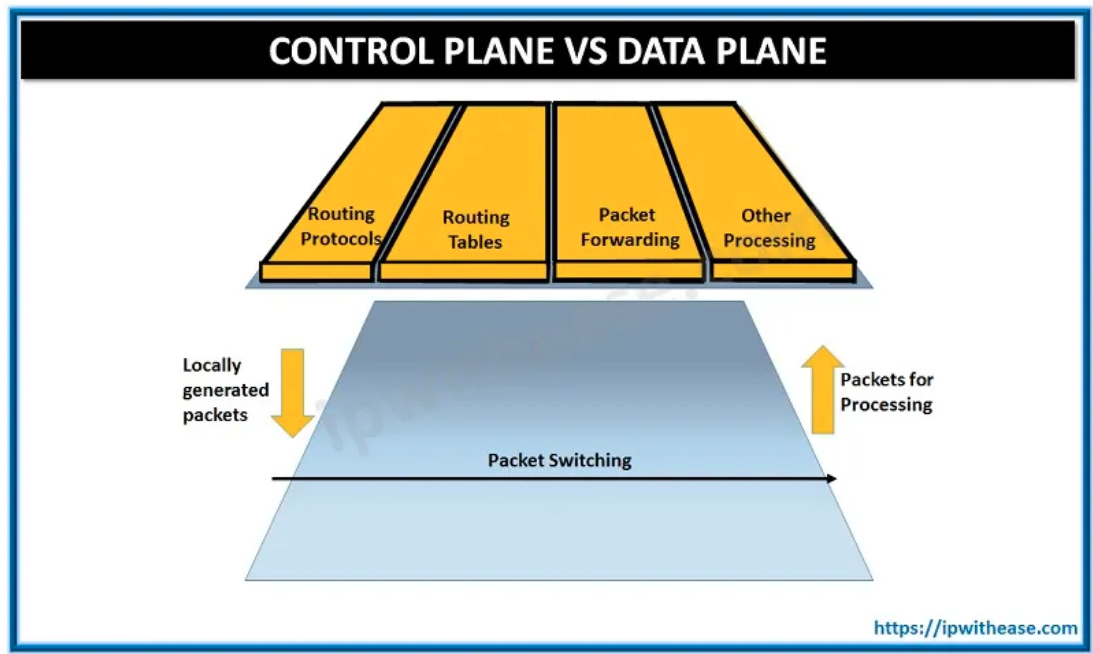
Control Plane vs Data Plane
In the last post we discussed the control plane and the data plane in detail. In this post we will emphasize on the difference between the two.
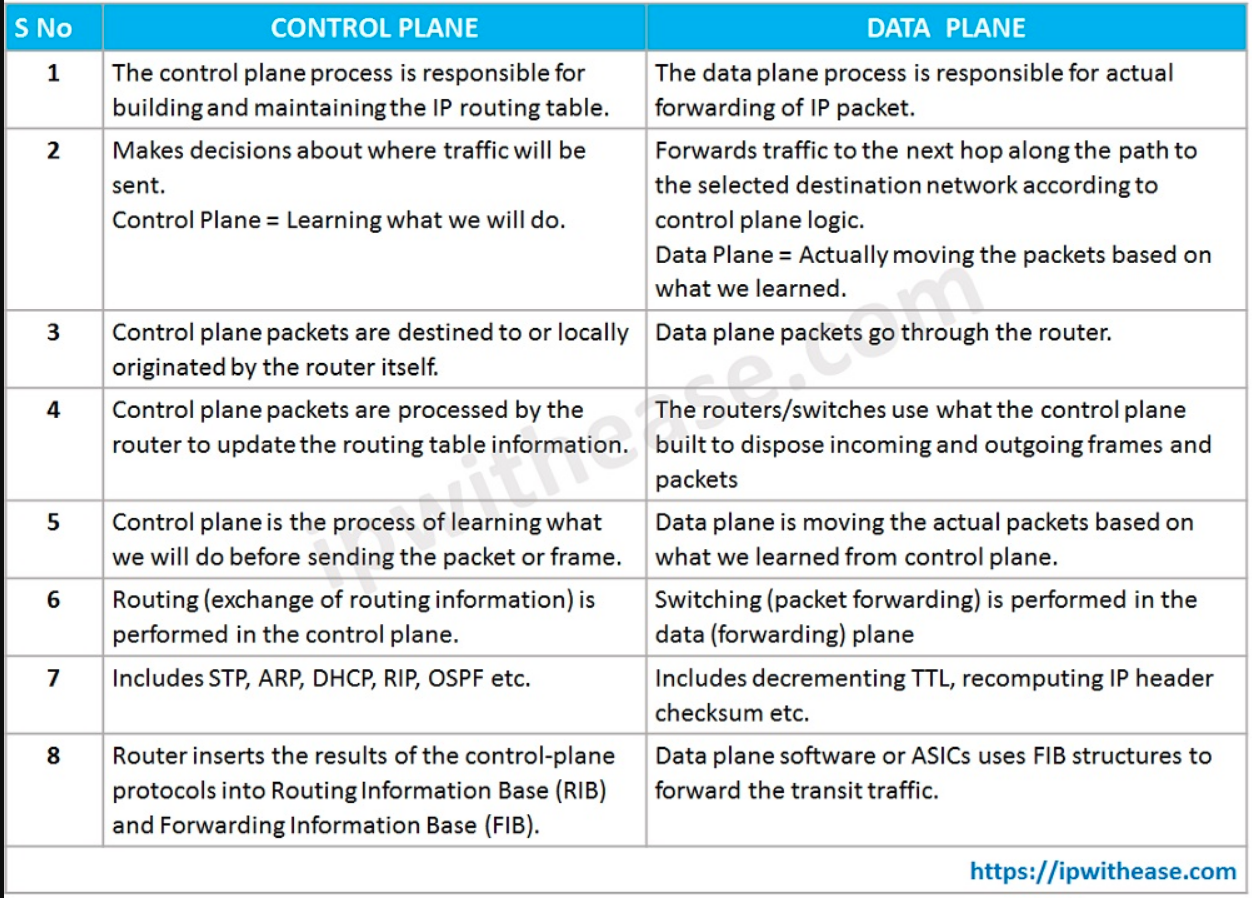
Below table describes the Control Plane vs Data Plane in detail -:
| S.No. | CONTROL PLANE | DATA PLANE |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The control plane process is responsible for building and maintaining the IP routing table. | The data plane process is responsible for actual forwarding of IP packet. |
| 2 | Makes decisions about where traffic will be sent. Control Plane = Learning what we will do. |
Forwards traffic to the next hop along the path to the selected destination network according to control plane logic. Data Plane = Actually moving the packets based on what we learned. |
| 3 | Control plane packets are destined to or locally originated by the router itself. | Data plane packets go through the router. |
| 4 | Control plane packets are processed by the router to update the routing table information. | The routers/switches use what the control plane built to dispose incoming and outgoing frames and packets |
| 5 | Control plane is the process of learning what we will do before sending the packet or frame. | Data plane is moving the actual packets based on what we learned from control plane. |
| 6 | Routing (exchange of routing information) is performed in the control plane. | Switching (packet forwarding) is performed in the data (forwarding) plane |
| 7 | Includes STP, ARP, DHCP, RIP, OSPF etc. | Includes decrementing TTL, recomputing IP header checksum etc. |
| 8 | Router inserts the results of the control-plane protocols into Routing Information Base (RIB) and Forwarding Information Base (FIB). | Data plane software or ASICs uses FIB structures to forward the transit traffic. |
![]()
Download this Data Plane vs Control Plance table here.
Question: Why do we separate the control plane and the data plane?
Answer: The Software control of the network can evolve independently of the hardware. Infact separation of control and data plane helps in areas like network virtualization, Layer 3 routing decision taking , Egress selection i.e. selection of destination path. This approach helps in more control over decision logic. Separation of both the planes also supports Denial-of-Service attack detection.
Question: What is control plane in networking?
Answer: The control plane is that part of a network which carries information necessary to establish and control the network. It is part of the theoretical framework used to understand the flow of information packets between network interfaces or the control plane is the part of a network that carries signaling traffic and is responsible for routing. The routing table contains destination addresses and the outgoing interface associated with them. Control packets originate from or are destined for a router.
In Routing, control plane refers to the all functions and processes that determine which path to use to send the packet or frame. Control plane is responsible for populating the routing table, drawing network topology, forwarding table and hence enabling the data plane functions. Means here the router makes its decision. In a single line it can be said that it is responsible for How packets should be forwarded.
Some key features of control plane are enlisted below –
- Control plane refers to the all functions and processes that determine which path to use to send the packet or frame.
- It is responsible for building and maintaining the IP routing table.
- Control plane responsible about how packets should be forwarded.
- Control plane performs its task independently.
- In general, we can say in control plane it is learned what and how it can be done.
- Control plane packets are processed by router to update the routing table.
- It includes Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) etc.
- Control plane packets are locally originated by the router itself.
- Control plane acts as a decision maker in data forwarding.
- Routing is performed in the control plane.
Question: What is data plane and control plane in MPLS?
Answer: MPLS Control Plane:
- MPLS control plane indicates how the updates are sent from one PE to another PE router.
- MPLS Control Plane is used to build FIB table from the information of RIB and LFIB table based upon label exchange protocol.
- Control Plane makes use of label exchange protocol to create and maintain label internally and to exchange label with other device.
- The label exchange protocol bind label with network learned via routing protocol.
- Label exchange protocol includes MPLS LDP, CISCO TDP and BGP (used by MPLDVPN), RSVP used by MPLS TE.

MPLS Data Plane:
- MPLS Data Plane indicates how the data will flow from one PE to another PE router.
- Data Plane forward packets to the appropriate interface based on the information in the LFIB or the FIB table.
- As the IP packet arrives, an IP routing lookup is performed and verification is done if any label is associated. The assocated label in the packet is checked by LFIB, which swaps the label and processes it to forward toward destination. If no label is assigned with IP Packet, it will have processed as normal IP Packet by FIB.
Question: What is the main function of the data plane?
Answer: Data Plane forwards the traffic according to control plane logic. It performs –
- IP forwarding
- Layer 2 switching
In Routing, data plane refers to all the functions and processes that forward packets/frames from one interface to another based on control plane logic. Routing table, forwarding table and the routing logic constitute the data plane function. Data plane packet goes through the router and incoming and outgoing of frames are directed based on control plane logic. It is responsible for moving packets from source to destination and also called as forwarding plane.
Below points give details on data plane –
- Data plane refers to all the functions and processes that forward packets/frames from one interface to another based on control plane logic.
- It is responsible for forwarding actual IP packet.
- Data plane is responsible for moving packets from source to destination.
- Data plane performs its function (data bits transfer) depending on data plane instructions or path set.
- In general, we can say that in data plane the actual task is performed based on what is learned.
- The forwarding plane/data plane forwards the packets based on the built logic of control plane.
- It includes decrementing Time to Live (TTL), re-computing IP header checksum etc.
- Data plane packets go through the router.
- Data plane acts as a decision implementer in data forwarding.
- Switching is performed in the data plane.





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通