Debian / Ubuntu Linux: Setup Wireless Access Point (WAP) with Hostapd
Step #1: Install hostapd
Type the following command:# apt-get install hostapd
Sample outputs:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following NEW packages will be installed: hostapd 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 15 not upgraded. Need to get 346 kB of archives. After this operation, 877 kB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://debian.osuosl.org/debian/ squeeze/main hostapd amd64 1:0.6.10-2 [346 kB] Fetched 346 kB in 2s (151 kB/s) Selecting previously deselected package hostapd. (Reading database ... 267669 files and directories currently installed.) Unpacking hostapd (from .../hostapd_1%3a0.6.10-2_amd64.deb) ... Processing triggers for man-db ... Setting up hostapd (1:0.6.10-2) ...
Step #2: Configure hostapd
Edit /etc/default/hostapd, enter:# vi /etc/default/hostapd
Uncomment and set DAEMON_CONF to the absolute path of a hostapd
configuration file and hostapd will be started during system boot:
DAEMON_CONF="/etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf"
Save and close the file. Next create a text file called /etc/hostapd/hostapd.conf, enter:
Set interface name:
### Wireless network name ### interface=wlan0 ### Set your bridge name ### bridge=br0
Set driver name:
driver=nl80211
Set country name code in ISO/IEC 3166-1 format. This is used to set regulatory domain. Set as needed to indicate country in which device is operating. This can limit available channels and transmit power.
### (IN == INDIA, UK == United Kingdom, US == United Stats and so on ) ### country_code=IN
Set your SSID:
ssid=nixcraft
Set operation mode (a = IEEE 802.11a, b = IEEE 802.11b, g = IEEE 802.11g)hw_mode=g
Set channel number (some driver will only use 0 as value)
channel=6
Set wpa mode to 2:
wpa=2
Set your passphrase (WiFi password):
wpa_passphrase=MyWiFiPassword
Set key and auth optionsmanagement for WPA2:
## Key management algorithms ## wpa_key_mgmt=WPA-PSK ## Set cipher suites (encryption algorithms) ## ## TKIP = Temporal Key Integrity Protocol ## CCMP = AES in Counter mode with CBC-MAC wpa_pairwise=TKIP rsn_pairwise=CCMP ## Shared Key Authentication ## auth_algs=1 ## Accept all MAC address ### macaddr_acl=0
Save and close the file.
How Do I start / stop / restart AP?
Use the following commands:# /etc/init.d/hostapd start
# /etc/init.d/hostapd stop
# /etc/init.d/hostapd restart
Step #3: Configure /etc/network/interfaces
You can setup wlan0 in standalone mode or bridge it with eth0. The bridge mode will open your wireless client to access rest of the LAN and you will able to connect to the Internet. Most user bridge the wireless interface with the AP's Internet-connected interface.
Set br0 (wlan0+eth0) in bridge mode
You need to install bridge-utils package for configuring the Linux Ethernet bridge:# apt-get install bridge-utils
Sample outputs:
Reading package lists... Done Building dependency tree Reading state information... Done The following NEW packages will be installed: bridge-utils 0 upgraded, 1 newly installed, 0 to remove and 15 not upgraded. Need to get 32.7 kB of archives. After this operation, 176 kB of additional disk space will be used. Get:1 http://debian.osuosl.org/debian/ squeeze/main bridge-utils amd64 1.4-5 [32.7 kB] Fetched 32.7 kB in 1s (25.5 kB/s) Selecting previously deselected package bridge-utils. (Reading database ... 267692 files and directories currently installed.) Unpacking bridge-utils (from .../bridge-utils_1.4-5_amd64.deb) ... Processing triggers for man-db ... Setting up bridge-utils (1.4-5) ...
Edit /etc/network/interfaces, enter:# vi /etc/network/interfaces
Modify or set config as follows:
auto lo br0
iface lo inet loopback
# wireless wlan0
allow-hotplug wlan0
iface wlan0 inet manual
# eth0 connected to the ISP router
allow-hotplug eth0
iface eth1 inet manual
# Setup bridge
iface br0 inet static
bridge_ports wlan0 eth0
address 192.168.1.11 netmask 255.255.255.0 network 192.168.1.0 ## isp router ip, 192.168.1.2 also runs DHCPD ##
gateway 192.168.1.2 dns-nameservers 192.168.1.2
Save and close the file. At this stage I recommend that you
reboot the computer or restart all services as follows (may not work
over remote ssh session):# /etc/init.d/networking restart
# /etc/init.d/hostapd restart
OR# reboot
A note about DHCPD server
Since you are running your WAP in bridge (br0) mode, DHCPD is not required on your WAP. It can use DHCPD server located anywhere on the LAN. In this example 192.168.1.2 is an ISP router with DHCPD running on it. If you are not using DHCPD server, setup as follows:
A note about Firewall
You can install a firewall to protect from attacks. See how to install shorewall on Debian or Ubuntu Linux.
How do I troubleshoot WAP problems?
You will find WPA auth log info in /var/log/syslog file:# tail -f /var/log/syslog
Find out if DHCPD relay working or not:# tcpdump -n port 67 or port 68
Make sure firewall is not blocking required ports:# /sbin/iptables -L -n -v | less
Make sure correct mac address are assigned and br0 is up and running:# ifconfig br0
# ifconfig | grep HW
# brctl show
# brctl showmacs br0
Use these 8 Linux commands to find out wireless network speed, signal strength and other information: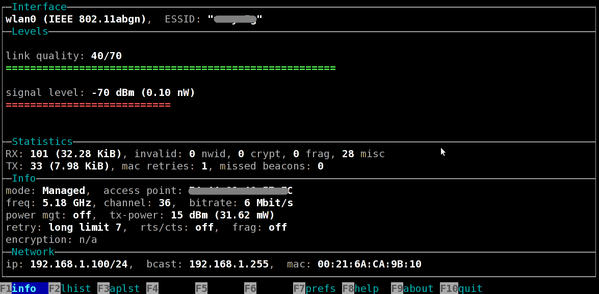
Finally, make sure you use latest version of the following software
- Linux kernel
- Wireless card drivers and firmware
- hostapd
References
- hostapd documentation from the Linux kernel wireless wiki.
- Download latest version of hostapd from the official web-site or read documentation here or run the command vi /usr/share/doc/hostapd/examples/hostapd.conf.gz
- man pages - hostapd, brctl command, and interfaces


